Neck and Cervical Spine Anatomy
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
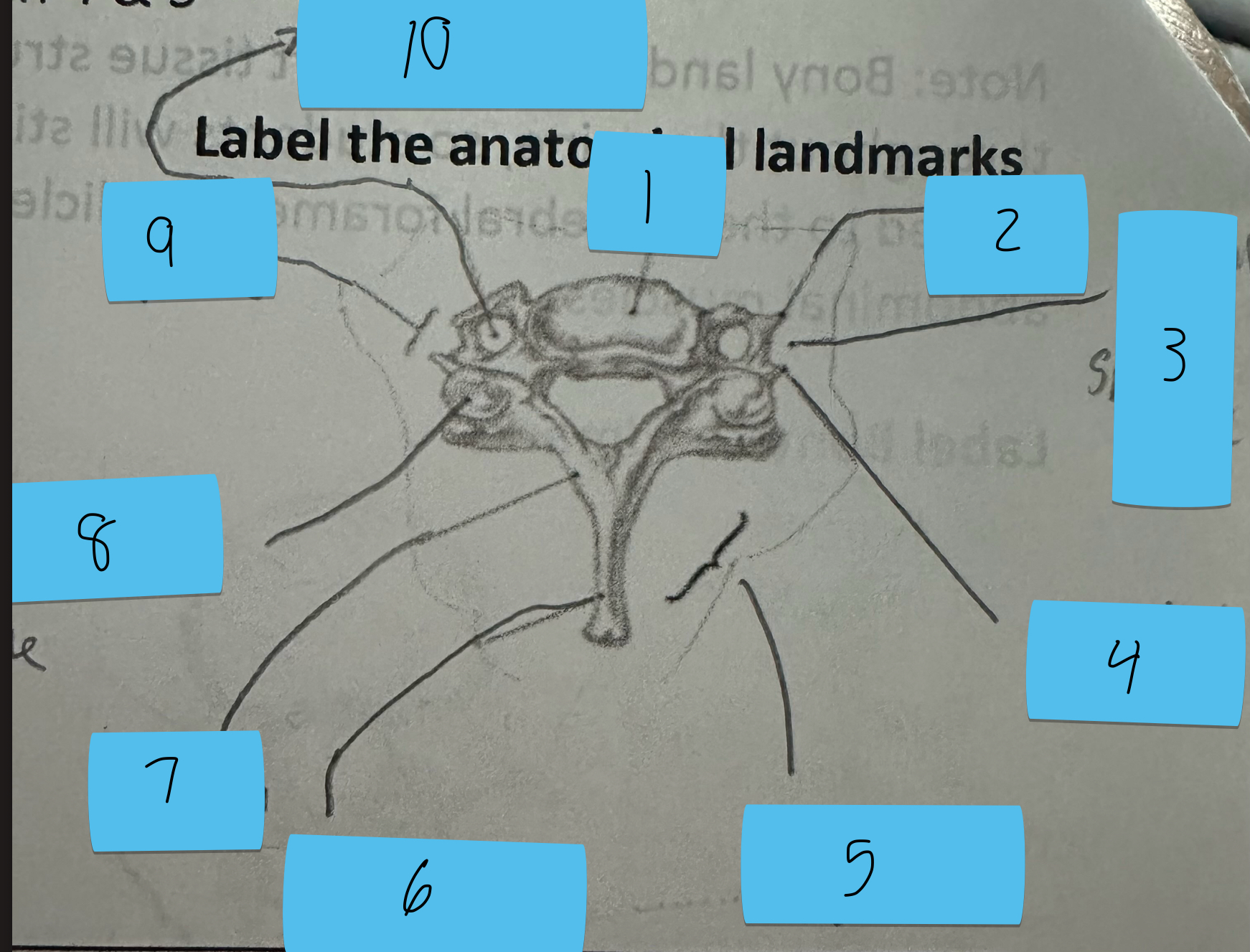
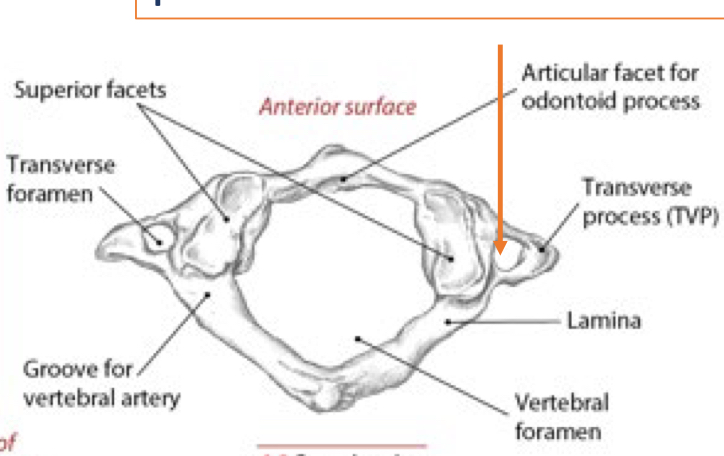
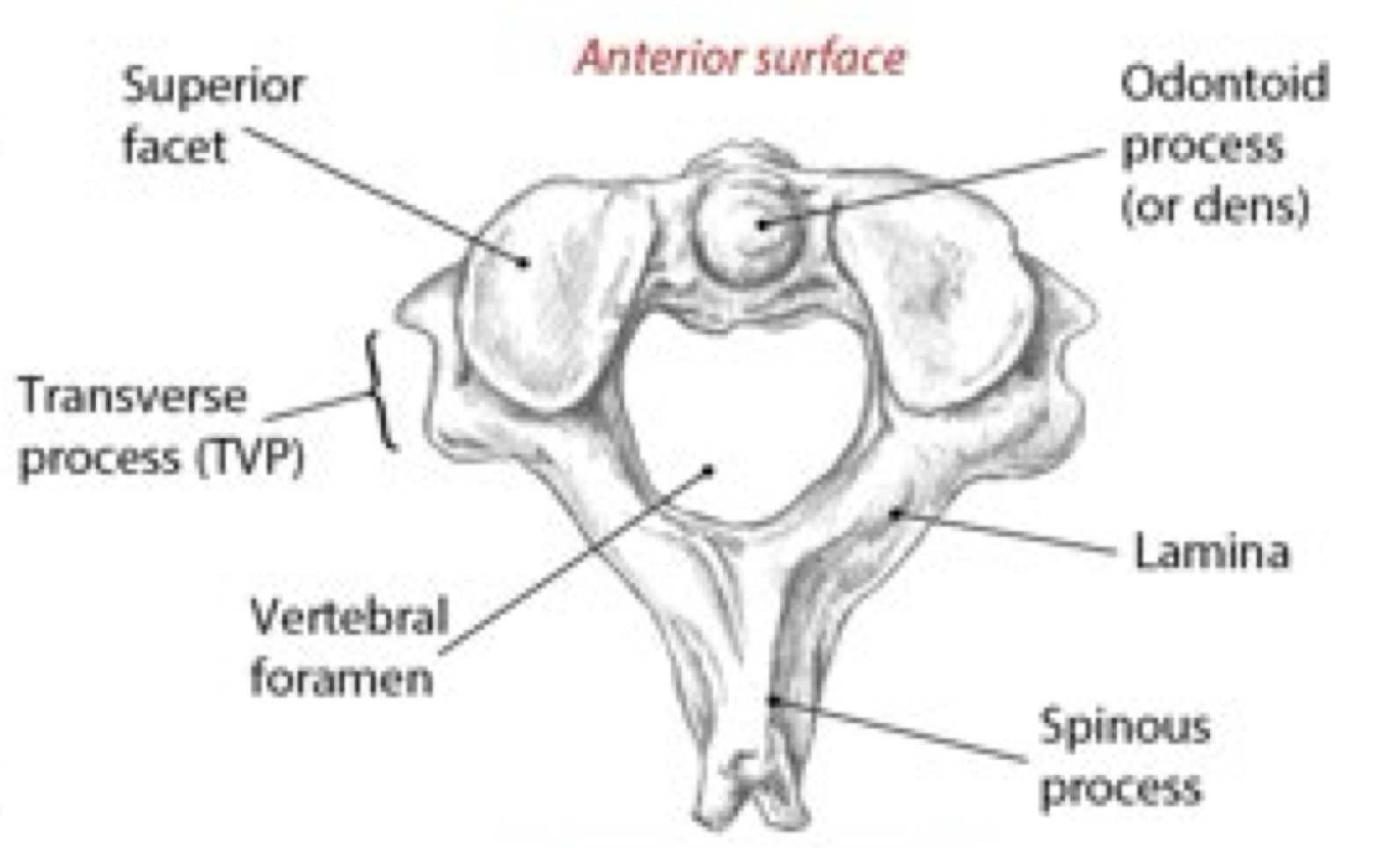
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (1)
Body of cervical vertebrae
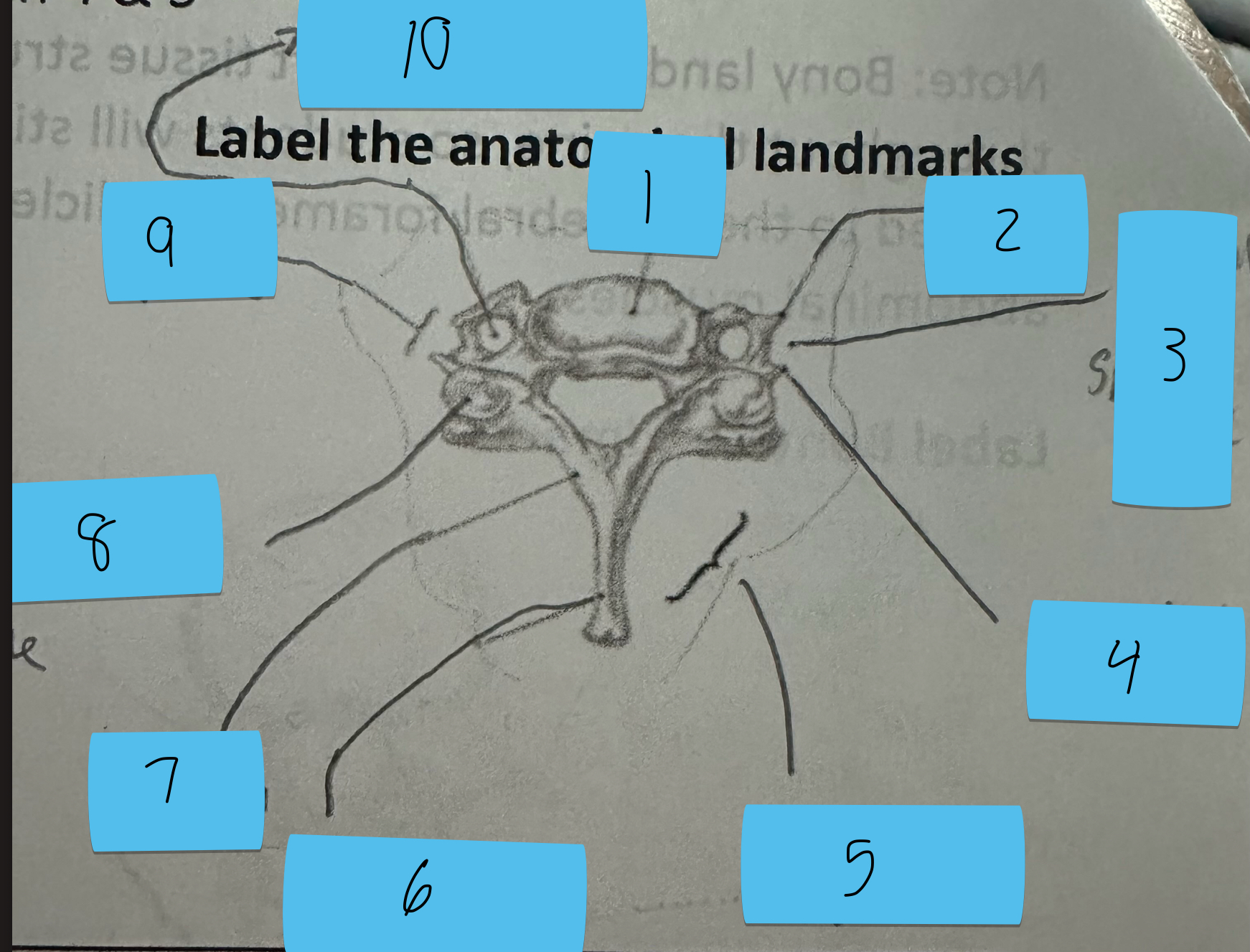
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (2)
Anterior tubercle of transverse process: attachment for anterior scalene
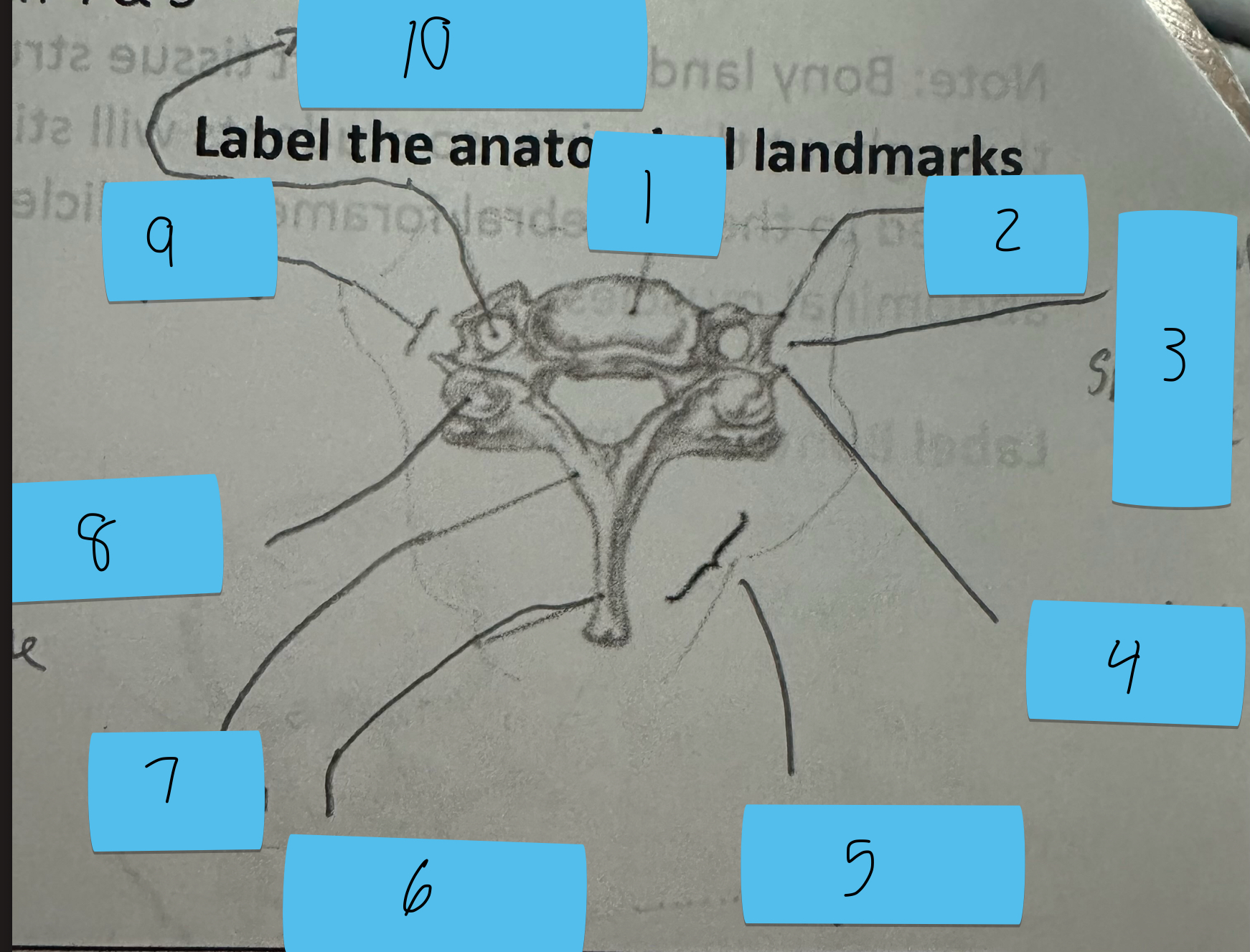
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (3)
Canal for spinal nerve
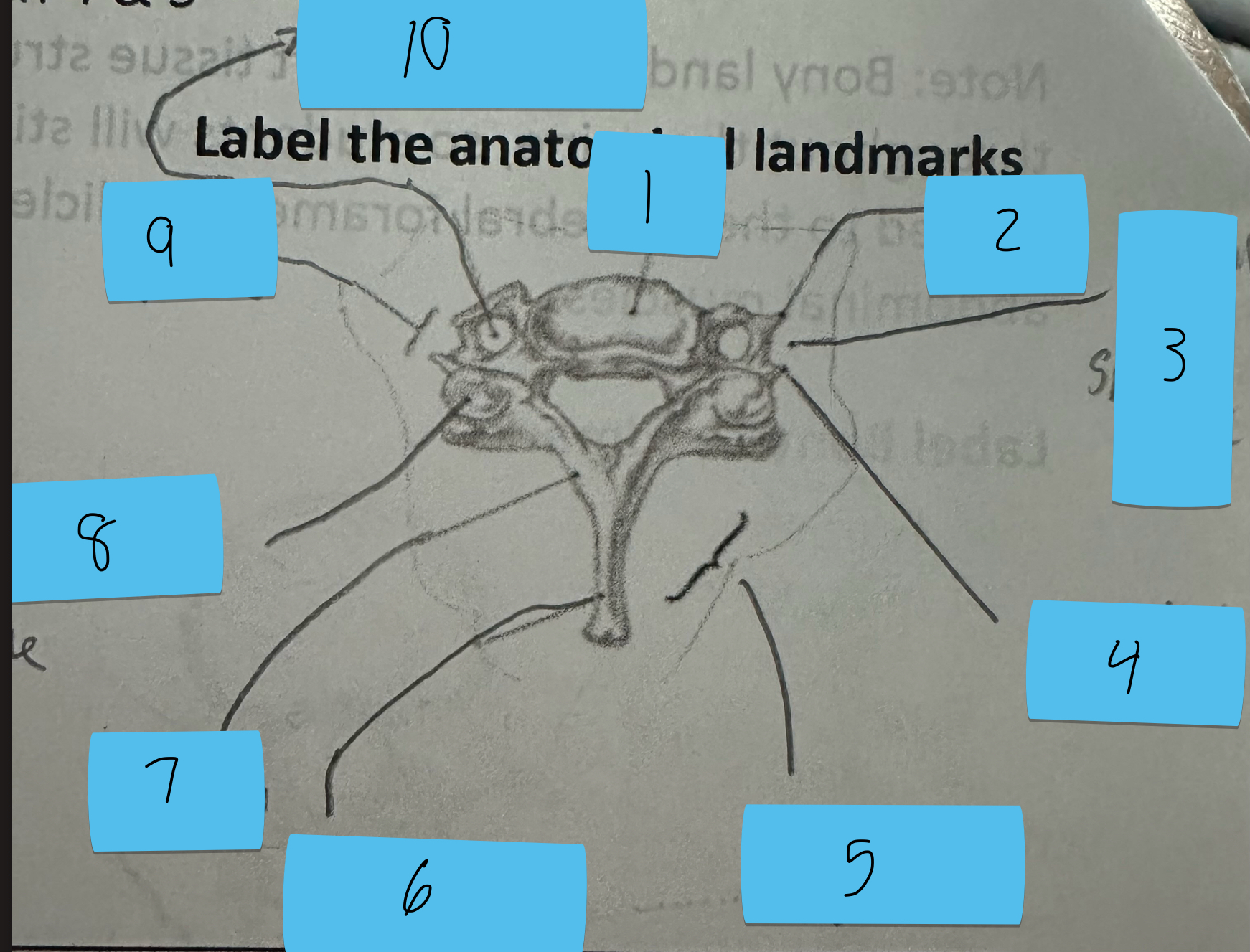
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (4)
Posterior tubercle of transverse process: attachment for middle and posterior scalene
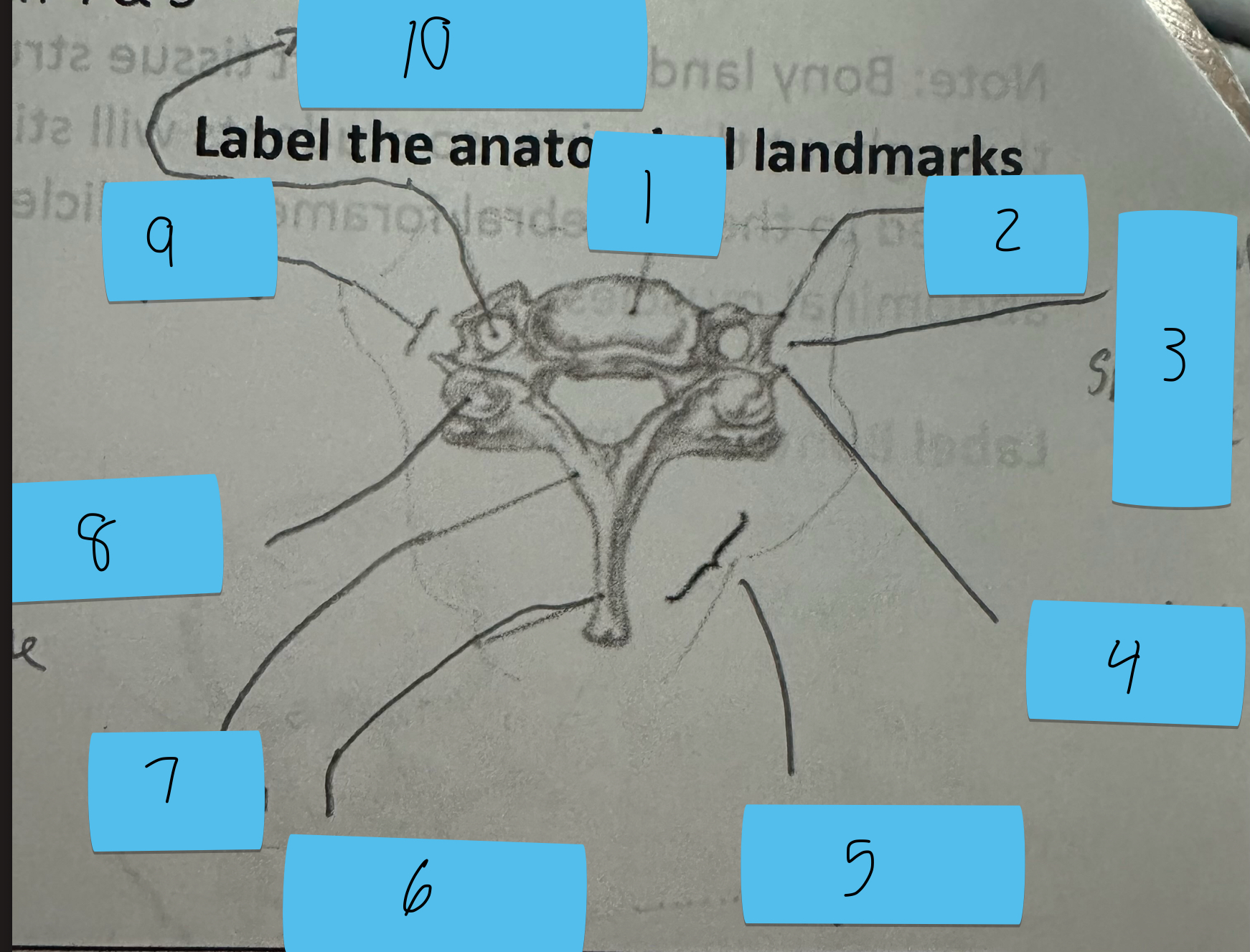
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (5)
Lamina groove of cervical spine: attachment for semispinalis capitis
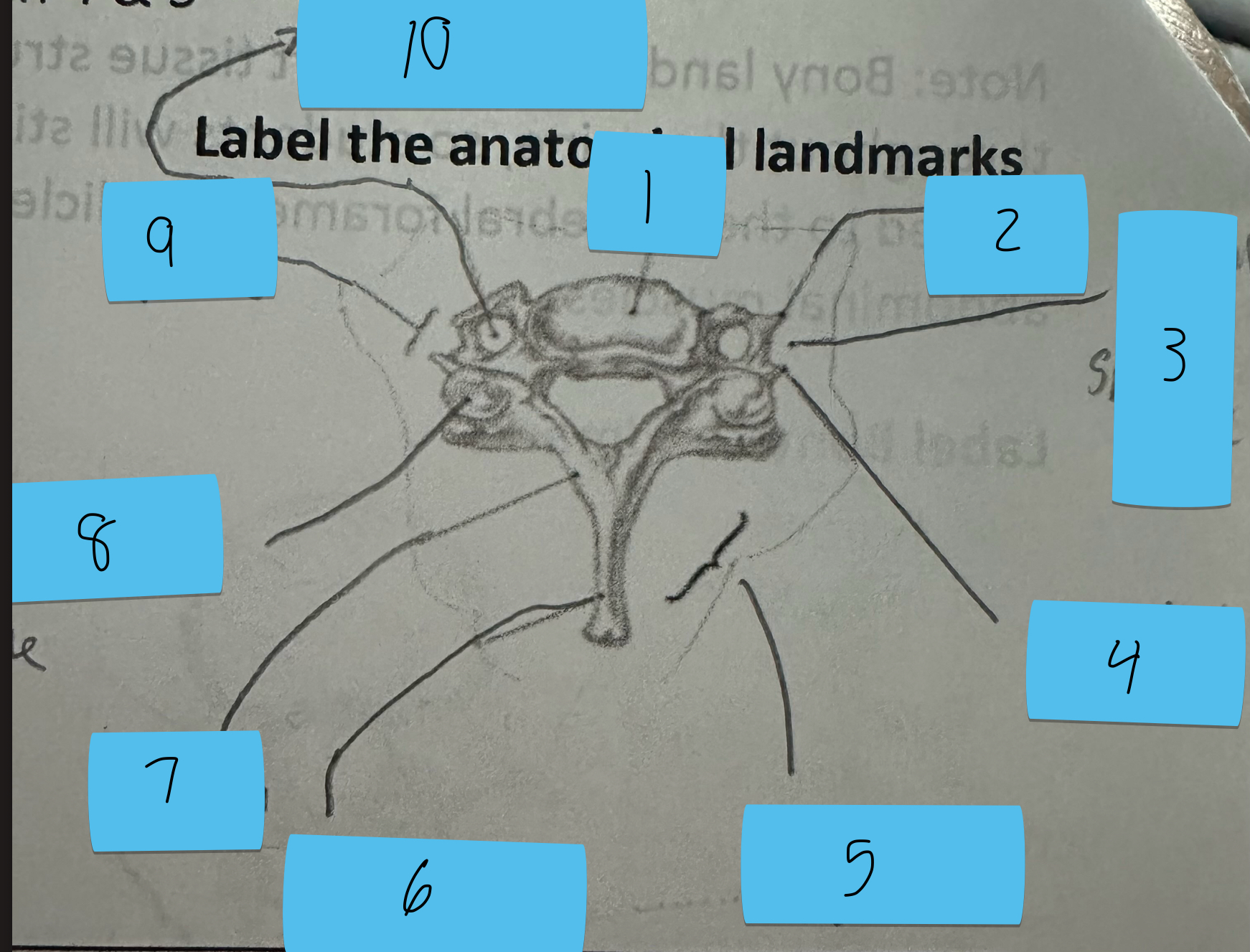
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (6)
Spinous process of cervical spine: serves as attachment for muscles
