Cholesterol lowering agents
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What are the biochemical classes of lipids?
prostaglandins
triglycerides
unsaturated (oil)
saturated (fats)
phospholipids → very polar
steroids
cholesterol
cholesterol esters (CE) → more lipophilic than C
What are cholesterol esters?
fatty acids esterifying C3 hydroxyl
more lipophilic than cholesterol
What are the ingested lipids?
TGs
phospholipids
cholesterol
CE
What is the 1st step of the lipid cycle?
ingested lipids form big micelle structures → chylomicrons
outer: cholesterol + phospholipids
inner: TG + CE
combined via the hydrophobic effect to allow globule movement
What is the structure of chylomicrons? How do they move through the aqueous system?
outer: cholesterol and phospholipids
aqueous components
inner: TGs and CE
lipophilic components
hydrophobic effect allows movement through the aqueous system
aqueous parts cover the lipophilic ones
What is the 2nd step in the lipid cycle?
chylomicrons undergo hydrolysis by lipases
loses most of its TGs
new particle = remnant chylomicron
inner: CE>TG
much smaller than chylomicron
What is the 3rd step in the lipid cycle?
remnant chylomicrons go to the liver and are digested by lysosomes
product: free cholesterol
stored by esterification into CE
metabolized into bile acids
What is the 4th step of the lipid cycle?
liver recombines the 4 componenets into very small particles with the same inner and outer orientation
TG content = very high
very low density (VLDL)
coated with apo-lipoproteins (direct the globule into a specific tissue)
What is the apo-lipoprotein that is selective to the coronary arteries?
apo-B100
What happens to the chylomicron when it is traveling in the lymph?
picked up by adipose tissue and skeletal muscle
both tissues extract FAs from TGs via lipolipase to use for energy
deposited in adipose tissue
What is VLDL?
very low density lipoprotein
high TG content
What is IDL?
intermediate density lipoprotein
CE>TG content
What is LDL?
low density lipoprotein
mostly just CE
loss of all TG
dangerous because apo-B100 will bind to coronary arteries
goes to other tissues where CEs are hydrolyzed to make free cholesterol
increases density of globule
What is HDL?
returns to liver for recycle
What is the correct name for cholesterol lowering agents?
antihyperlipoprotein drugs

Nicotinic acid (Niaspan)
vitamin B3 (niacin)
pyridine group
COOH group
effective in lowering LDL and raising HDL
good oral absorption → active transport because it is small + polar
poor lipophilicity
adverse effect: flushing
due to peripheral vasodilatory effects
metabolized in liver → nicotinamide
What is the MOA of nicotinic acid?
unknown
may enhance lipoproteinase
breaks down chylomicrons → increases catabolism of LDL
may interfere w/ apo-protein synthesis
Why does nicotinic acid have an ADR of flushing?
because it is also a peripheral vasodilator
Gemfibrozil (Lopid)
aryloxyisobutyric acid derivative
isobutyric acid group
lowers both cholesterol + TGs
used PO
>99% PPB
metabolized aliphatic hydroxylation then conjugated
unknown MOA
What is the dose of gemfibrozil?
600 mg BID
How is Lopid metabolized?
aliphatic hydroxylation
conjugation
fenofibrate
enhances catabolism of TG rich particles
reduces secretion of VLDL
leads to hypotriglyceridemic effects
What are statins?
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors
effectively block conversion of HMG-CoA → mevalonic acid
What are the effects of statins?
inhibits HMG-CoA reductase
inhibits endogenous cholesterol biosynthesis in liver
decreases LDL
T/F: statins decrease dietary cholesterol
FALSE
no effect on dietary cholesterol
What is process of cholesterol synthesis?
acetyl CoA
3 hydroxy-3-methyl Gluteryl CoA
HMG CoA reductase
mevalonic acid
cholesterol
What are the key features of statins?
5 C backbone w/ hydroxyl + carboxyl groups
coenzyme A structure replaced w/ highly lipophilic area connected to mevalonic acid
What are the properties of statins?
good absorption from stomach and GI
PPB is high
OH = polar but hydrophilicity is outnumbered by the lipophilcity
similar potency = 20-40 mg
rosuvastatin is dosed 5-10 mg due to the resistance to metabolism from the sulfonamide group
Describe how statins are metabolized.
high 1st pass, low bioavailability
undergoes phase II conjugation
undergoes further hydroxylation
lovastatin (Mevacor)
napthalene ring
very carbon rich = lipophilic
similar to HMG CoA structure
PRODRUG

pravastatin (Pravachol)
more hydrophilic than others
simvastatin (Zocor)
PRODRUG
atorvastatin (Lipitor)
very large lipophilic area
off sets hydroxyl groups
fluvastatin (Lescol)
rosuvastatin (Crestor)
has sulfonamide group
resistant to liver metabolism
lower dose: 5-10 mg
What are bile acids?
metabolites of cholesterol
liver breaks down cholesterol to bile acids
excreted into GIT to emulsify lipids
approximately 97% of bile acids are reabsorbed into liver via enterohepatic circulation
What happens is bile acids become sequestered (trapped) in the GIT?
liver cholesterol will be depleted
sequestration (adsorption) prevents reabsorption into liver
What are the chemical properties of bile acid sequestrants?
positively charged N
quaternary = no absorption
needs to stay in GIT and work locally
reacts with COOH
polymeric lipophilic area
reacts with bile acid lipophilic backbone

