Reproduction
1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Sexual reproduction
fusion of haploid gametes to from a zygote
Asexual reproduction
new individuals are generated without the fusion of gametes
What are the four types of asexual reproduction?
budding, pinches off from parent, like yeast
Fission: parent splits into two: sea anemone
Fragmentation: regeneration of body after breaking; starfish
parthenogenesis: egg developing without fertilization
What are the three types of parthenogenesis?
Haploid, automixes, and apomixes
Haploid parthenogenesis
developed into a haploid organism that may still reproduce. Male honey bees.
Diploid: apomixes
Do mitosis and produce female clones
Diploid: automixes
via meiosis, produce males or females who are genetically different from the parent.
How can parthenogenesis occur?
It requires a mating behavior in order for ovulation to occur. After ovulation progesterone is high so the female exhibits male like behavior. When progesterone is low the female exhibits female like behavior.
What are the costs of sexual reproduction?
only pass on half of your genes
mate may kill you or have bad genes
requires energy to find mate
What are the benefits of sexual reproduction?
bad genes can leave more easily
greater genetic variability leading to quicker adaptations
ability to reproduce anywhere
What are some costs of asexual reproduction?
bad genes stay in the population
lack of genetic variation
reduced adaptability
What are some benefits of asexual reproduction?
they have good genes favorable for the environment
save energy since they don’t have to look for mates
rapid population growth
