Endocrine System 다이어그램 | Quizlet
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Which type of cell signaling synthesizes and secretes hormones into the bloodstream?
endocrine
Which type of cell signaling secretes enzymes into ducts?
exocrine
Sudoriferous, sebaceous, mucus, digestive, and mammary glands are examples of what kind of gland?
exocrine
What is the cell signaling where the target is nearby?
paracrine
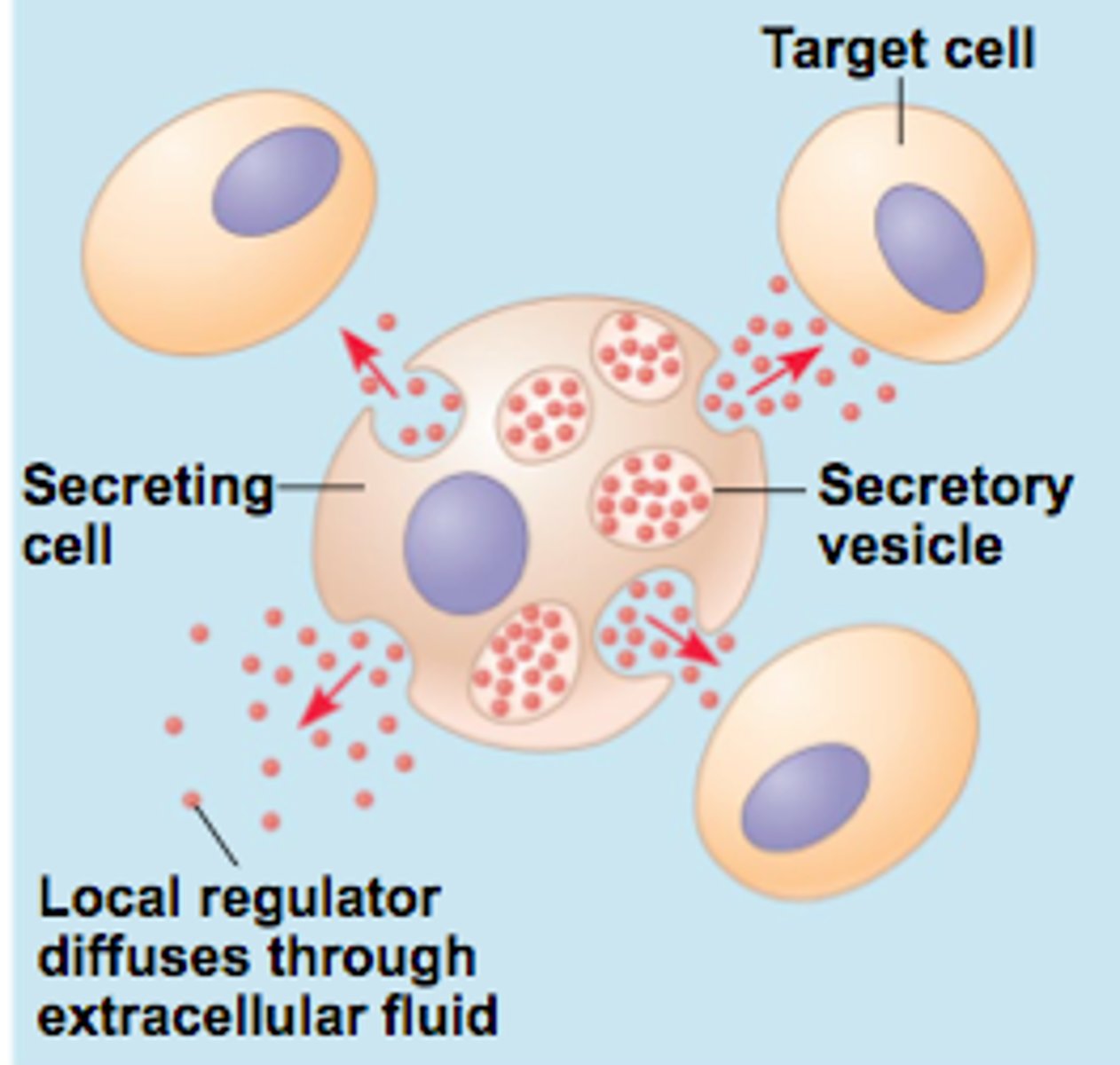
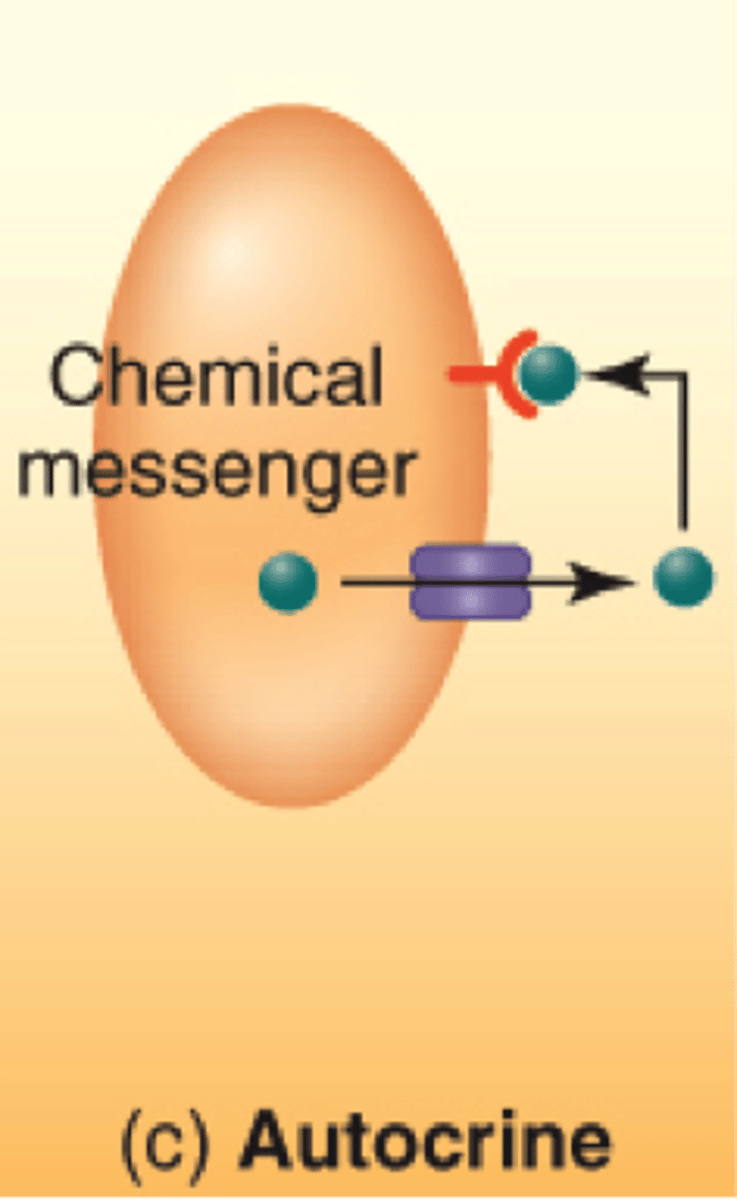
What kind of cell signaling utilizes hormone or chemical messengers that bind to receptors on the same cell?
autocrine
What is the name for the substances that are transported throughout the body in blood to stimulate an action?
hormones
(Note: a small amount has a large impact)
What are the 3 categories of hormones?
1. peptide
2. steroid
3. tyrosine derivatives
Which category of hormone is synthesized in the
rough ER and modified in Golgi?
peptide
(Note: acts on surface receptors typically via secondary messengers)
When a peptide hormone is manufactured in the ER, what is it called?
pre-prohormone
When a peptide hormone is cleaved in the ER lumen, what is it called?
prohormone
After a peptide hormone leaves the ER lumen, where does it get cleaved again to reach its final form?
golgi
The golgi packages peptide hormones into what to be released in exocytosis?
secretory vesicles
Peptide hormones are soluble in what?
water
(Note: can move freely though blood but can't diffuse well through cell membrane of effector - target cell)
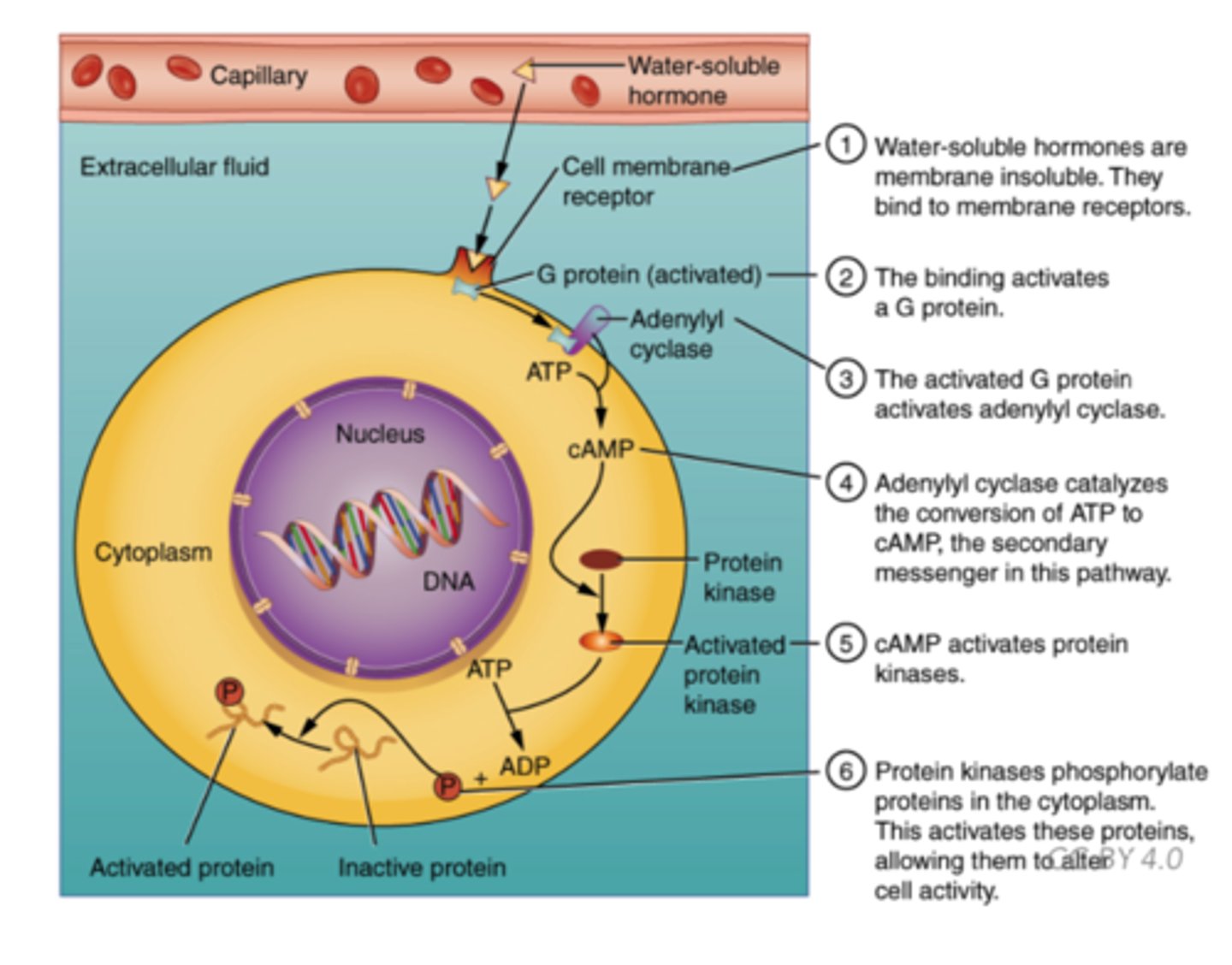
How do peptide hormones enter the target cell?
attach to membrane- bound receptor to trigger an effect
Receptors on target cell may act as what to increase membrane permeability to specific ions?
ion channel
Receptors on the target cell may activate or deactivate what to act as ion channels?
intrinsic membrane proteins
Receptors on target cell may activate what to create a cascade of effects?
intracellular second messenger systems
(Note: hormone is the 'first' messenger, and other chemicals act as the 'second' messenger)
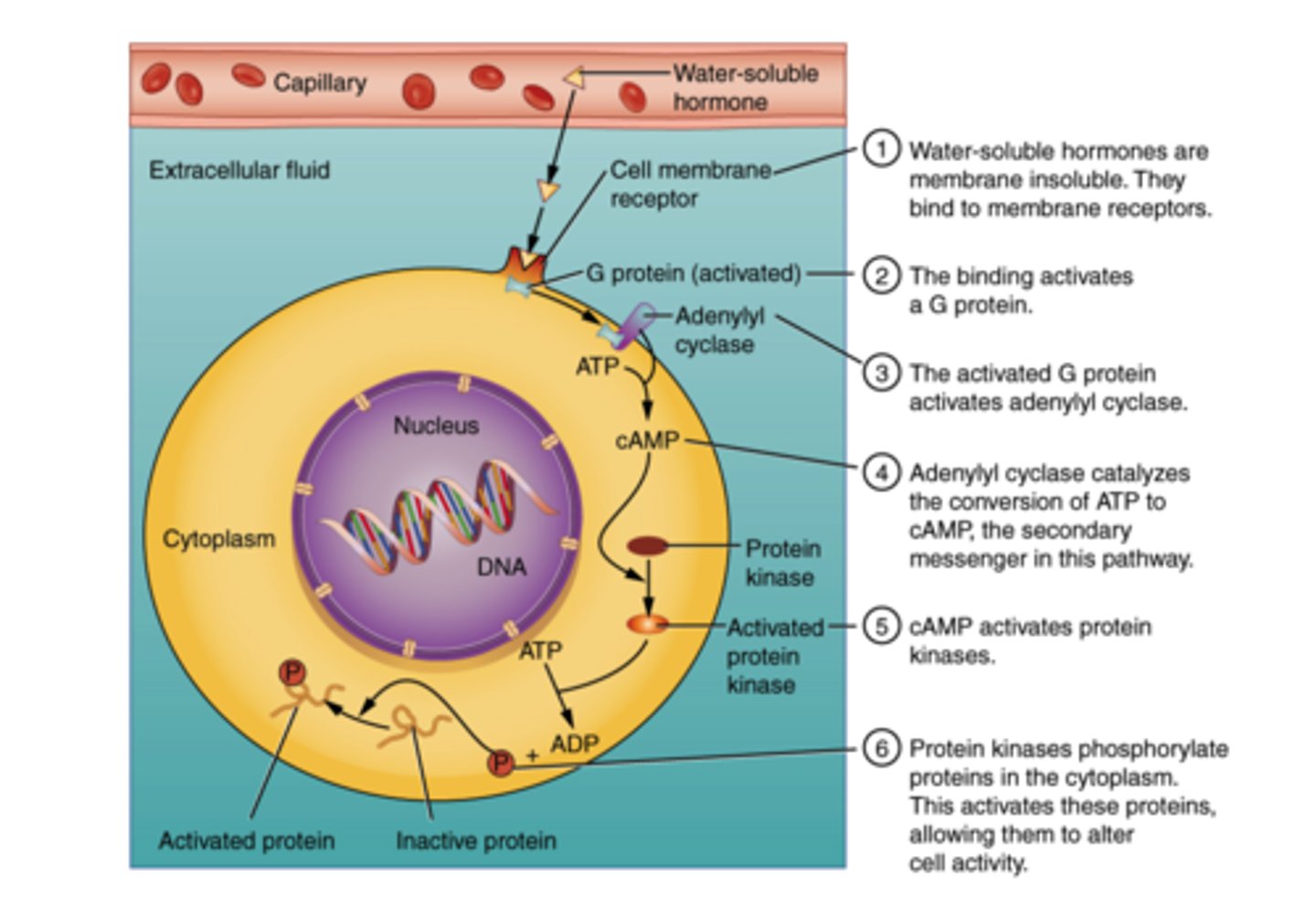
A protein stimulating the production of second messengers is an example of what process?
