3.5 Chem 12 Altering Solubility of a Salt
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
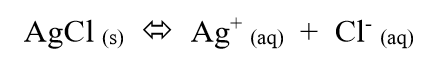
if we increase the rate of dissolving more than the rate of crystallization
then more AgCl will leave the solid state and enter the aqueous state
the solubility of AgCl increases
(if a substance is highly soluble, it dissolves more)
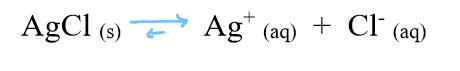
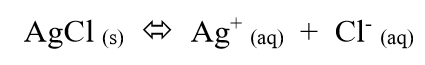
if we increase the rate of crystallization more than the rate of dissolving
then more Ag and Cl will leave the aqueous state and enter the solid state
solubility of AgCl decreases
(if a substance has low solubility, almost none of it dissolves)
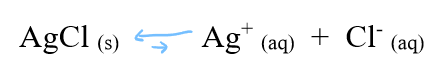
decreasing the solubility of the solid in eqm
shifts to the solid side
increasing the solubility of the solid in eqm
shifts to the ions side
increasing and decreasing the solubility refers to the ___
solid salt
changes in solubility are accomplished by
altering the concentration of the dissolved ions
![<p>increasing [ ] of ONE ion in this system</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a6eeb6b6-3cbb-4afe-afae-f850f2c906c3.png)
increasing [ ] of ONE ion in this system
shifts system left
to use up added ions
therefore, causing more solids to form
adding AgNO3 increases [Ag+]
adding NaCl increases [Cl-]
common ion effect
lowering solubility of a salt by adding a second salt which has one ion IN COMMON with the first salt
common ion effect is used to
prevent a salt from dissolving to any great extent or to force a particular dissolved ion to leave a solution