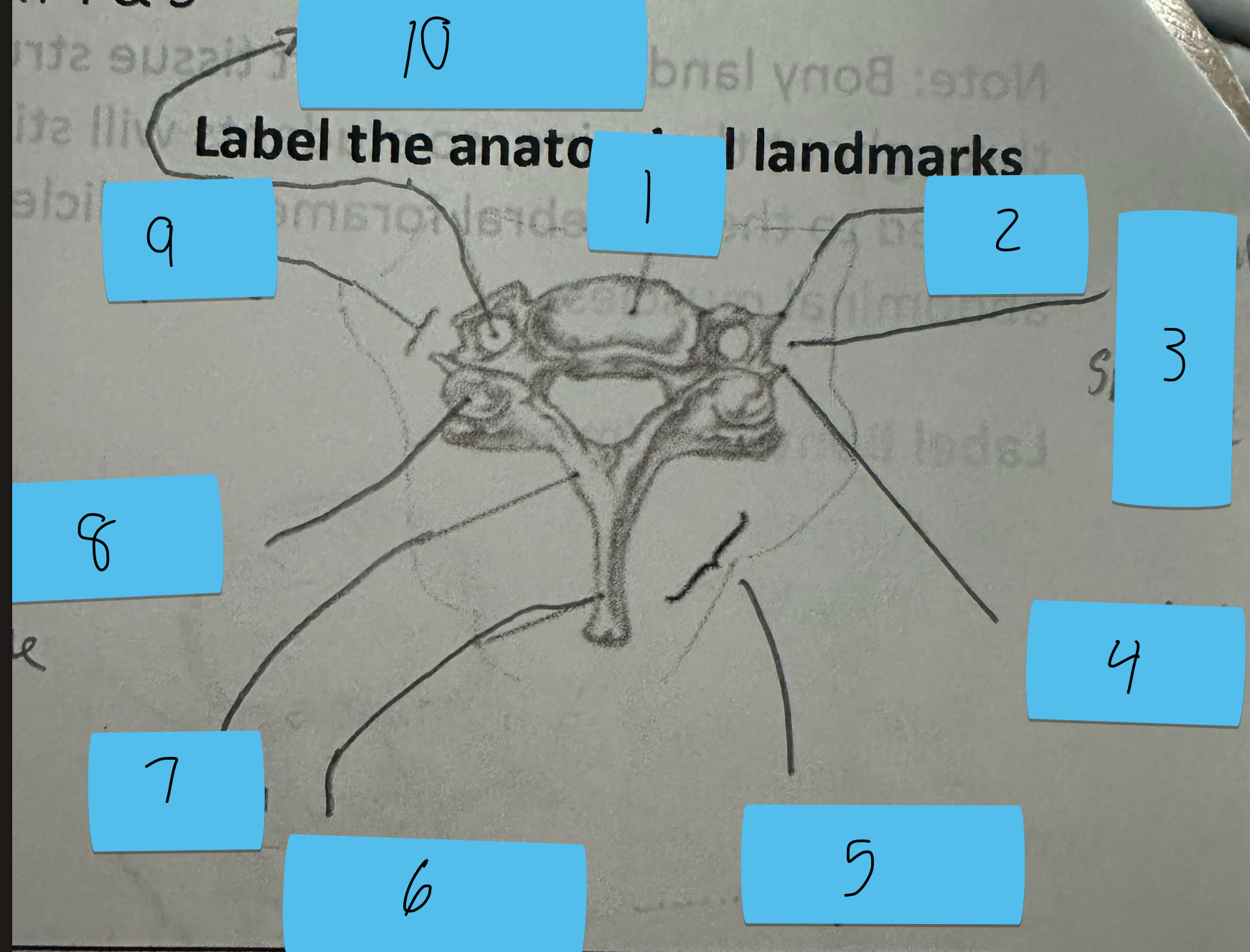
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (7)
Lamina of cervical spine: attachment for multifidus
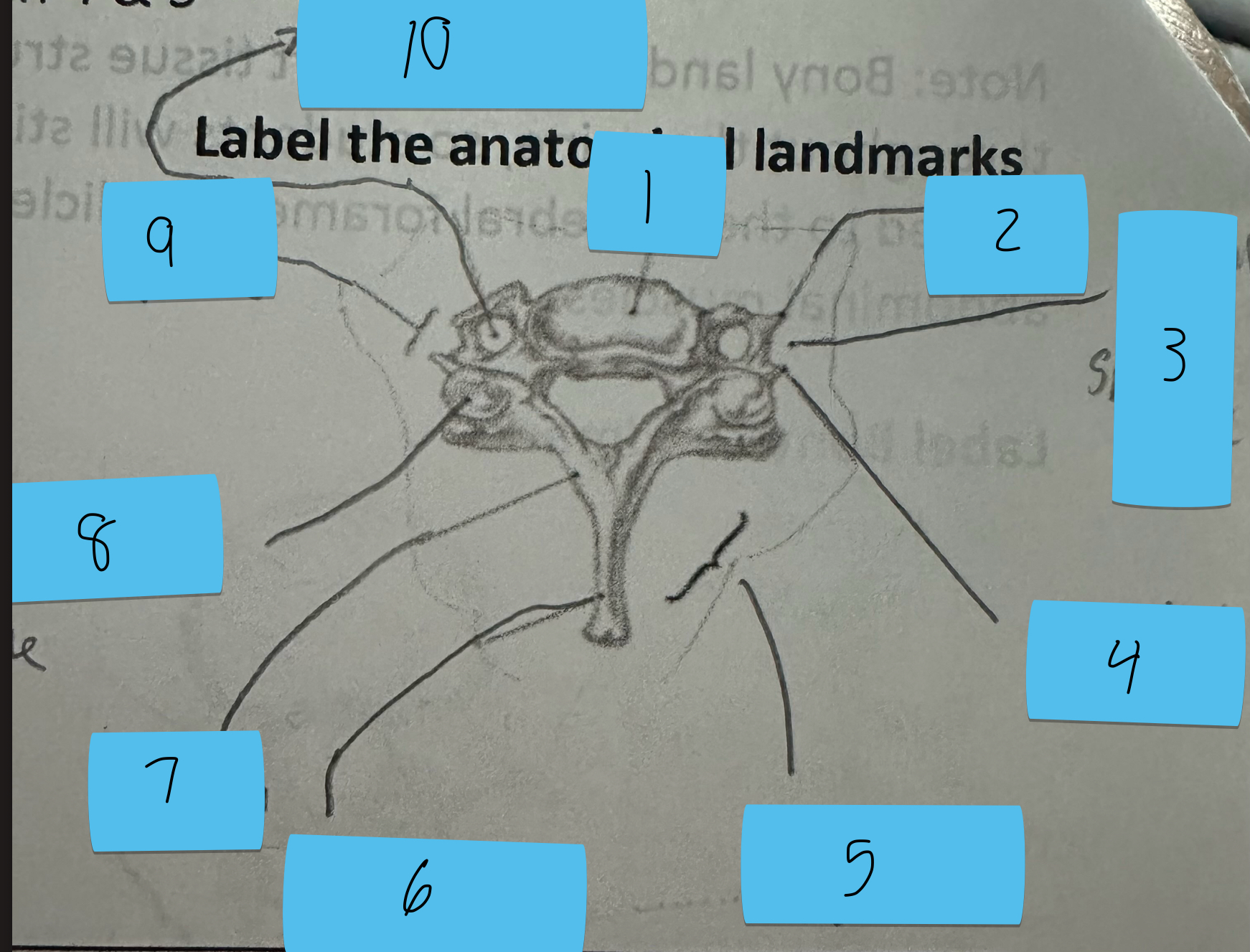
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (8)
Superior facet of cervical spine: form facet joints (flexion, extension, rotation, lateral flexion of neck)
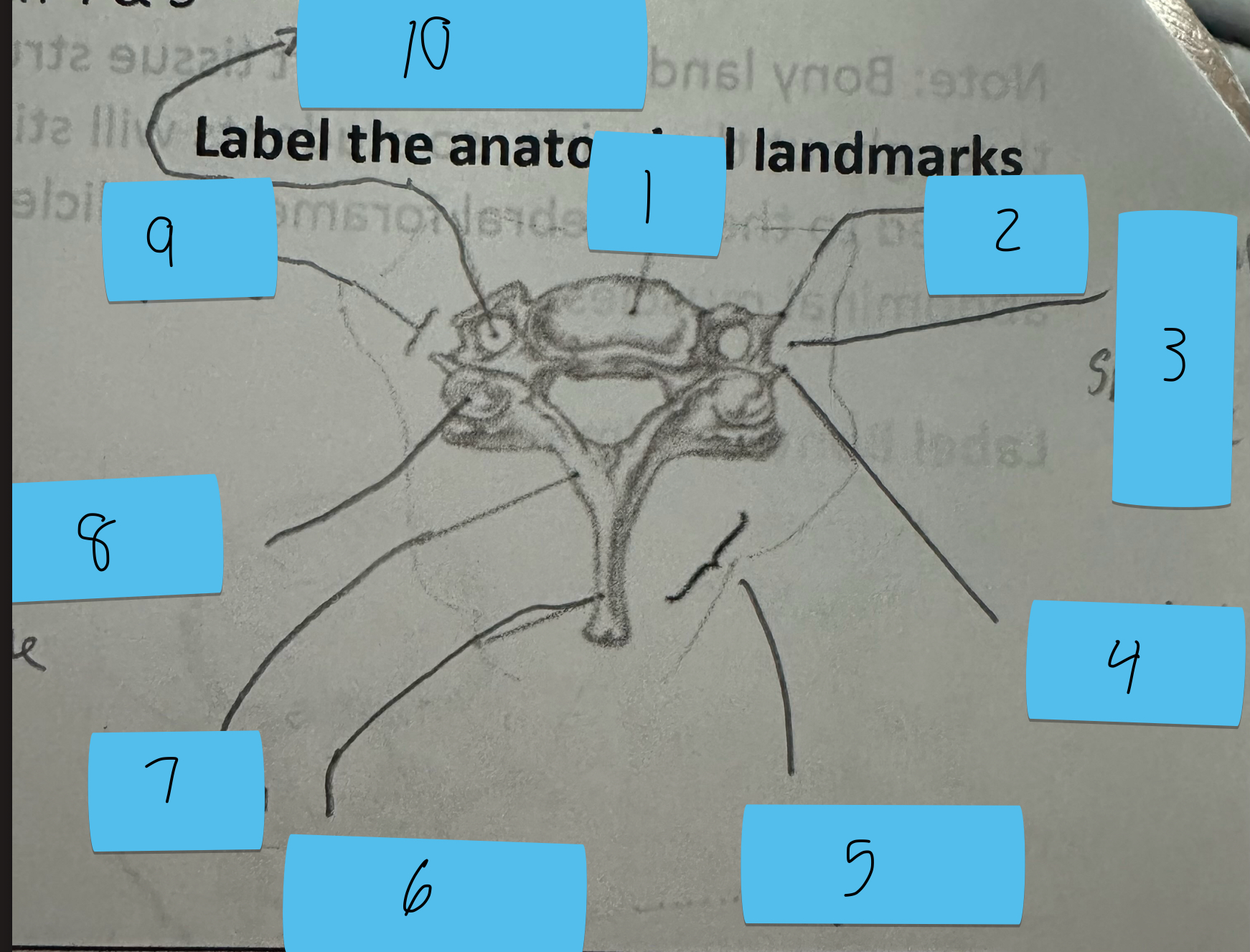
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (9)
Transverse process of cervical spine: serve as attachment scalenes and erector spinae
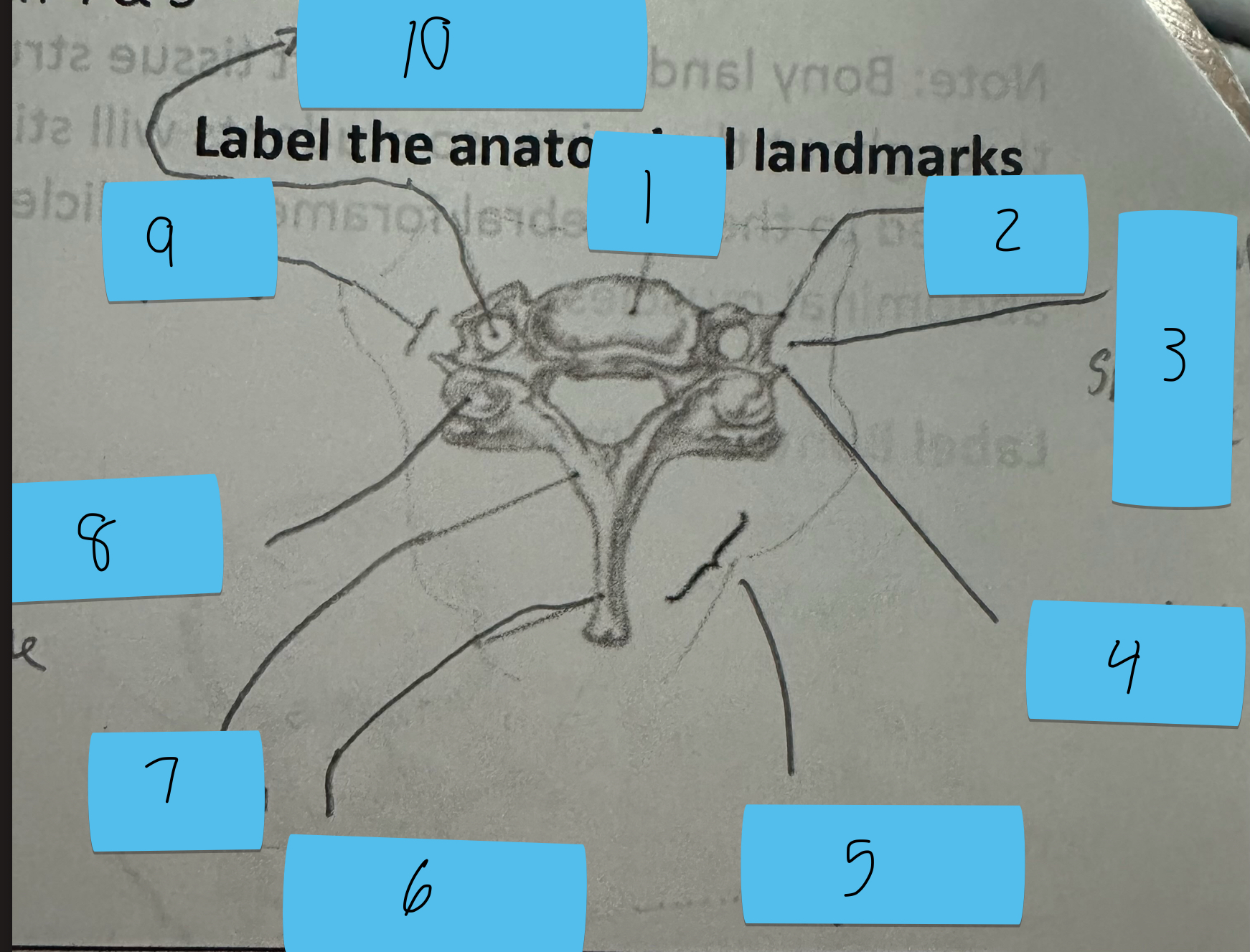
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (10)
Transverse foramen of cervical spine: passageway for vertebral artery
Identify this structure and anatomical significance
Atlas (C1): supports skull; articulates with C2 to allow head to rotate; site of Jefferson’s fracture
Identify this structure and anatomical significance
Axis (C2): supports skull; allowss for C1 to rotate; site of Hangman’s fracture
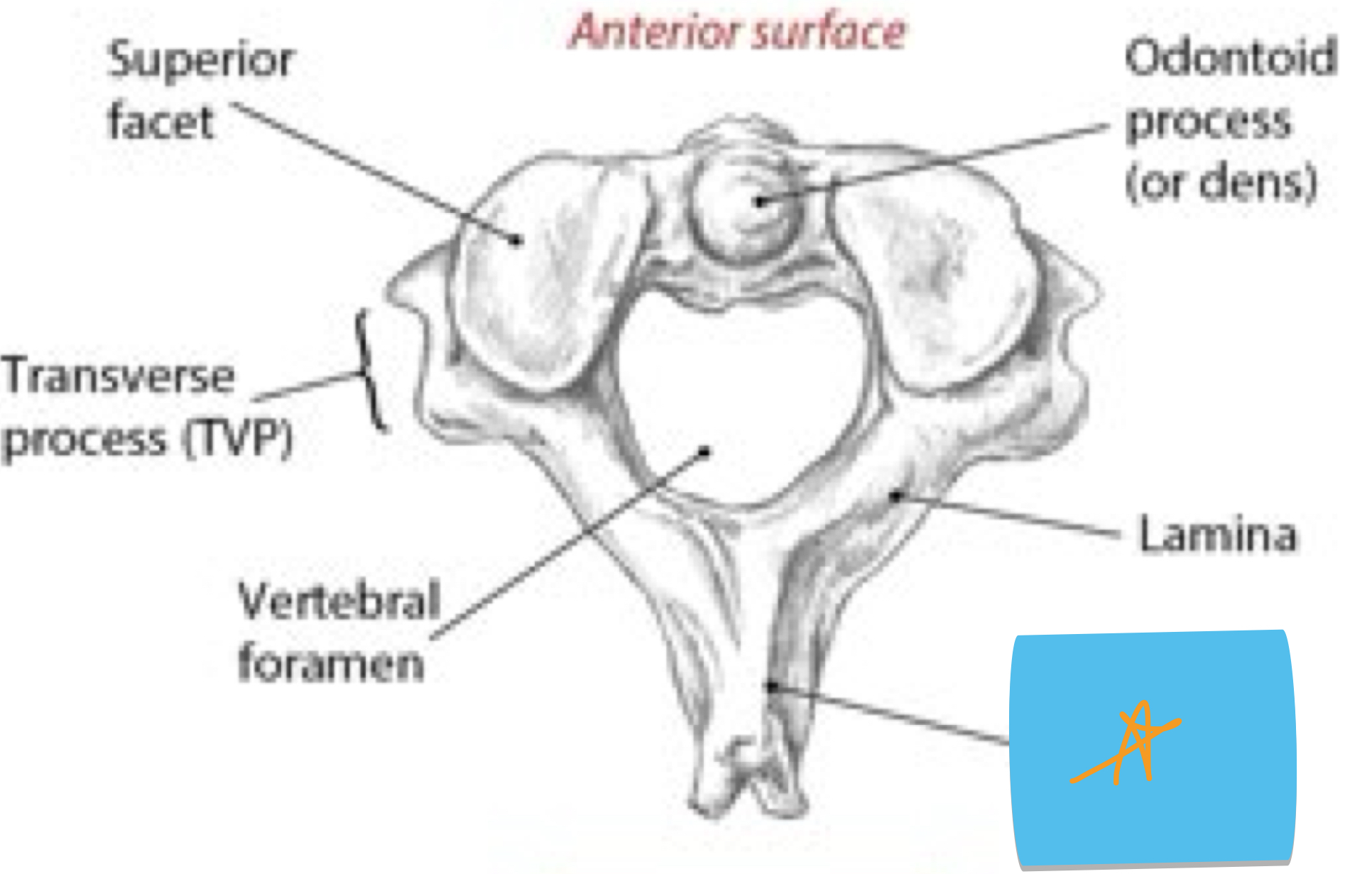
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (black star)
