CD3 Endodontics Study Set: Key Terms & Definitions
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
171 Terms
True or False:
You can heat a root canal spreader instrument?
False!
You can ONLY heat the root canal plugger instruments
What is a root canal plugger instrument used for?
Its used to compact filling material during VERTICAL condensation
CAN BE HEATED
What is the root canal spreader used for?
Used to compact filling material during LATERAL condensation
NOT to be heated, NOT to be used to find canals
What does the color of the endodontic file indicate?
It indicates the size of the tip
What is the function of stainless steel K-files?
Penetration and enlargement
What is the shape of the tip for stainless steel K files?
Square or rectangular
How long is the cutting edge on all of the stainless steel K-files?
16 mm
Why are K files (hand files) single use?
Files show signs of wear during normal uses. Single use reduces the risk of file breakage during use and increase patient safety.
Cutting efficiency is therefore achieved when a new instrument is used for each patient.
Single use files eliminate cross contamination
What is the pH of Calcium Hydroxide?
12.5
aqeuous and radiopaque
The endodontic irrigating syringe features a ______ vented needle
side
Why are 5 radiographs needed for completing an RCT?
1. Recognize anatomical information
2. Prevent incidence of endo mishape
3. Predict eventual outcomes
4. Insurance claims (need pre/post of)
5. Legal protection
The apical constriction is typically located ~_______ from the radiographic apex
0.5
True Or False:
