Anatomy Lab 1: Plane/Axis and the Skull
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Describe the sagittal plane
Divides the body in two symmetrical halves, has a frontal axis, allows flexion and extension ie) bicep curls, shoulder press, squats
Describe the frontal/coronal plane
Divides the body in front and back halves, has a sagittal axis, allows abduction and adduction (move towards or away from midline of the body) ie) jumping jacks, lateral raises, side shuffle
Describe the transverse plane
Divides the body in top and bottom half, has a longitudinal axis. Allows rotation movements ie) shaking head, throwing a frisbee,
What is circumduction?
occurs in the frontal and sagittal planes. includes (in order) flexion, abduction, extension, adduction ie) moving upper limb in a circle
Turning toes to point laterally at a 45 degree angle is what motion?
hip external/lateral rotation
Turning the toes to point medially at a 45 degree angle is what movement?
hip internal/medial rotation
Turning the soles of the feet to face each other is what movement?
Sub-talar inversion
Turning the soles of feet to face laterally is what movement?
sub-talar eversion
Raising up on your toes is what movement?
ankle plantarflexion or toe extension
Bringing the dorsum of the foot closer to the anterior leg is what movement?
ankle dorsiflexion
How are joints classified?
Structurally: design of the joint with respect to tissue components
Functionally: type and amount of movement that occurs dependent on structure
What are fibrous joints
typically synarthrosis, does not move a lot, such as the sutures of skull, and distal tibiofibular joint
what are cartilagenous joints
have little movement, amphiarthrosis, connected by hyaline or fibrocartilage. ie) symphysis pubis or invertebral discs
what are synovial joints
freely movable joints, diarthrosis, contain synovial fluid and a joint capsule. ie) hip, knee, elbow, temporomandibular joint
Examples of uni-axial joints
elbow, ankle, distal interphalangeal
examples of biaxial joints
wrist, 2nd metacarpophalangeal
examples of multiaxial joints
shoulder and hip
What are ligaments
they are the structural support for all types of joints compromised of dense connective tissue and connect bones to bones
What is the difference between capsular or accessory ligaments in synovial joints?