Odontoid process (dens): aids in stability while rotating head on axis
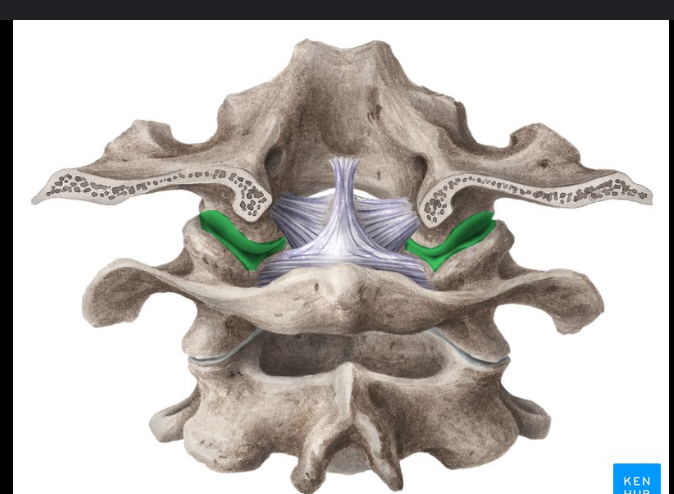
Identify this structure and anatomical significance
Atlanto-occipital joint: articulation between occipital and atlas; synovial joint allowing for flexion, extension, lateral flexion of head
Identify this structure and anatomical significance
Atlanto-axial joint: articulation between atlas/axis; allows rotation of head; composed of a pivot and 2 lateral joints
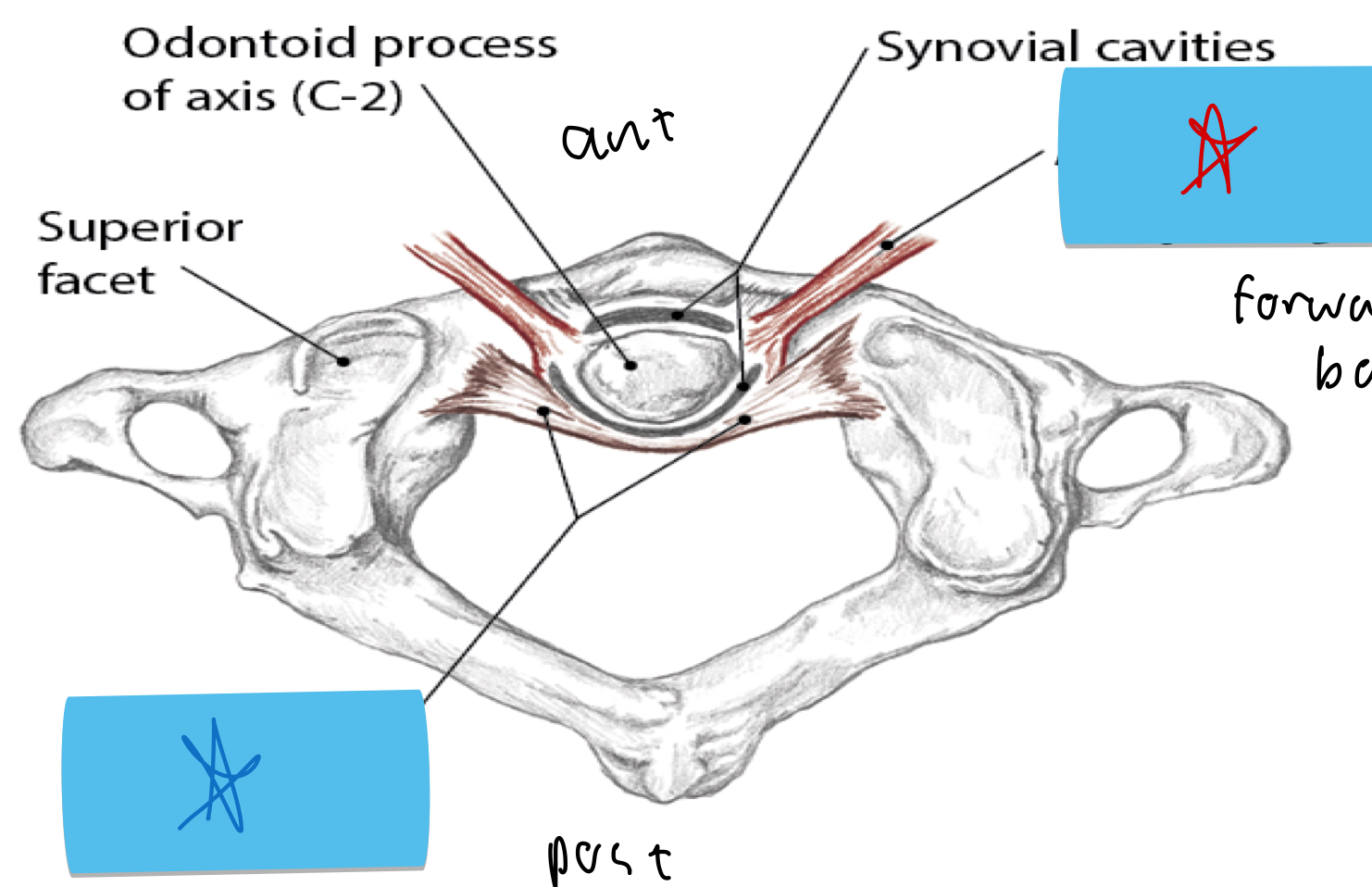
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (red star)
Alar ligament: helps stabilize head and neck; leads to instability when ruptured; sprained in whiplash
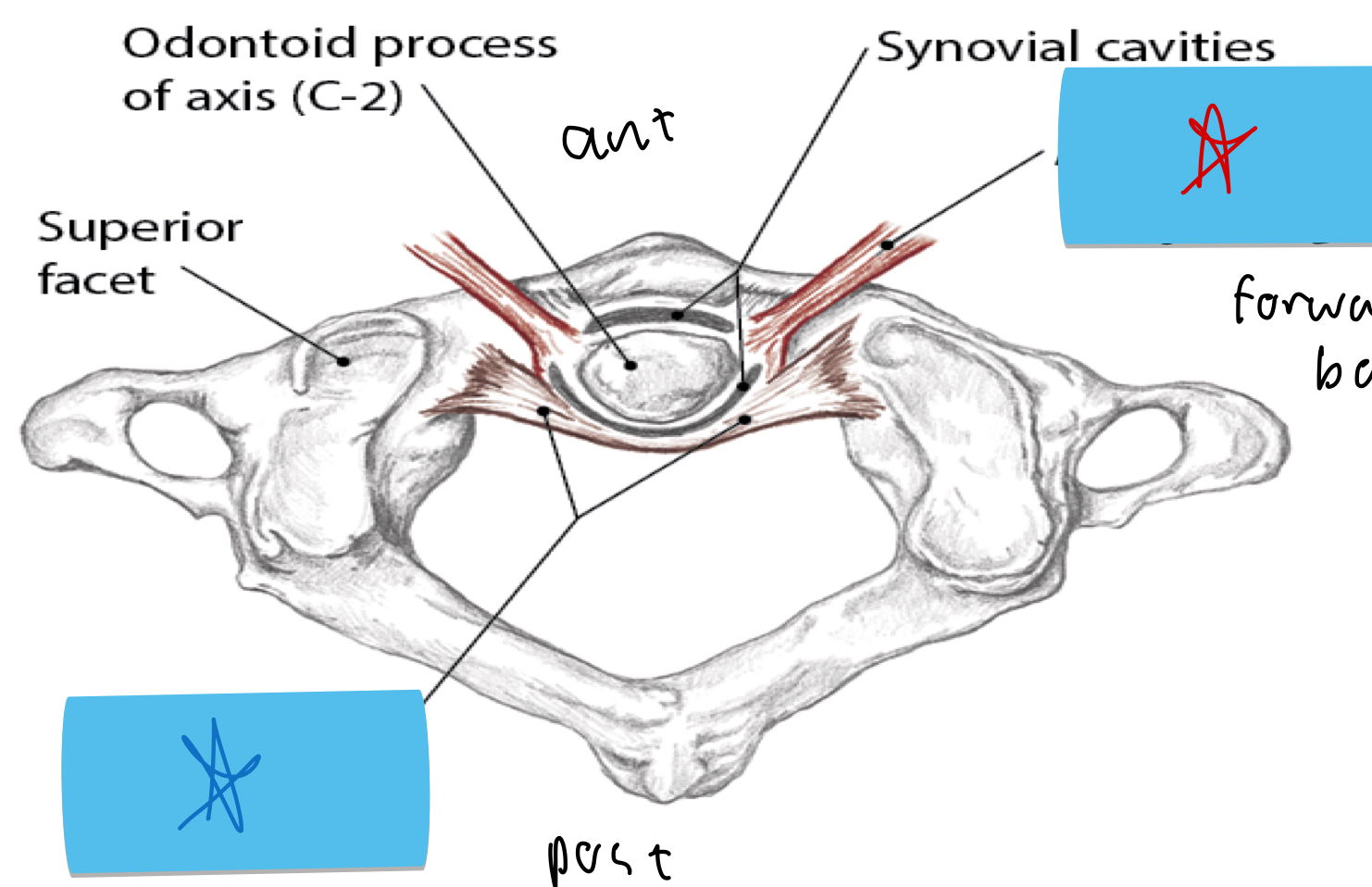
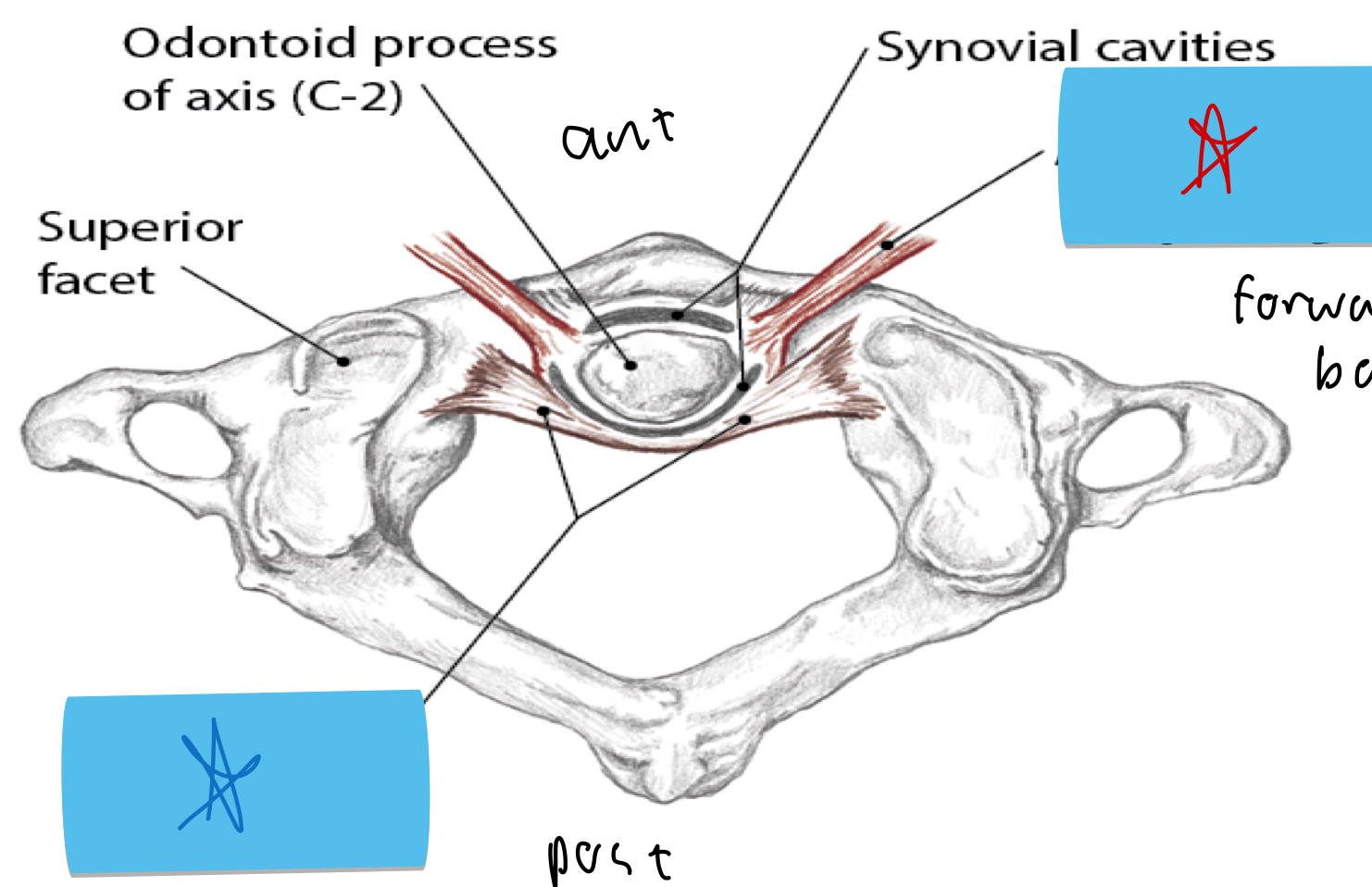
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (blue star)
Transverse ligament of atlas: help stabilize head and neck; keeps dens in place
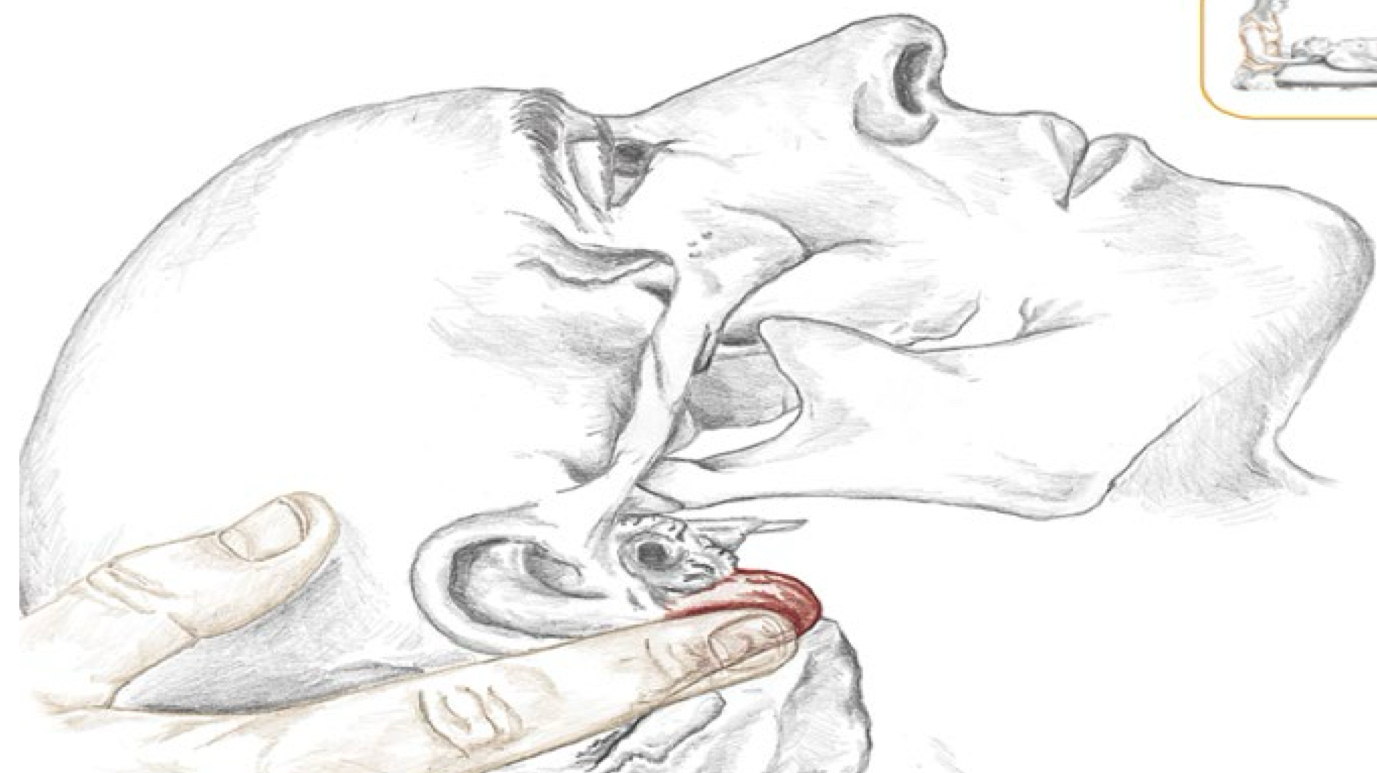
Identify this structure and anatomical significance
Mastoid process: large superficial bump behind earlobes; attachment for sternoclediomastoid, longissimus
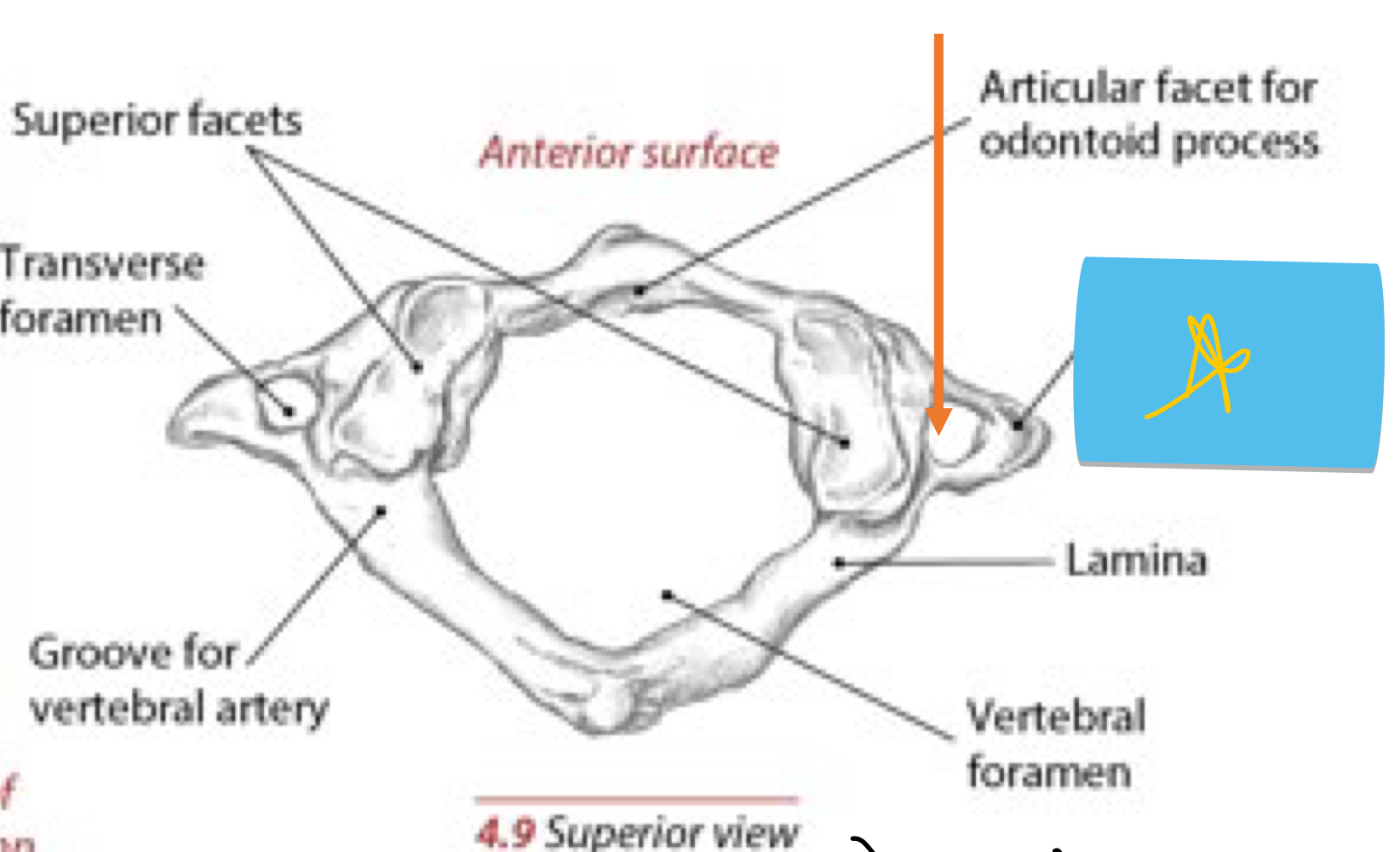
