LD Intro
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
-OLDCARTS
-mechanism of injury
-ROS: MSK, neuro, vascular
-Past, medical, social hx
-meds/allergy/immunizations
-physical exam
history
1. inspection for wounds, swelling, discoloration, deformity
2. assessment of range of motion of joint and proximal and distal or injury
3. palpation for tenderness and deformity
4. assessment of neurovascular status
-special testing for non traumatic injury when applicable
physical exam components
-some injury might not need radiographically apparent on first day
-dx of fractures may be purely clinical until 7-10 days after trauma, when enough bony resorption has occured at the fracture site to reveal a lucency on plain radiographs
imaging
-if wound presents in setting of fracture treat as open fracture
-tetanus, abx, ortho consult
-if reducing pain obtain imaging before and after reduction
-examine joint above and below the joint in question
joint exam pearls
-X ray
-CT scan
-MRI
-US
-Serology
diagnostic test of MSK/Rheum
-uses ionizing radiation to produce imaging of internal structures
-2D images of bone and joints
-photons
X ray
-primar imaging of suspected fractures
-evaluating joint alignment and deformities
-assessment of bone density
-detection of joint space narrowing
-identify erosion in inflammatory arthritis
-monitor of fracture healing
-visualize calcification
-assessment of spinal alignment
x ray common uses