You should am to obturate teeth AT LENGTH (~0.5 mm from the radiographic apex)
True
True or false: Practitioners electing to perform endodontic treatment are not legally held to the same standard of care as endodontists.
False:
Dentist electing to perform RCT are held to the same standard as endodontists
What are the principals of canal shaping?
Develop continuously tapering cone
"flow" across multiple places
Maintain location of foramen
Keep foramen as small as practice
What is the tip shape of ProTaper Next rotary file?
Rectangle
*2 points of contact at all times
What is the tip shape of ProTaper Universal?
Triangle
*3 points of contact as all times
What is the percent of children/teens in the USA who will have tooth injuries?
30%
What are the main etiologies of trauma injuries?
*Sports Related
Accidents
Physical Abuse
Fights
Drugs/Alcohol
Disability
Which teeth are most commonly injuried?
Anterior teeth
When evaluating dental trauma, what should you acquire during their medical history evaluation?
Lost of consciousness due to the injury
Headache, Nausea, Vomiting
Bleeding disorders
Current meds
Allergies
Tetanus immunization
Why do we care about the dental history of the trauma?
WHEN the trauma happened is critical to the treatment and the prognosis of the tooth going forward.
Ask your patient: HOW, WHEN, WHERE?
What is the one issue with pulp testing after a trauma injury?
Its not always accurate immediately following trauma
When is pulp testing considered accurate after a trauma injury?
Typically 3 months
What are the different types of tooth fractures that can occur?
Crown fracture
