The Child with Gastrointestinal Dysfunction
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is Appendicitis
○Inflammation of appendix- could rupture and cause peritonitits bc you could put fecal matter into peritoneal cavity
○Symptoms
○Abd pain, McBurney’s point- right lower quadrant , rebound tenderness- push and when you let go theres pain. , fever, N&V, guarding- don’t want you to touch lower right quadrant., periumbilical pain.
○Diagnosis, history/ pyshicla, CBC, urinalysis, CT
○Pain, hydration, support, infection, education
Could perforate and rupture- if they have a sudden relief of pain worried about peritonitis. will feel better when ruptures
Tx- surgery,
or drain if ruptured- will pull out bacteria and junk while irrigating it, then wait a few weeks until surgery
if not ruptured- go in and remove it
Early assessment and intervention could prevent this
Surgery - pre and post op care- IV fluids, pain management, abx,
If had Surgery- splint incision- can put pillow on stomach if they have to cough, s/s infection, respiratory we need to arelate lungs- blow bubbles, incentive spiromotor, advance their diet slowely and then progress, Watch for N/v even after. if olfer kid- adolecnece body image is important.

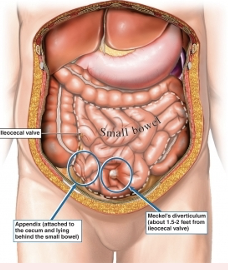
What is Meckel Diverticulum
○Out-pouching ( buldge) of ileum containing gastric or pancreatic tissue that secretes acid – causes ulceration in pockets of the bowel.. Congenital malformation- 2-4%- more common in males.
○Symptoms
○Often asymptomatic
○Painless rectal bleeding, “currant jelly”- will look like strawberry jelly stools- blood mixed w muscus , abd painful and tight, signs of obstruction, hypotension if bleeding severe- watch s/s of shock
○Diagnosis & Treatment- hx, physical, imaging, scanning
○Nursing Management
○Pre and post-op care- tx- will remove affected bowel.
○If showing signs shock before surgery or hypotensive fix before surgery
Test stool for blood. lab work,
○I and O important to monitor , pain control,
after surgery- watch s/s infect, pain, iv fluids, NGT to decompress stomach, monitor return of normal bowel fx
WHat is Peptic Ulcer Disease
○Chronic condition of ulcers affecting stomach or duodenum
○Symptoms
○Epigastric pain- high up pain , nocturnal pain- when lay down at night , oral regurgitation, heartburn, weight loss, hematemesis- blood in stool or vomit , melena
○Diagnostics
○Management
○Releive discomfort and promote healing
○If dt H pylori- will be tx w antibitotics
○PPI, anatacids, H2 antagonist meds- pepsid,
○Can be so severe- may hemmorage , or hypotensive shock- give blood transufion and IV fluids
○Surgery- they can cut the vagus nerve- helps control stomach acid.- saved if aggressive, reocurring, doesn’t go away w meds

What are the types of hepatitis
Type | Hep A | Hep B | Hep C | Hep D | Hep E |
Route | Fecal-Oral | Most occur perinatally in children | Blood and body fluids; Perinatal | Blood and body fluids | Fecal-oral |
Contaminated food or water | Any bodily fluid | Drug use, sexual transmission Can effect liver | Previously infected with HBV | Contaminated food or water; Not common in children |
How do we tx hepatitis
○Treatment- don’t need to know meds
○Goals and Prevention – from replicating, catch early, look s/s for worsening liver fx, prevent spread disease.
○Cluster care bc get tired easily
○Nursing Management
○Diet- like vit k
○Rest
○Medications- vaccines, educate, hand washing, standard precuations, teach to make sure meds are sfae to give if liver impaired.