receptor mediated endocytosis
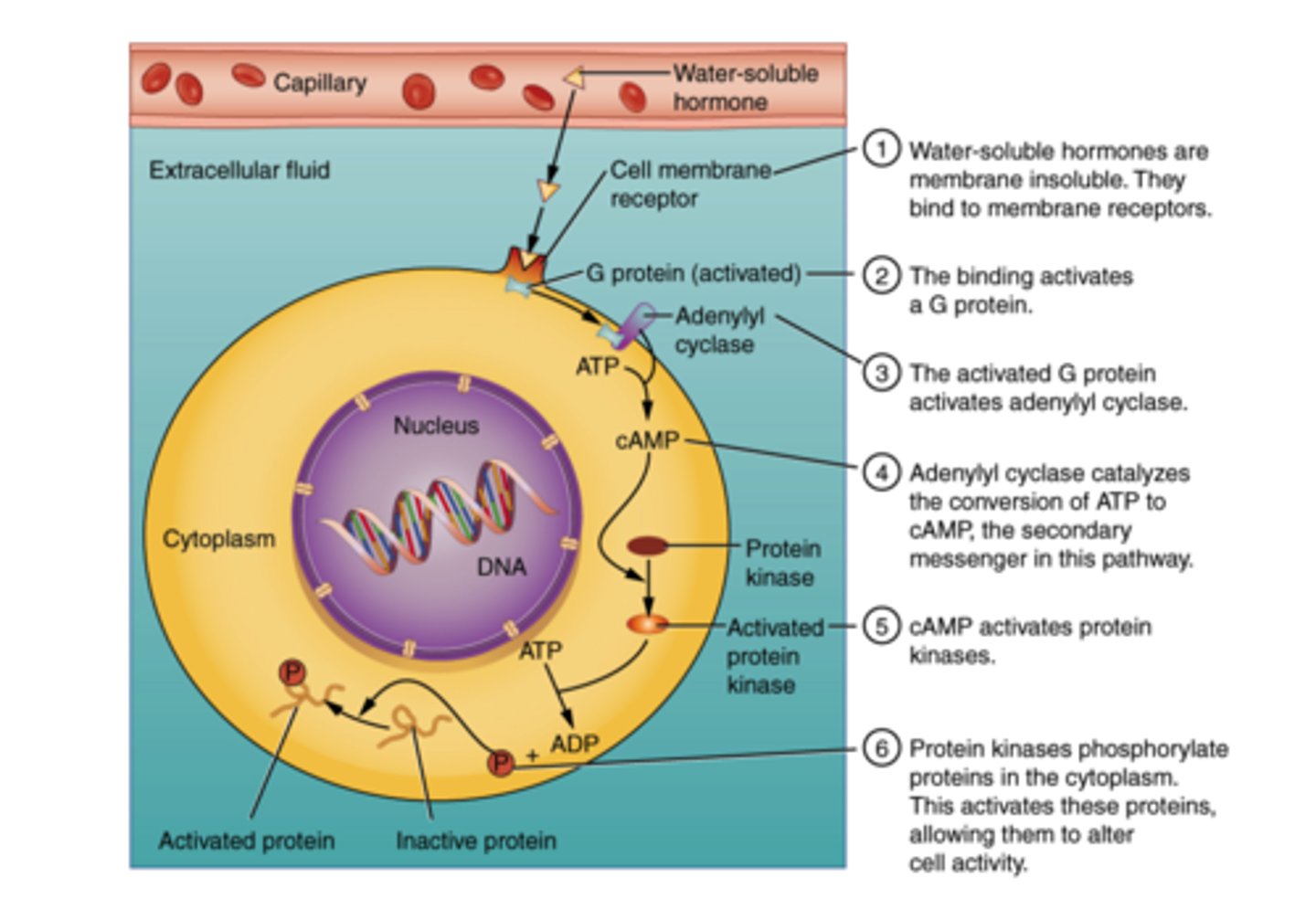
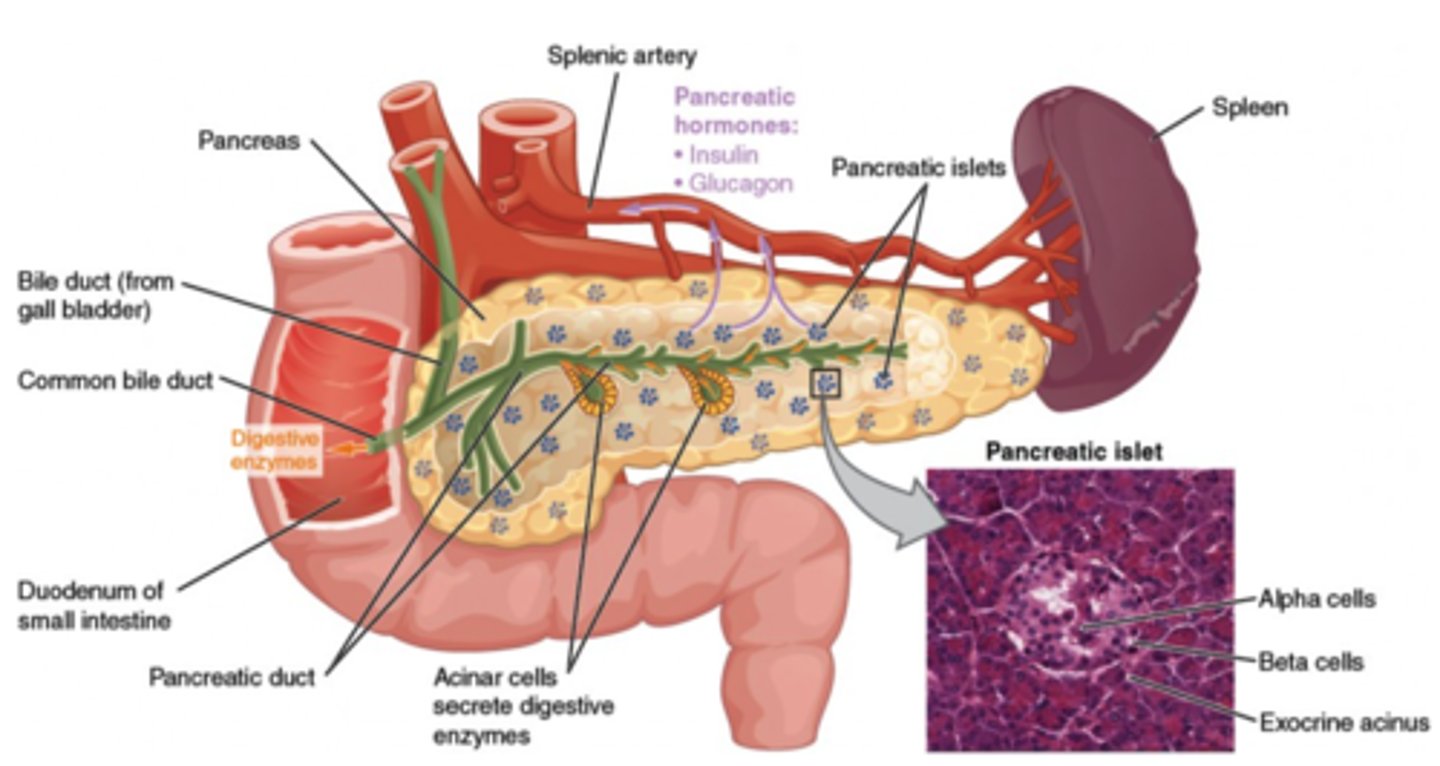
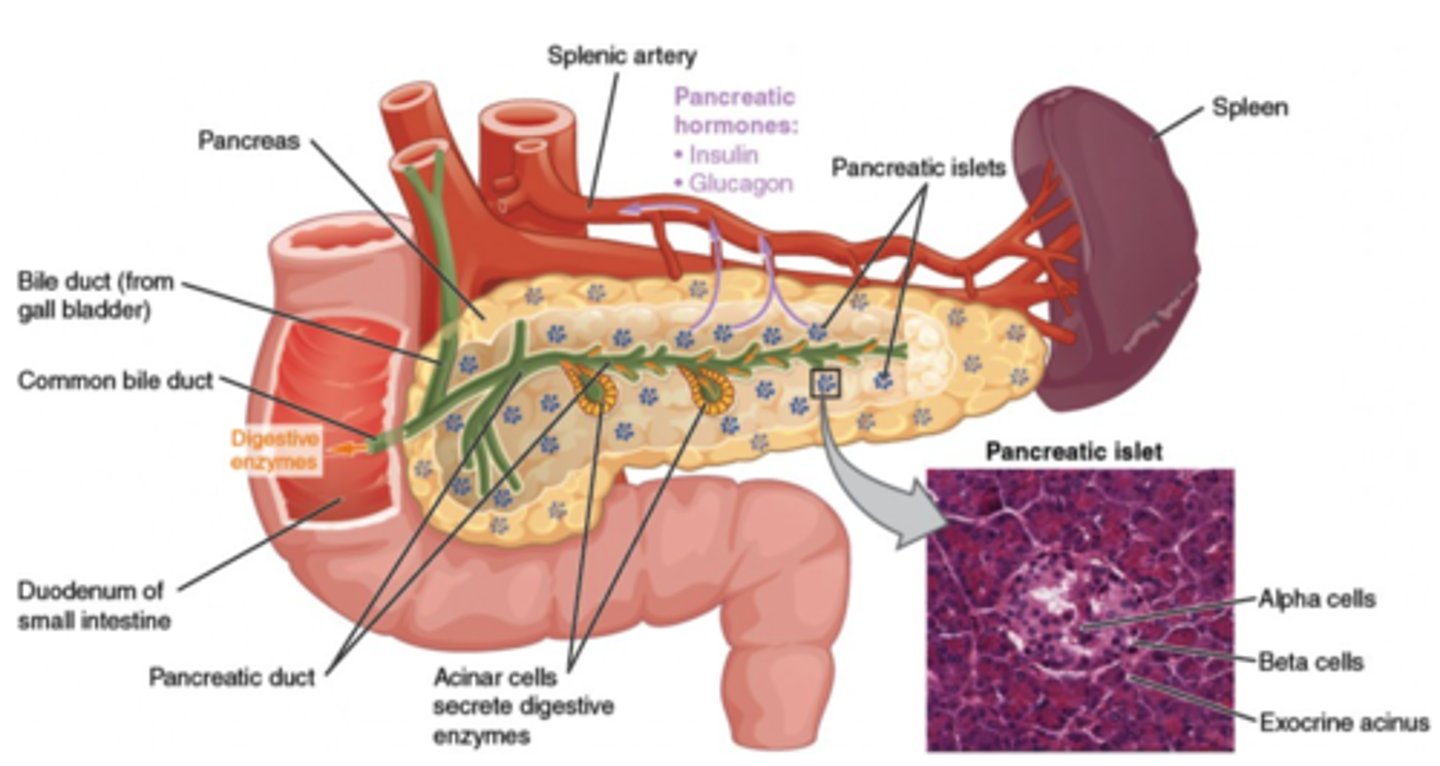
What kind of gland is the pancreas?
exocrine and endocrine
(Note: it releases digestive enzymes via the pancreatic duct, and insulin + glucagon into blood)
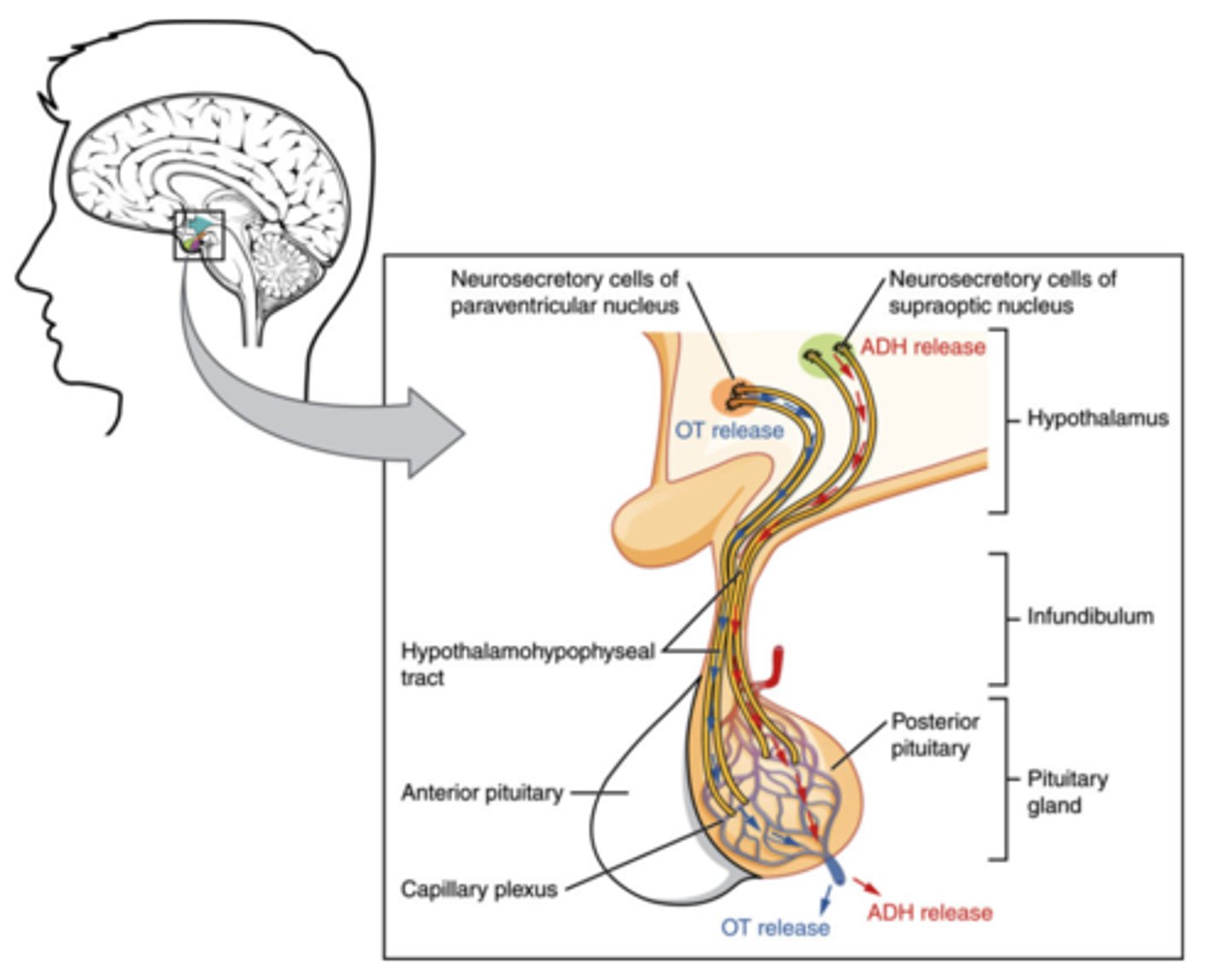
What structure secretes FSH, LH, ACTH, hGH, TSH, and prolactin?