Crown-root fracture
Root fracture
Alveolar Fracture
What is the most common type of fracture?
Crown fracture (75% of all injuries)
What is the definition of an uncomplicated crown fracture?
Enamel fracture or enamel-dentin fracture that does NOT involve the pulp
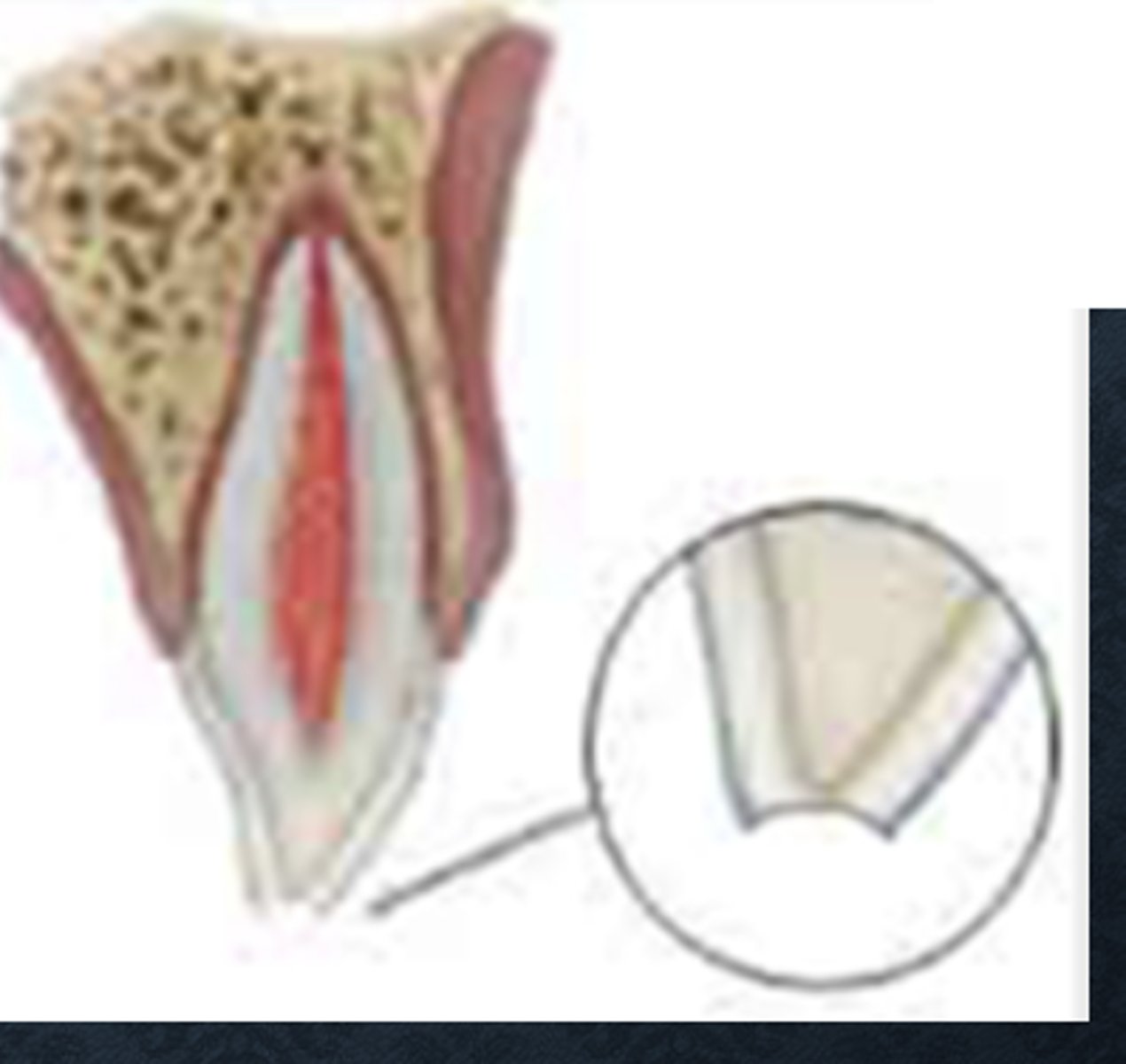
What is the diagnosis of an uncomplicated crown fracture?
PA radiographs
Evaluate size of pulp chamber and stage of root development
Pulp test
What are the goals of an uncomplicated crown fracture?
Maintain pulp vitality
Restore normal esthetics and function
What is the treatment for an uncomplicated crown fracture?
Repair
No NS-RCT is needed
What is the definition of a complicated crown fracture?
Enamel-Dentin fracture with pulp exposure
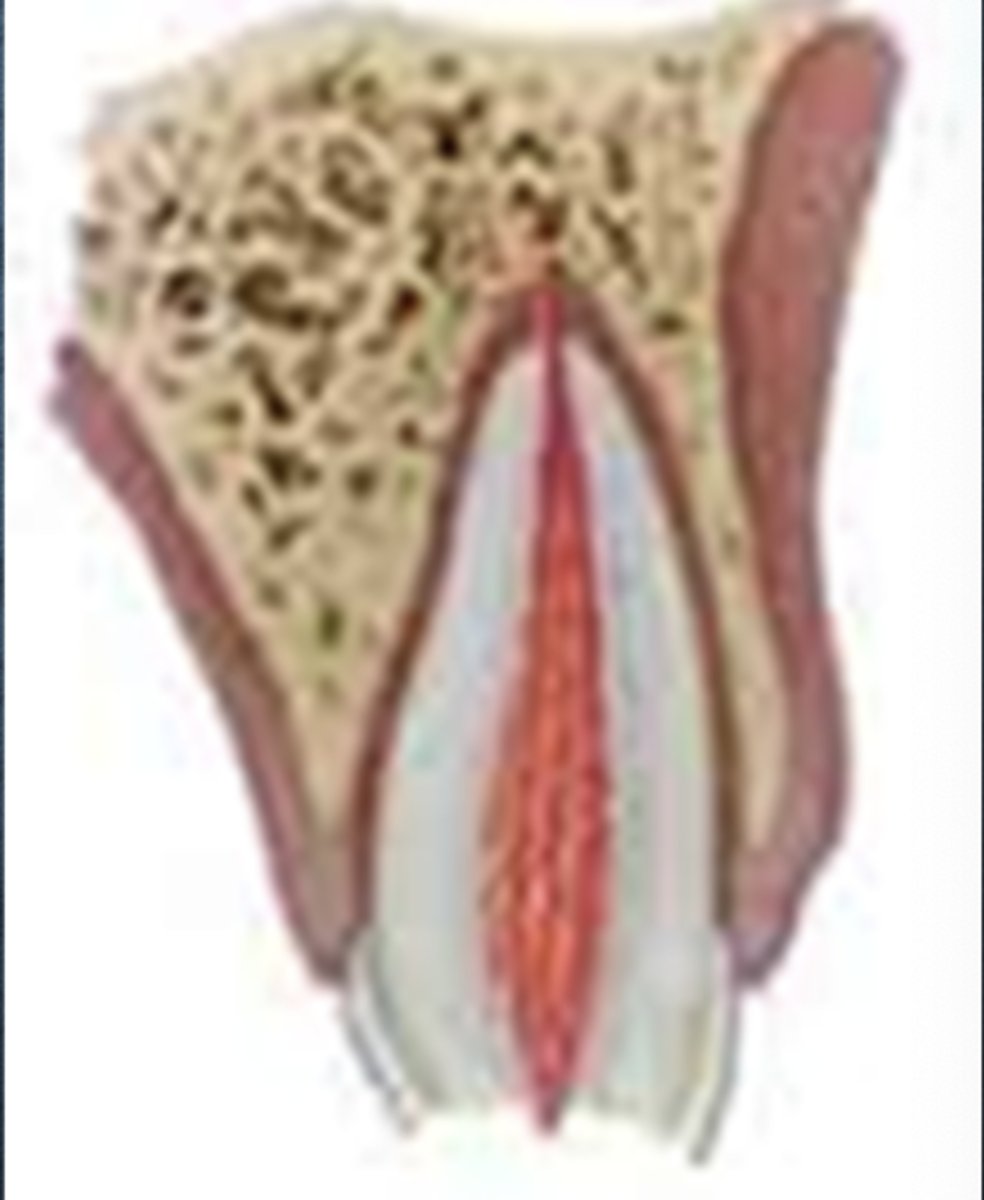
What are the determining factors for how we treat a complicated crown fracture?
How large the exposure is
Is hemostasis possible
What is the growth stage/apical development of the root
What are the indications to do a pulp cap on a complicated crown fracture?
Short exposure period after trauma (<24hr)
Small exposure
Not associated with PDL injury
How should you pulp cap an adult tooth?
Cover the pulp with calcium hydroxide/MTA
Restore tooth
How should you pulp cap an open apex (immature) tooth?
Try to maintain pulp vitality*
Perform pulp capping or partial pulpotomy with CaOH/MTA + coronal seal
What is the definition of a crown-root fracture?
Involves enamel, cementum, and dentin
May or may not expose the pulp
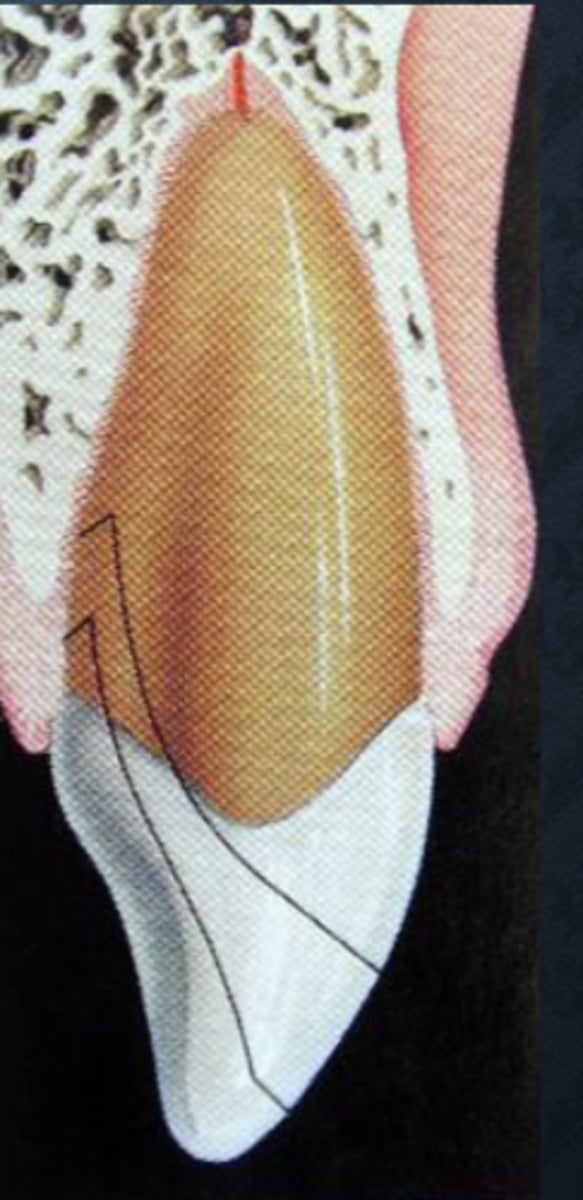
What is the diagnosis of a crown-root fracture?