-quick, widely available
-relatively inexpensive
-good for bone imaging
x ray advantage
-limited soft tissue visualization
-exposure to ionizing radiation
-2D representation of 3D structures
x ray disadvantage
-air attenuates x ray a little
-fat attenuates x ray more than air, less than water
-bone attenuates x ray the most
x-ray attenutation
-two views: AP and Lateral
-tow joints: joint above and below
-two occasion: repeat x ray
-tow limbs: compare
rule of two
-normal bone will show smooth, homogenous cortex surrounding the medullary space
-A: adequacy, alignment
-B: bones
-C: cartilage
-S: soft tissue
x ray interpretation
-anatomic relationship between bone on x ray
-fractures and dislocations may affect alignment
alignment
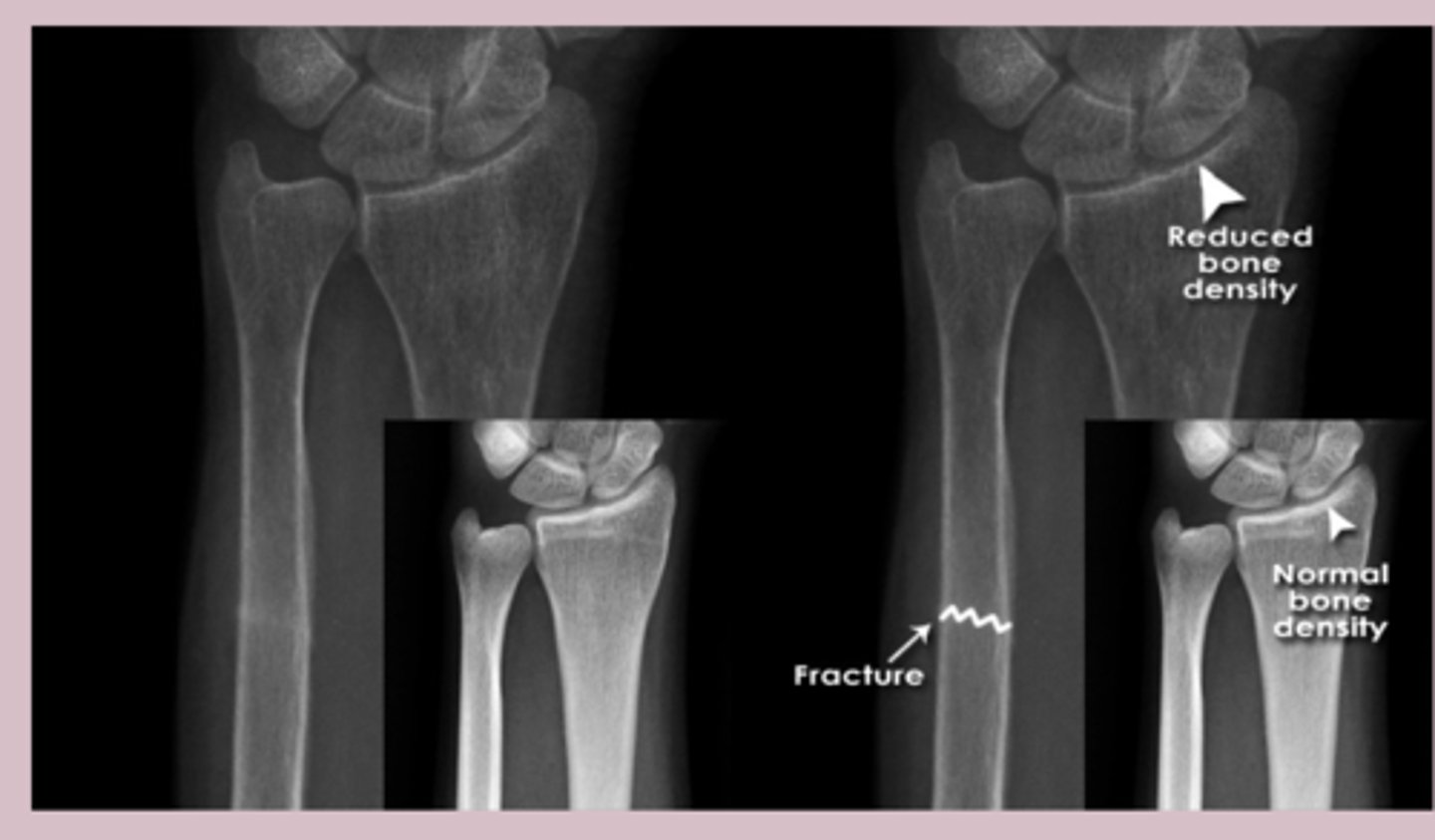
-examine for fracture line or distorsions
-length, bone density
bones
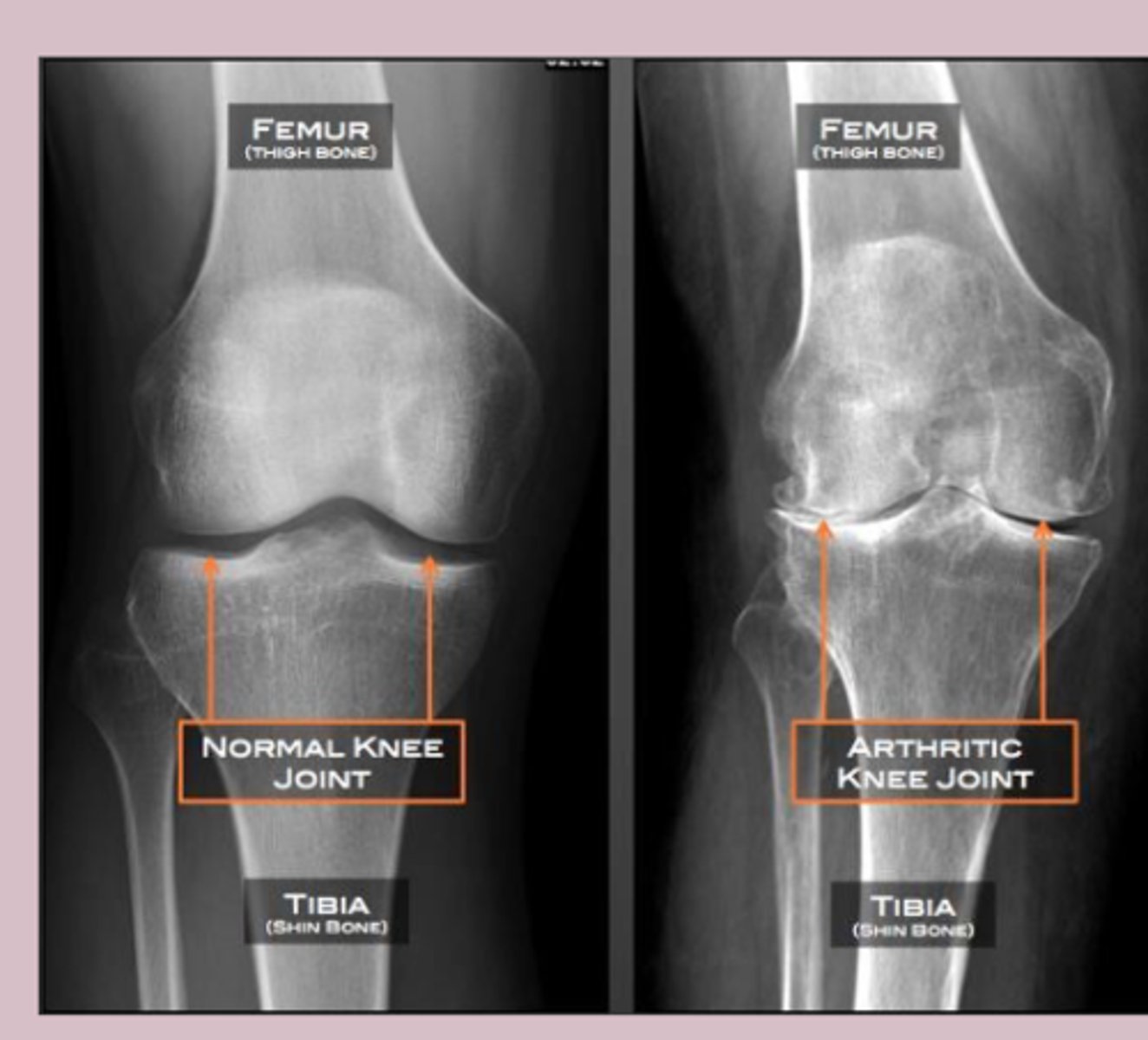
-implies to examine the joint space on x ray
-widening of joint space signifies ligamentous injury and fracture
-narrowing of joint space
cartilage
-look at soft tissue
-swelling and joint effusions > signs of occult fracture
-foreign body
-air
soft tissue
-uses X ray and computer processing to create detailed cross sectional images
-3D visualization of bones and tissue
CT scan
-preoperative planning for joint replacement
-assessment of spinal conditions
-evaluation of bone tumors
-detailed imaging of joint erosion
