Alkanes and alkenes
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What are alkanes?
Hydrocarbons that contain only carbon - carbon or carbon - hydrogen single bonds
What is the general formula for alkanes?
CnH2n+2
Describe the melting and boiling points of alkanes and alkenes in general and down the series
Gradually increase down the homologous series
Forces of attraction between molecules increase as their size increases
Gases at r.t.p.
Simple molecular substances with weak forces of attraction between molecules
Describe the viscosity of alkanes and alkenes
Alkanes become more viscous as their molecular size increases
Stronger forces of attraction between alkane molecules, restricting flow
Longer chains lead to molecules getting entangled
Describe the solubility of alkanes and alkenes
Insoluble in water but soluble in most organic solvents
Liquid alkanes are often used as solvents for other compounds
What are the conditions for the combustion of alkanes and alkenes? (+O2)
Excess oxygen for complete combustion and limited oxygen for incomplete combustion
What is produced during the combustion of alkanes and alkenes?
CO2 + H2O (excess O2)
CO + H2O (limited O2)
Why is combustion of alkanes harder down the series?
Mr increases → flammability decreases → incomplete combustion
What are the conditions for substitution of alkanes?
Presence of UV light
Due to alkanes’ unreactivity → requires very high energy
Limited halogen (mono-sub.)
Excess halogen (multi-sub.)
What is the substitution of alkanes?
One or more hydrogen atoms in an alkane are replaced by other atoms like halogen (e.g. Cl and Br) atoms
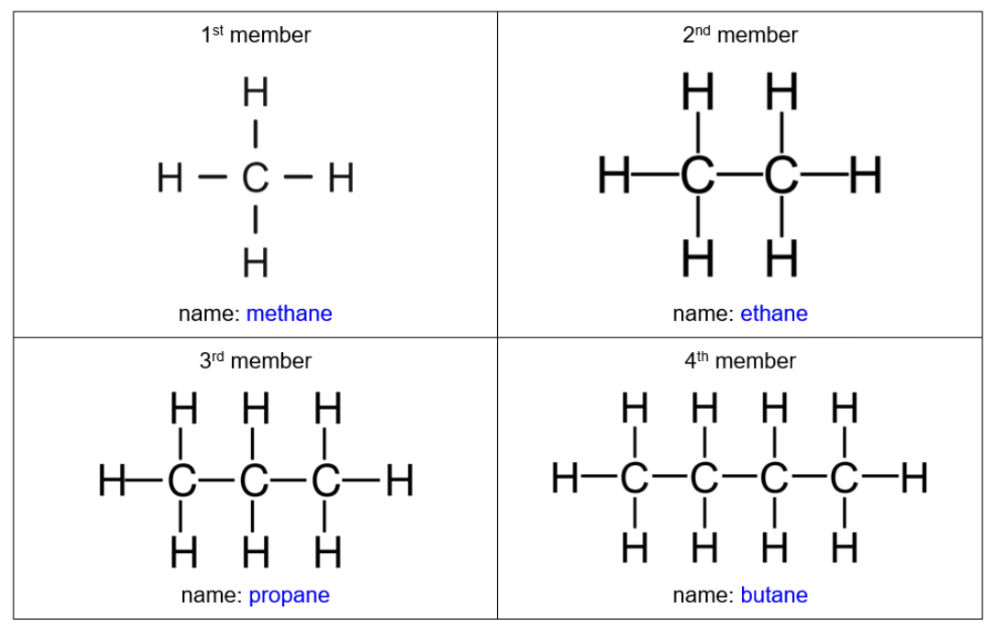
Diagrams of alkanes
What are alkenes?
Hydrocarbons that contain C = C double bonds
*C = C functional group
What is the general formula for alkenes?
CnH2n
How is the combustion of alkenes as compared to alkanes?
Alkenes → sootier flame
Alkanes → less sooty flame
Are alkenes likely to undergo complete or incomplete combustion?
Incomplete
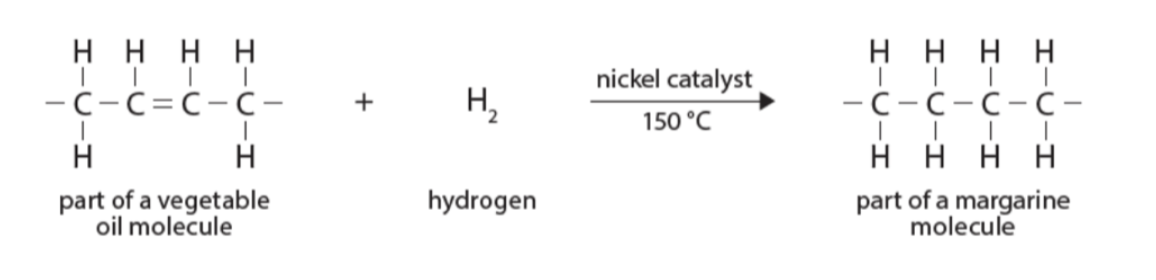
What are the conditions for the hydrogenation of alkenes? (addition of hydrogen)
150ºc
Presence of a nickel catalyst
Compare the reactivity of alkenes and alkanes
Alkenes → reactive
Alkanes → generally unreactive
What are the conditions for bromination of alkenes? (addition of bromine)
Room temperature
Absence of UV light
What is the color change of bromination of alkenes?
Reddish-brown → colourless
What are the conditions for the hydration of alkenes? (addition of steam)
300ºc
60atm
Presence of H3PO4 [phosphoric (V) acid] as a catalyst
What is the product of the hydration of alkenes?
Alcohol
What are the conditions of addition polymerization of alkenes?
Pressure
Presence of catalyst
What are the conditions for the production of alkenes via cracking of alkanes? (decomposition)
500ºc to 700ºc
1atm
Presence of Al2O3 or SiO2 as a catalyst
Describe the electrical conductivity of alkenes and alkanes
Do not conduct electricity in any state
How do alkenes and alkanes react differently with bromine?
Alkanes → bromine remains orange
Alkenes → orange bromine decolourises
What are the differences between saturated and unsaturated compounds?
Saturated → C - C single covalent bonds with all carbon atoms bonded to 4 other atoms
Unsaturated → C = C double covalent bonds with more atoms added across the carbon
What is the test for unsaturation?
Add aqueous bromine to each sample in the absence of UV light
Br (aq) remains brown when shaken with saturated hydrocarbons (alkane)
Alkanes undergo substitution with halogen only in the presence of UV light
Br (aq) decolourises when shaken with unsaturated hydrocarbons (alkenes)
Alkenes undergo halogenation (addition) spontaneously even when light is absent
Do saturated or unsaturated fats have higher molecular mass and why?
Saturated fat has relatively higher molecular mass / size
Hydrogen atoms are added to each C = C bond
The greater the level of saturation, the higher the melting point
Do saturated or unsaturated fats pack more closely to one another and why?
Saturated fats are more linear in shape, so they clot our arteries more effectively
Unsaturated fats have less linear and more irregular shapes, so they cannot clot our arteries effectively
What are the states of saturated and unsaturated fats at r.t.p. and pressure
Saturated → solids → strong IFA, can stack well
Unsaturated → liquids → weak IFA, cannot stack well
What is glucose from plants converted to?
Ethanol and CO2 using yeast in aqueous solution at temperatures below 30ºc
How can margarine be manufactured from vegetable oil?