(quizlet) Pharm E1: HIV and STIs
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
which cells does HIV target?
cells expressing CD4 receptors → T-helper lymphocytes, monocytes, etc.
what is the mainstay of treatment for HIV?
Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART)
life cycle of HIV
1. binding
2. fusion
3. reverse transcription
4. integration
5. replication
6. assembly
7. budding
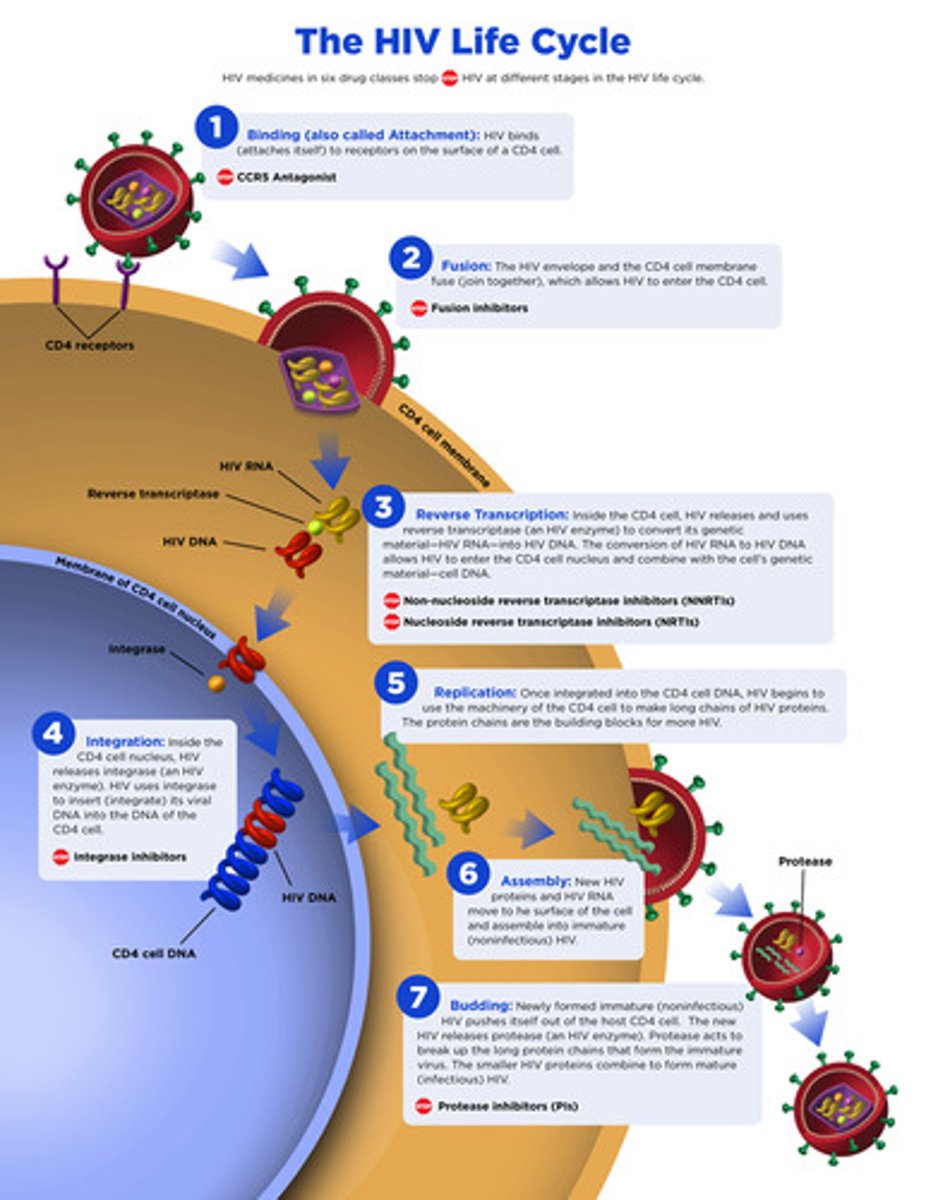
which enzyme allows integration of HIV into the host DNA?
integrase
what are the 3 main phases of HIV?
1. acute (acute retroviral syndrome or mononucleosis-like illness, latent period)
2. chronic
3. terminal (AIDs → PJP, Kaposi's sarcoma, etc)
what is the main monitoring for HIV?
1. CD4 cell count (check immunosuppression)
2. viral load (check replication of virus)
what does the CD4 count indicate?
extent of immune damage
what are the main drug classes for treatment of HIV?