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (yellow star)
C1 transverse process: deep to sternoclediomastoid; distal and anterior to tip of mastoid process
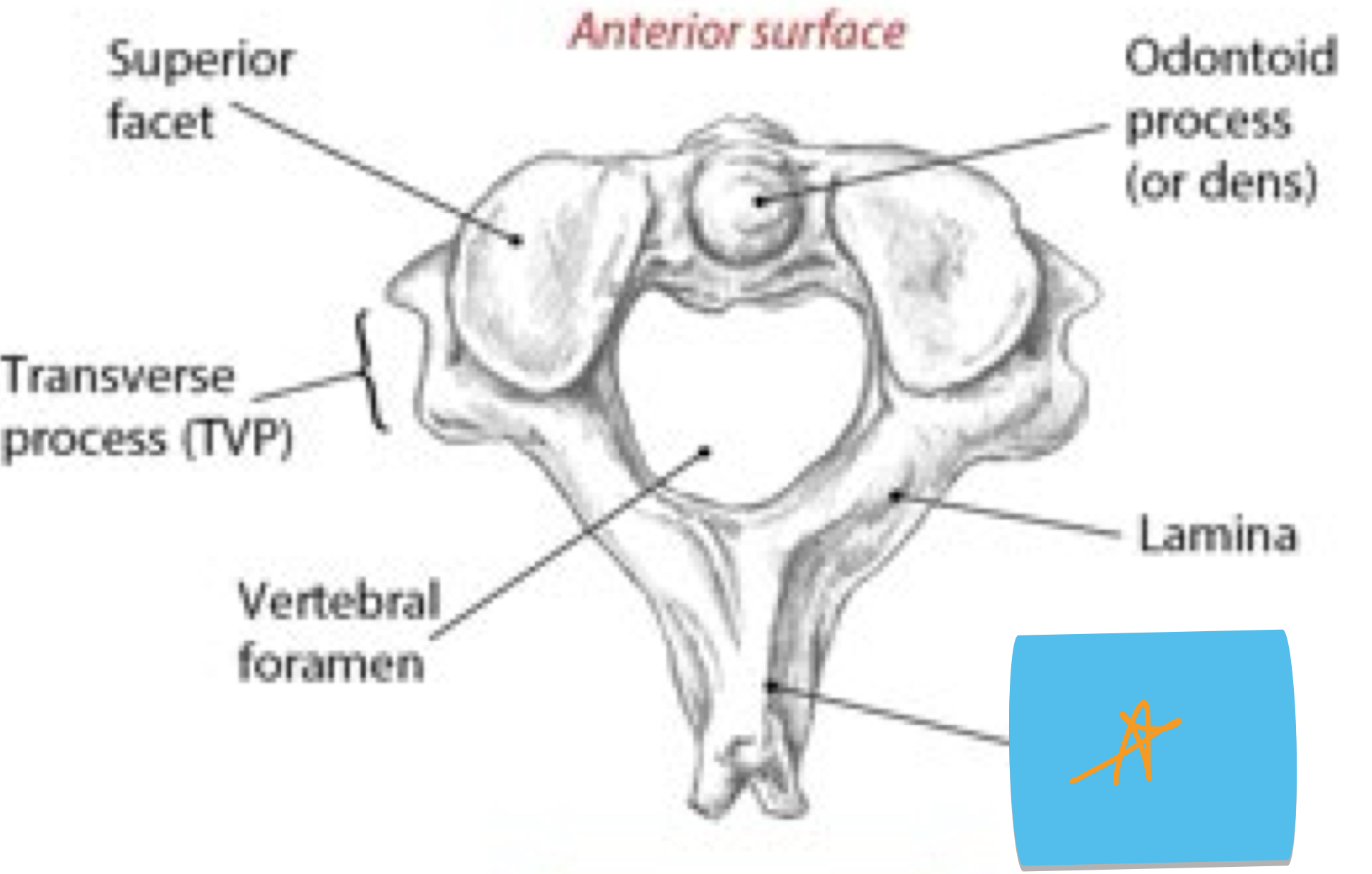
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (orange star)
C2 spinous process: attachment for several muscles; superficial to palpate
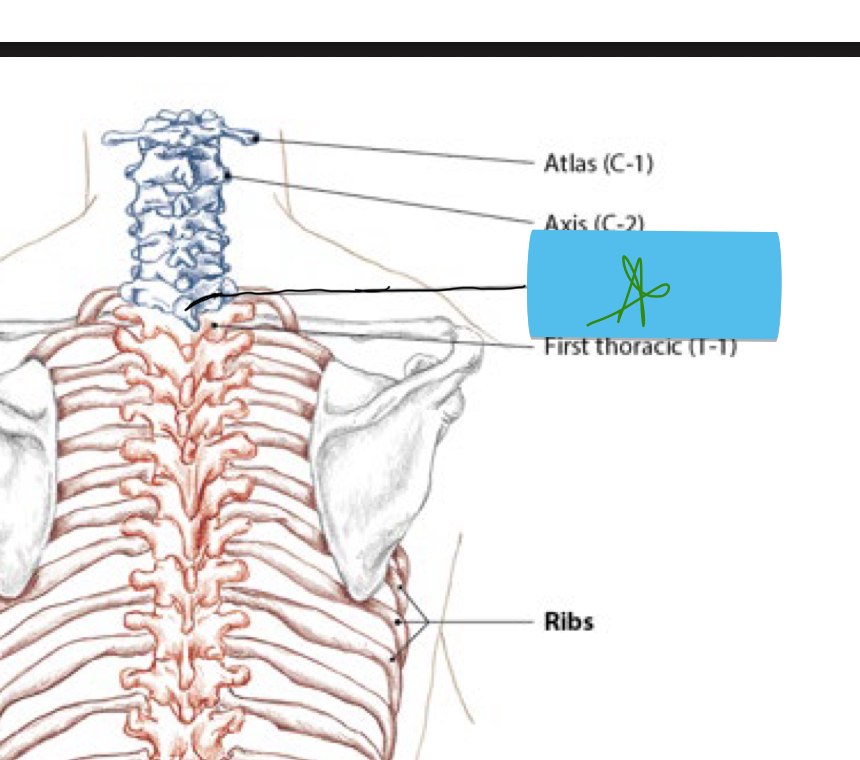
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (green star)
C7 spinous process: attachment for upper trapezius and ligamentum nuchae; bony prminence when neck is flexed
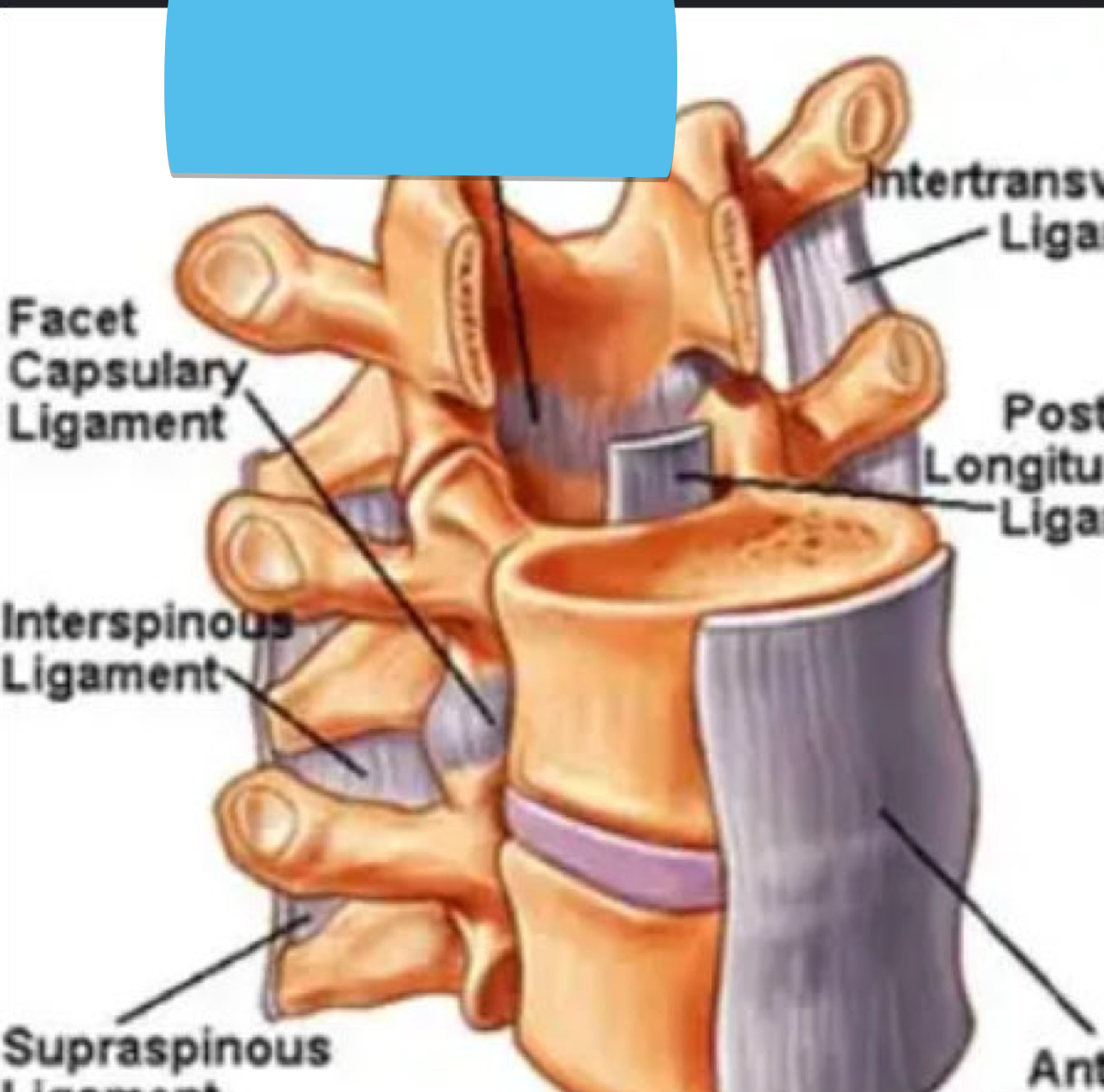
Identify this structure and anatomical significance
Ligamentum flavum: prevents excessive morion on posterior aspect of spine
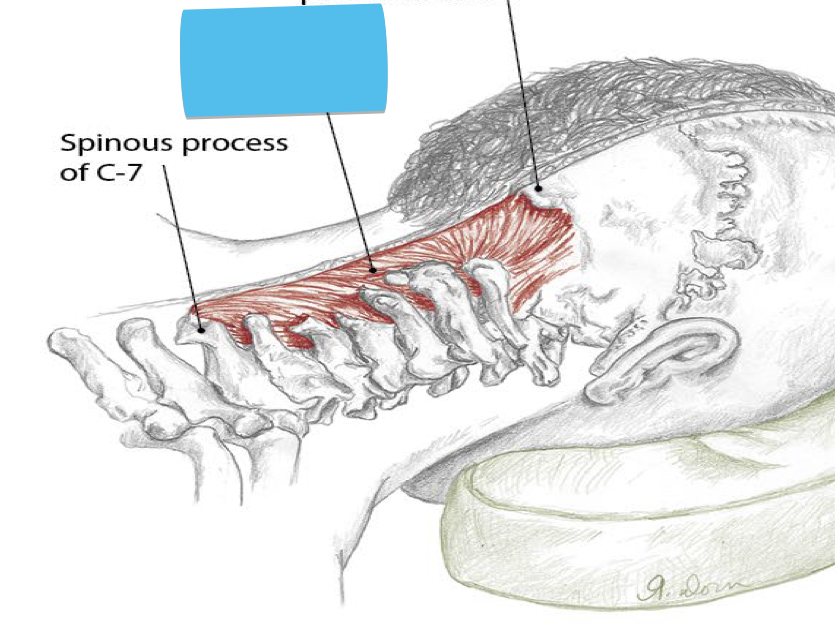
Identify this structure and anatomical significance
Ligamentum nuchae: stabilizes head and neck; attachment for trapezius, splenius capitis; runs along sagittal plane from external occipital protuberance to spinous process of C7
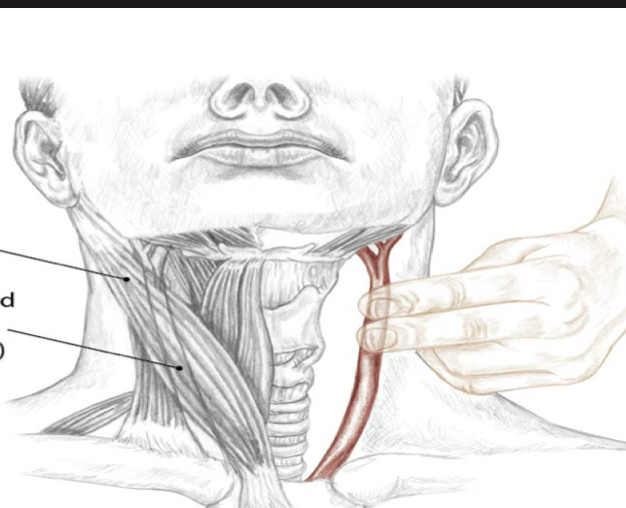
Identify this structure and anatomical significance