-assessment of sacroiliac joint
-evaluation of lung involvement in systemic disease
CT scan common uses
-high resolution 3D images
-excellent for bone detail
-faster than MRI
CT advantages
-higher radiation exposure
-limited soft tissue contrast compared to MRI
-may need contrast agents
CT disadvantage
-uses strong magnetic field and radio waves to produce detailed images
-excellent for soft tissue visualization
MRI
-evaluation of ligament and tendon injury
-assessment of cartilage damage
-diagnosis of stress fracture
-evaluation of spinal cord and nerve root compression
-early detection of inflammatory changes
-assessment of synovial joint
-evaluation fo soft tissue
-monitoring treatment response
MRI common uses
-no ionizing radiation
-superior soft tissue contrast
-can detect early inflammatory changes
MRI advantages
-time consuming
-expensive
-contraindicated in patients with metal implants
MRI disadvantage
-high frequency sound waves to produce real time images of soft tissue and structures
ultrasound
-evaluation of tendon and ligaments
-assessment of joint effusion
-guidance of joint and soft tissue injection
-detection of foreign body
-screen for giant cell
-monitoring treatment
-evaluation of superficial massess
ultrasound common uses
-no ionizing radiaiton
-real time
-can be performed at POC
-allows comparison with contralateral side
-relatively inexpensive
ultrasounds advantages
-high operator dependent