cholestyramine Cl (Questran)
bile acid sequestrant
polymer of styrene
quaternary ammonium
adverse effect: severe constipation
drug absorbs water alone with bile acid
nonselective
Why is the nonselectivity of cholestyramine a problem?
will sequester anything that is highly lipophilic
can lead to DDIs
contraceptives (lipophilic + acidic)
vitamin K (lipophilic + acidic)
causes problems with clotting
may decrease absorption of all nonwater soluble vits (KADE)

colestipol HCl (Colestid)
bile acid sequestrant
polymer of tetraethylenepentamine
non-quaternary ammonium
but protonated in GIT
secondary + tertiary amines
constipation side effect
How do cholestyramine and colestipol lower plasma LDL levels?
by indirectly increasing the rate at which LDL is cleared from the bloodstream
What are cholesterol transporter inhibitors (CTI)?
lowers plasma cholesterol levels by inhibiting transport and absorption of cholesterol at the brush border of the SI
binds to specific cholesterol transport protein
inhibits exogenous cholesterol absorption from food
How does the body compensate for the decreased absorption of cholesterol from the GIT?
upregulates LDL receptors + produces more HMG-CoA reductase to try to make more cholesterol
given in combo drugs like Vytorin (simvastatin + ezetimibe)
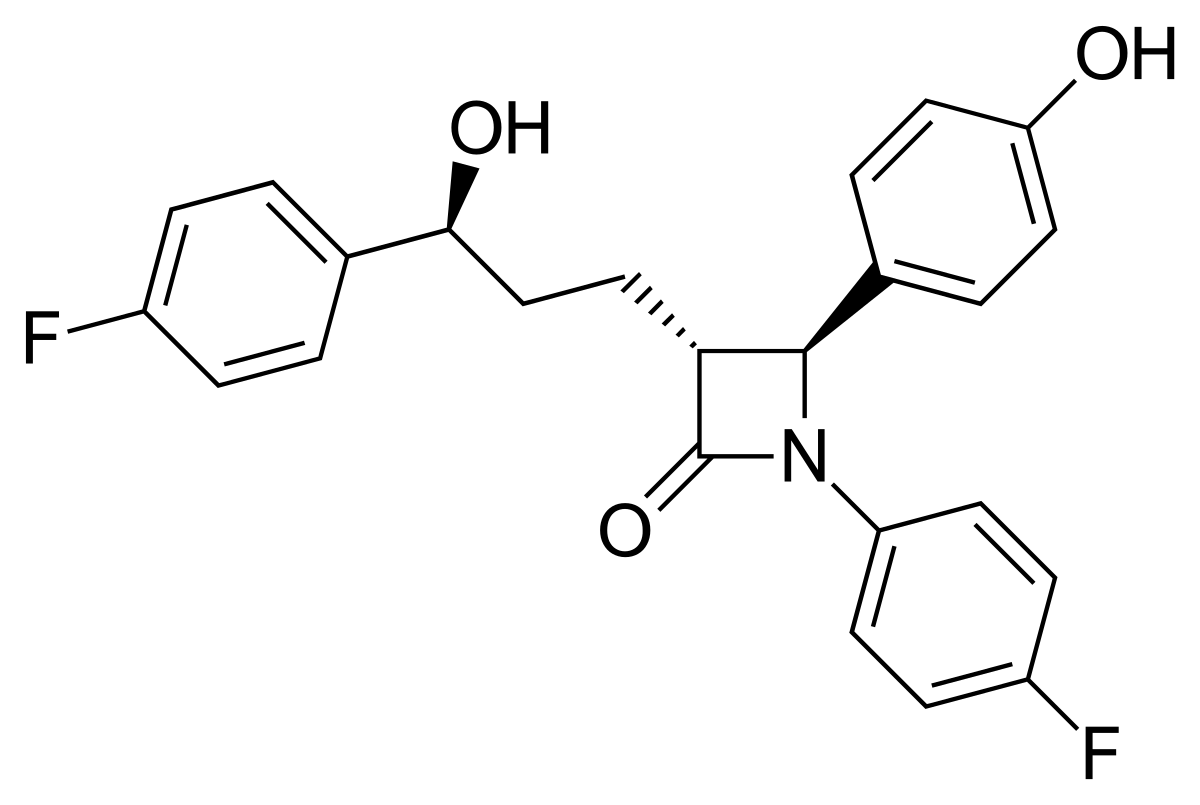
ezetimibe (Zetia)
CTI
very lipophilic
very poor dissolution rate
conjugated in phase II w/ glucuronic acid → goes back to GIT + interacts with transporter
Which statins are prodrugs?
lovastatin (Mevacor)
simvastatin (Zocor)