2+ PA radiographs
Pulp test
What is the treatment for crown root fractures?
Perform endodontic treatment, then restore with post and crown
What is the percentage of root fractures that occur?
7%
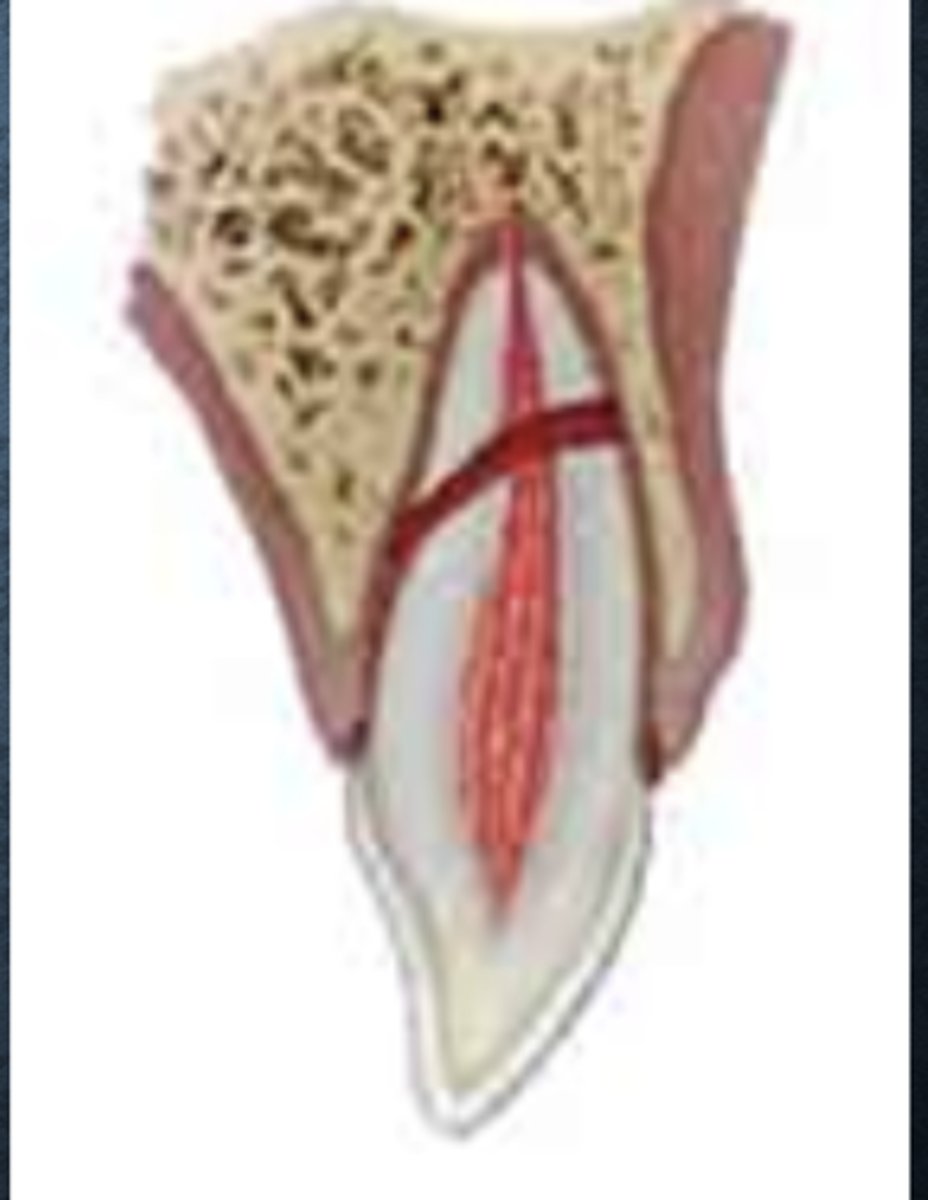
What is the definition of a horizontal root fracture?