anterior pituitary
(Note: examples of peptide hormones)
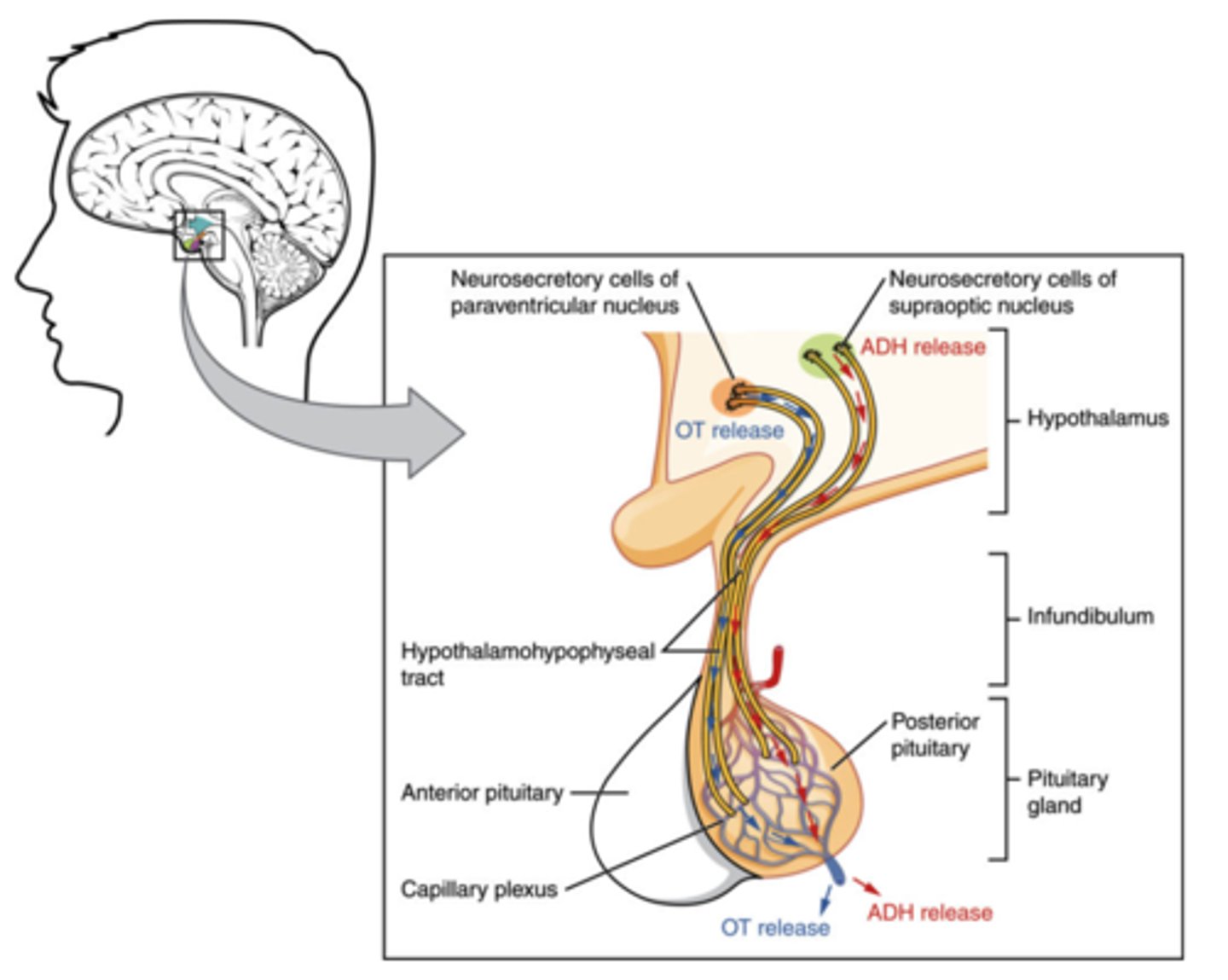
Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) is secreted by what structure?
posterior pituitary
(Note: examples of peptide hormones)
Glucagon and insulin are secreted by what structure?
pancreas
(Note: examples of peptide hormones)
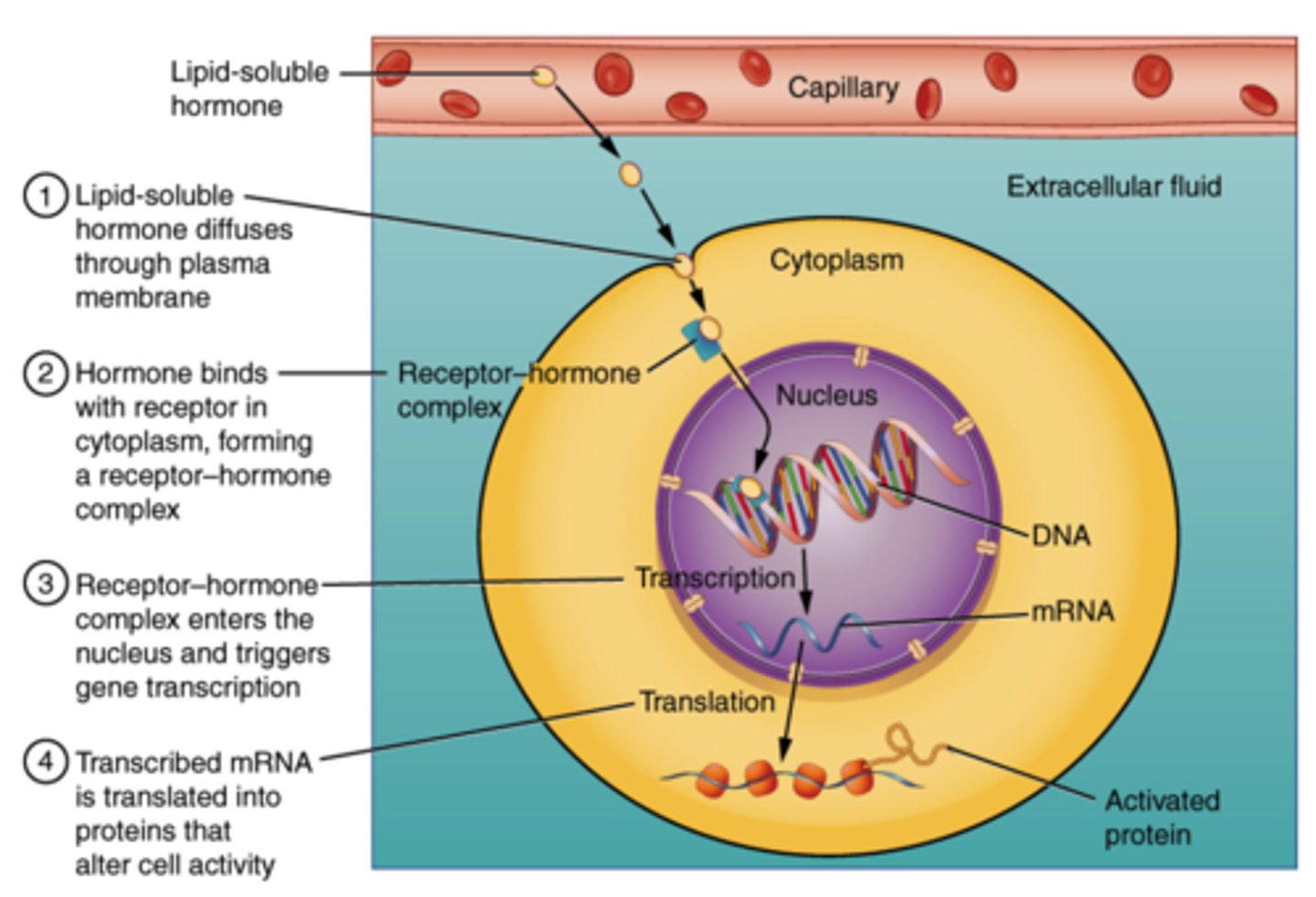
Which category of hormone is synthesized from cholesterol in the smooth ER, are hydrophobic, and have intracellular receptors?
steroid
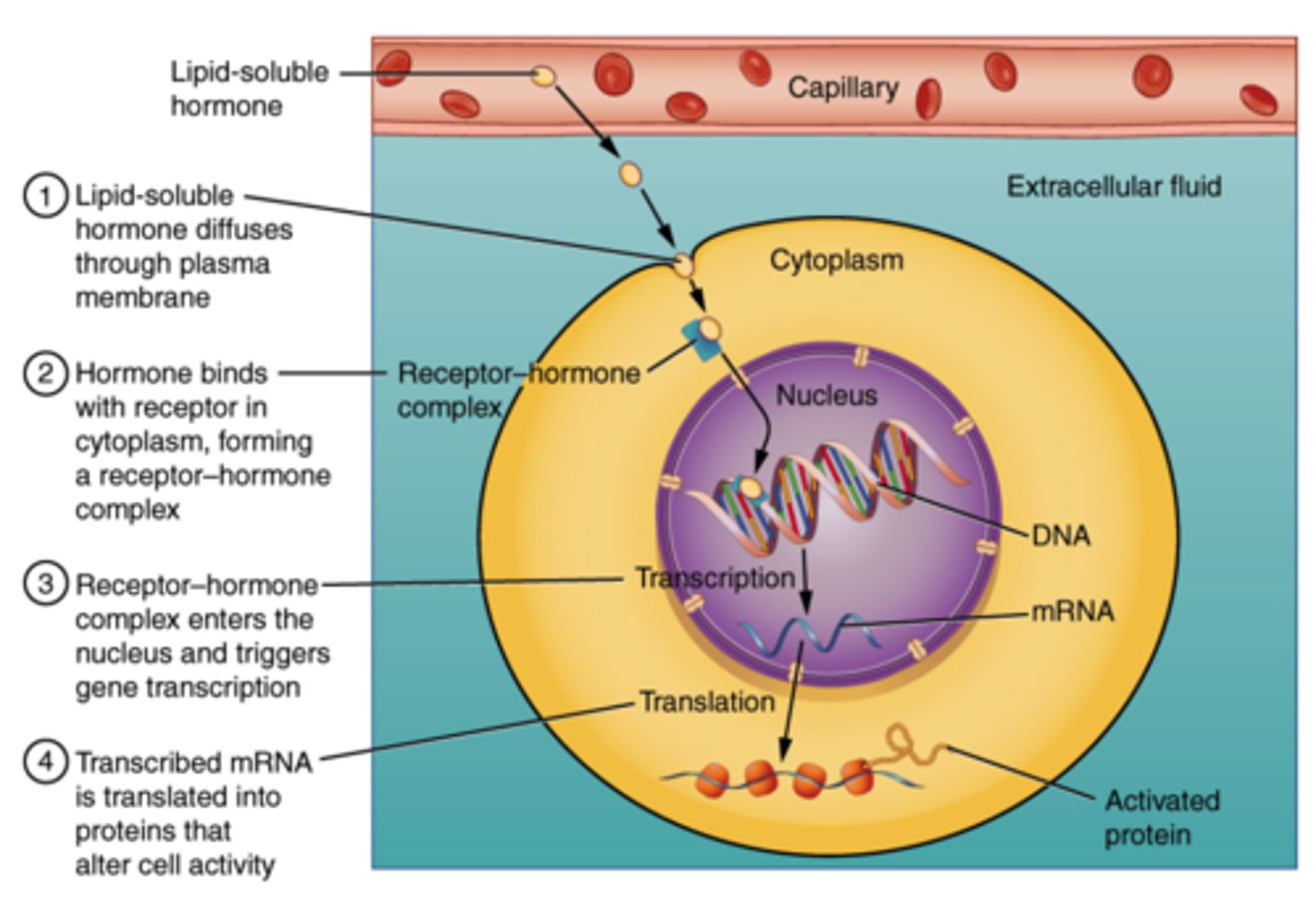
What is the process called when a steroid hormone diffuses into a cell and activates a portion of DNA?
direct stimulation
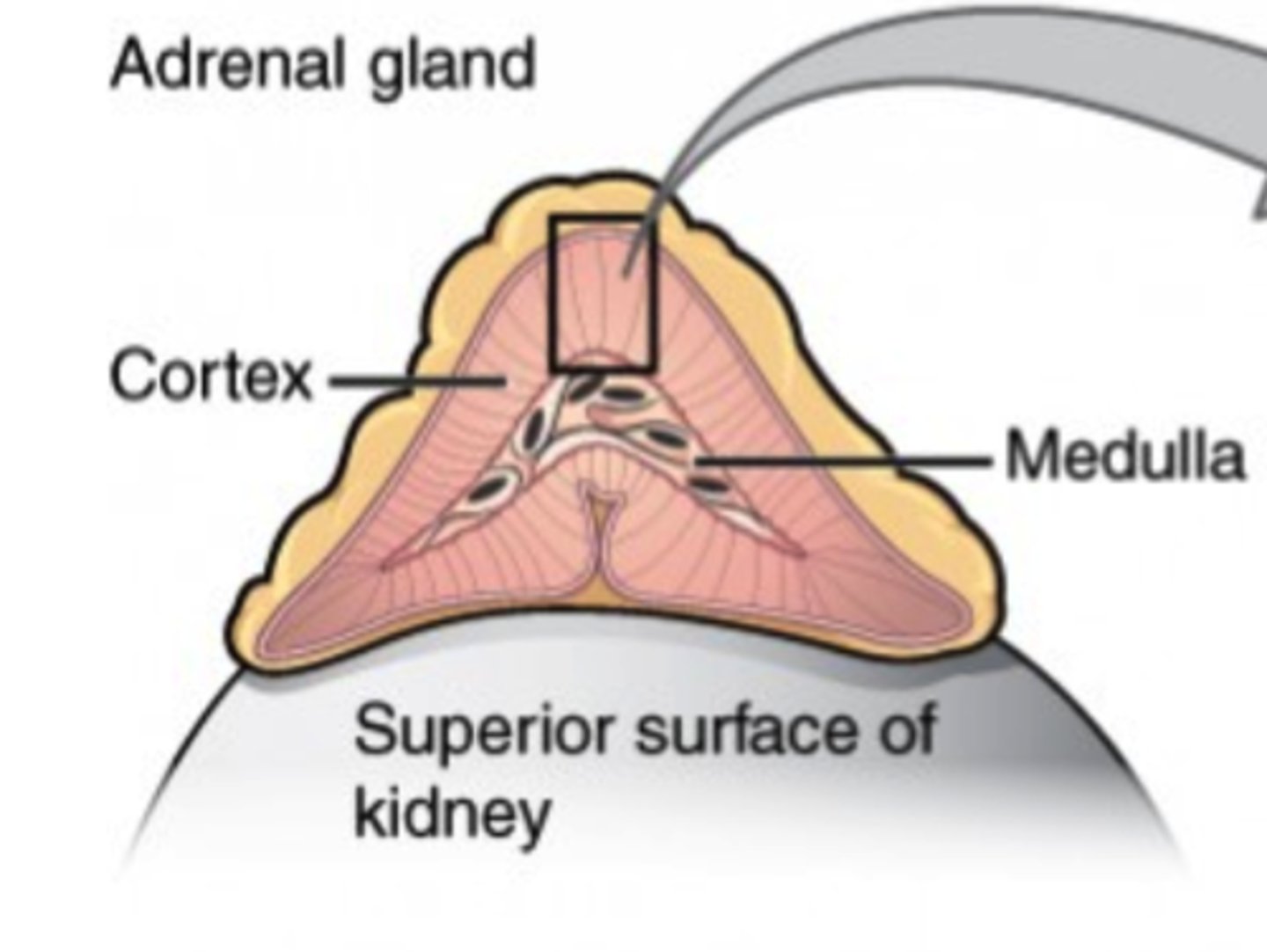
glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids (cortisol
and aldosterone) are secreted by what structure?
adrenal cortex
(Note: examples of steroid hormones)
estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone are produced by what structure?
gonads
(Note: examples of steroid hormones - estrogen and progesterone are also secreted by the placenta)
Which category of hormones are formed by enzymes in cytosol or on the rough ER?
tyrosine derivatives
Which tyrosine derivative hormones are lipid-soluble, require a protein carrier in the blood, and bind to receptors in the nucleus?
thyroid hormones
What is the time frame of thyroid hormone action?