○Education
What is Biliary Atresia- closed or absent
○Extrahepatic bile ducts fail to develop or are closed
○Symptoms
○Asymptomatic, mild jaundice, abd distension, hepatomegaly
○Progresses to splenomegaly, bruising, prolonged bleeding, intense itching for build up of bile, putty-like white or clay stools, tea-colored urine
○ Nursing Management
○ Medical Management
○ Kasai Procedure
Juandice will last. Could be immune or viral response
Can lead to cerosis, liver failure, death
Failure tot thrive- don’t grow and develop,
Educate and support, teach tepid baths- lukewarm, don’t want them to scratch- pat skin, keep nails cut short, cluster care- tire easily.
Diagnose early to hopefully survive
Have vit k before procedures
Fat soluble vitamin- a, d, e, k
Can still be breast fed-or bottle enteral or tpn formula
What is the kasai procedure
oRemoves blocked bile duct and attaches a part of small intestines= new flow for bile.
o1/3 still have to have a liver transplant even w this procedure
What is cirrhosis
oOccurs as result of hepatitis, biliary atresia, infection, autoimmune disorder, or chronic disease (hemophilia, CF)
Damage is not reversable.
S/S- jaundice, anemic, poor growth, weak, lethargic, acities,
No tx to stop progression- prognosis is poor without a liver transplant
Role- prevent complications and Monitor liver fx, tests,
identify early s/s
Risk for malnutrition, hemmorhage, ecncephalopathy- brain dysfunction
oGoal- Liver transplant

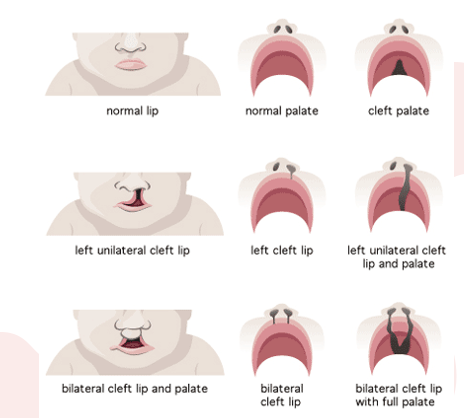
What is cleft lip and palate
can be separate as well
Check for other anomalies or syndromes
Exposure to toxins in utero or folate deficiency in mom might cayse, or unkown
○Maxillary processes fail to fuse
○Medical Management
Nursing Management pre-op
○Assessment- Presurgery- assessing, immediate concern= feeding- will interfere with suck. There are different models like johsnon and johsn that have a special model. Will suck more air- burb more frequently, keep more upright before and after feed, aspiration risk, keep bulb syringe nearby, lactation consulatant.
Nursing Management post-op
If have surgery- don’t want to put prone ( stomach), elbow immbolizers so don’t pull suture lines, don’t put anything in their mouth- promote healing. Resume feeds as tolerate post op
Team w kids- plastic surgeon, at risk for hearing problems. will have freq hearing screen.
Will repair cleft lip sooner- 2/3 months. Wait a little and repair cleft palette Repair palate 6-12 months bc want skeletal features to have time to grow. Don’t want to wait to long bc increase risk for speech delays
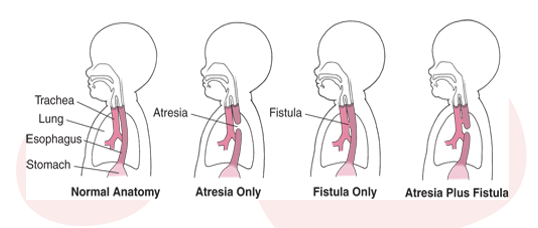
WHat is Esophageal Atresia & Tracheoesophageal Fistula (TEF)
○Esophagus ends in blind pouch or connects to trachea by fistula- fistula connecting trachea to espohagus
Symptoms
○Excess saliva, drooling, 3 C’s
○Apnea
○Increased distress post feed
○Abd distension
○Diagnosis
RF- polyhydramnios- too much amniotic fluid.