1. integrase inhibitors (InSTI)
2. nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NtRTIs)
3. NONnucleuoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs)
4. protease inhibitor (PI)
5. entry/fusion inhibitors
6. coreceptor inhibitors
which drugs are NtRTIs?
1. thymidine analogs → stavudine (Zerit), zidovudine (Retrovir)
2. deoxycytidine analogs → emtricitabine (Emtriva), lamivudine (Epivir)
3. deoxyguanosine analogs → Abacavir (Ziagen)
4. Deoxyadenosine → didanosine (videx), tenofovir (viread)
don't need to know the analogs
what is the MOA of NtRTIs?
- requires phosphorylation to the triphosphate form
- competes for sites on reverse transcriptase
- prevents DNA elongation
chain terminators
which NtRTIs have more pronounced adverse effects?
stavudine, didanosine, zidovudine
newer agents lack as many side effects → abacavir, tenofovir, emtricitabine, lamivudine
what are the adverse effects of NtRTIs?
peripheral neuropathy
pancreatitis
lipoatrophy
myopathy
anemia
lactic acidosis with fatty liver
which drug requires genetic mutation prior to therapy d/t hypersensitivity and increased risk for anaphylaxis?
abacavir
what is the MOA of NNRTIs?
bind to reverse transcriptase adjacent to catalytic site and force conformation change preventing DNA production
you CAN use with NtRTIs!
which drugs are NNRTIs?
-delavirdine
-Nevirapine
-efavirenz
-etravirine
-rilpivirine
what are the adverse effects of NNRTIs?
rash
transaminitis → check LFTs
single viral mutation can confer resistance to entire class
which NNTRI is not effected by viral mutations?
etravirine → all the other would not work anymore!
which drugs are protease inhibitors?
("-navir")
1. Atazanavir
2. Darunavir
3. Fosamprenavir
4. Indinavir
5. Lopinavir
6. Ritonavir
7. Saquinavir
8. Tipranavir
9. Nelfinavir
what is the MOA of protease inhibitors?
inhibits protease enzyme preventing virus from making mature proteins
which drug class may cause a buffalo hump?
PIs
what are the adverse effects of PIs?
GI distress
increased lipids
glucose intolerance
altered fat distribution
which PI is a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor?
ritonavir (and cobicistat but not a PI)→ leads to higher drug levels, less frequent dosing
look for other interactions
how are PIs metabolized?
liver
which drug only has activity against HIV-1?
enfuvirtide (Fuzeon) → peptide injection
fusion inhibitor
which drug is a CCR5 antagonist?
Maraviroc (Selzentry) → blocks HUMAN receptor and not the virus → can only use in correct strain of the virus (test prior)
what are the adverse reactions of Maraviroc?
rash
hepatotoxicity
which drugs are integrase inhibitors?
-tegravir
Raltegravir (Isentress)
Dolutegravir (Tivicay)
Elvitegravir (Viteka)
Bictegravir
which integrase inhibitor is co-formulated with emtricitabine and tenofovir?
bictegravir**
what is the MOA of integrase inhibitors?
bind to integrase and prevent viral DNA from being incorporated into chromosomal DNA
keep interactions in mind with anti-TB drugs!
rifampin is an inducer
which drugs induce CYP3A4?
Efavirenz
Etravirine
Nevirapine
what is the minimum amount of drugs to start a patient with HIV on?
3
2/3 are NRTIs
know the regimens*** will be a test question
2 NRTIs PLUS something else
example: 2 NRTIs plus an integrase inhibitor → tenofovir + emtricitabine + raltegravir
what are the reasons for poor adherence to HIV drug regimen?
1. psych illness
2. substance abuse
3. adverse effects
4. unstable social circumstances
which resistance testing is more beneficial?
phenotypic testing (more $$ and slower) → provides resistance info for complex mutation patterns
which type of resistance testing is more affordable and quicker?
genotypic (usually done first) → checks for specific genetic mutations that are known to confer resistance to specific drugs
which HIV drug should be avoided due to risk of neural tube defects?
Efavirenz
which drug is recommended intrapartum to prevent transmission?
Zidovudine → fetuses should also receive it for 4-6 weeks after birth
what is the 4 week regimen used after high risk exposures (post exposure prophylaxis)?
Tenofovir
Emtricitabine
Raltegravir
TER = Treat Every Risk
which drug is used for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP)? who should use it?
daily tenofovir/emtricitabine (Truvada) → men who have sex with men (MSM), sero-discordant couples, IV drug abusers
need to be HIV negative prior to initiation
which drug is good for pts who cannot tolerate oral drugs or have low compliance with daily drugs?
cabotegravir (Vocabria)
what are the reasons for changing HIV drug regiments?