Muller’s rachet
bad genes stay in the population and get passed on which decreases fitness.
Red Queen Hypothesis
If the predator is adapting and you aren’t, you will get obliterated
How can you reduce the cost of finding a mate?
Simultaneous hermaphrodite
sequential hermaphrodite
be chosen when finding a mate
Simultaneous Hermaphrodite
containing both female and male reproductive systems. Annelids
Sequential Hermaphrodite
Starting as one sex then changing to the other under certain circumstances.
give examples of sequential hermaphroditism
muscles begin as males as they age they become females
Guppies store sperm in a much with sugars to self fertilize under the right conditions
Angler fish fuse with their partner since they rarely see on another
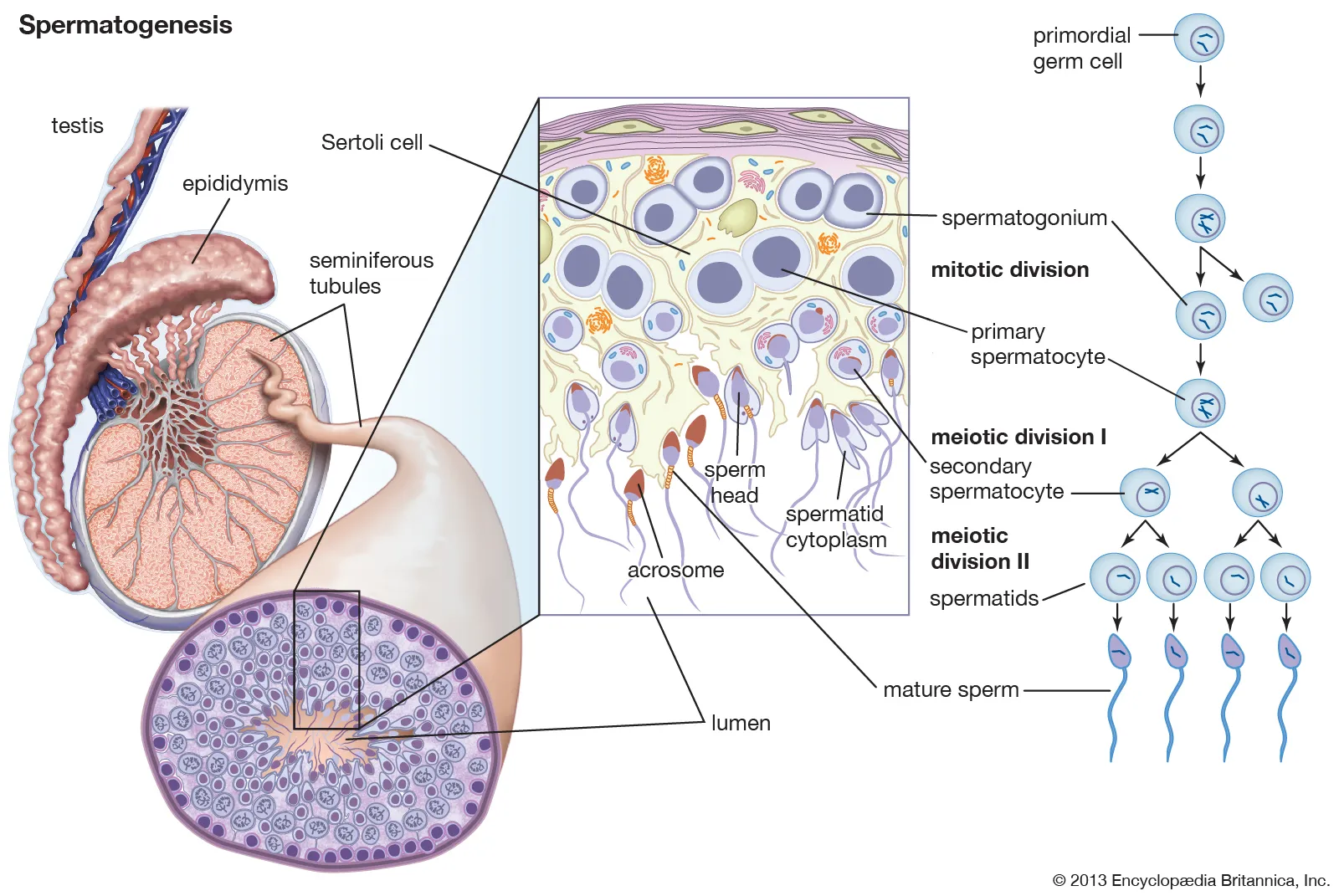
Describe the process of Spermatogenesis
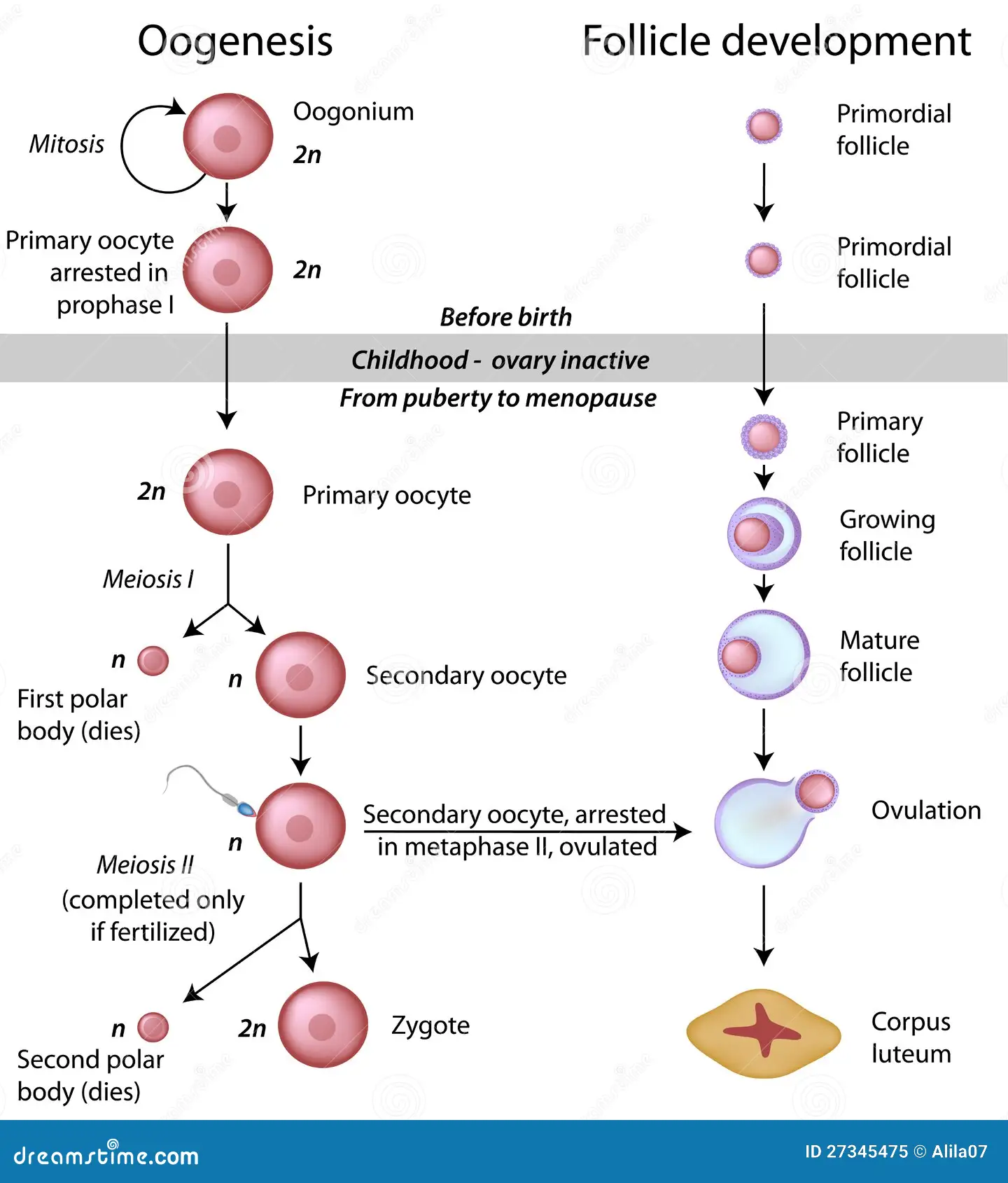
Describe the process of oogenesis and follicle development
How does the timing of spermatogenesis differ from
oogenesis?
Spermatogenesis begins after puberty and goes into completion. Oogenesis starts before birth and stops at meiosis 1 prophase; after puberty it continues up until metaphase 2 of meiosis. oogenesis only goes to completion once it is fertilized.
How does the number of gametes produced differ
between spermatogenesis and oogenesis?
Spermatogenesis produces 4 haploid sperm whereas oogenesis only produces 1 haploid egg with multiple polar bodies
How might gametogenesis be related to sexual selection?
Oogenesis favor fewer but higher quality eggs where as spermatogenesis favors making a lot of sperm but not worrying about quality