If see coughing, cyanosis, choking
Might sneeze and fluid will come out nose
Cant pass NGT
Will do radiographic studies, or while pregnant,
Watch for resp ditress, maintain airway, keep NPO, resp support, remove secretions to prevent aspiration and pneumonia, keep uright for drainage
How to you tx Esophageal Atresia & TEF
Nursing Management
○Airway, NPO
○Prevent complications
○Suction
Medical Management
○Surgery in stages- might wait for espohagus to grow,
Emotional support and education
If have fistula most important thing to correct first, then wait to connect esophagus to rest of digestion system.
Surgery- monitor resp, pain
Gastric tubes placed, iv fluids, possibly abx, progress feeding if tolerate
What is a replogle tube
○Double lumen tube inserted into stomach via mouth or nose- conncected to suction on wall.
○One lumen for draining saliva
○Other lumen works as air vent
○Provides decompression
○Avoids secretion overflow into trachea

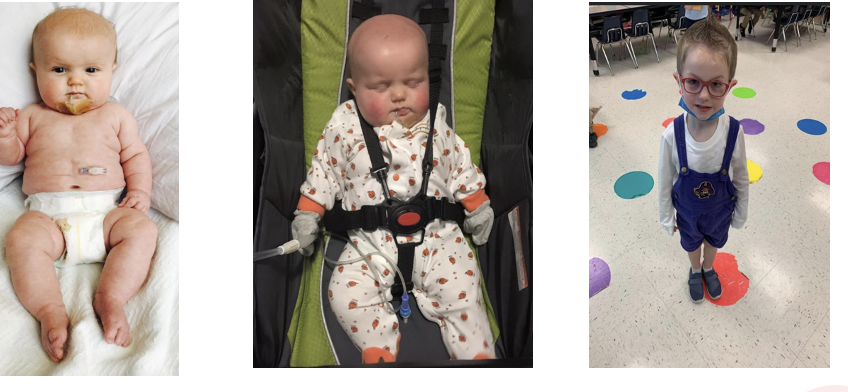
WHat is Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis
○Hypertrophy of pyloric muscle with obstruction of gastric outlet
Symptoms
○Projectile vomiting
○Visible peristalsis
○Olive-sized mass upper abdomen
○Diagnosis and Treatment - US, upper GI, labs to check
Correct electrolute imabalances before surgery
Preop- keep NPO, NGT to decompress stomach, check ouput freq, fluids, prootote comfot, pacifiers, swadall
After sugery- start clear fluids then progress, pain s/s infect, when change diaper don’t push on incision and pull their legs up, slide diapers underneath,
Nursing Management
Msucle thickens and causes projective vomiting
Increase in 1st born white babies or family hx. Detected 2-8 wks after birth
Wont have bild in it
Can throw up to 8ft.
Will be irratible, not grow, dehydrate, failure to thrive
Peristalsis- olive shaped mass.
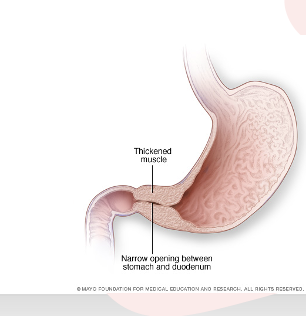
What is a Diaphragmatic Hernia
○Abd contents - organs in stomach push on chest cavity. protrude into lung cavity through diaphragm. The diaphragm didnt form completely , Life threatnening
Symptomsxx x.
○Resp distress, sunken abd, bowel sounds in chest
○Barrel chest bc everything being pushed up, dyspnea, cyanosis
○Diagnosis- US prior to birth or x ray after
○Medical Management: Life Threatening- Airway, NG/OGT, IVF, surgery
○Nursing Management
Monitor, IVF, post-op care
NICU- resp support, itnutbate them, immed drop NGT to decompress stomach- will help reduce the pressure on their lungs. do not bag mask ventilate them- bc you will inflate instestines w air
Umbilical artery catheter for IV fluids
ECCMO- pumps and oxygen outside of body- allows lungs and heart to rest
Propolactic abx, surgery asap
Keep upright- put head higher so we can keep things down, watch resp complic, decrease stimuli
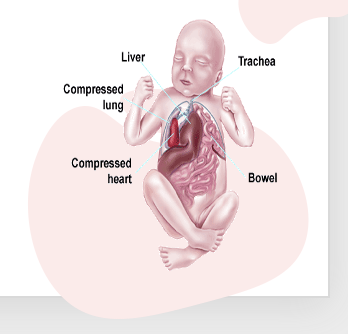
What is Omphalocele and Gastroschisis
○Protrusion of abdominal contents through abdomen
○Omphalocele- through umbilical cord (covered)- clear membrane covering it.