Fracture involving dentin, cementum, and the pulp (ENAMEL IS NOT INVOLVED)
Coronal fragment is usually mobile and sometimes displaced
the apical segment is usually NOT displaced
What is the prognosis of a horizontal root fracture?
Apical 1/3> Middle 1/3 > Cervical 1/3
What is the diagnosis of a horizontal root fracture?
2+ PA radiographs taken at different angles (or a CBCT scan)
What is the treatment for horizontal root fracture?
Immediate reduction of the fracture segments
Complete immobilization of the coronal segment
Splint 3-4wks (or 4 months)
Endodontic treatment starts IF pulp necrosis occurs
What is the probability that a horizontal root fracture will become necrotic?
Pulp necrosis is 25% change
How long should a splint be in place is the fracture is in the apical third or middle third?
4 weeks
How long should a splint be in place if the fracture is in the cervical third?
4 months
What is the diagnosis of an alveolar fracture?
When the mobility of one tooth is tested, several other teeth move
Hematoma in adjacent attached gingiva or mucosa
What is the treatment for an alveolar fracture?
Reposition
Splint
What is the definition of a tooth concussion?
No displacement
No mobility
Usually sensitive to percussion and or tender to touch
What is the treatment for a tooth concussion?
Flexible splint is optional- can be used for comfort of the patient for 7-10 days
What is the definitino of a tooth subluxation (loosening)?
Tooth is tender to touch and mobile, but not displaced
Hemorrhage from gingival sulcus possible
What is the diagnosis of a tooth subluxation?
2+ PA radiographs with NO radiographic abnormalities
What is the treatment for a tooth subluxation?
Flexible splint is optional - 7-10 days
What is the definition of tooth extrusion (partial avulsion)?
Elongated mobile tooth
Partial displacement of tooth out of socket
Angulated radiograph: increase PDL space
What is the treatment for a tooth extrusion?
Reposition
Stabilize tooth with flexible splint for 1-2 weeks
What is the definition of a lateral luxation?
Displacement of a tooth buccally or lingually
Usually accompanied by fracture of socket
Usually locked into bone
Not tender to the touch, not mobile
What is the diagnosis of a lateral luxation?
2+ Angulated PA radiographs
What is the treatment for a lateral luxation?
Reposition the tooth into normal position
Confirm with radiograph
Stabilize tooth with flexible splint for 1-2 weeks
Follow up to see if its necrotic or needs NS/RCT
What is the definition of intrusion?
Apical displacement of tooth into the alveolar bone
Tooth is driven into the socket, compression the PDL
Tooth appears to be shortened or missing
Severe type of luxation injury
What is the treatment for intrusion in tooth with an immature root formation?
Spontaneous reposition/ re-eruption
What is the treatment for intrusion in a tooth with a mature root formation?
Reposition the tooth with ortho or surgical extrusion
Initiate endo treatment within first 2 weeks
Prognosis is POOR
What is the definition of avulsion?
The tooth is seperated from the socket completely
PDL is torn
What is the most critical factor in avulsion healing?
Minimize the extra-alveolar time
Immediate replantation = best prognosis
What are the effects of dry extra-oral time?
If the PDL dries out prior to replantation, there is an inflammatory response on the root surface, ankylosis, loss of the tooth
What are different types of storage media for avulsions?
Hanks Balanced Salt Solution
Milk
Saliva
0.9% Saline
Tap Water
Contact lens solution
Gaterade
For avulsed teeth, how should you hold them?
You should ONLY handle the crown only
DO NOT touch the root of the tooth
Do not scrub tooth
Do not wrap in tissue or cloth
What is the treatment for avulsion?
Place tooth in HBSS
Obtain radiographs
Gently aspirate the injured area without entering the socket. Irrigate lightly with saline.
DO NOT CURETTE THE SOCKET
Early replantation of an avulsed tooth is less than ____ mins
60
In an immature apex, what is the goal for an immature avulsed tooth if its been out of the mouth for less than 60 mins?