Carotid artery: primary blood supplier of head and neck
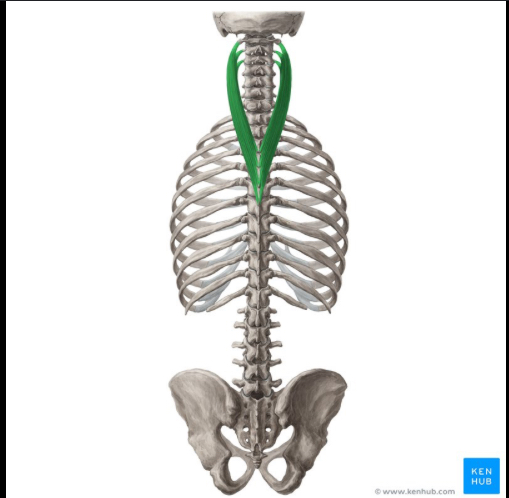
Identify this structure and anatomical significance
Splenus cervicis: deep to spleunus capitis; generally located in lamina groove of upper T-spine/C-spine
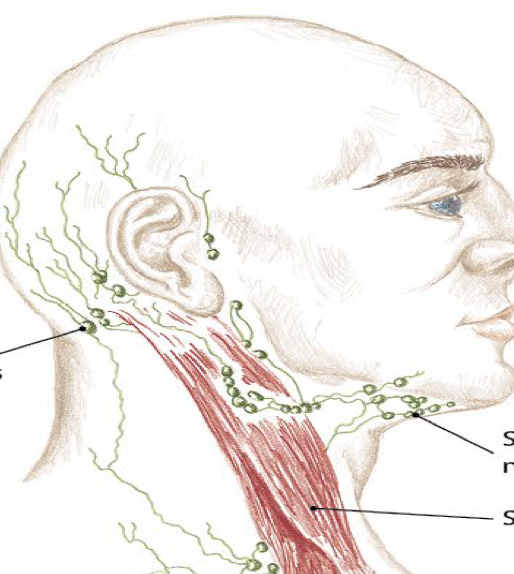
Identify this structure and anatomical significance
Cervical lymph nodes: superficial and deep; superficial along underside of mandible, posterior and inferior to earlobe; tender on palpation; swell/enlarge in infection
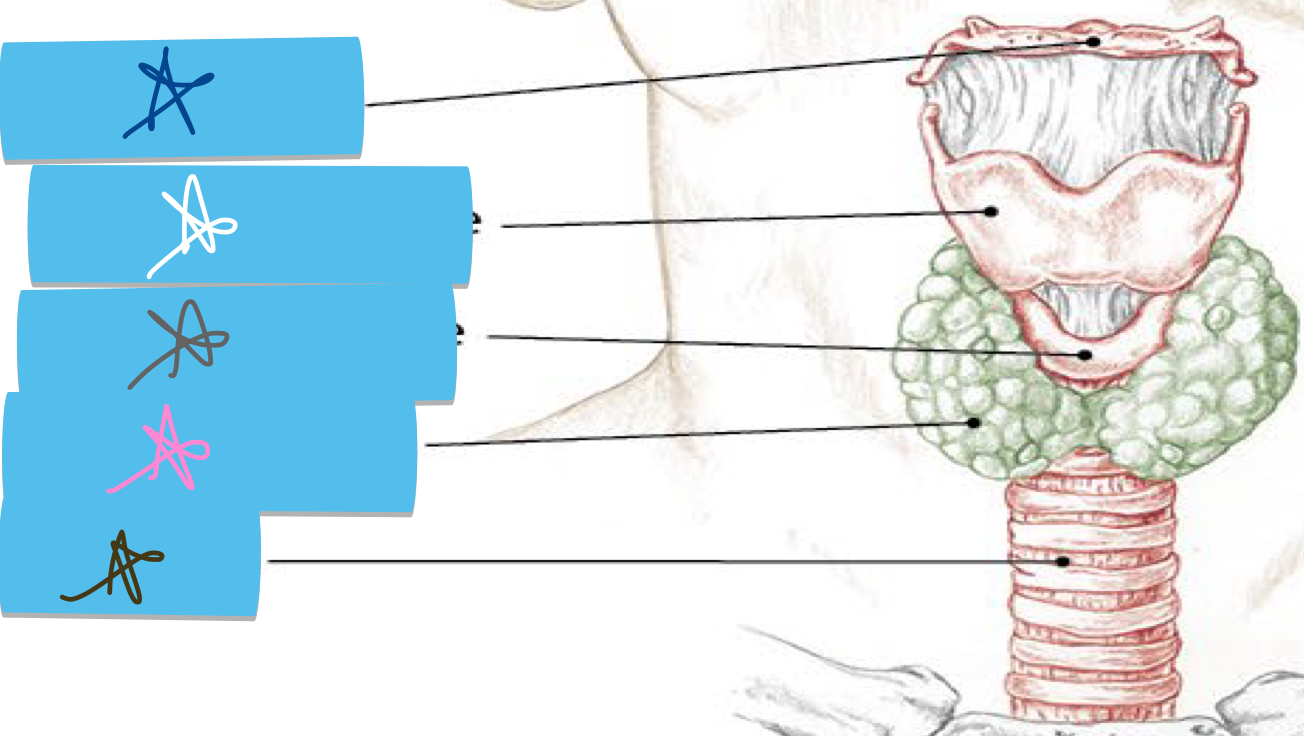
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (pink star)
Thyroid gland: between jugular notch and cricoid cartilage; soft texture on top of trachea
Identify this structure and anatomical significance
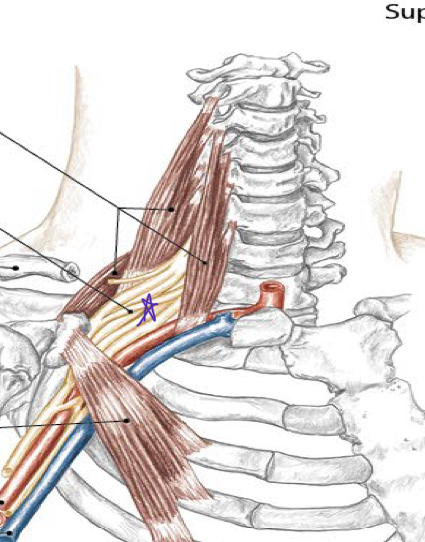
Brachial plexus: large bundle of nerves innervating shoulder and upper extremity; tenderness at Erb’s point; compression/traction = sharp, shooting sensation down arm
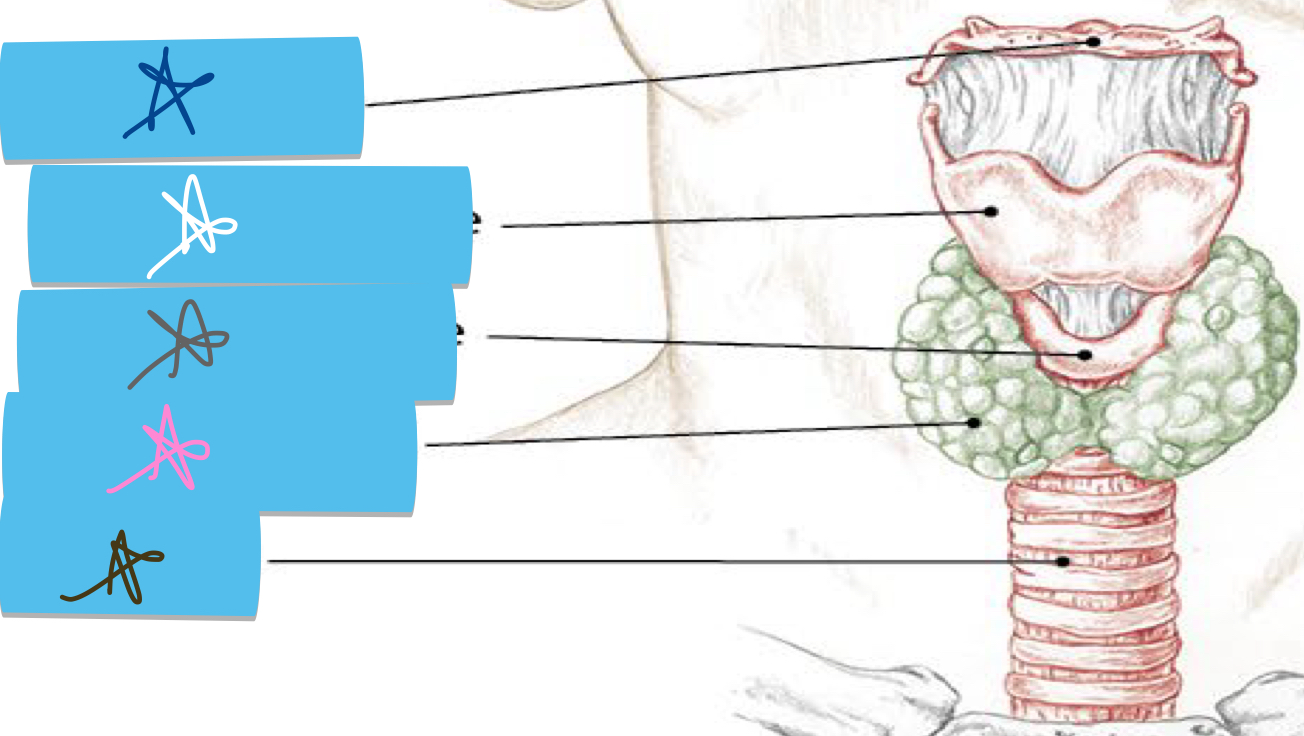
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (brown star)
Trachea: airway; thick cartilage deep to thyroid gland