○Gastroschisis- no membrane covering organs
○Diagnosis- Associated w other defects, Can detect at US, can deliver vag or c sect
○Medical Management
Nursing Management
○Temperature
○Hydration
○Postop
At deliver- if organs outside body cover w sterile saline gauze, bowel bag bcs bowels radiate heat, surgery in stages- have to wait till hemodynamically stable
Good skin care
NGT for stomach decompression
NPO before sugery
Post op- concerned w circulation in lower extemetiies, return of bowel fx, fluid and electrolyte balance.
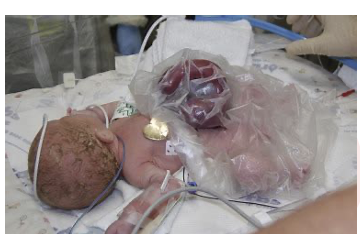
What is a silo
•Temporary housing unit
•Reduces contents slowly depending on type
•Helps reduce intestinal edema Helps recuded inflammation and slowly go in.
What is Intussusception
○Portion of intestine prolapses and telescopes into another- pushed
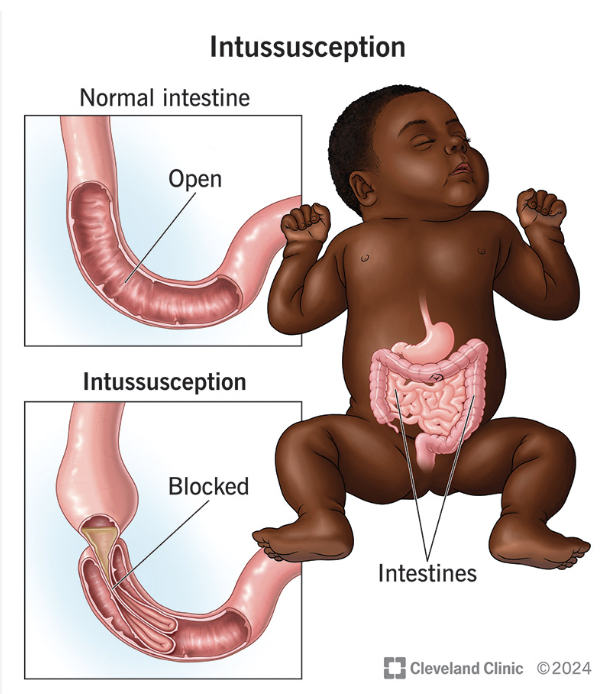
Symptoms
○Abd pain + vomiting
○Currant jelly stools
○Palpable sausage-shaped mass in RUQ or mid-upper
○Diagnosis and Treatment- US
○Nursing Management
○Fluids and electrolytes
Monitor, assess, meds
Blood flow obstructions, hemmorhage
More common boys 3 months to 6 years
Tx- ar barium air enema and sometimes the pressure pushed bowel where its supposed to be and correct itself , if it doesn’t= surgery, are at risk for it occurring again. Borwn poop= resolved
WHat is Volvulus (Malrotation)
○Twisting of intestines and cut off blood flow and cause necrosis of bowels
Symptoms
○Intermittent bilious vomiting
○Firm, distended abdomen
○Irritable, painful
○Bloody stools
○Diagnosis- upper GI w contrast
○Nursing management
Surgery, Keep npo, iv fluids, ngt stomach decompression, surgery
Check vs, return of bowel sounds after surgery, IV fluids, progress to regular diet
Sometimes need colon resection and ostomy.