The response has a latent period and increased duration
What is the function of thyroid hormones in the body?
increase transcription of many genes in nearly all cells of the body
Which type of tyrosine derivative includes epinephrine and norepinephrine that are water-soluble, dissolve in blood, bind receptors on the target tissue, and mainly act via second messenger cAMP?
catecholamines
T3 and T4 (thyroxine) are which type of hormones?
thyroid hormones
Where are hormone receptors located?
on the membrane or inside the cell
How can hormone regulation occur with respect to receptors?
increasing or decreasing the number of receptors in response to hormone amount
How can a single hormone have different effects with the same external receptors?
signal transduction pathways or effector proteins differ
What is the kind of feedback mechanism where the effector is the control point?
negative feedback
(Note: not the concentration of the hormone)
Which endocrine gland monitors the external environment and internal conditions of the body?
hypothalamus
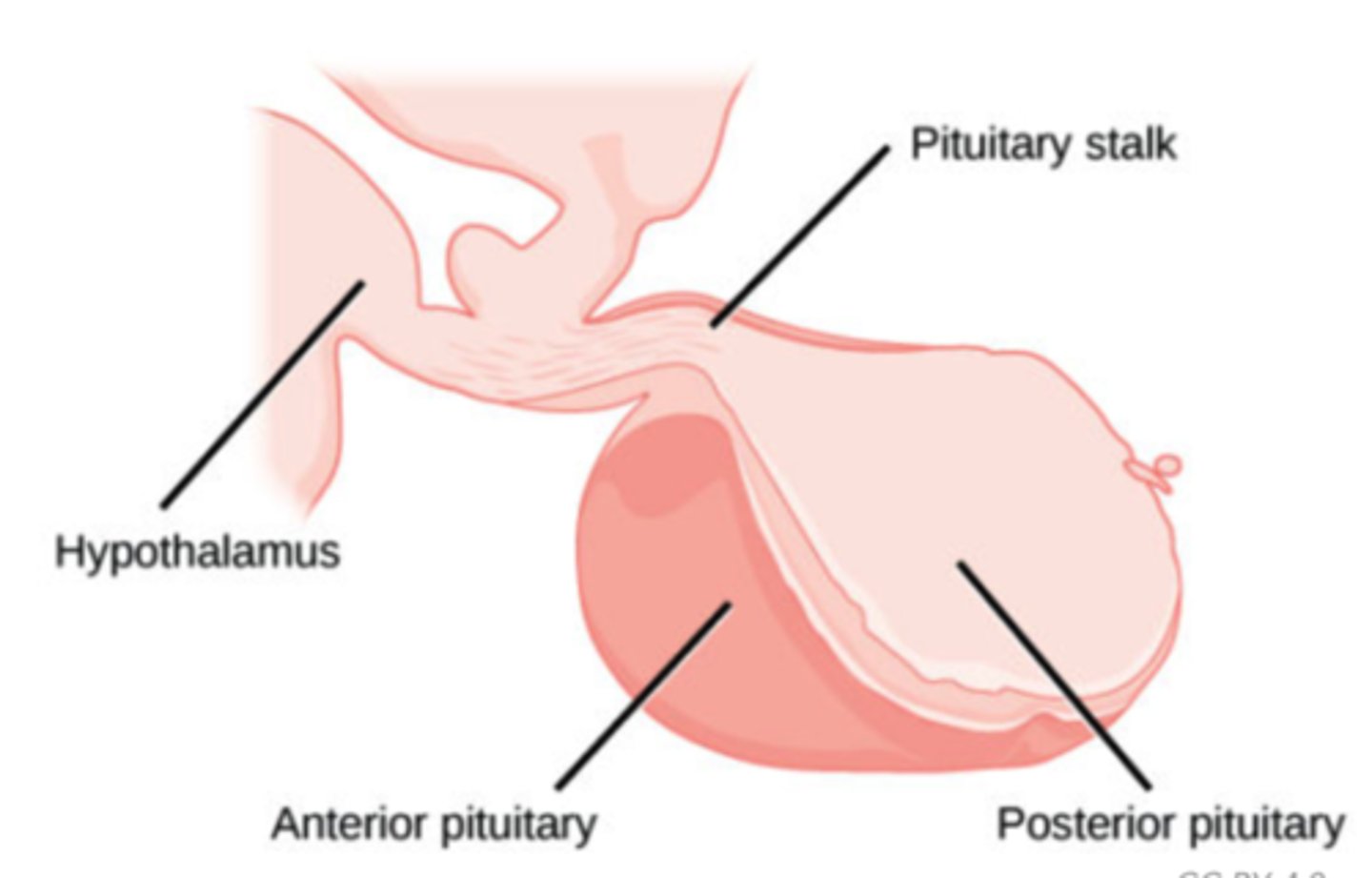
The hypothalamus contains neurosecretory cells that link the hypothalamus to what structure?
pituitary gland
(Note: considered the link between the endocrine and nervous system)
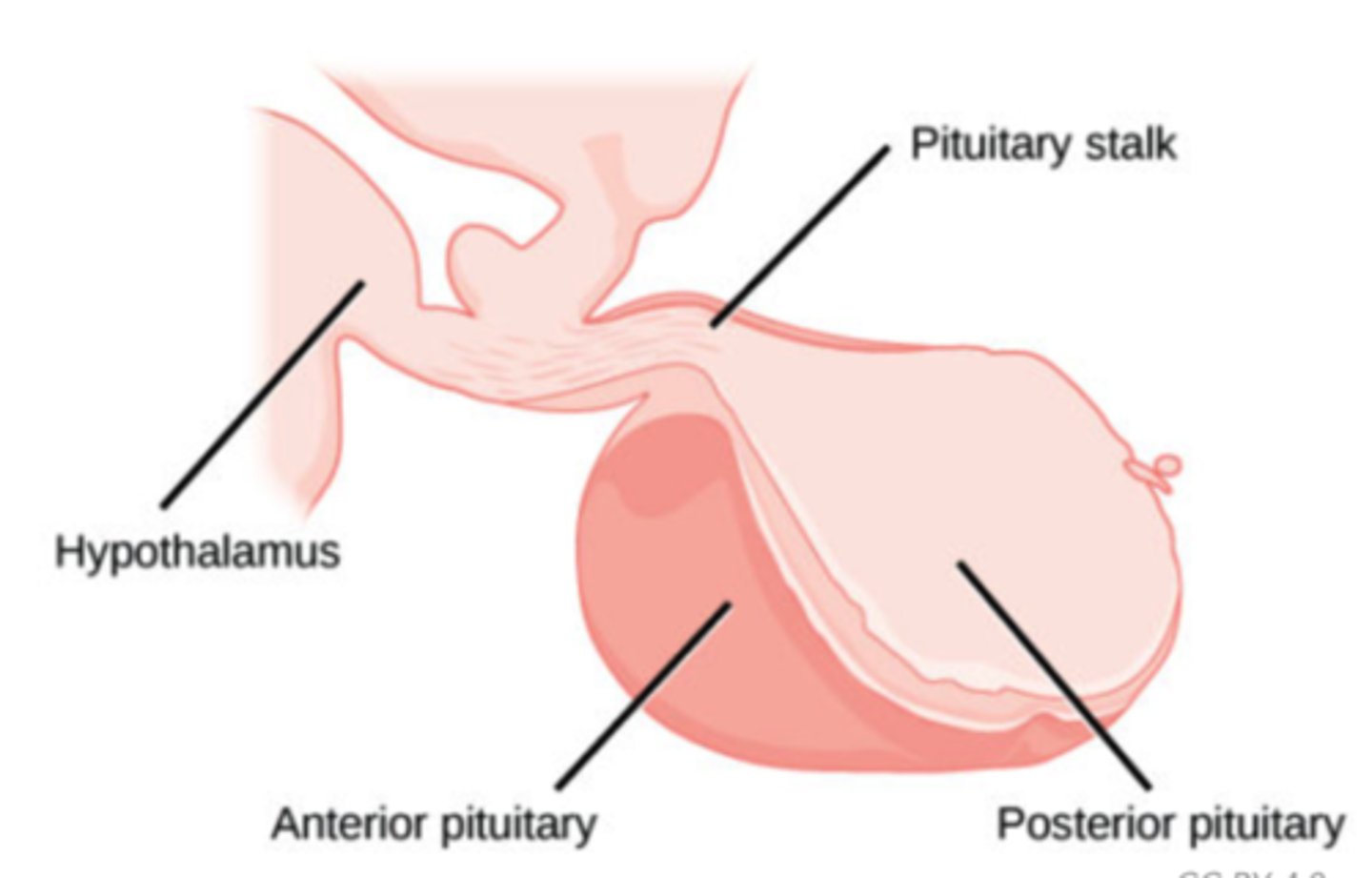
How does the hypothalamus regulate the pituitary?
1. negative feedback mechanisms
2. secretion of releasing and inhibiting hormones.
ADH (vasopressin) and oxytocin to be stored in the posterior pituitary are secreted by what structure?
hypothalamus
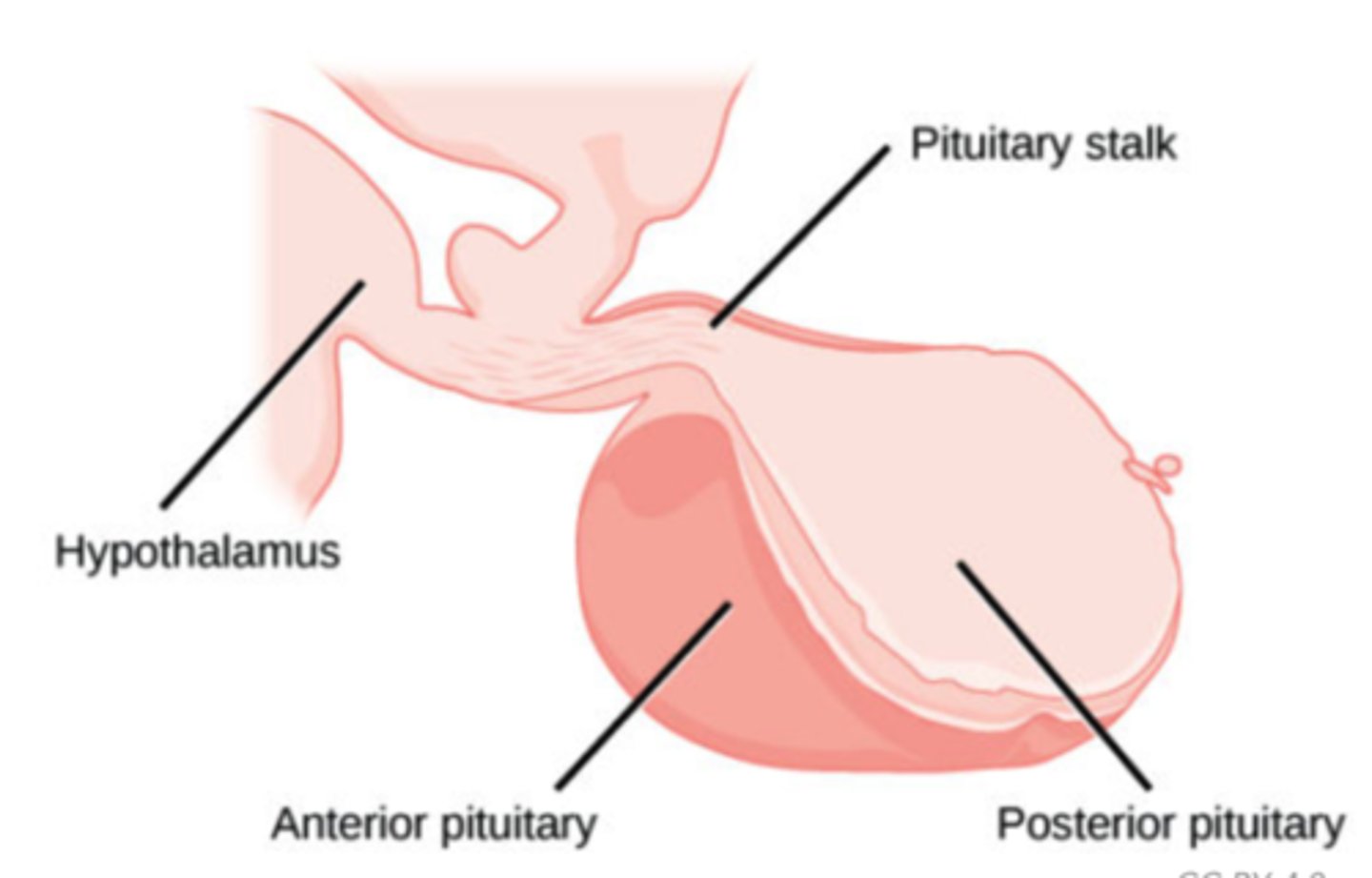
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from neurons, which stimulates the anterior pituitary to secrete FSH and LH are secreted by what structure?
hypothalamus
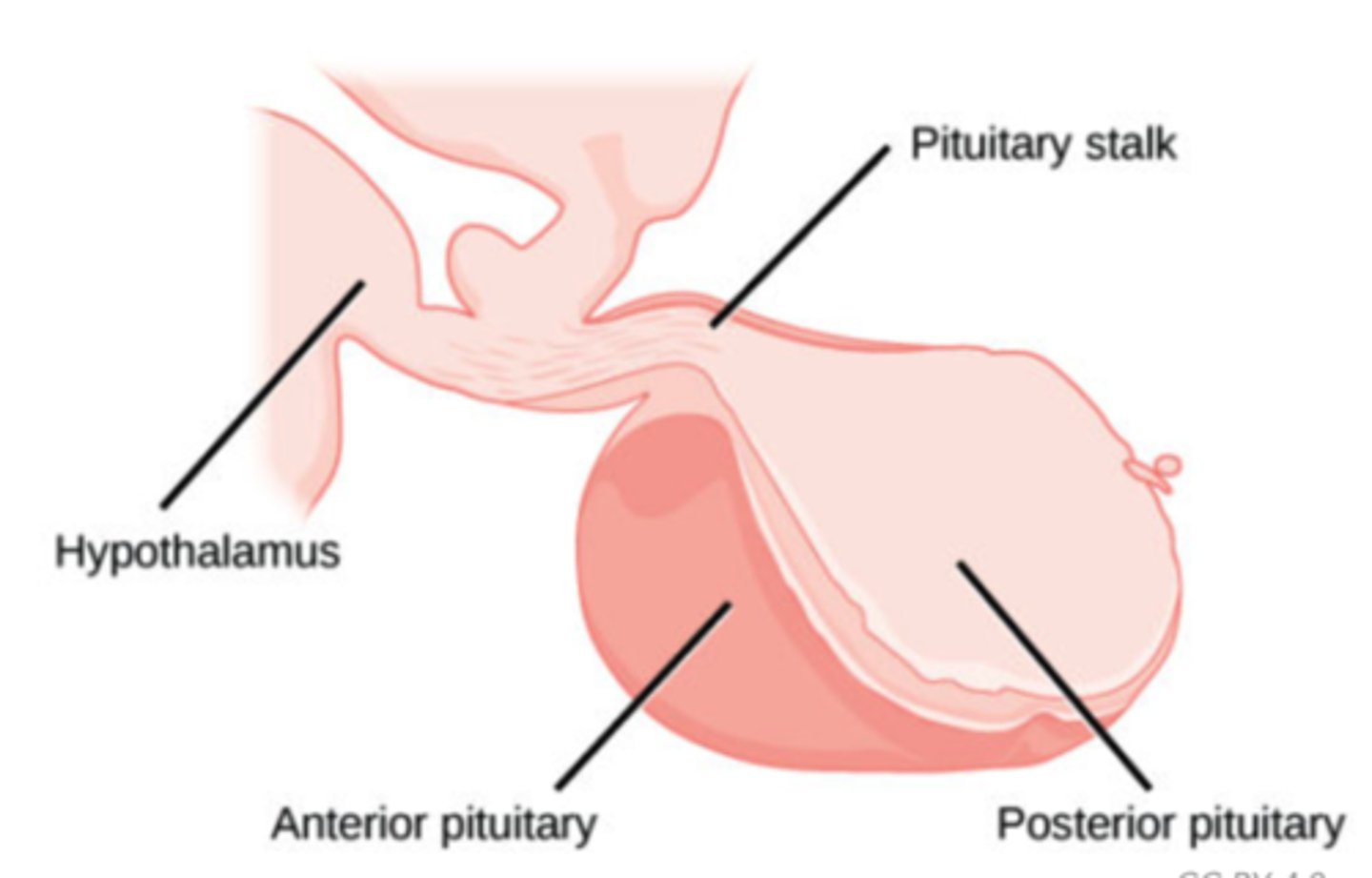
What structure mainly regulates hormone production by other glands, and is regulated itself by the hypothalamus?