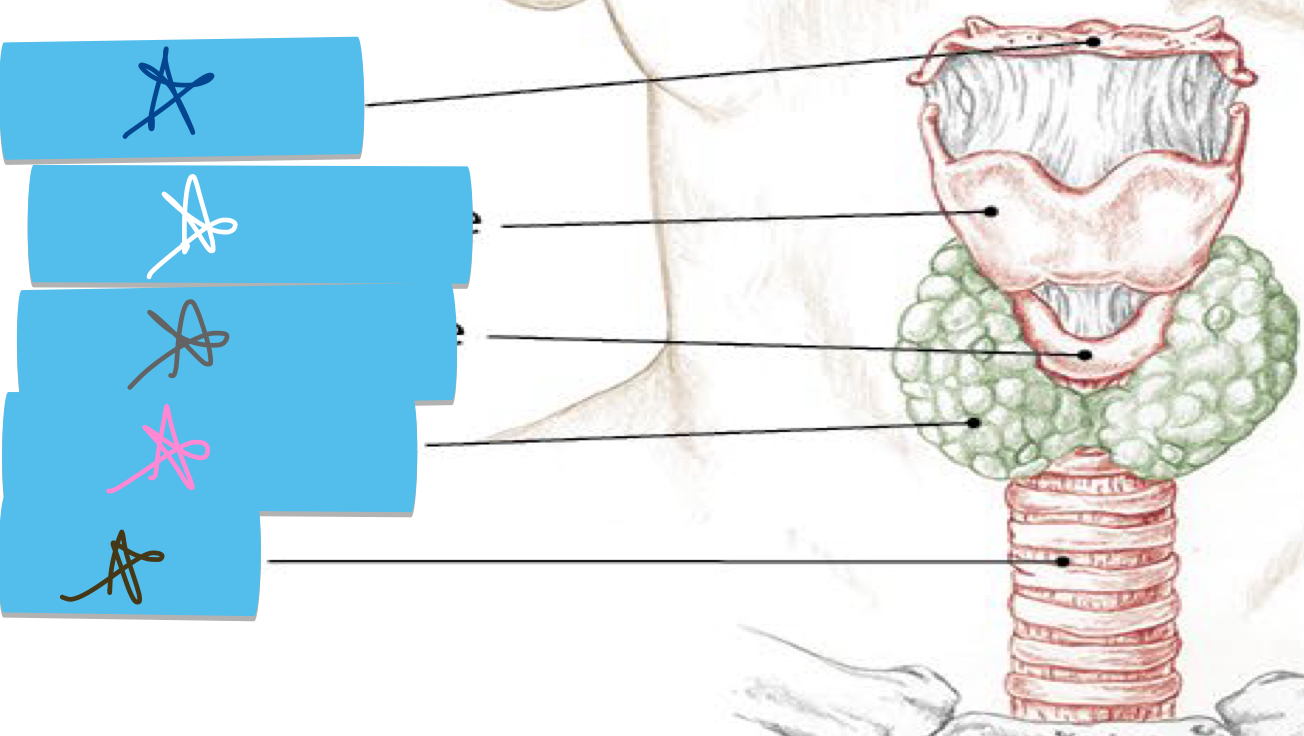
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (gray star)
Cricoid cartilage: between trachea and thyroid
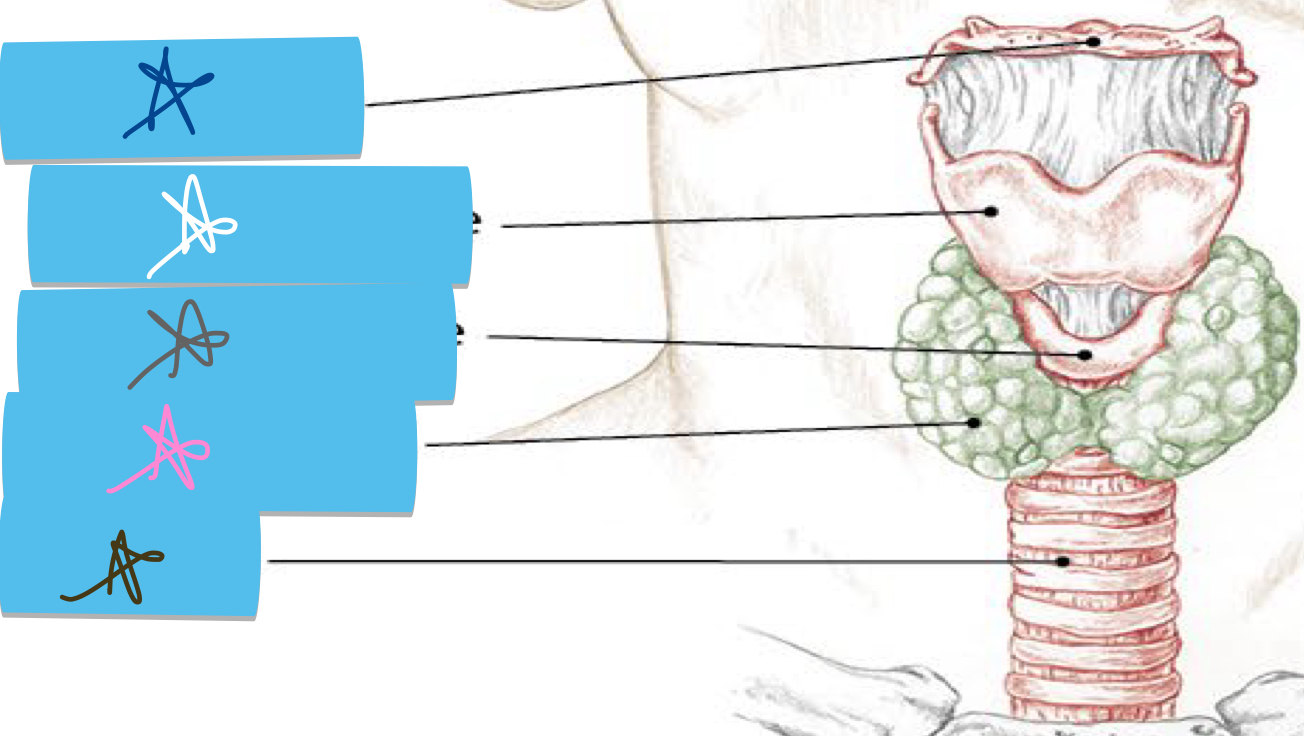
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (white star)
thyroid cartilage: prominent/larger than cricoid (Adam’s apple); superior to cricoid
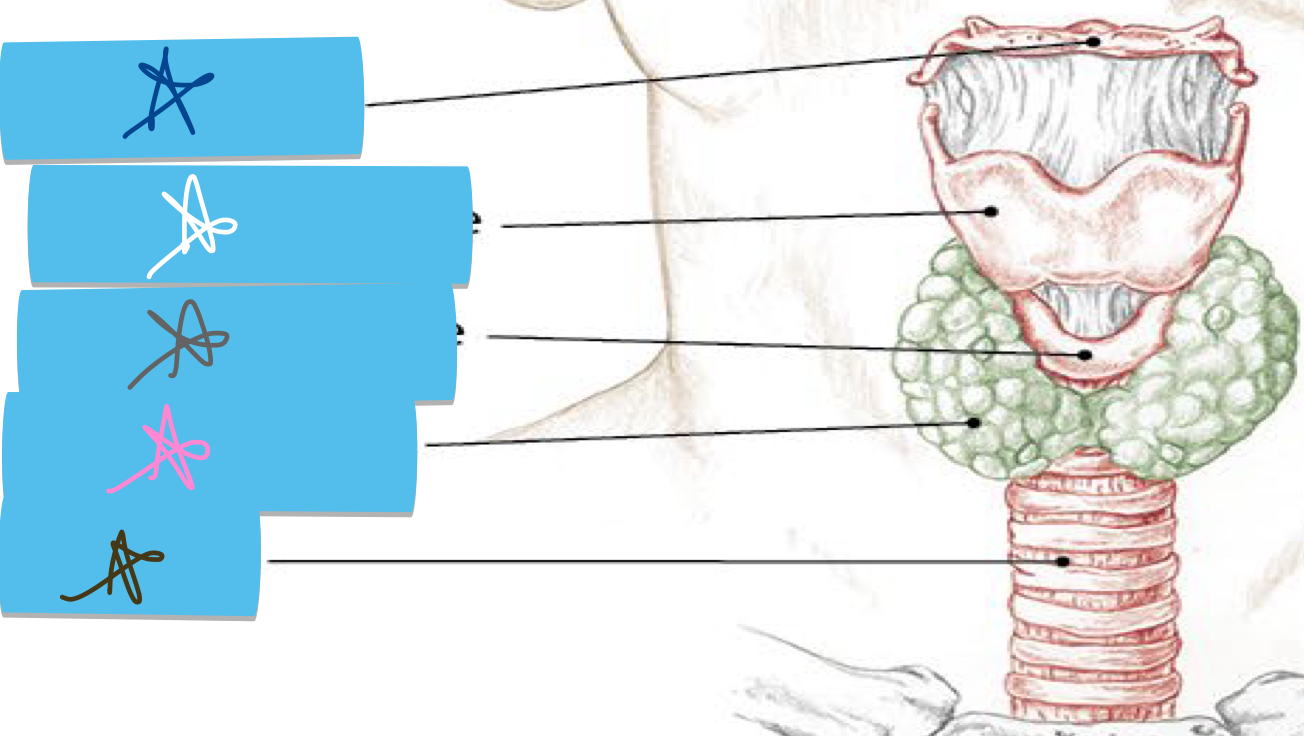
Identify this structure and anatomical significance (dark blue star)
Hyoid: site of muscle attachments in throat and neck; rises when swallowing
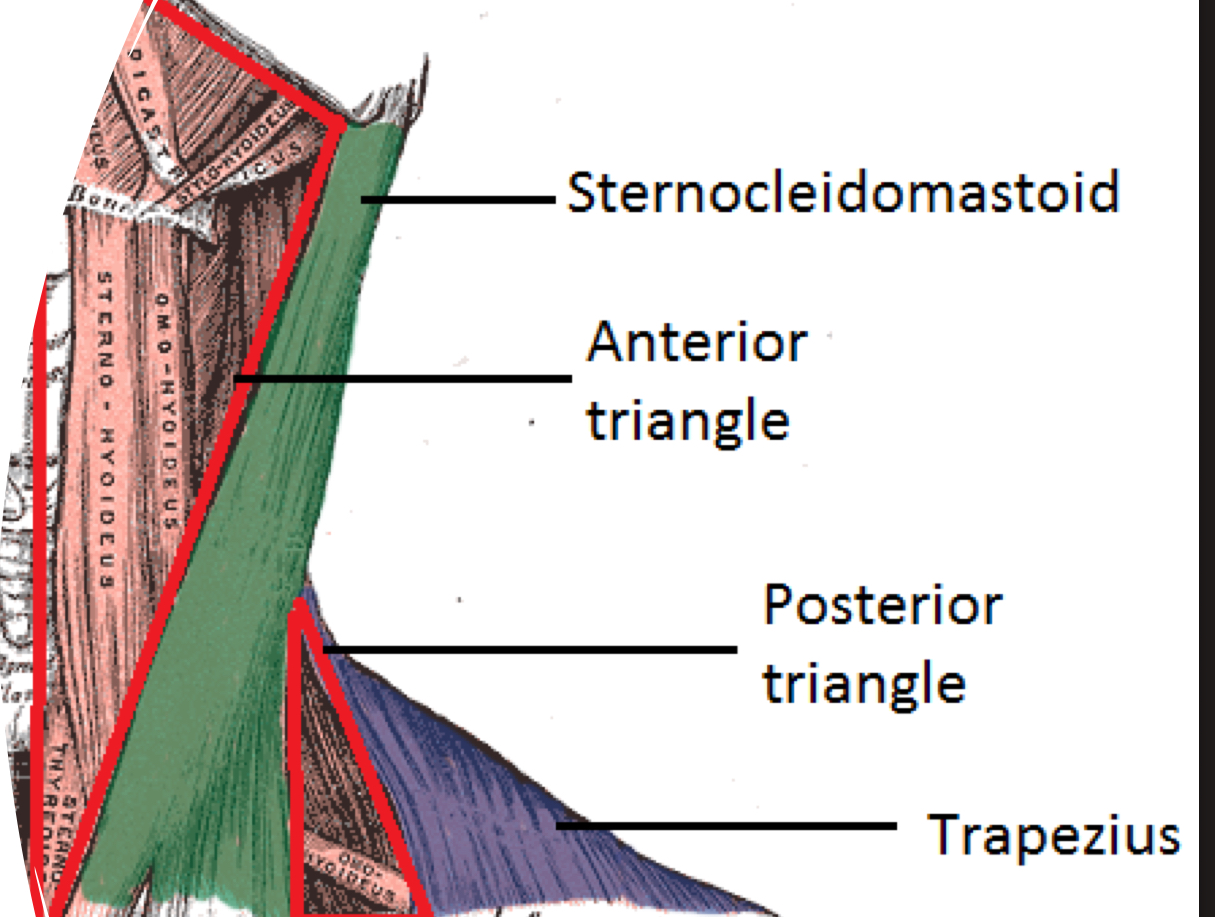
Anterior triangle of neck
borders: sternoclediomastoid (lateral), base of mandible (superior), trachea (medial)
function: allows carotid artery to pass through
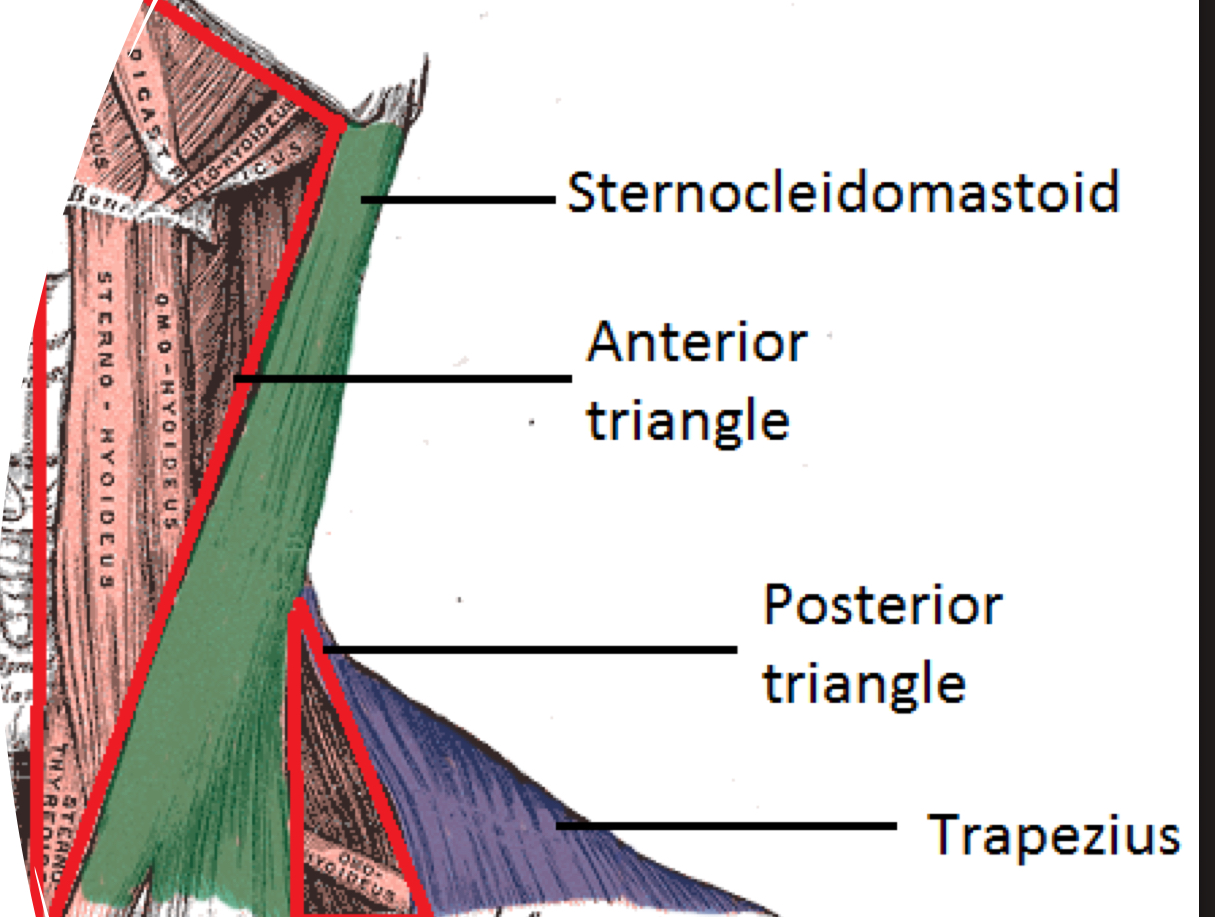
Posterior triangle of neck
borders: sternocleidomastoid, clavicle, upper trapezius
function: allows from brachial plexus, subclavian artery, and subclavian vein to pass through
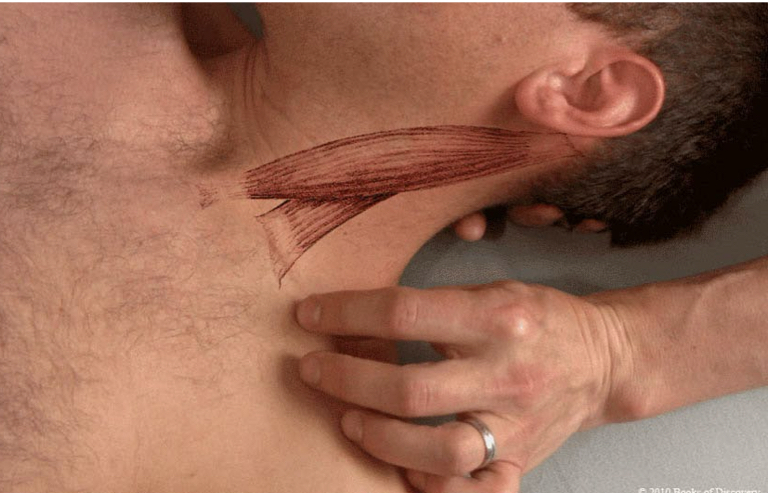
Sternocleidomastoid
origin: sternal head: top of manubrium
clavicular head: medial 1/3 of clavicle