-limited penetration in deep structure
-may have limited utility
-not as effective for bone imaging
ultrasound disadvantages
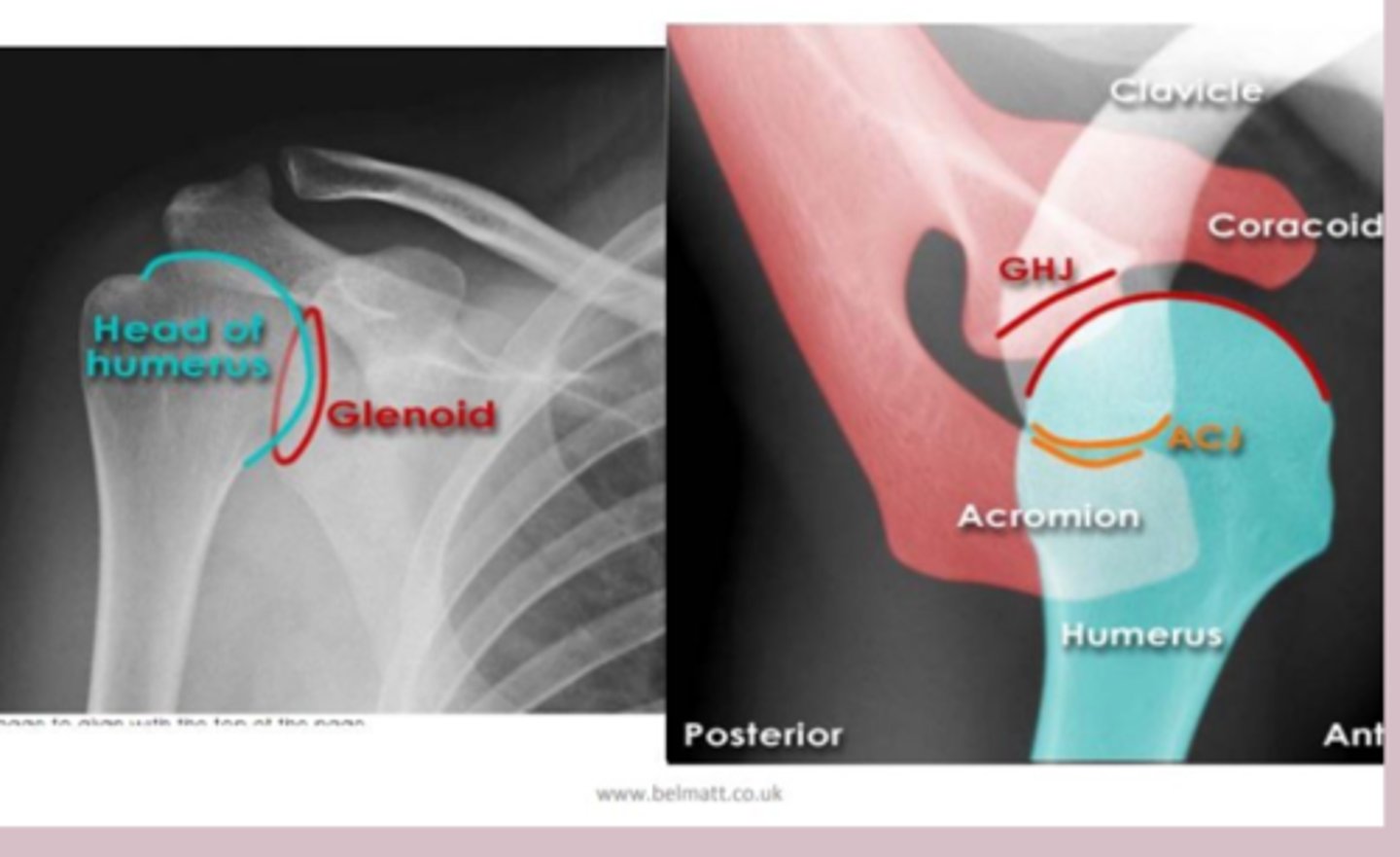
shoulder
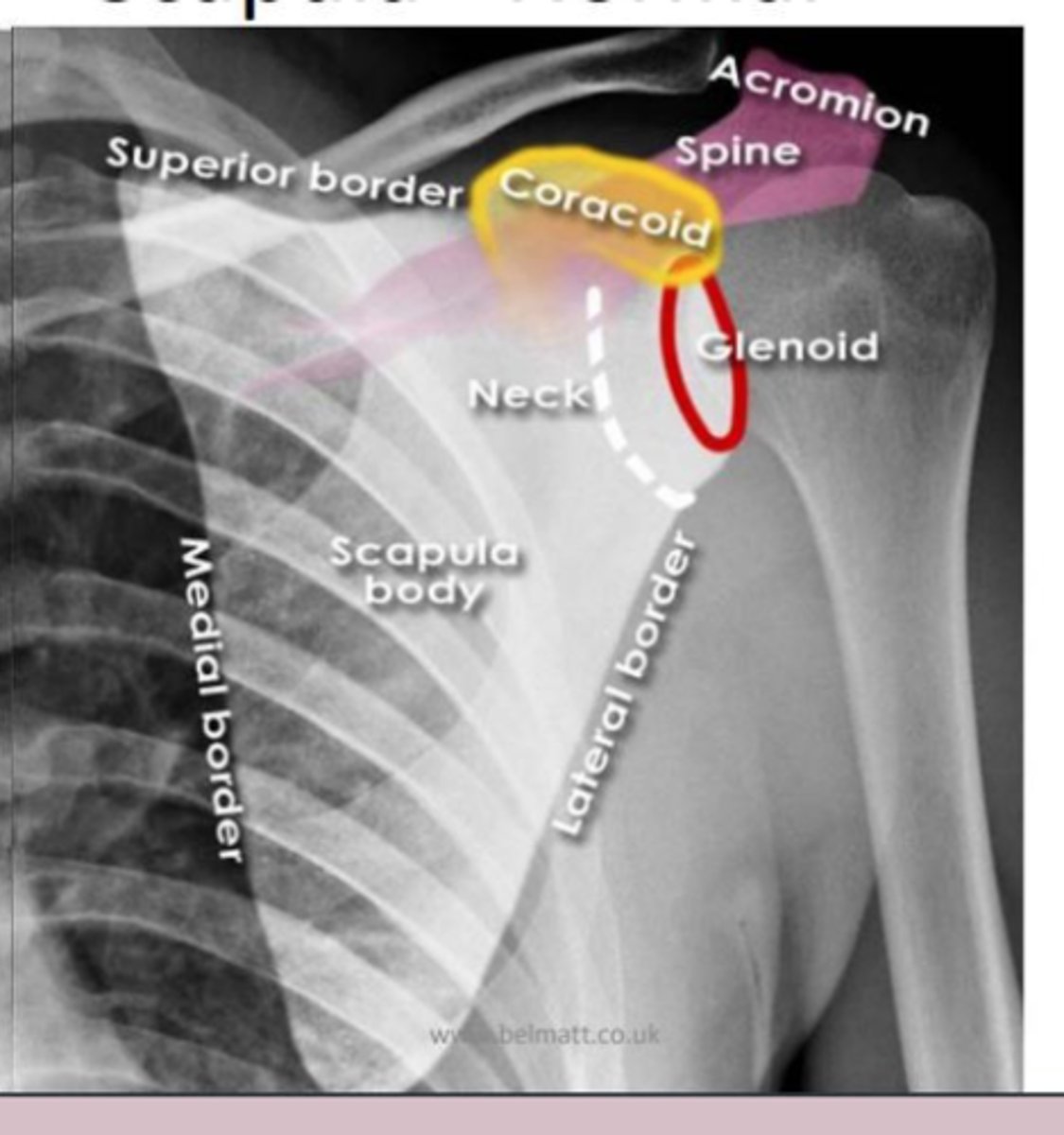
scapula
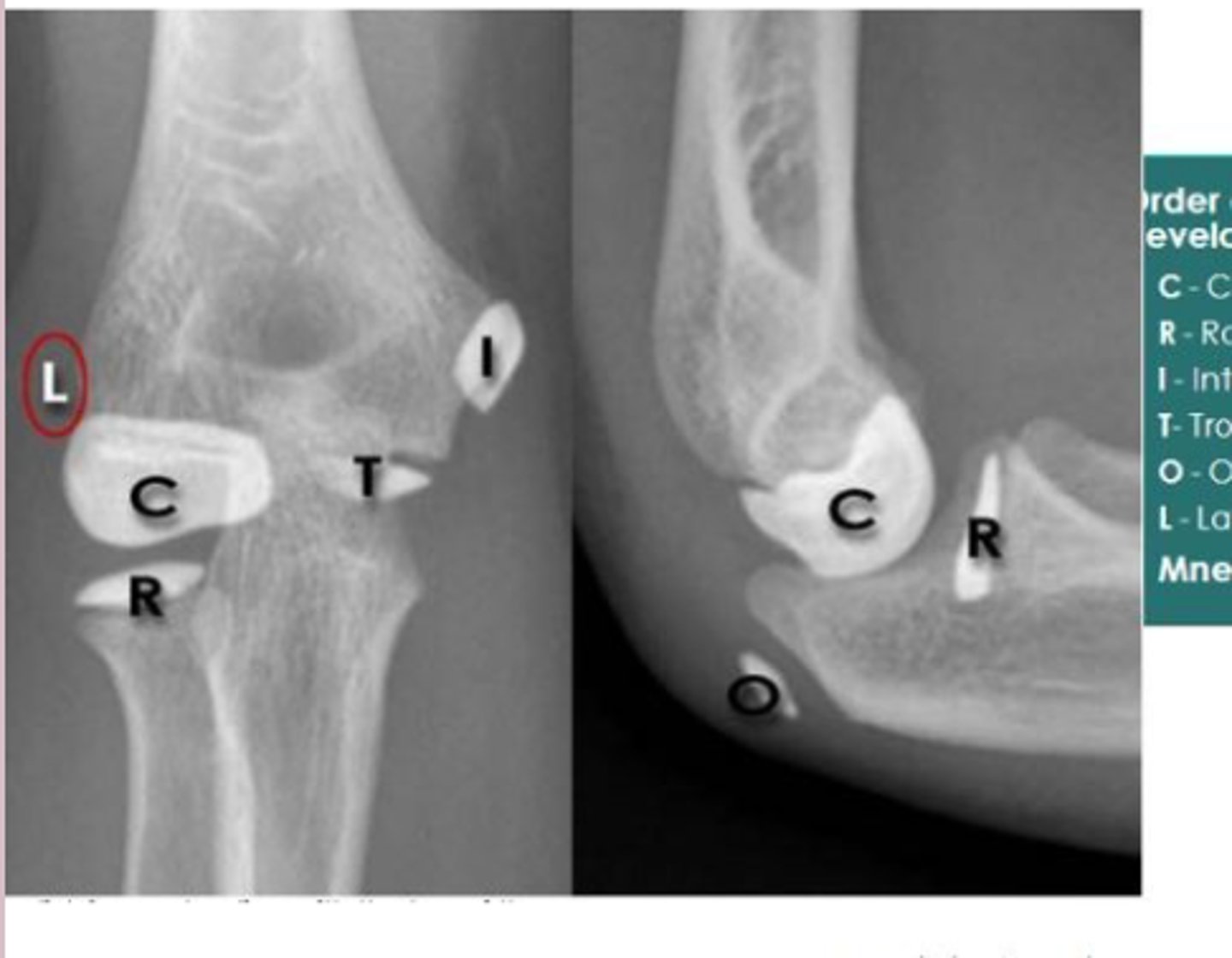
elbow
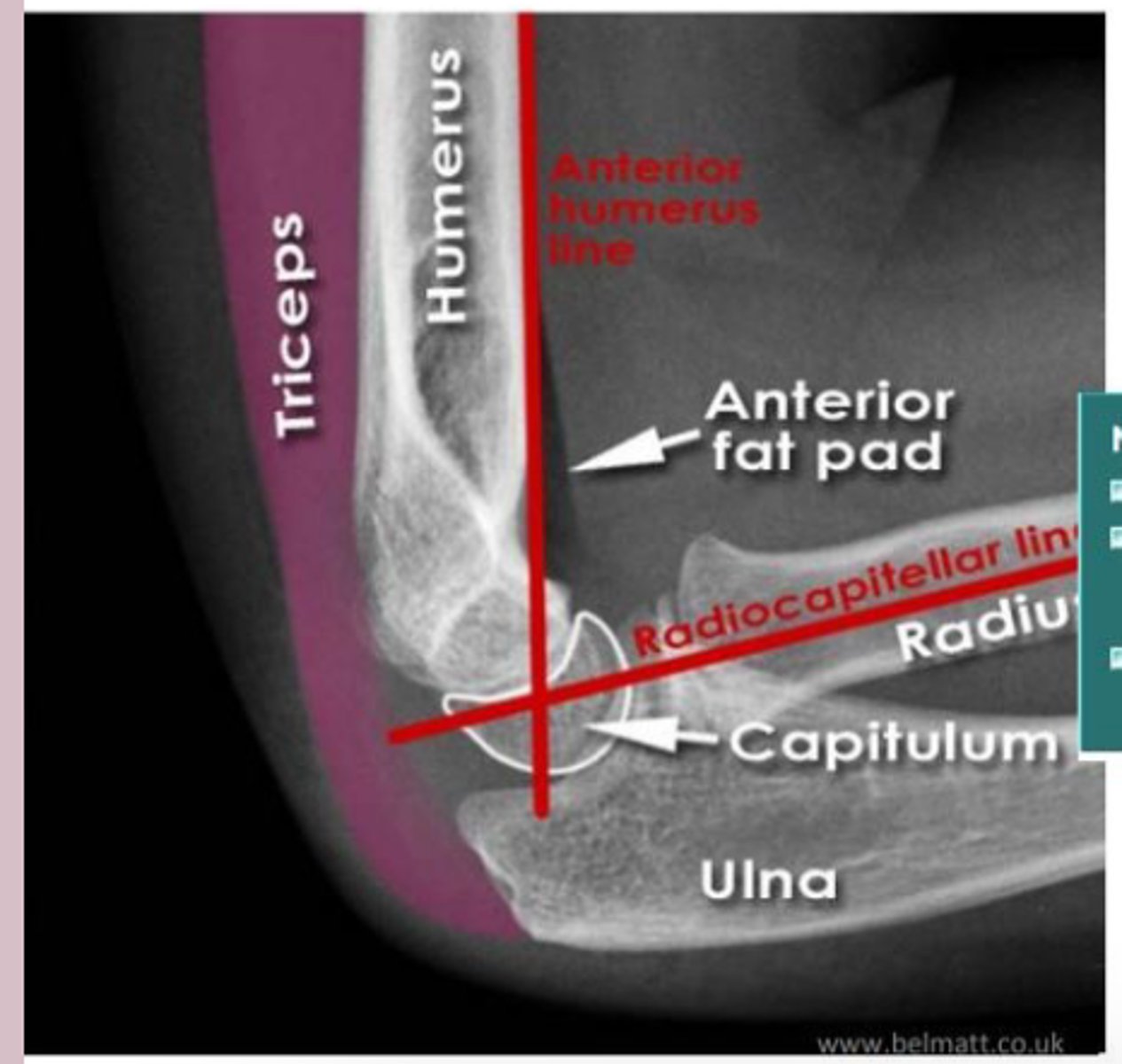
elbow lateral
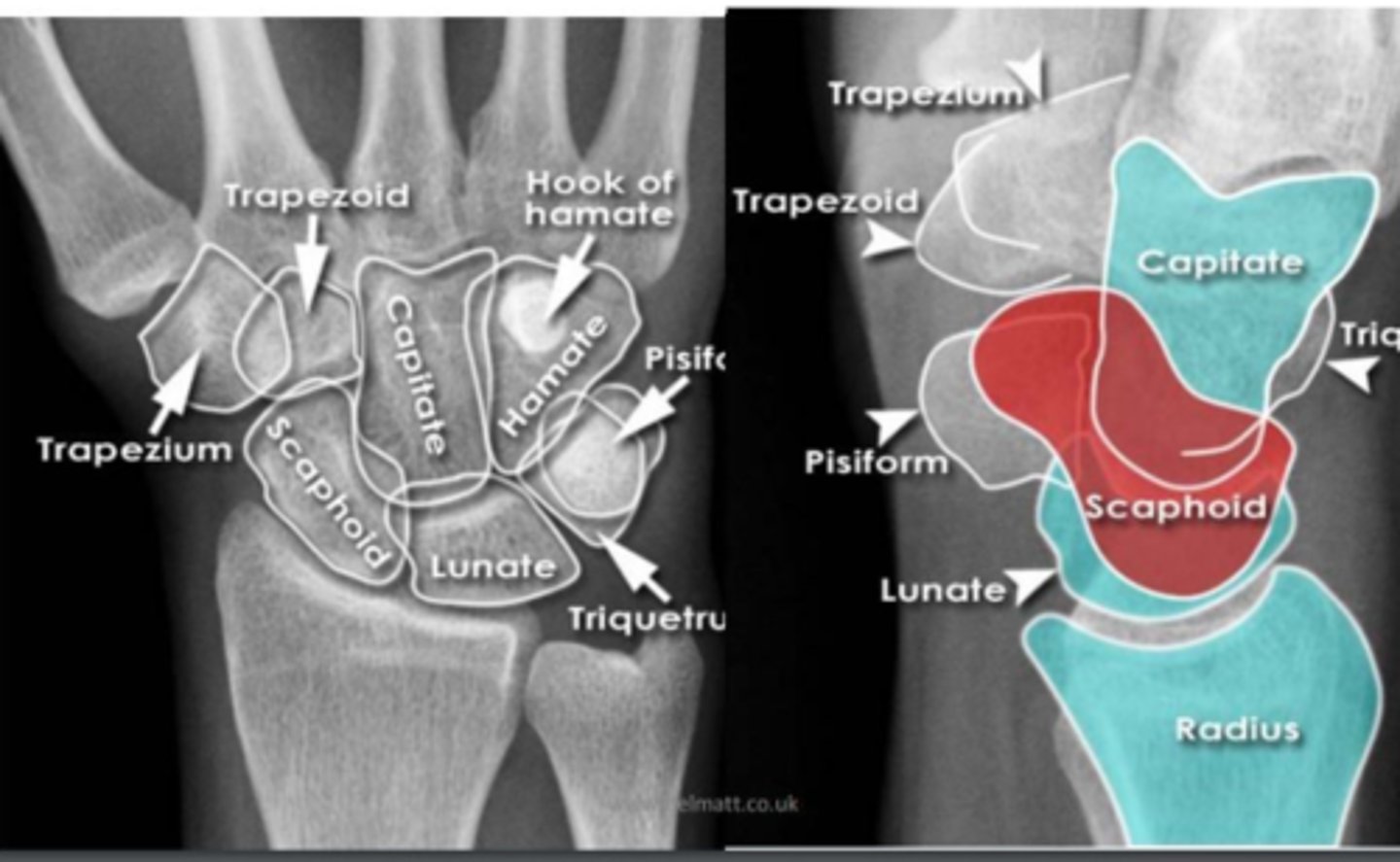
wrist
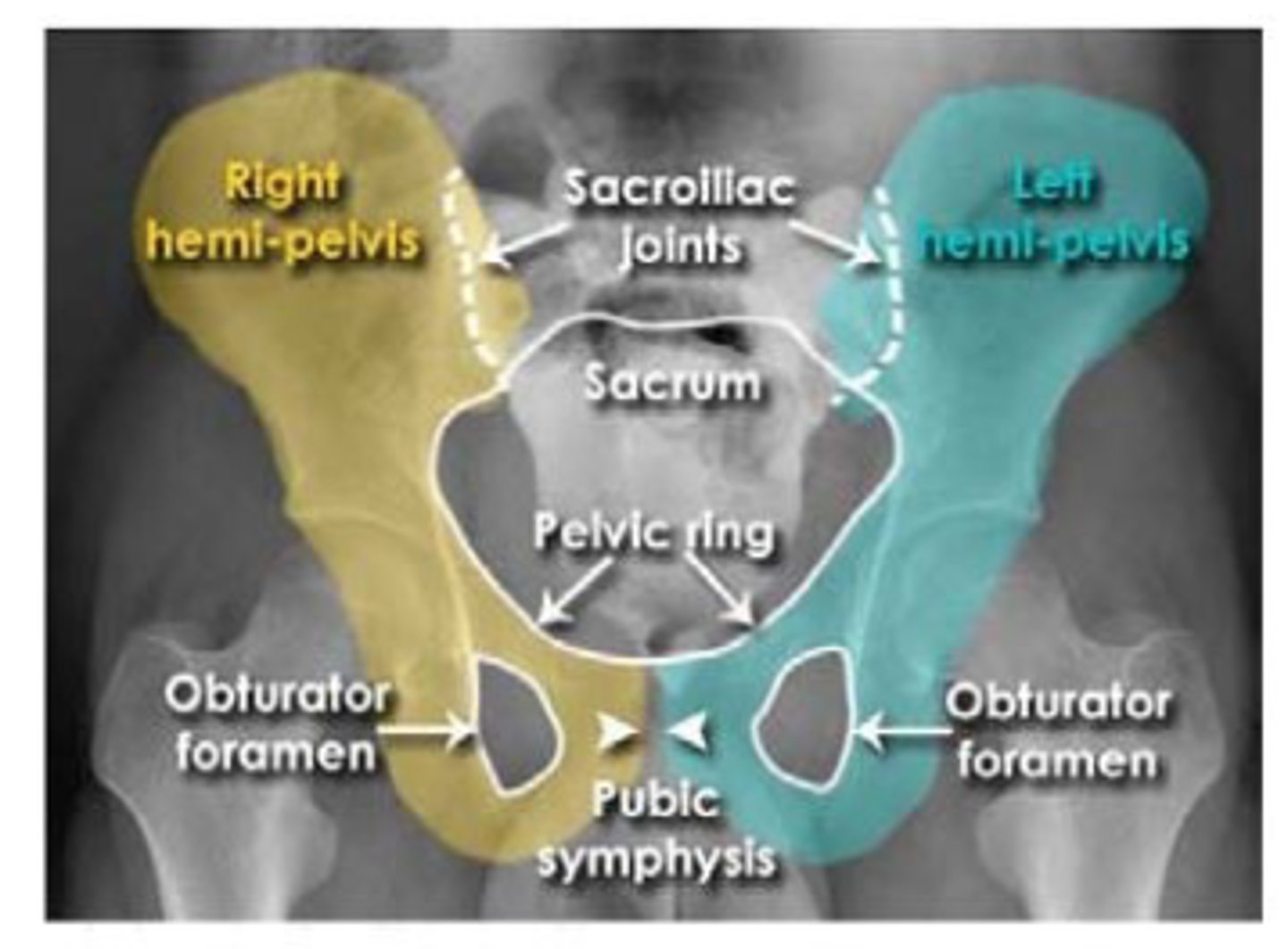
pelvis
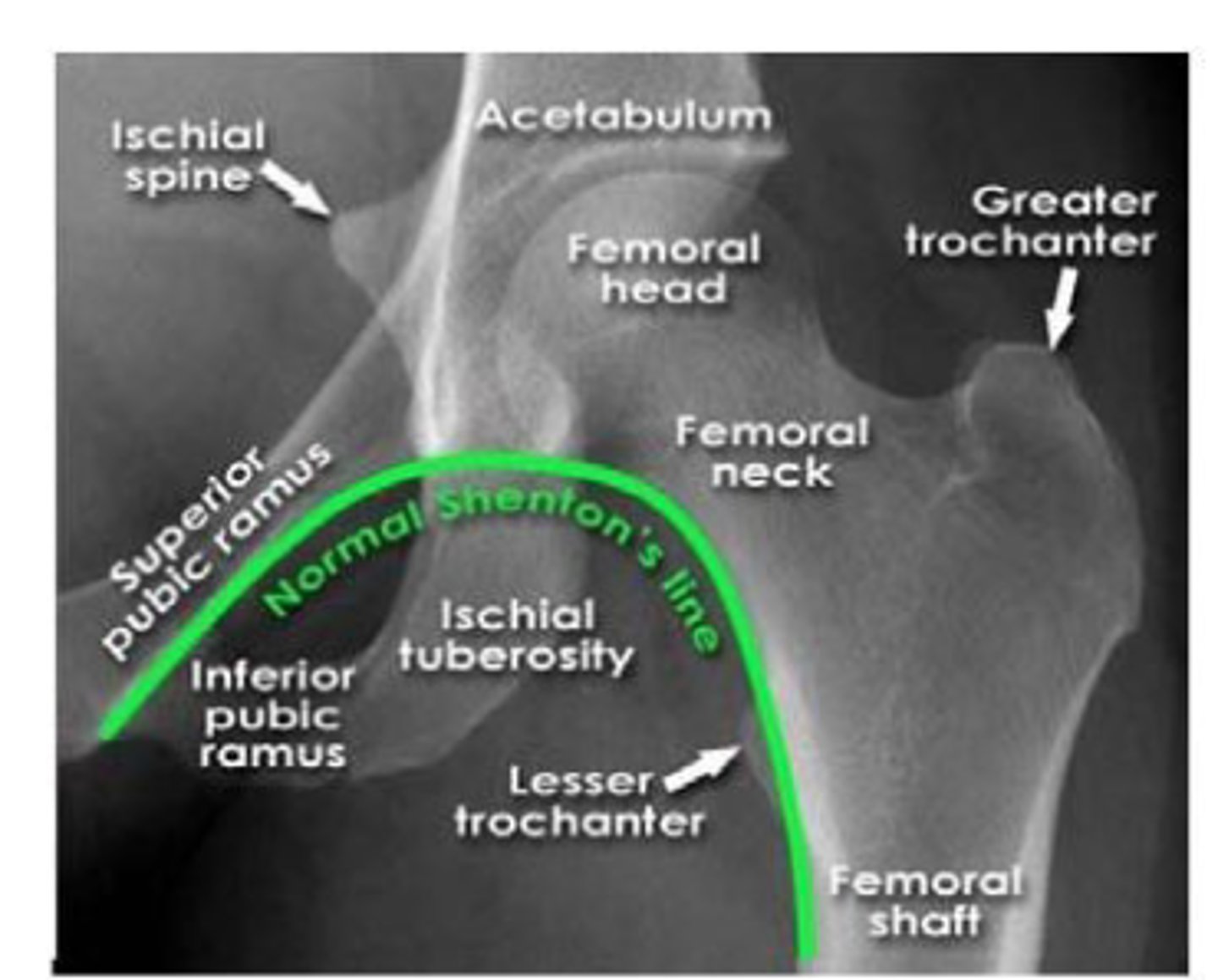
hip
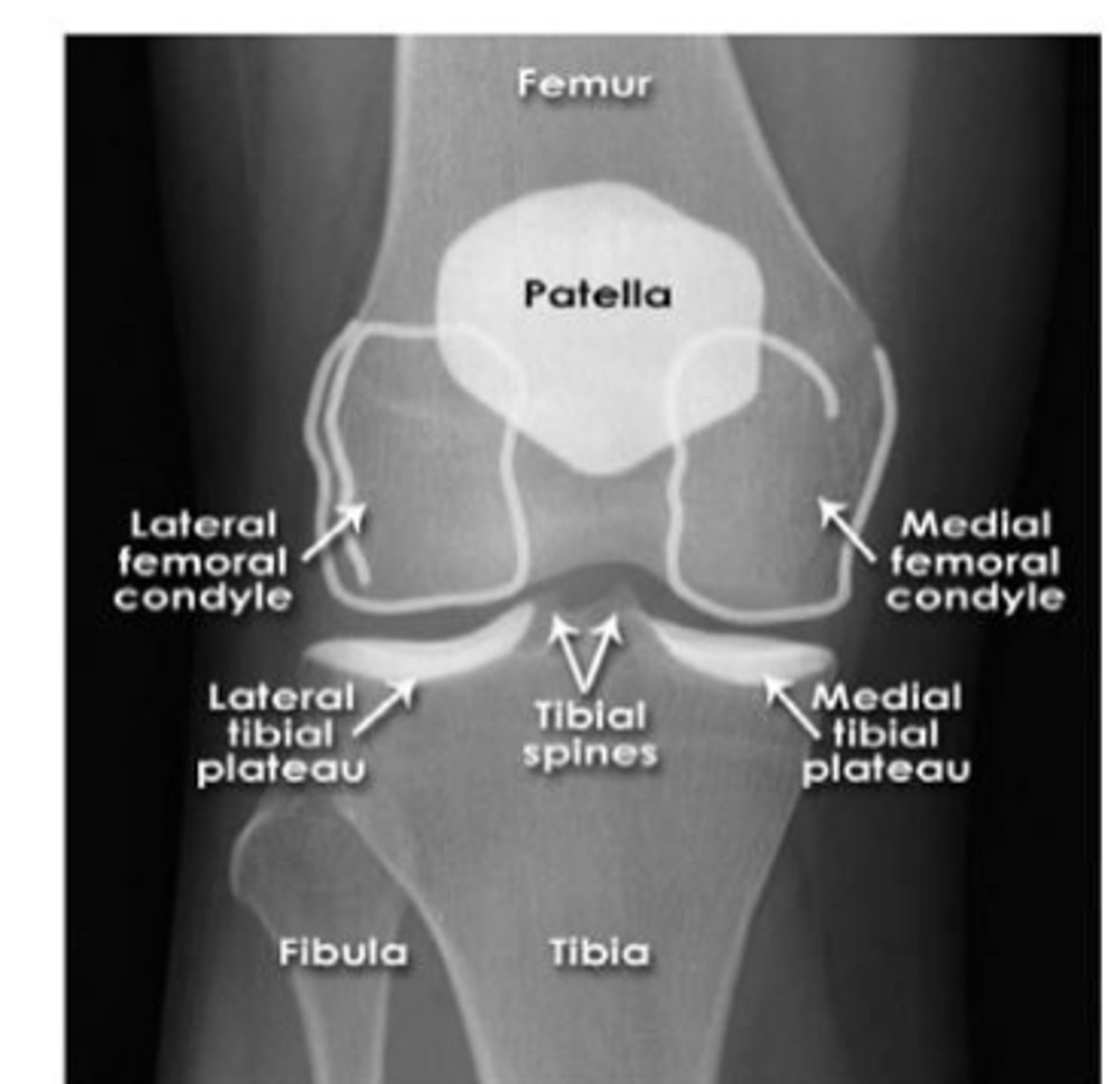
knee
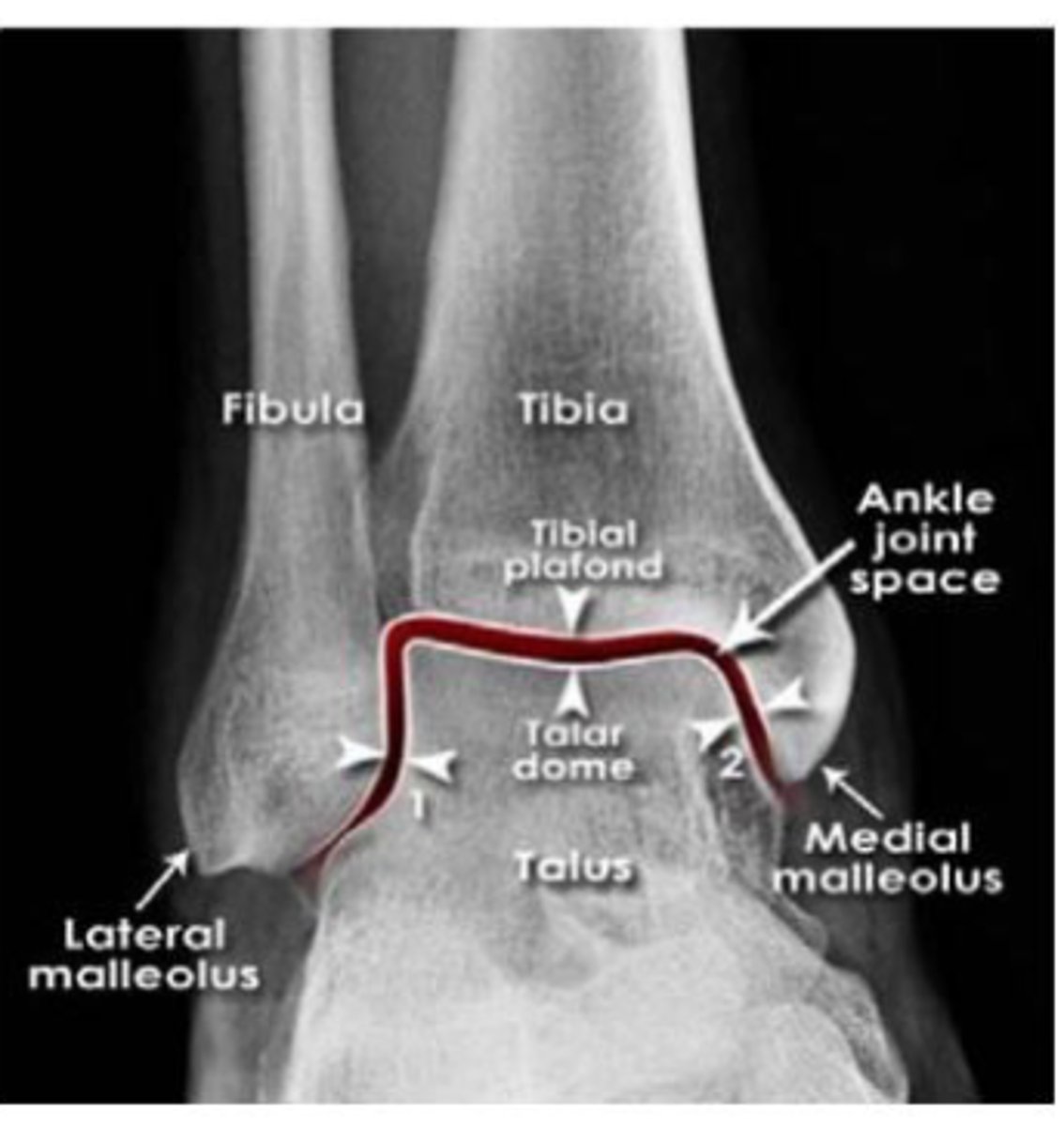
ankle
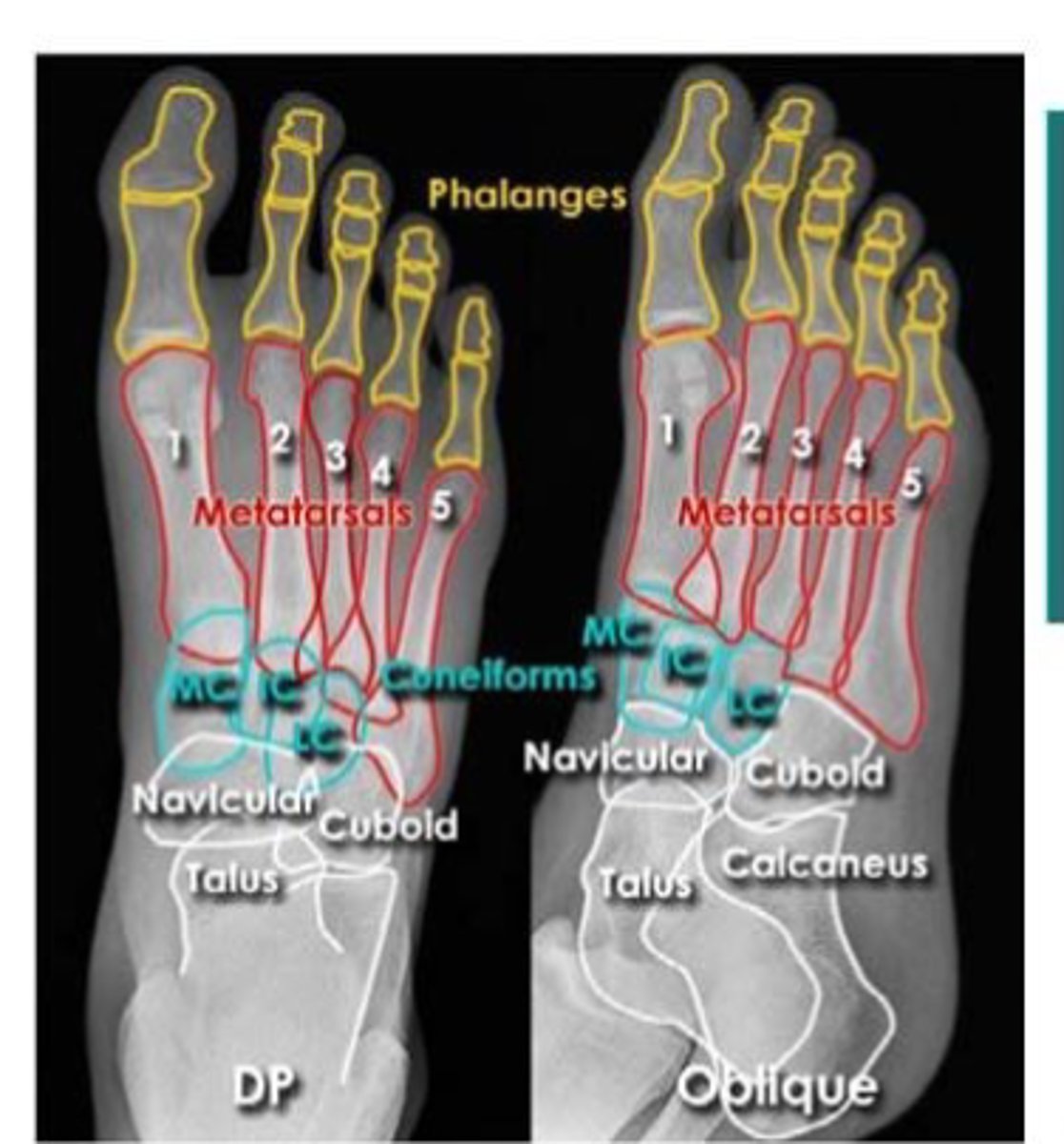
foot
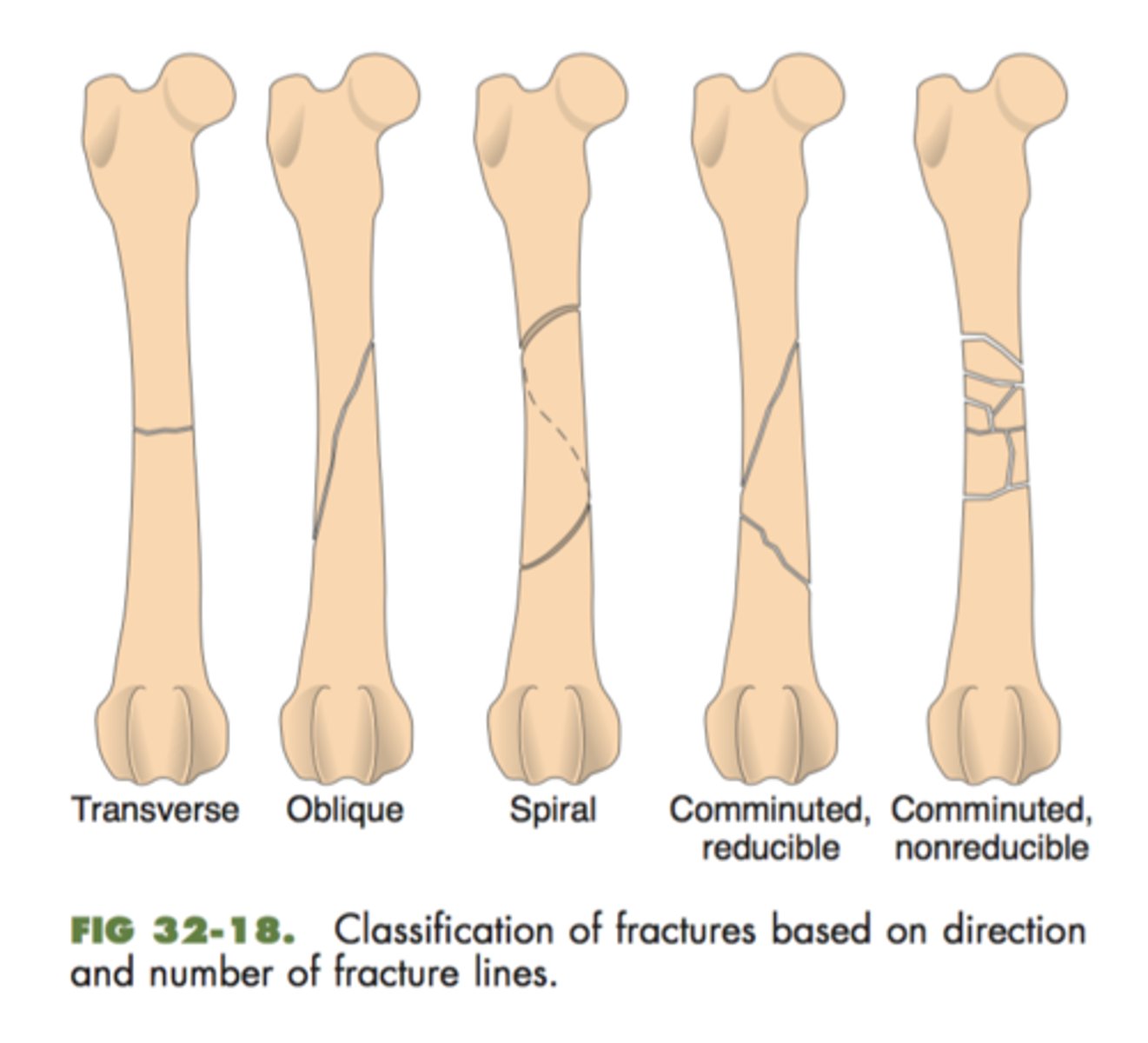
-transverse
-oblique
-spiral
-comminuted
direction of fracture