anterior pituitary
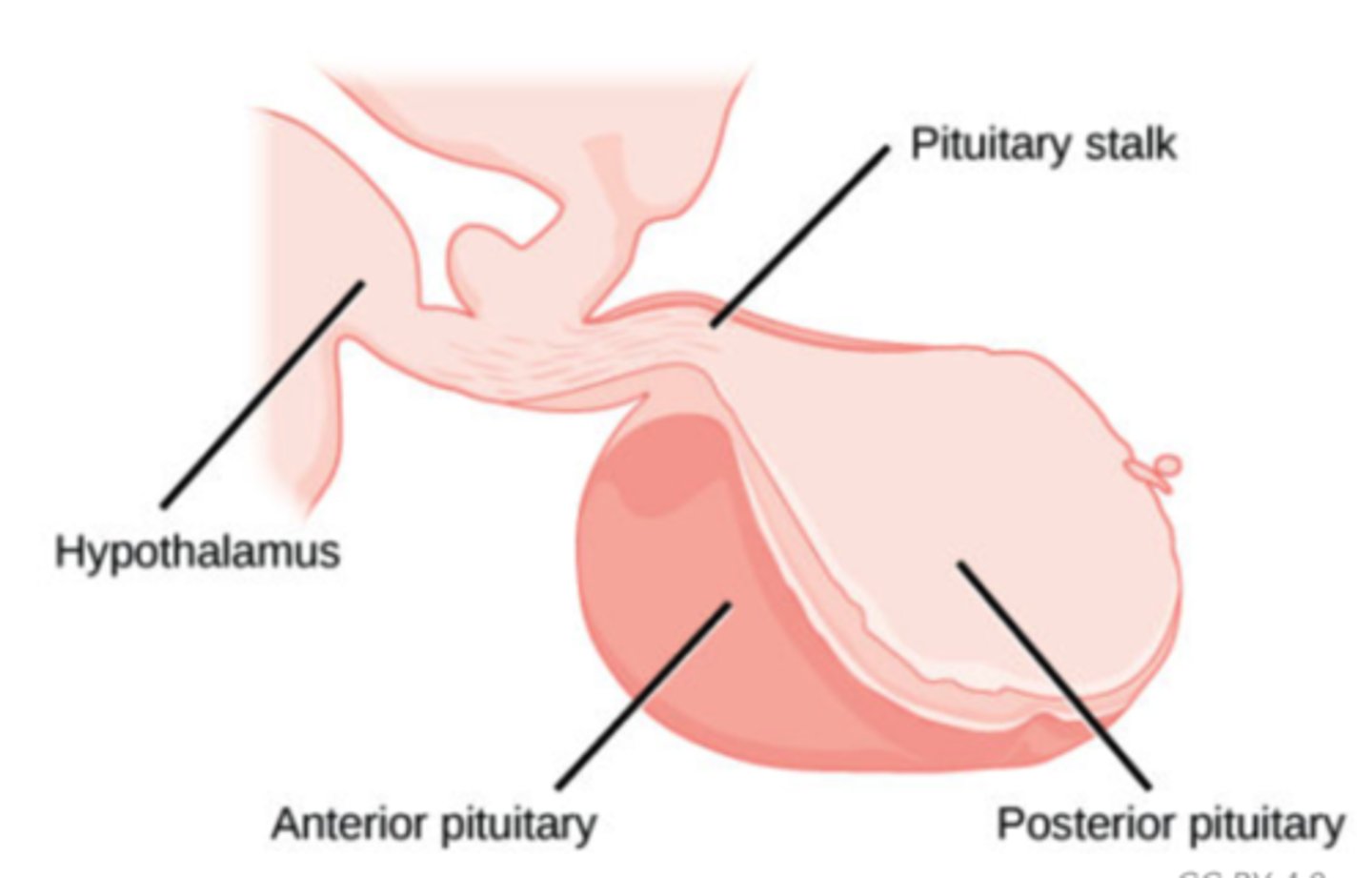
What type of hormones directly stimulate target organs?
direct (non-tropic) hormones
Which direct (non-tropic) hormone stimulates bone and muscle growth?
hGH (somatotropin)
Which direct (non-tropic) hormone stimulates growth in almost all cells of the body through metabolic modification?
hGH (somatotropin)
Which direct (non-tropic) hormone stimulates milk production in females from mammary gland cells?
prolactin
What can inhibit prolactin release?
hypothalamus
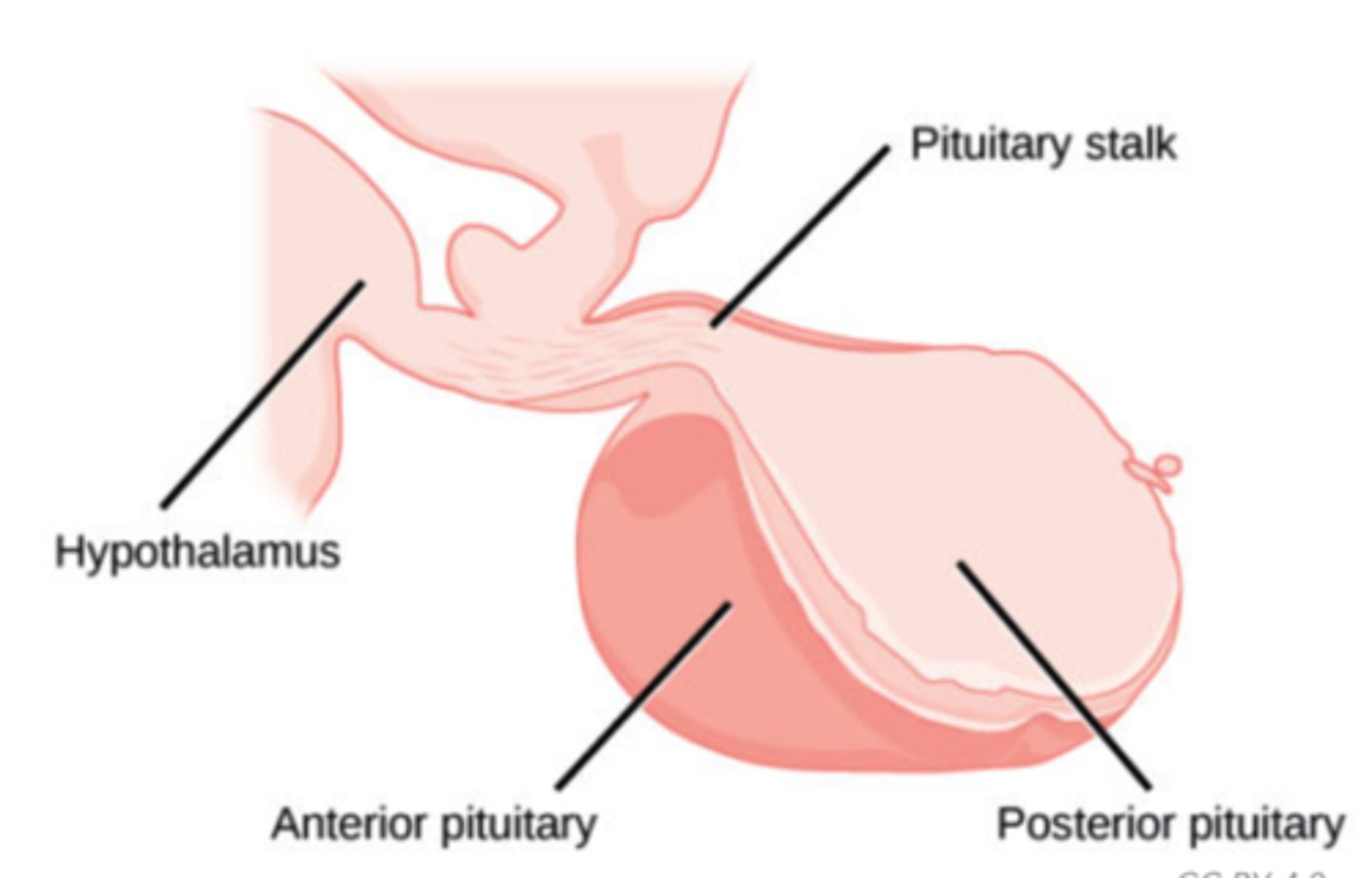
Suckling stimulates the hypothalamus, which stimulates what structure to release prolactin?
anterior pituitary
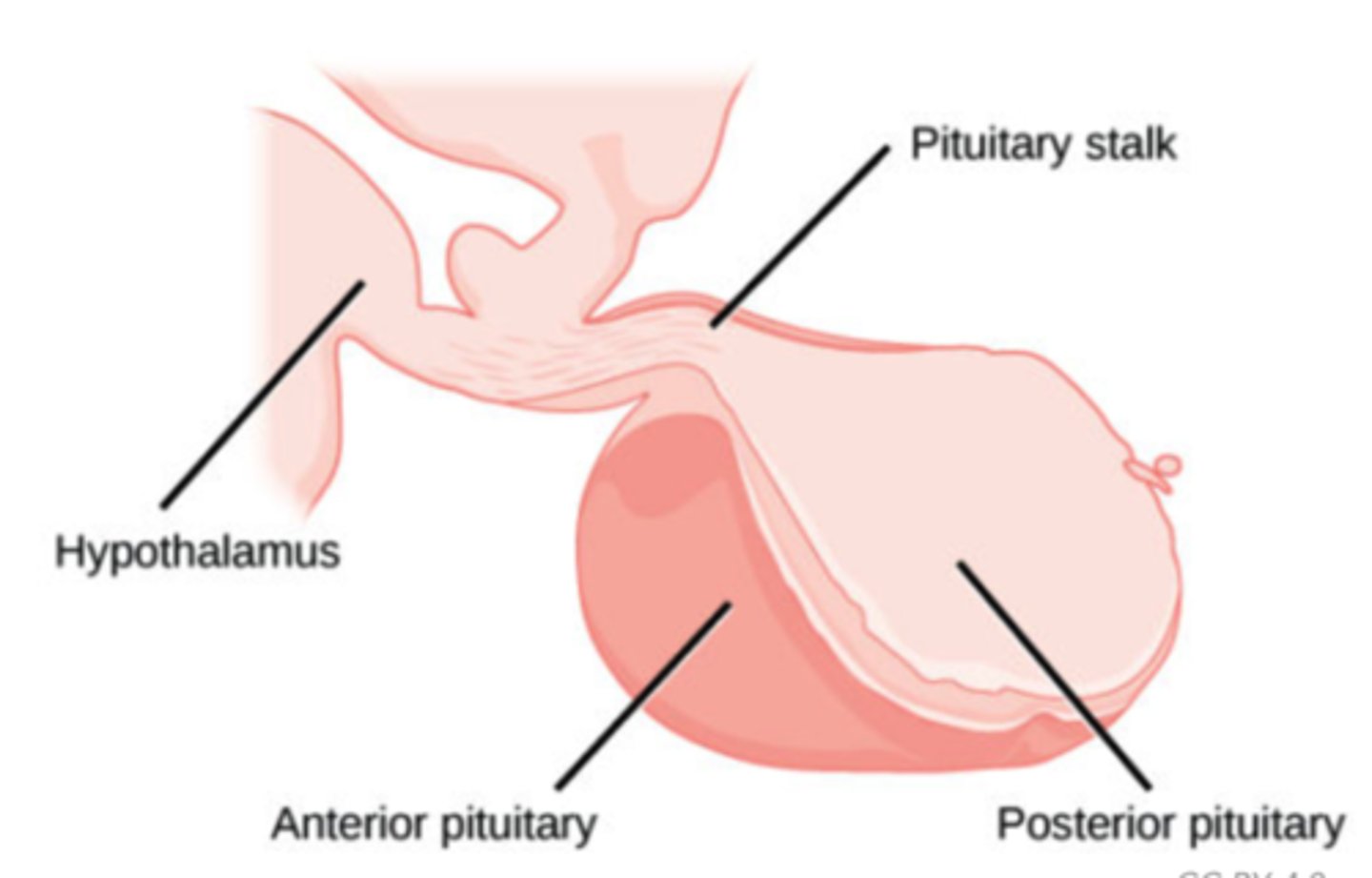
Why is there no milk production before birth?
inhibitory effects on hypothalamus by progesterone and estrogen
Which direct (non-tropic) hormone stimulates melanocytes to produce and release melanin?
melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH)
Which direct (non-tropic) hormone inhibit perception of pain (is technically a neurohormone)?
endorphins
Which type of hormone stimulate other endocrine glands?
tropic hormones
Which tropic hormone stimulates adrenal cortex —> release glucocorticoids via second messenger cyclic AMP?
ACTH
Release of ACTH is stimulated by which factors?
many types of biological stress
(Note: glucocorticoids are stress hormones)
Which tropic hormone stimulates the thyroid gland which in turn increases in size, cell number, and rate of secretion of hormones T3 and T4?
thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
T3 and T4 concentrations have what kind of effect on TSH release?
negative feedback effect
(Note: at both the anterior pituitary and hypothalamus)
Which tropic hormone in females, stimulates the formation of the corpus luteum, and in males, stimulates testosterone production?
luteinizing hormone (LH)
Which tropic hormone in females, stimulates estrogen secretion, and in males, stimulates maturation of seminiferous tubules and sperm production?
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
What structure does not synthesize hormones, but stores ADH and oxytocin produced by the hypothalamus?
posterior pituitary
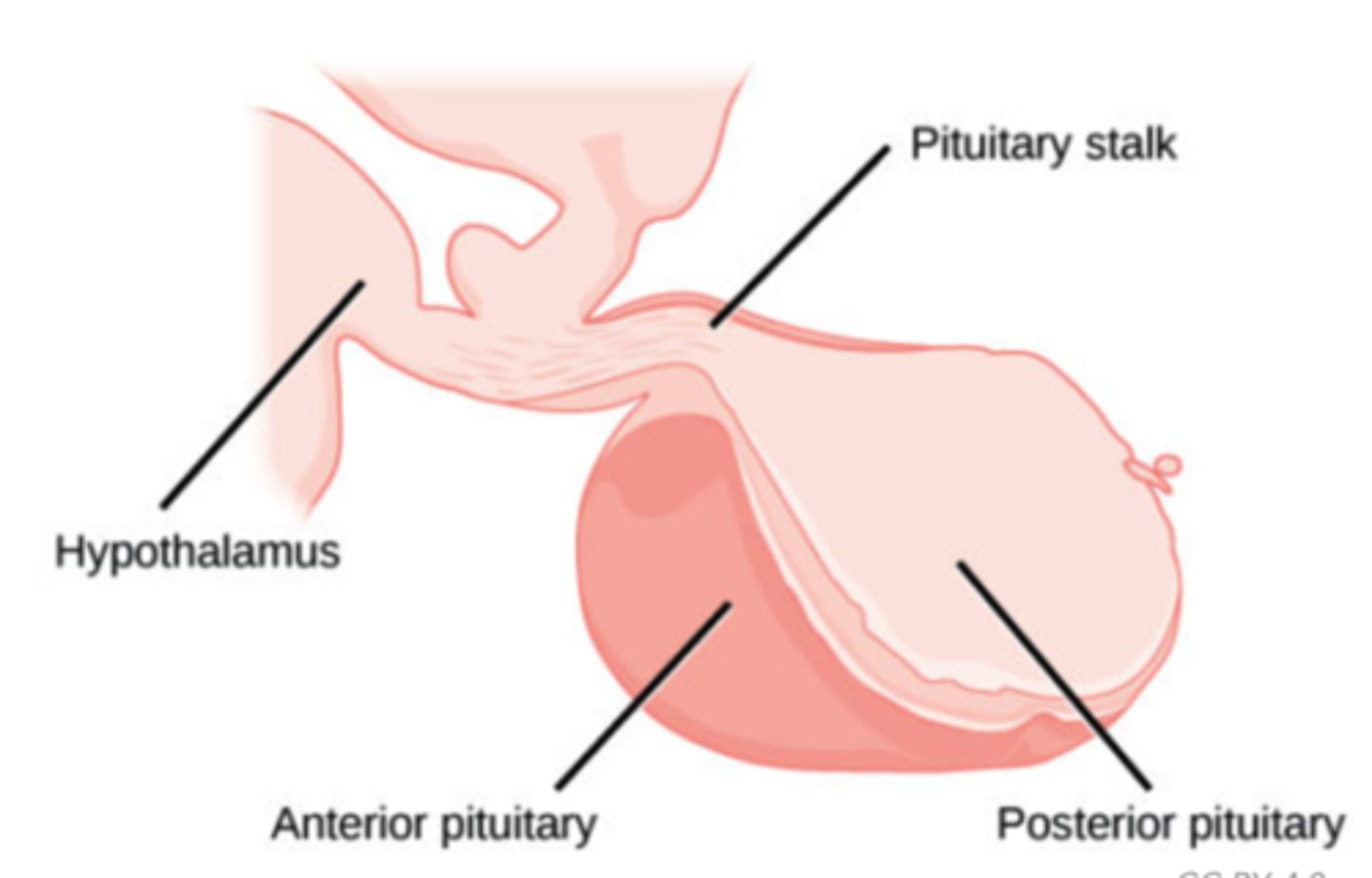
What hormone increases the reabsorption of water by increasing the permeability of the nephron's collecting duct, which leads to water reabsorption and increased blood volume and pressure?
anti-diuretic hormone (ADH/vasopressin)
Coffee and alcohol block ADH, therefore resulting in what effect?
increasing urine volume
Which hormone is secreted during childbirth, increases the strength of uterine contractions, and stimulates milk ejection?
oxytocin
How do hormones travel from the hypothalamus to the posterior pituitary and into the blood?
