Unit 1 & 2 Test
1/80
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
magnitude
Prefixes give the _________ of the measurement.
10^6
mega-
10³
kilo-
10^-1
deci-
10^-2
centi-
10^-3
milli-
0 kelvin
The point where there is virtually no particle motion or kkinetic energy, also known as absolute zero.
derived units
defined by a combination of base units (not SI)
independant
A base unit is ___________ of other units.
273.15
To convert from Celsius to Kelvin, add ___.__.
m/v
D = _______
accuracy
The closeness to an accepted value.
precision
The closeness of data to each other
error
The difference between an experimental value and an accepted value.
-20
Accepted value = 90, but estimate = 70. What is the error?
percent error
100(|error|/accepted value)
are
zeros between non-zeros ___ sig figs
are
zeros right of the decimal point ___ sig figs
are not
anything you can remove in scientific notation ___ sig figs
solids, liquids
______ and _______ resist compression.
sublimation
solid to gas
deposition
gas to solid
ionization
gas to plasma
plasma
gas without electrons (ionized)
capash
capeesh?
extensive property
An __________ __________ is dependant on the amount of substance present, such as mass, length, and volume.
intensive property
An ____________ ___________ is independant of the amount of substance present, such as density.
extensive properties
ductility
entropy
weight
heaviness
electrical charge
energy
momentum
concentration
chemical potential
intensive properties
density
magnetic field
elasticity
melting point
viscosity
electrical resistivity
sums
When rounding ____ or differences, the number of sig figs to the right of the decimal equals the limiting term’s number of decimal point places.
Solid
Definite shape and volume; resists compression.
Liquid
Indefinite shape and constant volume; resists compression.
Vapor
Form of a substance (gas) that is normally a liquid or gas at the given temperature.
Gas
Fills the entire container; highly compressible.
Intermolecular
______________ distance is the distance between particles.
Plasma
A gas without electrons (ionized).
Physical
________ properties can be observed/measured without changing the sample’s composition.
Physical properties
Boiling point, melting point, odor, density, viscosity, specific heat.
Viscosity
A physical property that means the resistance of flow.
Chemical
________ properties are the ability of substances to combine with or change into one or more other substances.
Chemical changes
Decomposing, rusting, exploding, burning, oxidizing.
Physical changes
Ripping, cutting, smashing.
Extensive
___________ properties are dependent on the amount of a substance present.
Intensive
_______ properties are independent of the amount of a substance present.
Extensive properties
Volume, ductility, entropy, chemical potential, weight, heaviness, length, mass, number of molecules, electrical charge, energy, momentum, concentration.
Intensive properties
Density, magnetic field, malleability, elasticity, melting point, viscosity, electrical resistivity.
Phase change
The transition of matter from one state to another.
Law of conservation of mass
Mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. It is conserved. The mass of the reactants is equal to the mass of the products.
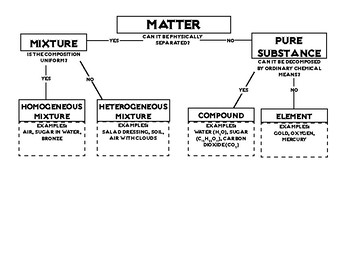
Mixture
A combination of two or more pure substances in which each pure substance retains its individual chemical properties
Heterogeneous
______________ mixtures contain individual substances that remain distinct.
Homogeneous
_____________ mixtures have a composition that is constant throughout.
Solution
Also known as a homogeneous mixture.
Colloids
Heterogeneous mixtures of intermediate sized particles (between 1 — 1000 nm) and do not settle out.
Suspension
Mixture containing particles that settle out if left undisturbed.
Filtration
A separation technique that uses a porous barrier to separate solid from liquid in a heterogeneous mixture.
Distillation
A separation technique for homogeneous mixtures based on the differences in boiling points of substances.
Crystalization
A separation technique for homogeneous mixtures that results in the formation of pure solid particles from a solution containing the dissolved substances.
Sublimation
The process of a solid changing directly to gas, which can be used to separate mixtures of solids when one sublimates and the other doesn’t.
Chromatography
A separation technique that separates the components of a mixtures on the tendency of each to travel across the surface of another material.
Element
A pure substance that can’t be separated into simpler substances by physical or chemical means.
Compound
Made up of two or more elements combined chemically (table salt and water).
Colloid
________ examples are blood, milk, and gelatin.
Orange juice
Example of a suspension.
Electrolysis

SI base units
seconds
meters
grams
Kelvin
mole
ampere
candela
92
__ elements occur naturally on Earth
law of definite proportions
a compound is always composed of the same elements in the same proportion by mass, no matter the size of the sample
law of multiple proportions
when different compounds are formed by a combination of the same elements, different masses of one element combine with the same relative mass of the other element in whole number ratios
percent by mass
the ratio of the mass of each element to the total mass of the compound expressed as a percentage
100(mass of element/mass of compound)
Dalton’s atomic theory
easily explains the conservation of mass in a reaction as the result of a combination, separation, or rearrangement of atoms
Dalton
John ______:
atoms are indivisible and indestructible
matter is composed of small articles called atoms
atoms in an element have the same size, mass, and chemical proporties
atoms differ by element
different atoms combine in whole number ratios to form compounds
atom
the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of the element
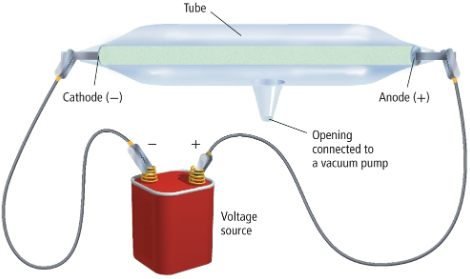
JJ Thompson
man who created the cathode ray tube and discovered electrons
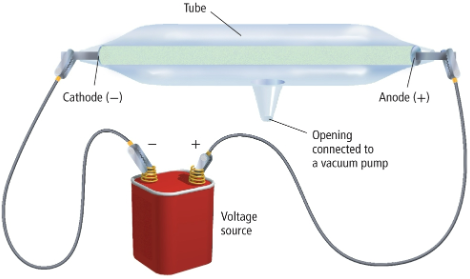
cathode ray
a ray of radiation that travels from the cathode to the anode when an electronic charge is applied (a stream of particles carrying a negative charge)
electrons
particles carrying negative charge
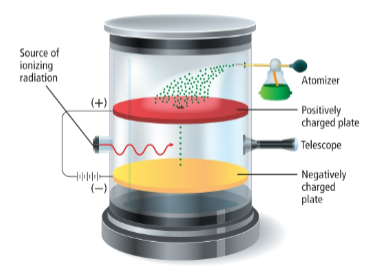
Robert Milkan
man who used the oil drop apparatus to determine the charge of an electron (coulombs)
plum pudding
JJ Thompson’s ____ _______ model of the atom states that the atom is a uniform, positively charged sphere that contains electrons

neutral
matter is _______
isotope
if the number of protons ≠ number of electrons, then the matter is an ________
Rutherford
studied how positively charged alpha particles interacted with solid matter using gold foil
atoms are mostly empty space
if they pass through, they go between the nucleus and electronic field
opposite charges attract
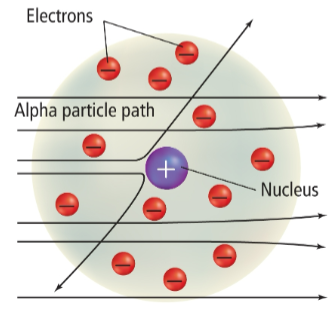
nucleus
a dense region in the center of an atom that contains almost all of the positive charge and almost all of the atom’s mass