insertion: mastoid process/lateral portion of superior nuchal line of occiput
action: unilateral: laterally flex head/neck to same side; rotate head/neck to opposite side
bilateral: flex neck/elevate rib cage during inhalation
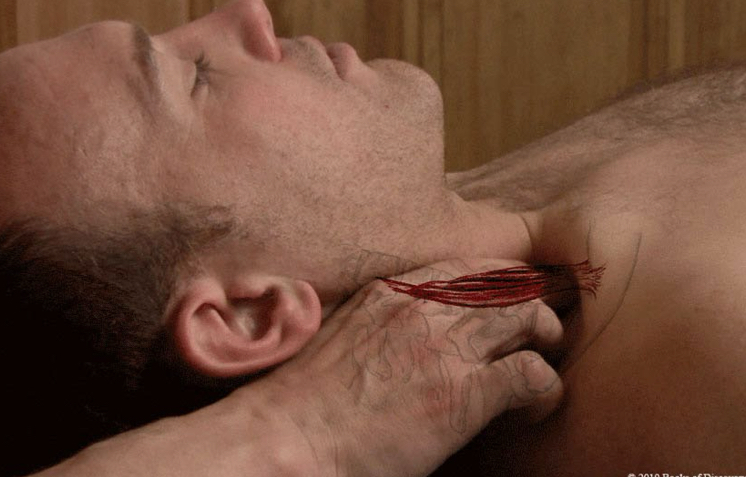

Anterior scalene
origin: anterior tubercle of transverse processes of C3-C6
insertion: 1st rib
action: flex head and neck; unilateral: laterally flex head/neck to same side; rotate neck to opposite side
bilaterally: elevate ribs during inhalation
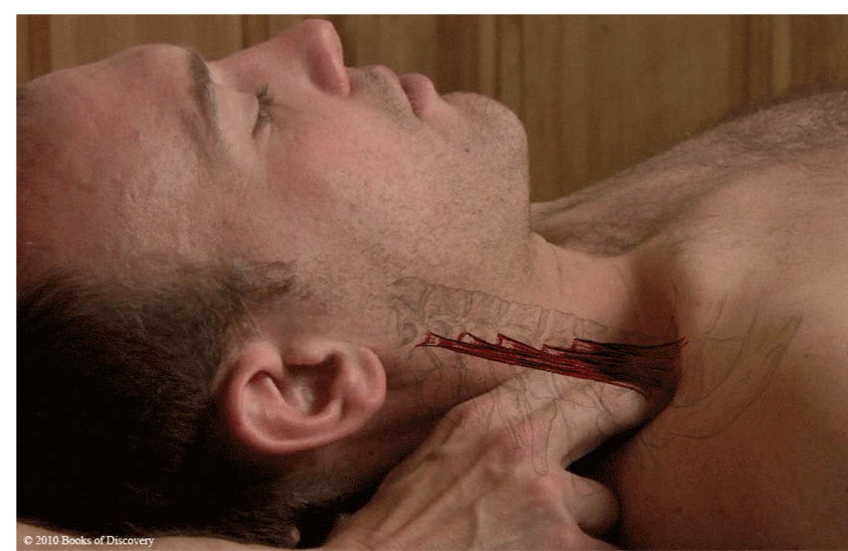
Middle scalene
origin: posterior tubercle of transverse processes of C2-C7
insertion: 1st rib
action: unilateral: laterally flex head/neck to same side; rotate neck to opposite side
bilaterally: elevate ribs during inhalation
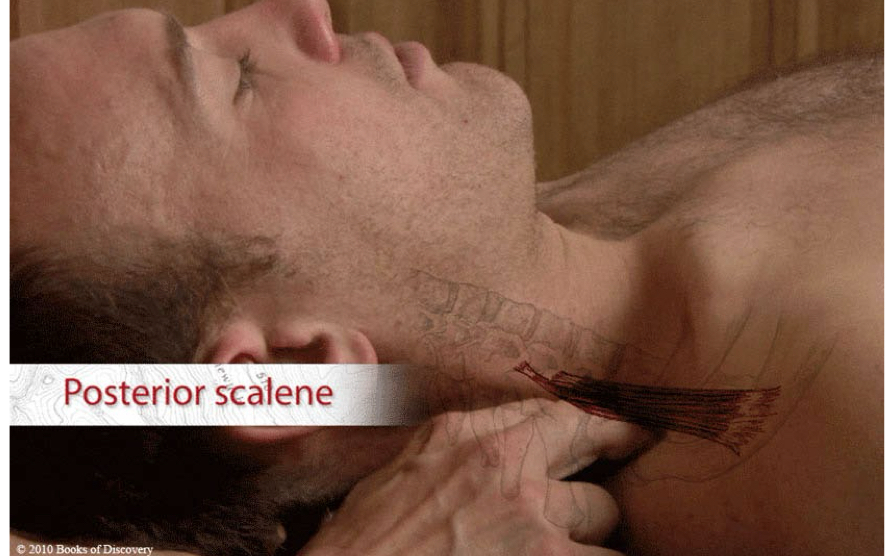
Posterior scalene
origin: posterior tubercle of transverse processes of C6/C7
insertion: 2nd rib
action: unilateral: laterally flex head/neck to same side; rotate neck to opposite side
bilaterally: elevate ribs during inhalation
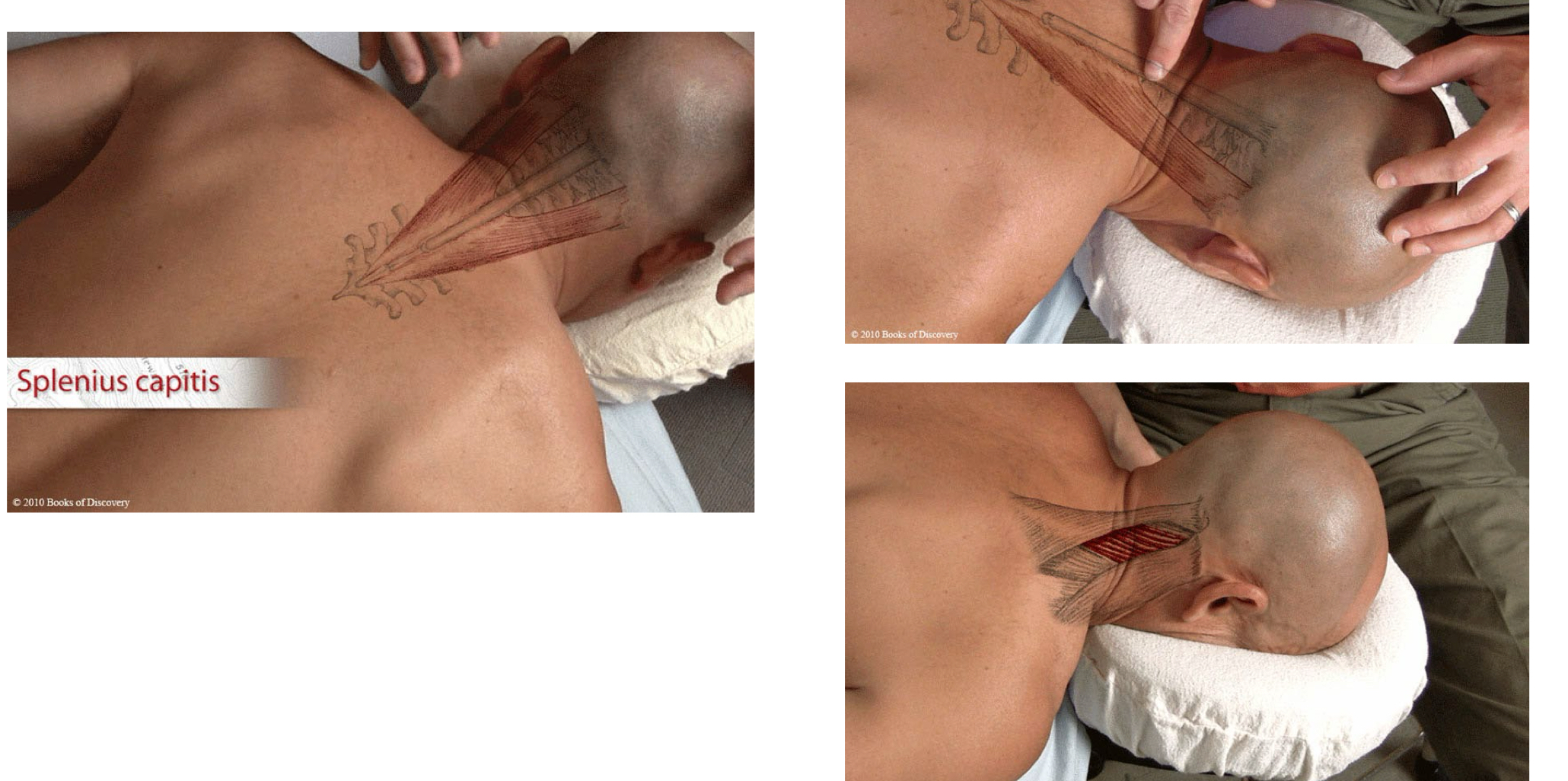
Splenius capitis
origin: mastoid process; lateral portion of superior nuchal line