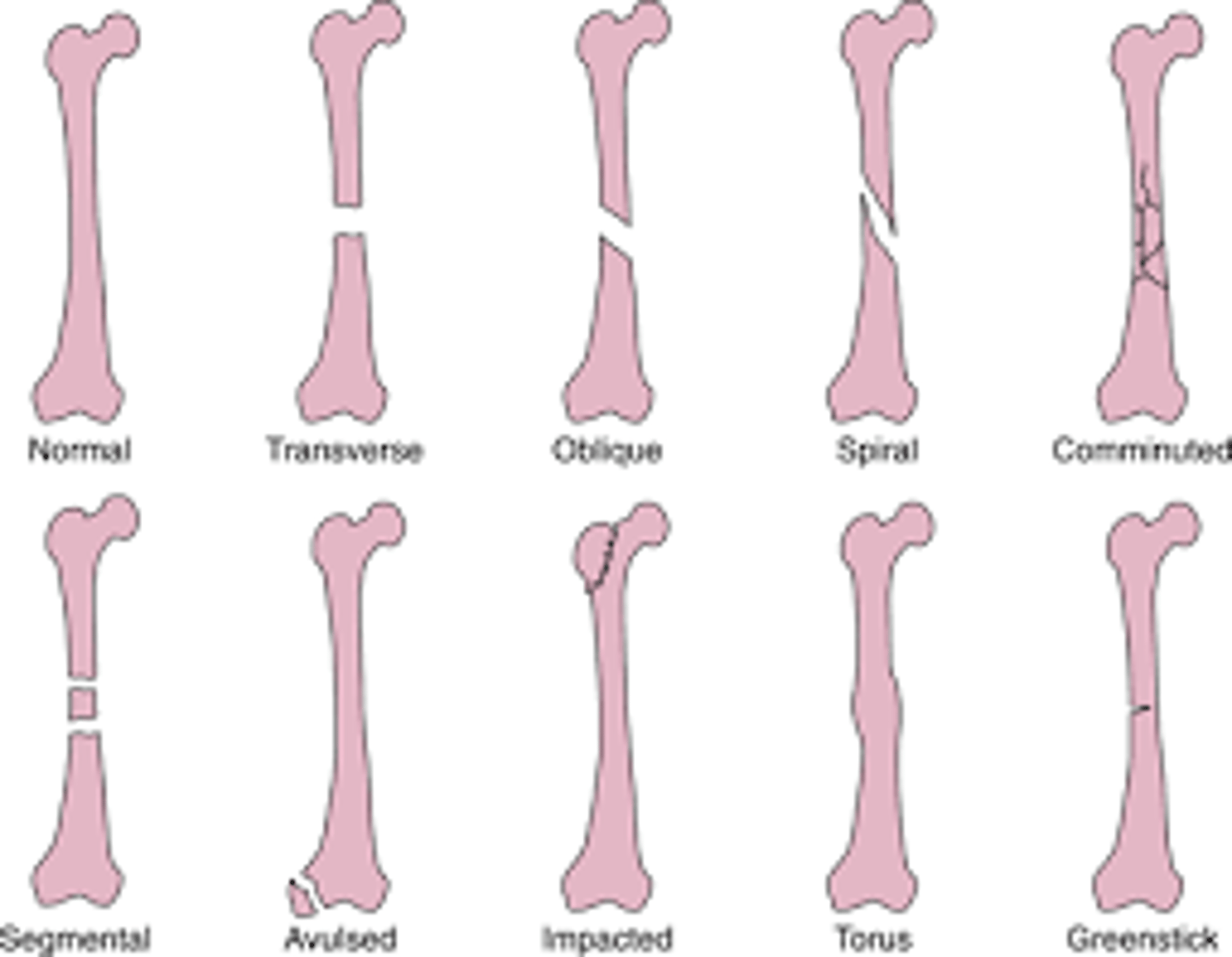
-segmental: two fractures in same bone
-impact: one fragment is driven into another
-compression: bone is crushed
-depression: portion of bone is pushed inward
fracture pattern
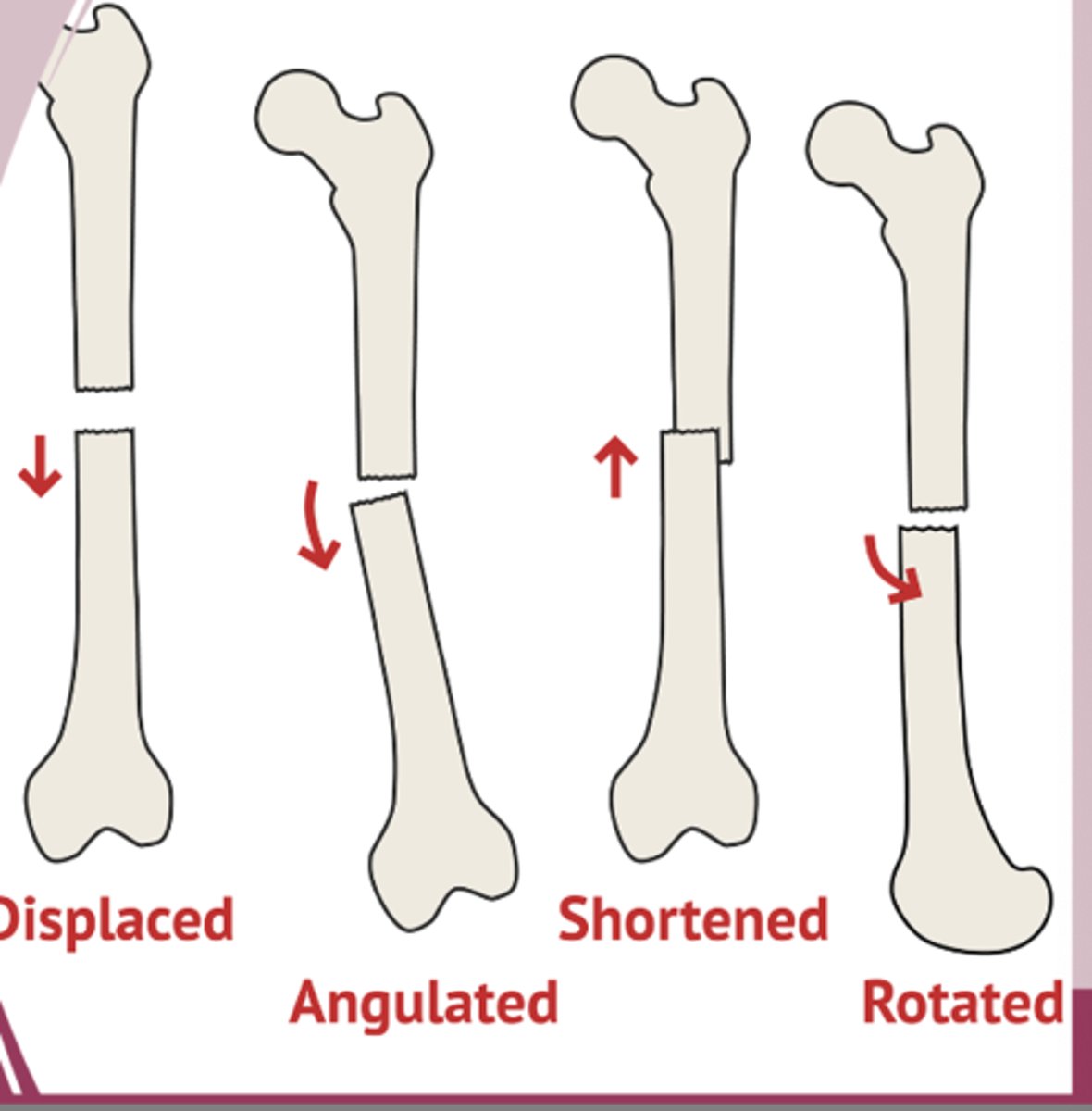
-nondisplaced: bone fragment maintain alignment
-displaced: bone fragment are out of alignment
-angulated: fragments are at an angle to each other
-rotated: one fragment twisted relative to other
-shortened: overlapping fragments reduce the bones normal length
fracture displacement
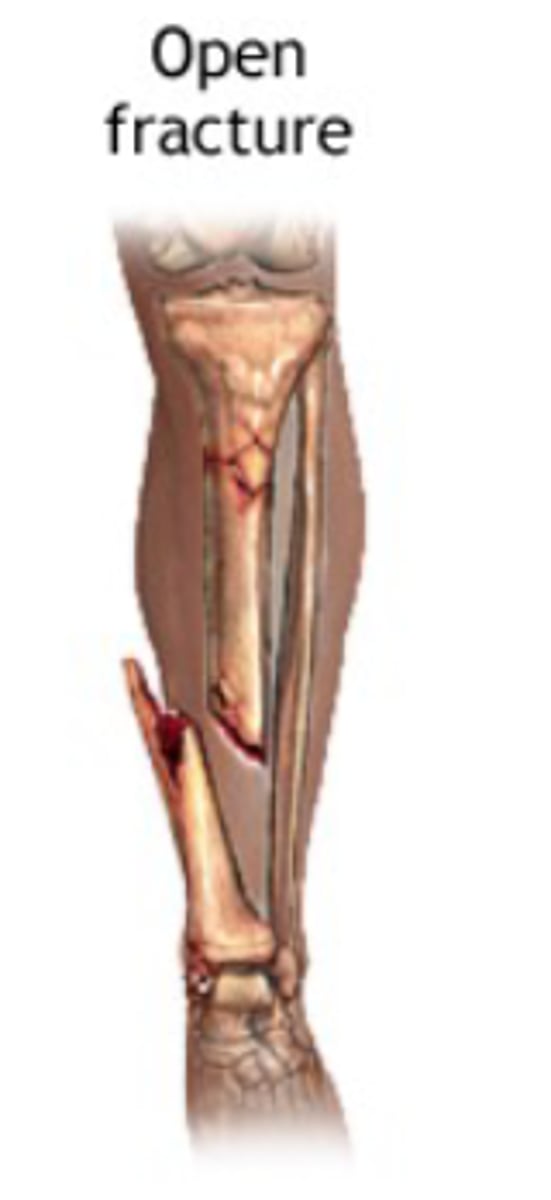
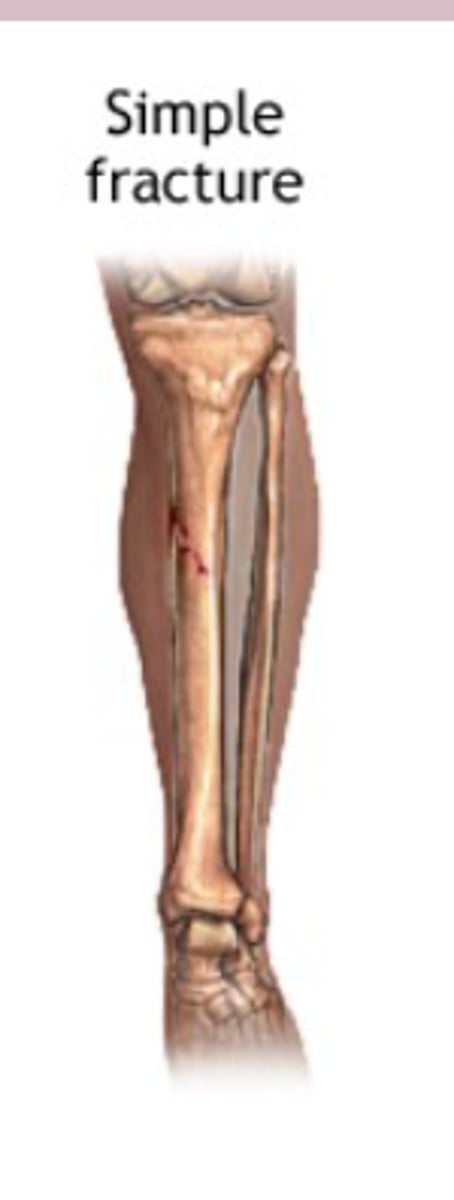
closed (simple) fracture
-open wound or break in the skin near the site of broken bone
open (compound) fracture