1. intolerable side effects
2. treatment failure (viral RNA>200)
3. documented resistance (from genetic mutation)
which CD4 count is assoc. with thrush? PJP?
thrush = 250 or less
PJP = 200 or less
idk if were being tested on that pic (slide 35), but he mentioned these
what often precedes HIV diagnosis?
opportunistic infections → often dx at the same time as HIV
what is the MC life-threatening OI in AIDS pts?
PJP → prophylaxis (3x/week bactrim) indicated when CD4 <200 or hx of thrush
what is the tx for PJP?
bactrim x21 days
what is used for treatment and prevention of opportunistic candidiasis (thrush)?
treatment = fluconazole
prevention = nystatin (not recommended for esophageal candidiasis)
fluconazole is a _________ inhibitor
CYP3A4 → check for interactions!!
why is Gonorrhea difficult to control?
rapid incubation and high number of asymptomatic pts
what are the complications seen from Gonorrhea?
more pronounced in women:
pelvic inflammatory dz → infertility/ectopic pregnancies, systemic infections
HIV spreads more easily in pts with ______________
gonorrhea
what is the tx for gonorrhea?
single IM dose of Rocephin
if gonorrhea and chlamydia are suspected, how should you treat?
Rocephin dose PLSU doxy x7 days now preferred
used to be azithro once (good for compliance)
what is used for gonorrhea/chlamydial eye infections in infants?
topical erythro for gonorrhea
oral erytro for chlamydial
what is the treatment for syphilis?
Penicillin G single dose
pen allergy = doxy or tetra
what tx is used for more advanced syphilis or neurosyphilis?
pen G IV intermittent or continuous
what is the tx for first episode infections of genital herpes?
acyclovir, valacyclovir, famcicilovir
the earlier the better
IV acyclovir can cause what?
renal, bone marrow, CNS toxicity
what is the benefit of chronic suppressive therapy vs. episodic therapy for recurrent genital herpes infections?
less asymptomatic viral shedding
what is the tx for Trichomoniasis?
Metronidazole or Tinidazole
warn abt alc use with metro
how do you decide who to treat for HBV?
monitoring of hepatic function and serological markers of viral infection → based on liver-related morbidity and mortality
what is the first approved therapy for HBV?
interferon-alfa (Intron A) → acts as a host cytokine → stimulates host immune system to mount a defense against HBV
what are the adverse effects of interferon-alfa?
- risk for infection in decompensated cirrhotic pts
- hepatic flares and precipitate hepatic decompensation in cirrhotic pts
-anaphylactic risk, flu-like sx
- depression, suicidal ideation, aggression
- blood dyscrasias
what is the black box warning on Interferon-A?
fatal or life-threatening neuropsychiatric, autoimmune, ischemic and infectious disorders
would interferon-A be a good option to treat someone with PMHx of severe depression?
prob not
which HBV drug can cause nephrotoxicity?
adefovir (hepsera) →activity against lamivudine resistant HBV
what drug is considered first line for HBV d/t safety and low resistance?
Entecavir (baraclude)
and Tenofovir (Viread)
what is the MOA of Daclatisvir (Daklinza)?
prevents viral RNA replication and virion assembly by binding to NS5A → distorts structure of protein and impairs function
$$$!
hep c tx
does daclatisvir require renal/hepatic adjustment?
no
what is the MOA of Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni)?
ledipasvir inhibits NS5A to block viral replication
sofosbuvir is a nucleotide prodrug that inhibits NS5B RNA polymerase (acts as chain terminator)
$$$
hep c tx
what is the MOA for Simeprevir (Olysio)?
inhibits NS3/4A protease which is the enzyme repsonsible for forming mature, functional HCV proteins
cannot be used by itself! use with interferon/ribavirin
what is the MOA of Ombitasvir?
NS5A inhibitor
given in combo with paritaprevir, ritonavir, technivie
hep C tx
can Ribavirin (Rebetol) be used during pregnancy?
NO! category X → may need to use 2 forms of birth control x6 months after discontinuation
which HCV drug can cause hemolytic anemia?
ribavirin
also can cause: suicidal ideation, depression, insomnia, dyspnea
what can occur with a single missed dose of HCV treatment?
resistance and failure
which HCV drug is used in difficult-to-treat pts?
ribavirin
prior treatment or cirrhosis can be causes