What are Pediatric Ostomies
○Opening into small or large intestine that diverts fecal matter providing an outlet
Pediatric considerations
○Lifestyle
○Anxiety
○Electrolyte imbalance
○Nutritional deficiency
Pre and post-op care
Can happen during surgery and or electively
At risk for electrolyte emablances,
Skin integrity
School ages- deomstrate, show them
What are Gastric Buttons
○Indications
○Multiple types and sizes
○Balloon or no balloon
○G-J Button: Jejunal portion for feedings, bypasses stomach
○Assessment
○Teach routine care
Ballon w inflate. Flesh onstomach, can get feedings, med, fluid
WHat are the common Ingested Agents
○Corrosives (batteries, house cleaners, denture cleaner)
○Hydrocarbons (gasoline, lighter fluid, paint thinner)
○Acetaminophen
○Salicylate (aspirin)
○Iron (vitamin or mineral supplement)
○Plants

How do you assess posioning- emergency tx
1.Assess victim:
Initiate CPR if needed (airway, breathing, circulation)
Take VS, reevaluate routinely
Treat associated complications
2.Terminate exposure:
Empty mouth
Flush eyes with NS or room temp tap water for 15-20 min
Flush skin and wash with soap and water, remove contaminated clothes
3.Identify the poison:
Ask questions, look for environmental clues
4.Prevent poison absorption:
Place child side-lying, sitting, or kneeling position with head below chest to prevent aspiration
Administer activated charcoal if ordered (usually 1g/kg unless amount of toxin is known), administer drug antidote, or perform gastric lavage
Don’t have to memorize
Adivse parent– need to call posion control and they will educate on next steps.
If don’t know what ingested- can go into hospital
How does lead posining affect symptoms
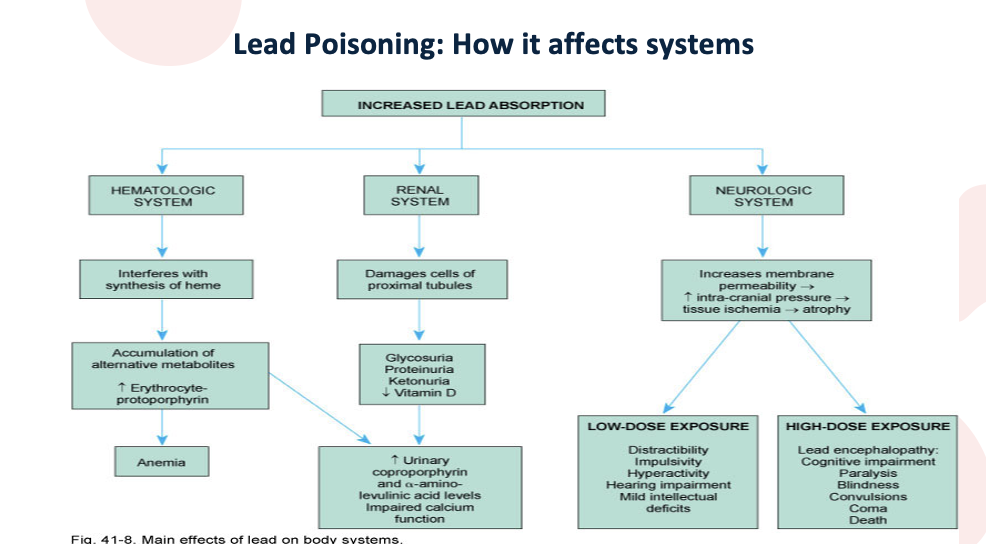
Don’t have to memorize. Absoprtion can effect systems. , toys, paint
Can cross blood brain barrier
If anemic can sbosrp lead faster
Draw blood an
What do you do for lead posioning
○Screening
○1-2 years old
○Low risk exceptions
Management
○Education
○Chelation therapy- pull lead out of body
○Prevention
Can give im injections- chelation. Remove lead from blood and organs. Side effects- hard on kidneys, make sure stay well hydrated.