Neural cell bodies of the hypothalamus synthesize the hormones, and are transported down axons to the posterior pituitary where they are released into the blood
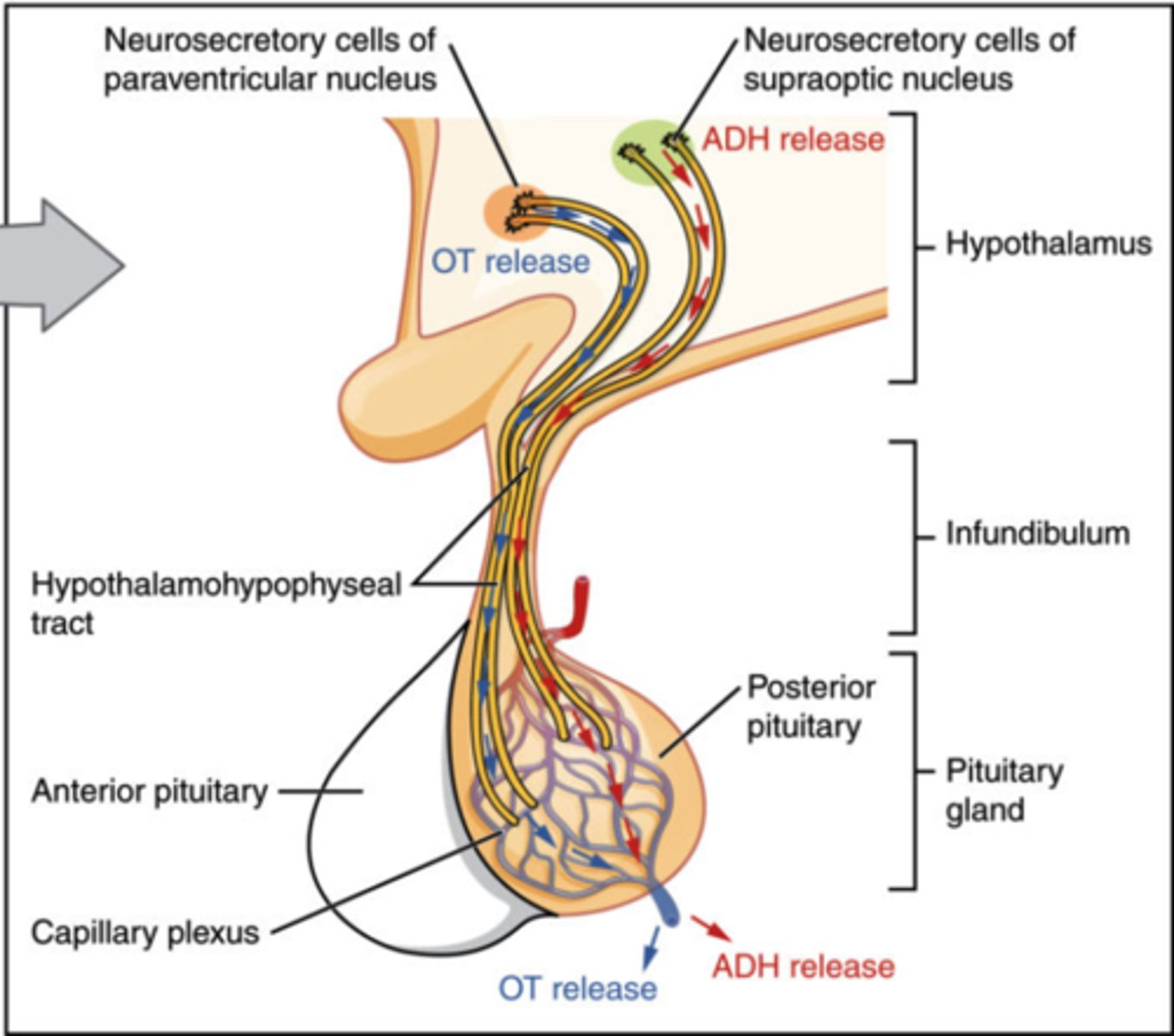
Which gland secretes melatonin which plays a role in the circadian rhythm?
pineal gland
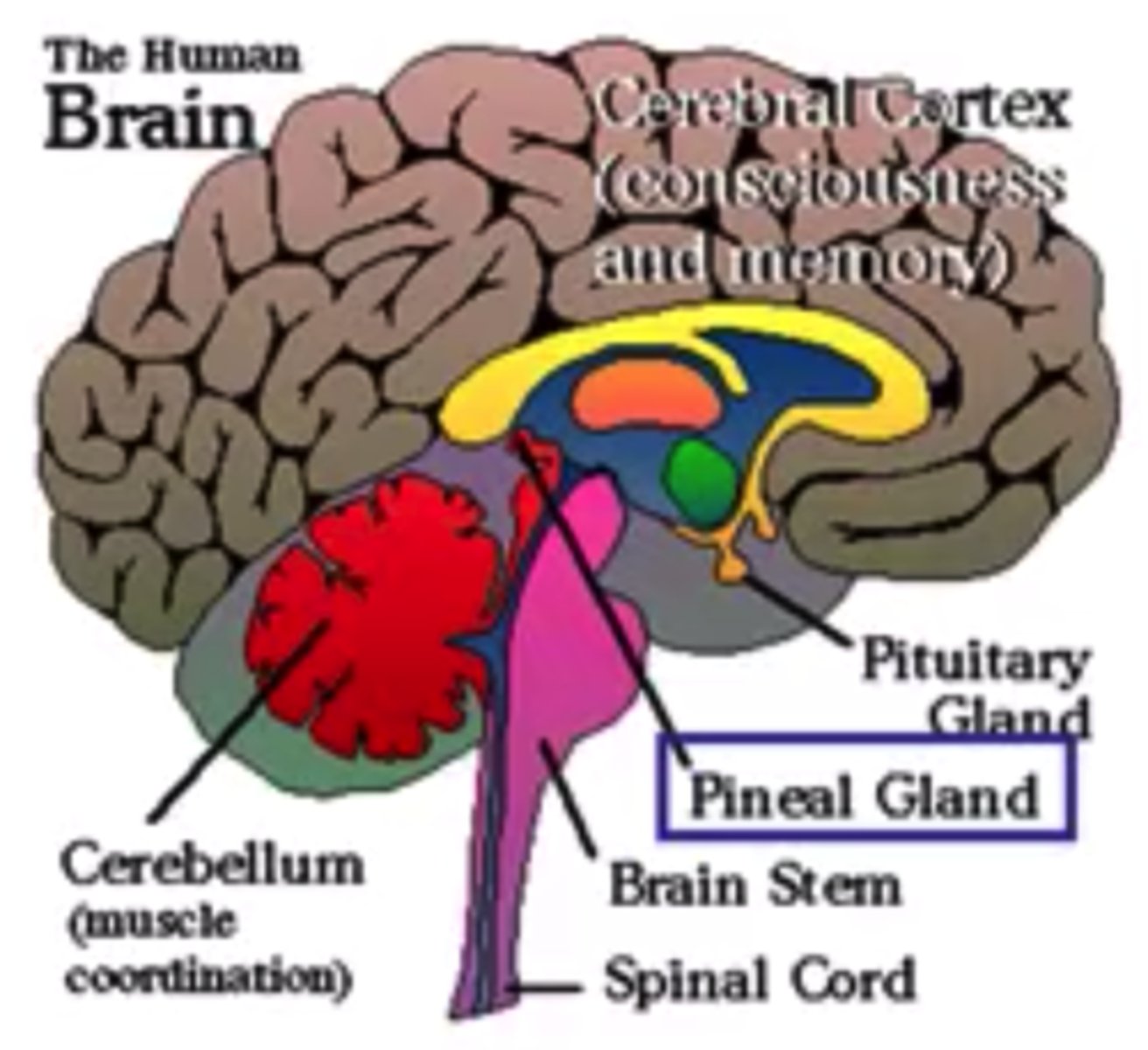
What are the endocrine glands in the human brain?
1. hypothalamus,
2. pituitary gland
3. pineal gland
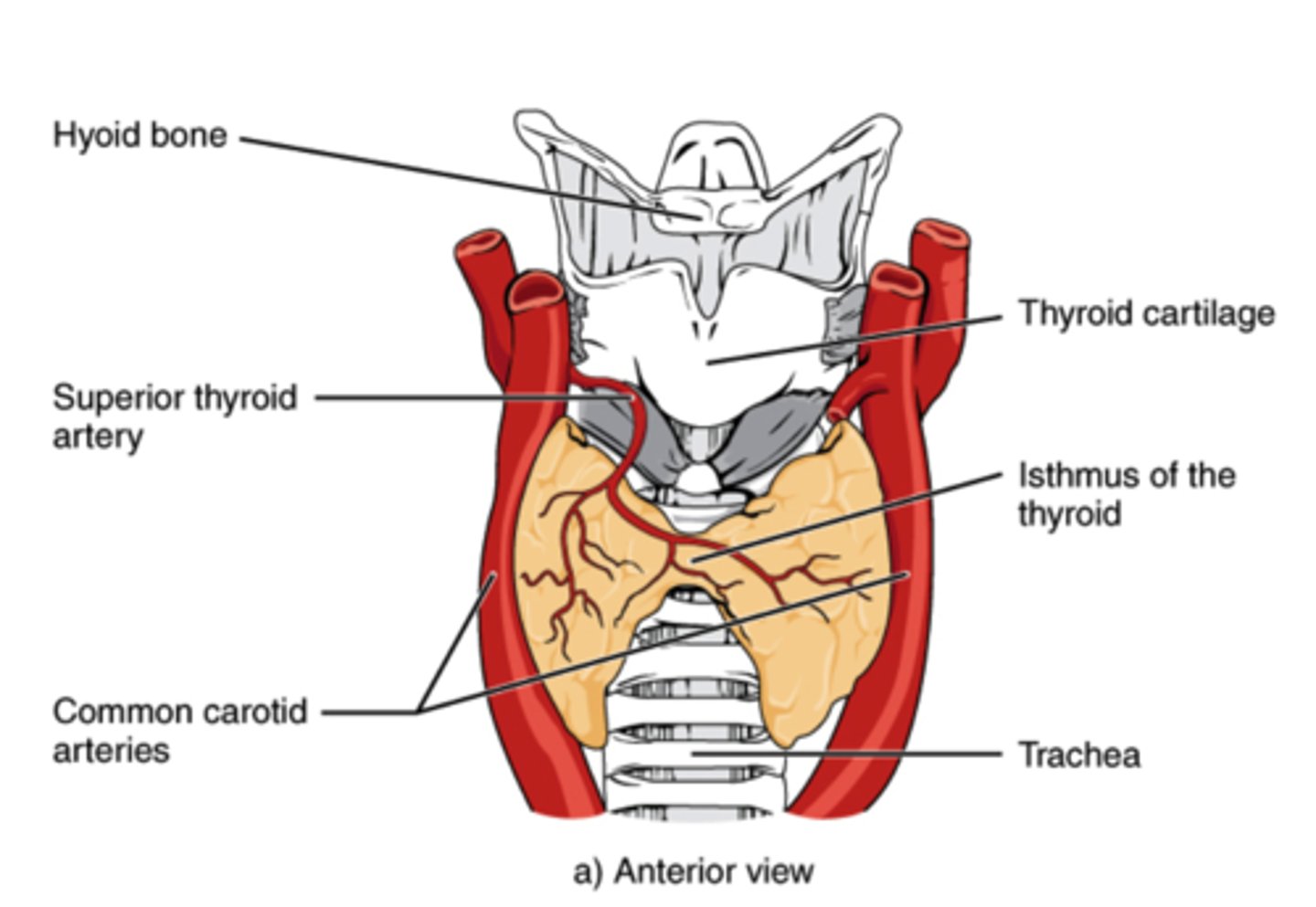
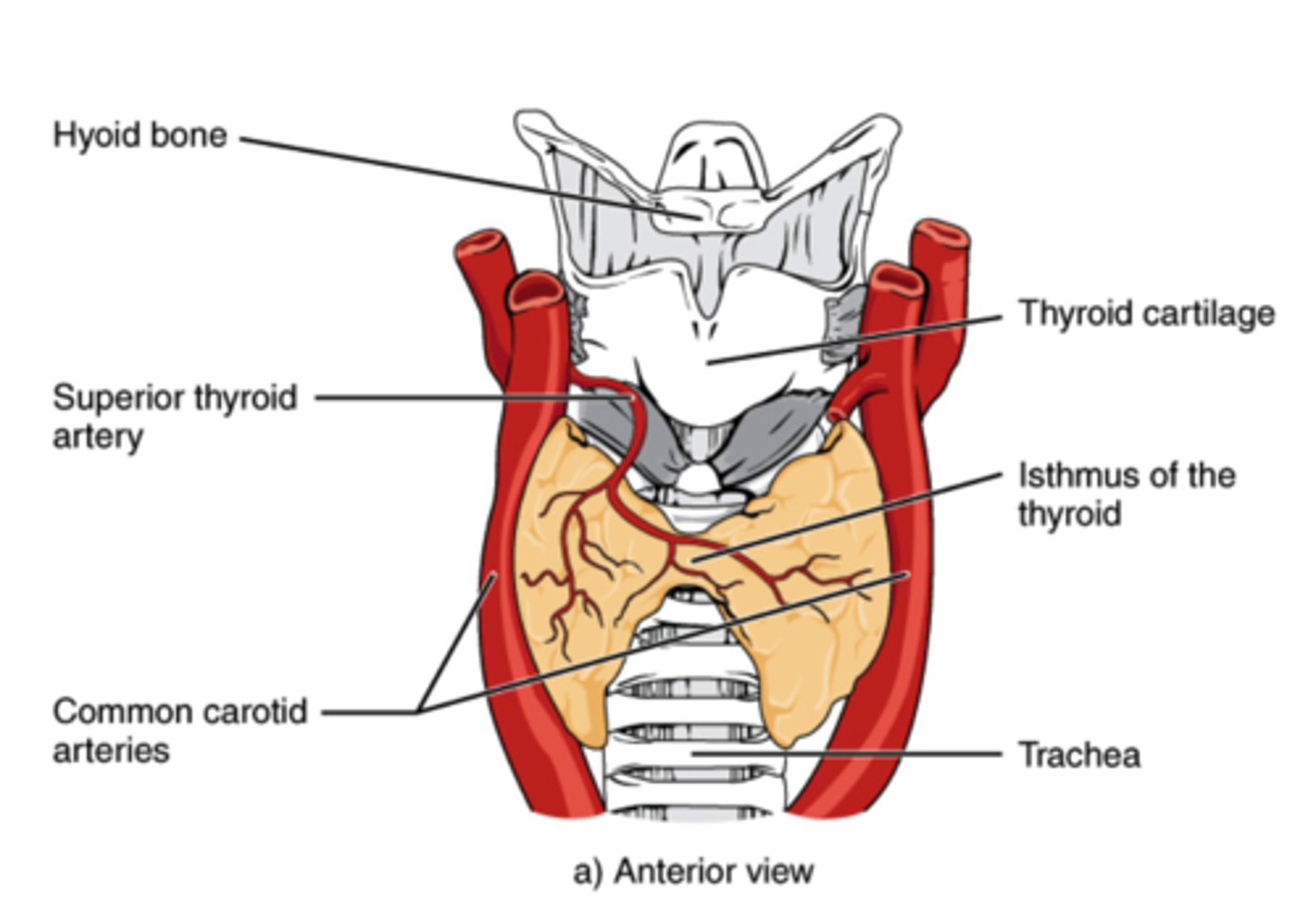
Which gland is located on the ventral surface of the trachea, just in front of the trachea?