capsular: thickening of the joint capsule
accessory: separate from the joint capsule
What passes through the foramen magnum?
spinal cord, meninges, blood vessels and adipose tissue
What is the purpose of foramina
allows passage of nerves and blood vessels
which parts of the brain lie in the:
anterior/middle/posterior cranial fossas?
frontal lobe, temportal lobe, and the cerebellum
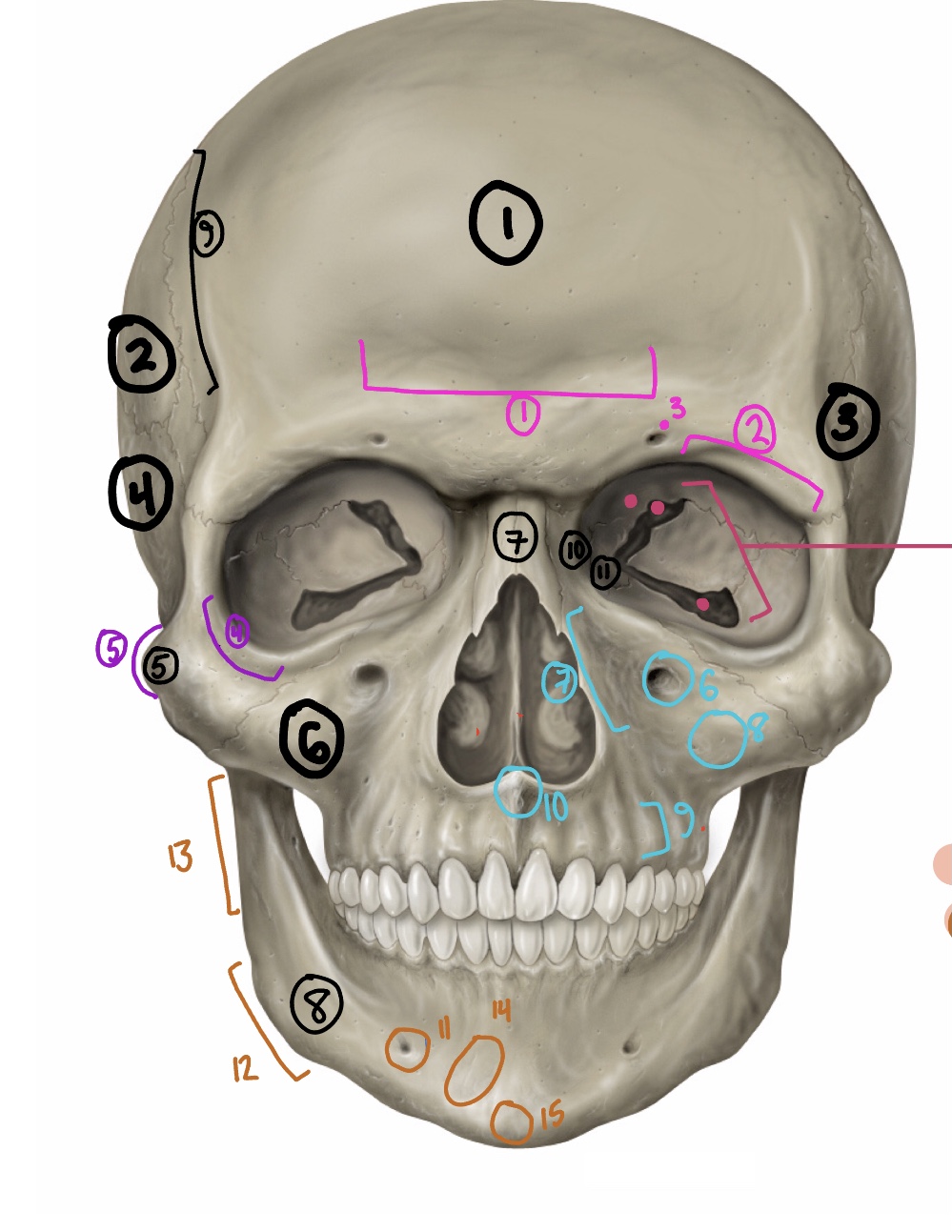
What are the BONES of this diagram/paired or unpaired?
Frontal bone, unpaired
Parietal bone, paired
Sphenoid, unpaired
Temporal, paired
Zygomatic, paired
Maxilla, paired
Nasal, paired
Mandible, unpaired
coronal suture
lacrimal, paired
ethmoid, unpaired
What are the frontal bone landmarks?
The supraorbital foramen (hole above eye) and margin, the frontal sinus (dent in forehead)
What is the landmark of the zygomatic bone
the infraorbital foramen (hole on the cheekbone close to the nose), from lateral and inferior view: zygomatic arch (where it connects to the temporal)
What is the landmark of the mandible
the mental foramen (hole near the chin), angle of the mandible (jawline), from the lateral view: coronoid process (meets the zygomatic bone), and the mandibular condyle (fits into the zygomatic arch, where the temporomandibular joint sits
What are the landmarks of the temporal bone?
From the lateral view: the mastoid process, external acoustic meatus (where the ear would be), and the styloid process (pointy stick)
From the inferior view: the zygomatic process (where it connects to the arch), the mandibular fossa (cavity where it connects to the mandible), and the external acoustic meatus and styloid process
What are the landmarks of the occipital bone?
from the lateral view: the lambda (small dent in the back of the head), the lambdoidal suture and the external occipital protuberance (bump on the bottom back of head).
from the superior view: the foramen magnum, the posterior cranial fossa where the cerebelum sits
from the inferior view: the occipital condyles (beside the foramen magnum) and the external occiptial protuberance
What are the landmarks of the sphenoid?
SELLA TURCICA, the foramen ovales (holes beside the sella), the optic canals (above sella), and the greater and lesser wings
What are the landmarks of the ethmoid?
the CRIBIFORM PLATE (where olfactory nerves exit), and the crista galli in the superior view