Revascularization of the pulp
No endodontic treatment is initially required
What is the treatment for an avulsed immature apex with an extra-oral dry time of <60 mins?
Rinse root surface w/ saline
remove coagulation from socket
Replant tooth
Splint for 1-2 weeks - flexible wire of a diameter up to 0.016" or 0.4mm
What is the treatment for an avulsed mature tooth with an extra-oral dry time of <60 mins?
rinse root surface w/ saline
remove coagulation frmo socket
Replant tooth
Splint for 1-2 weeks
Endodontic treatment is ALWAYS started within 7-10 days
follow-up
* this is the same tx for immature tooth >60 mins
What is the treatment for a mature avulsed tooth with an extra-oral dry time of >60 mins?
Remove debris and PDL
Soak tooth in NaF for 5 mins
Replant tooth
Splint for 4-6 weeks flexible wire w/ diameter of 0.016" or 0.4mm
Endo treatment started with 7-10 days
What type of splinting material can be used?
Flexible wire w/ diameter up to 0.016" or 0.4mm
OR
Nylon fishing line 0.13-0.25 mm
What is the function of creating a flexible splint for teeth?
Allows physiologic tooth movement during healing
In an avulsed/traumatized tooth, how long should calcium hydroxide be in place for?
1-2 months
What retentive restorative material should be avoided in avulsed teeth?
Try to avoid post placement
What are the factors affecting prognosis of an avulsion?
1. Extra-oral Dry time
2. Transport conditions
3. Time before endodontic treatment (7-10 days)
4. Splinting technique and time
(non-rigid, minimal time)
5. Stage of root development
6. Root surface treatment
What are three complications that can follow after traumatic injuries?
Pulp Necrosis
Pulp Canal Obliteration
Root resorption (inflammatory)
What is pulp obliteration?
a condition characterized by the pronounced deposition of hard tissue along the internal walls of the root canal that fills most of the pulp system leaving it narrowed and restricted.
What is a common finding in teeth with pulpal obliteration?
Yellow discoloration
This does NOT imply the presence of pulp or periapical disease
When is RCT indicated for pulp obliteration?
When there are clinical symptoms and/or definite radiographic findings suggestive of periapical disease
What is root resorption?
Loss of pre-cementum, cementoblasts and epithelial rests of Mallassez. Denuded root surface, hard tissue resorbing cells remove damaged periodontal ligament and cementum
What are the three types of external root resorption?
Surface resorption
Imflammatory root resorption
replacement root resorption *ankylosis
What is surface resorption (localized injury)?
Localized injury to cementum (concussion, subluxation)
Local inflammatory response
May/may not be visible on radiograph
No treatment is required
What is inflammatory root resorption?
Damage of the periodontium
Bacteria within tubules
2 visit NS/RCT
Which luxation injury has the worst prognosis?
Intrusion
What is replacement resorption?
Severe damange to the peridontium
Fusion of the tooth root with the adjacent alveolar bone
What is the diagnosis of replacement resorption (ankylosis)?
Tooth is immobile
High Percussive tone
No visible PDL space
What is the treatment of replacement resorption (ankylosis)?
Cannot be arrested or repaired
*Can survive for number of years
What is dentin hypersensitivity?
Short, exaggerated, sharp, painful response that is elicited when exposed dentin is subjected to thermal, mechanical, or chemical stimuli
What kind of pulpal diagnosis is associated with dentin hypersensitivity?
Reversible pulpitis
What is the hypothesis behind dentin hypersensitivty?
Brannstrom's hydrodynamic theory
What is Brannstrom's hydrodynamic theory?
Fluid movement in the dentinal tubules, following a stimulus, can initiate a reaction which causes pain
For dentin hypersensitivity.....What can fluid movement be caused by?
Dehydration, osmotic changes, mechanical probing, or thermal probing
For the dentin hypersensitivity experiment, what teeth were tested?
Premolars that were tx planned for orthodontic extractions
For dentin hypersensitvity, when the tooth is dehydrated this causes pain. What will help stop this pain?
Reapply fluid to the tooth
What type of stimulus causes an outward movement of fluid on the dentin?
Cold
What type of stimulus causes an inward movement of fluid on the dentin?
Heat
How is dentin hypersensitivity often treated?
Treated by covering the dentin
Desensitizing agent +/- restoration
What are biomaterials that are used in dentistry?
Bioceramics
Bioglasses