thyroid
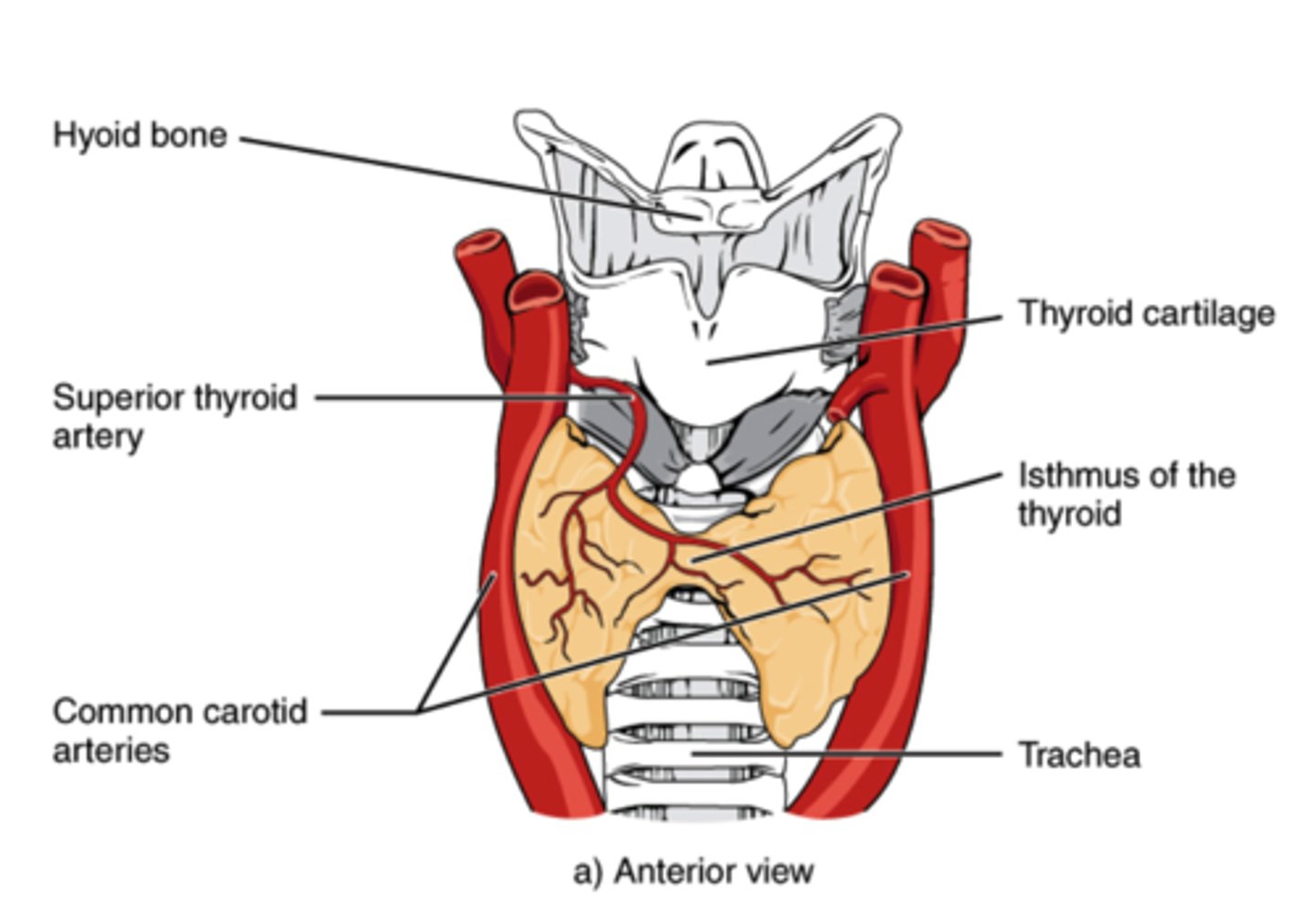
Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) are lipid-soluble derivatives of which amino acid?
tyrosine
Which hormones are necessary for growth and neurological development in children, as well as increasing basal metabolic rate (BMR) in the body (negative feedback on TSH)?
thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3)
Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) contain which notable periodic element?
iodine
What is the condition where the thyroid under-secretes, resulting in low heart rate, low respiratory rate, and low BMR?
hypothyroidism
What is the condition where the thyroid over secretes, increasing BMR and sweating?
hyperthyroidism
(Note: both hypo and hyperthyroidism lead to goiter, or enlargement of thyroid gland)
Which hormone is a peptide hormone that 'tones down' Ca2+ in blood?
calcitonin
calcitonin stimulates the activity of what cell?
osteoblast, which builds up bone by using the calcium in the blood
What does calcitonin do to plasma Ca2+ concentrations?
decreases them
(Note: inhibiting its release from bone)
What is calcitonin's effect on osteoclasts?
decreases activity and number
Which disorder of the thyroid results in dwarfism?
achondroplasia
Which disorder of the thyroid leads to premature aging, wrinkled skin, arthritis, and arteriosclerosis?
progeria
Which is the only gland that produces more than one type of hormone?
thyroid
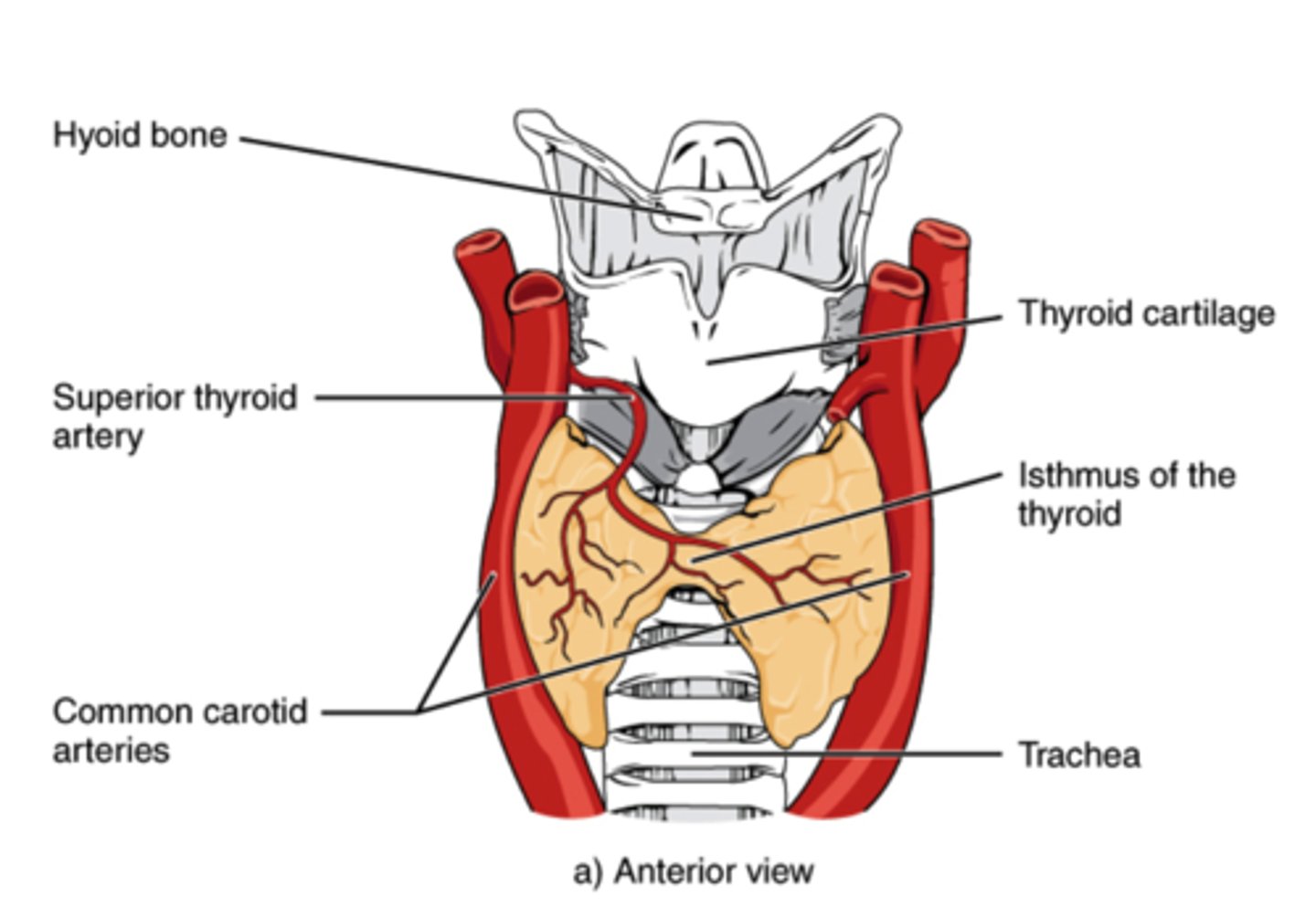
What are the four pea-shaped structures attached to the back of the thyroid?
parathyroid
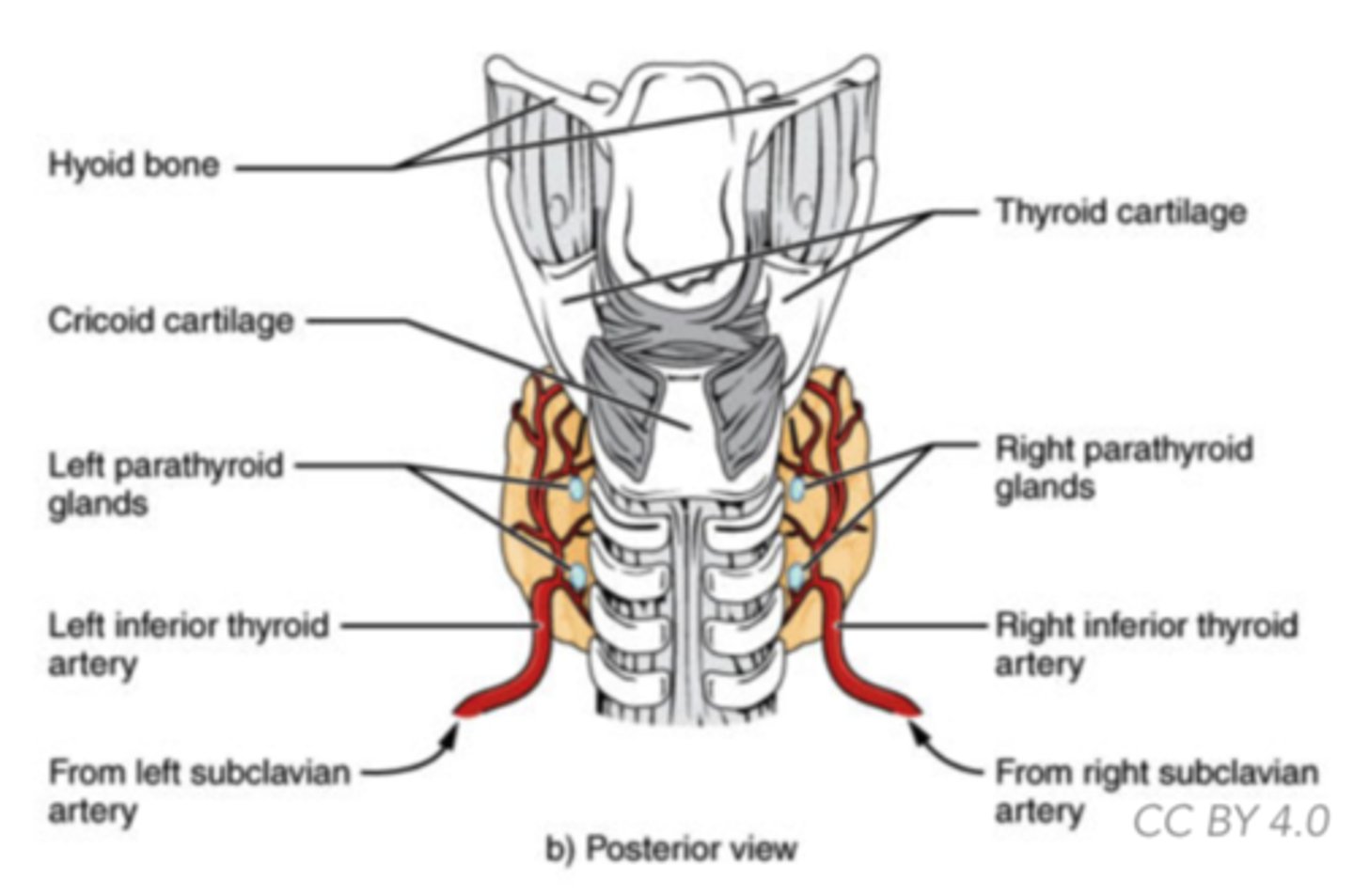
Which hormone is antagonistic to calcitonin?
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
PTH does what to Ca2+ concentrations in the blood?
raises them
(Note: stimulating release from bone)
What is the effect of PTH on osteocytes?
1. increases osteocyte absorption of Ca2+ phosphate from bone
2. stimulates osteoclast proliferation
What is the effect of PTH on kidneys?
1. increase Ca2+ reabsorption
2. excrete renal phosphate
3. increase production of vitamin D derived steroid, which increases Ca2+ uptake from gut
What regulates parathyroid activity?
Ca2+ plasma concentration
(Note: parathyroid glands grow or shrink accordingly)
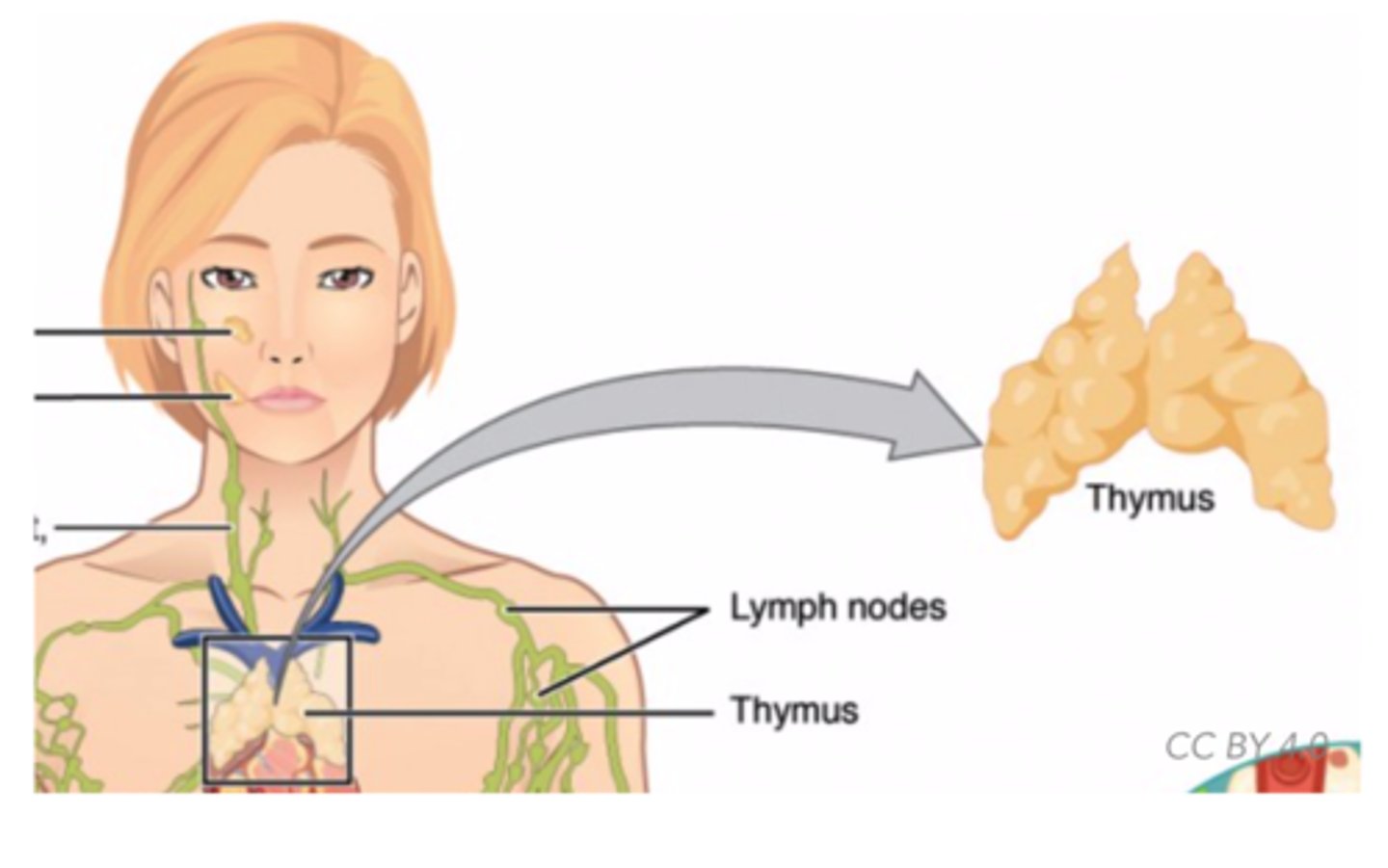
Which gland is involved in immune response, secretes thymosins that stimulate WBCs to become T cells that identify and destroy infected body cells?
thymus
Which gland rests on top of the kidneys?