insertion: inferior ½ of ligamentum nuchae; spinous process C7-T4
action: unilateral: rotate/laterally flex head and neck
bilateral: extend head/neck
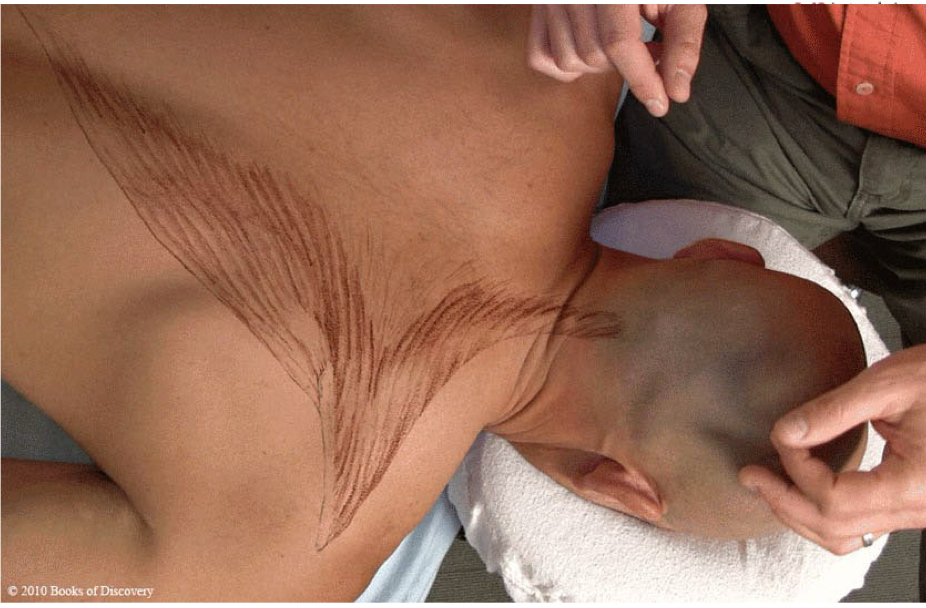
Upper trapezius
origin: external occipital protuberance, medial portion of superior nuchal line, ligamentum nuchae, spinous process of C7-T12
insertion: lateral 1/3 of clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula
action: bilateral: extend head/neck
unilateral: lateral flexion of head/neck; elevate/upwardly rotate scapula
Dens/odontoid fracture
caused by hyperextension/flexion with rotational/shearing force
Cervical dislocation
cervical spine shifted off; caused by high impact trauma
Whiplash
acute, rapid hypermovement causic eccentric contraction of muscles; leads to spasms, and compress ligaments (alar, tansverse, post/anterior longitudinal ligament)
Brachial plexus neurapraxia
caused by rapid stretch/compression
Thoracic outlet syndrome
3 primary causes: hypertrophy, cervical rib, pec minor compression; causes disruption to neurovascular structures (subclavian artery and vein)