adrenal gland
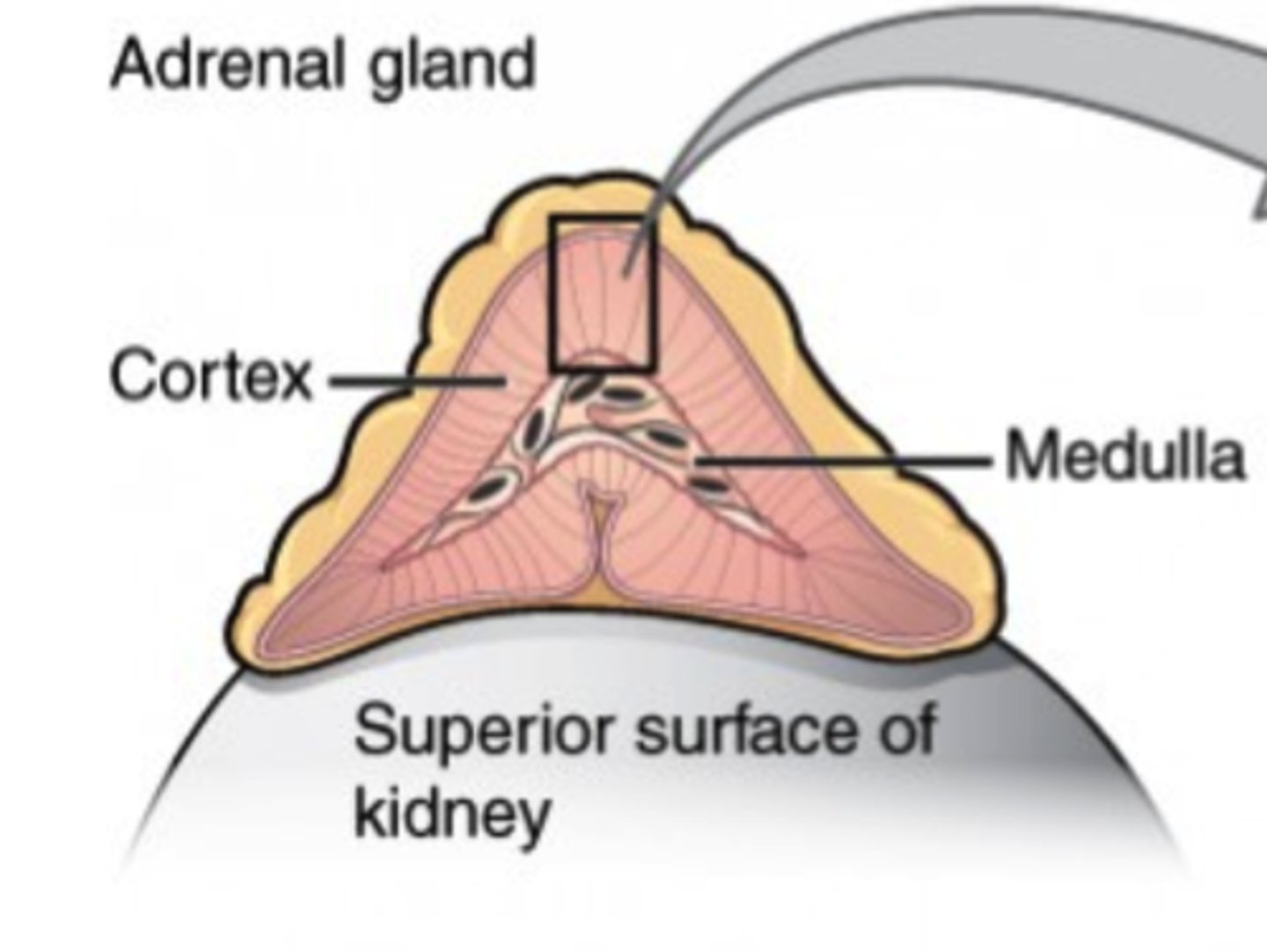
Which portion of the adrenal gland secretes only steroid hormones?
adrenal cortex (outer portion)
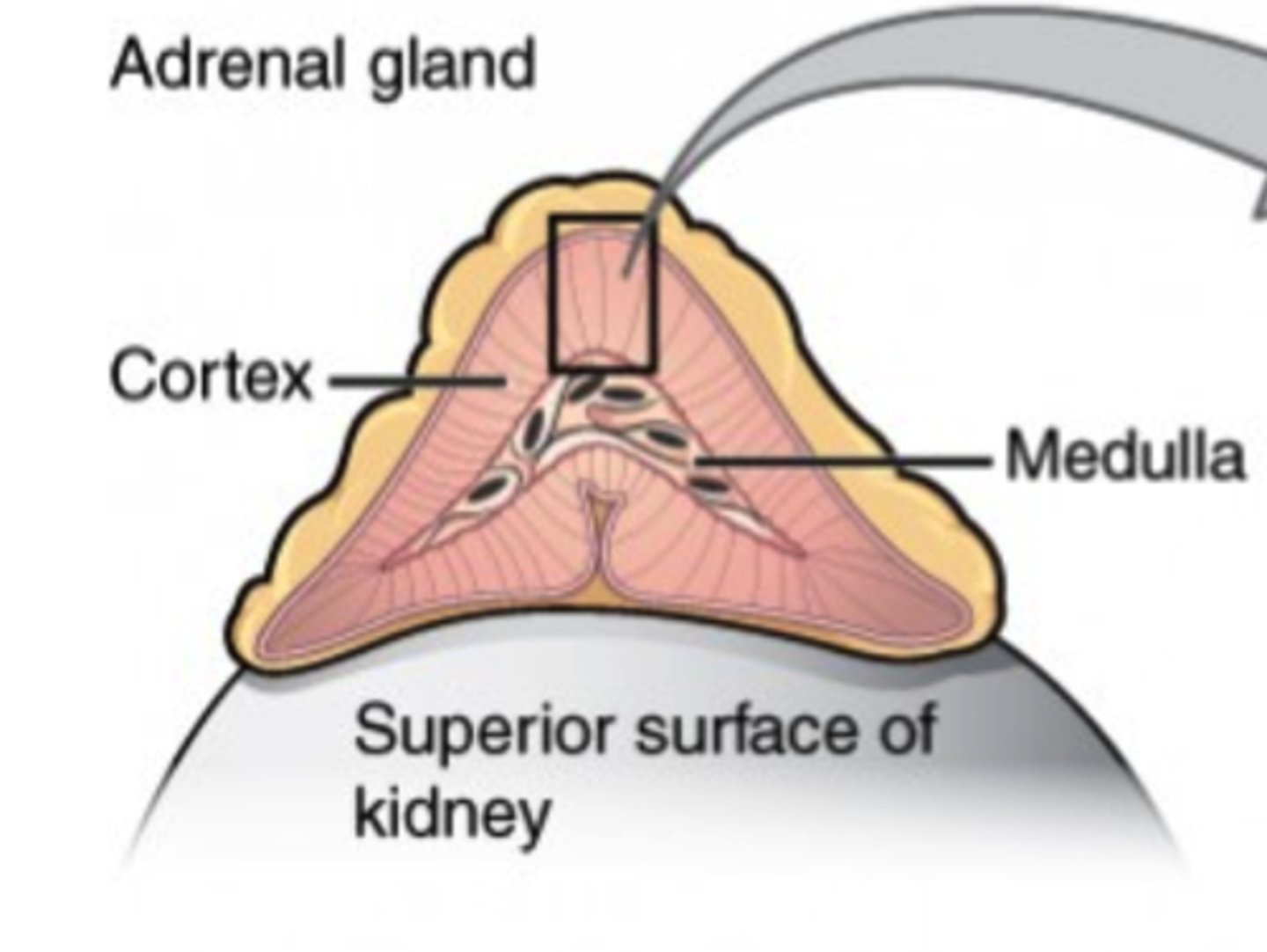
Which secretion of the adrenal cortex raises blood glucose levels, stimulating gluconeogenesis in the liver, and degrading adipose tissue to fatty acids for use as energy?
glucocorticoids (cortisol and
cortisone)
What do glucocorticoids cause in hepatic proteins and in non-hepatic amino acids?
degradation
(Note: This results in a corresponding increase in liver/plasma proteins, and amino acids)
What kind of hormone is cortisol?
stress
Which secretion of the adrenal cortex increases reabsorption of Na+ and excretion of K+ in kidneys?
Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone)
In what location does aldosterone act?
distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct of nephron
(Note: increase Na/Cl reabsorption and K+/H+ secretion)
What is the effect of aldosterone on blood pressure/volume?
increases both
(Note: results from net gain of particles drawing water in the nephron - has the same effect, but to a lesser extent, on sweat/ salivary glands and intestines)
Cortical sex hormones are secreted from which structure?
adrenal cortex
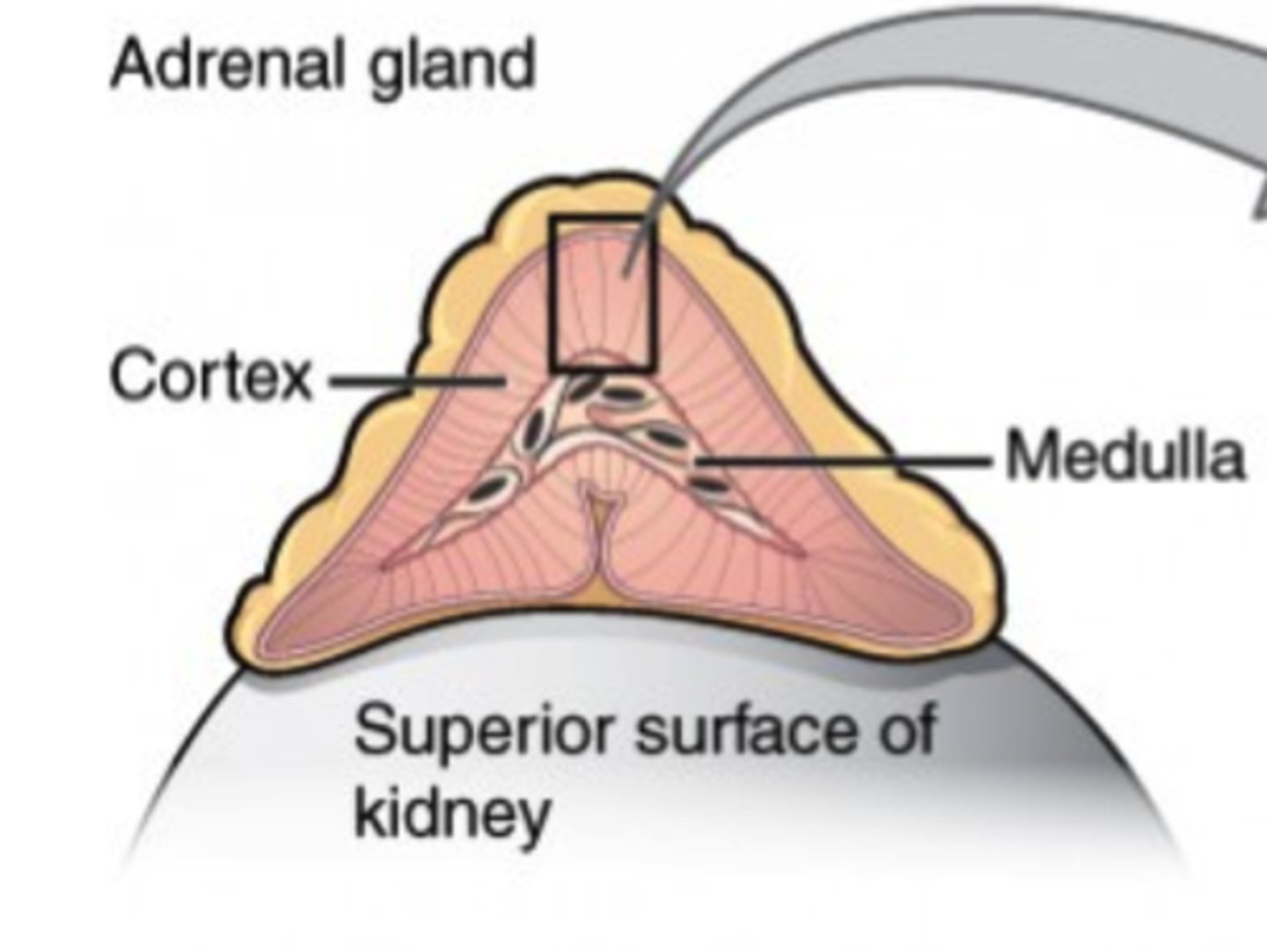
Androgens are which class sex hormones?
male
(Note: significant effect in females, but not in males because males have testes)
Which portion of the adrenal gland secrete fight or flight catecholamines?
adrenal medulla
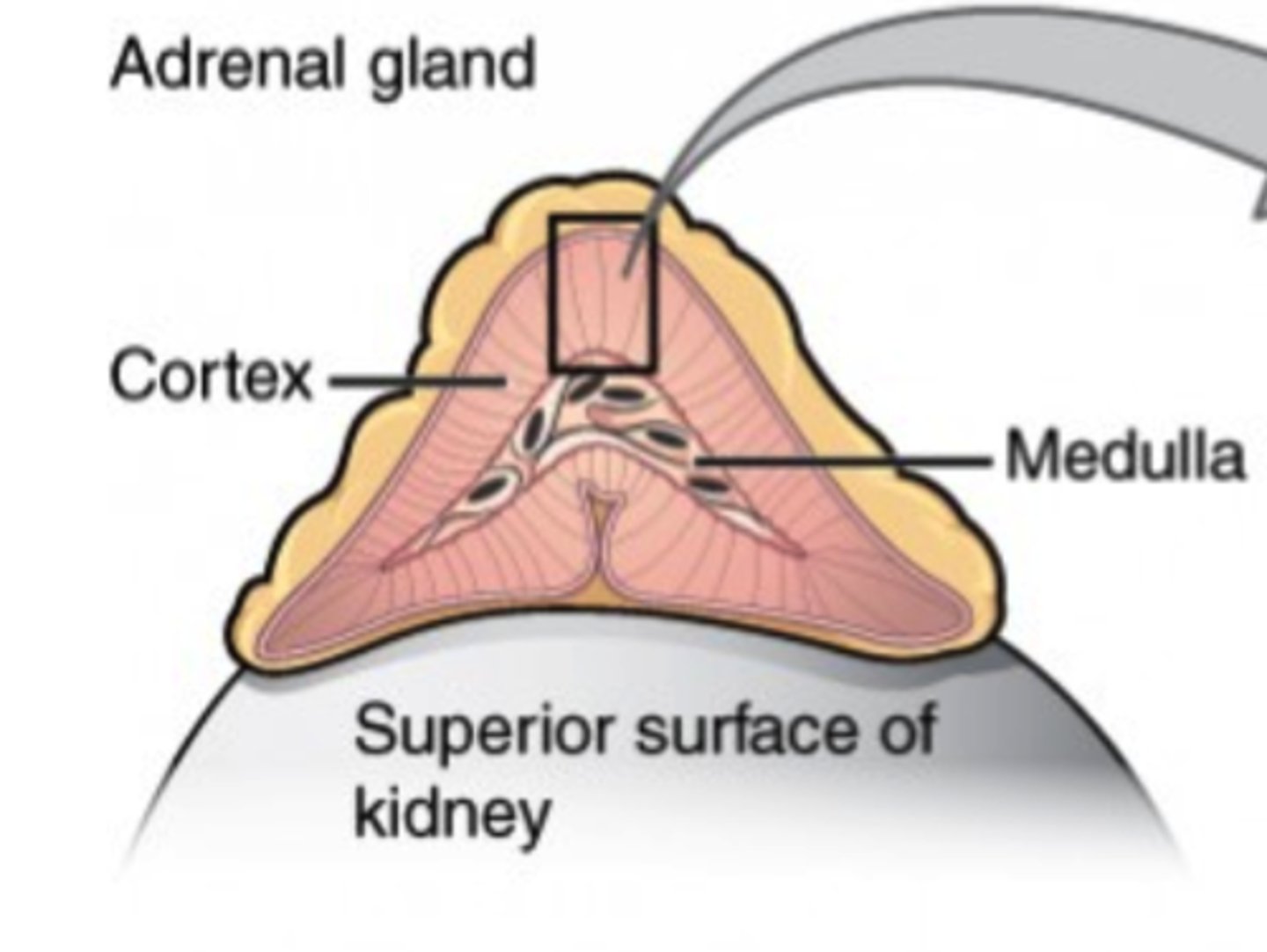
The "fight or flight" response produced by the adrenal medulla is similar to which system's function?
sympathetic nervous system
(Note: adrenal medulla's effect lasts longer, considered stress hormones)
Epinephrine and norepinephrine cause the body to do what with glycogen?
convert to glucose
Epinephrine and norepinephrine are vasoconstrictors to which structures?
internal organs + skin
Epinephrine and norepinephrine are vasodilators to which structures?
skeletal muscle