Anatomy of skeletal Muscle
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
what is the fascia of skeletal muscle
a thin sheath of fibrous tissue enclosing a muscle or other organ
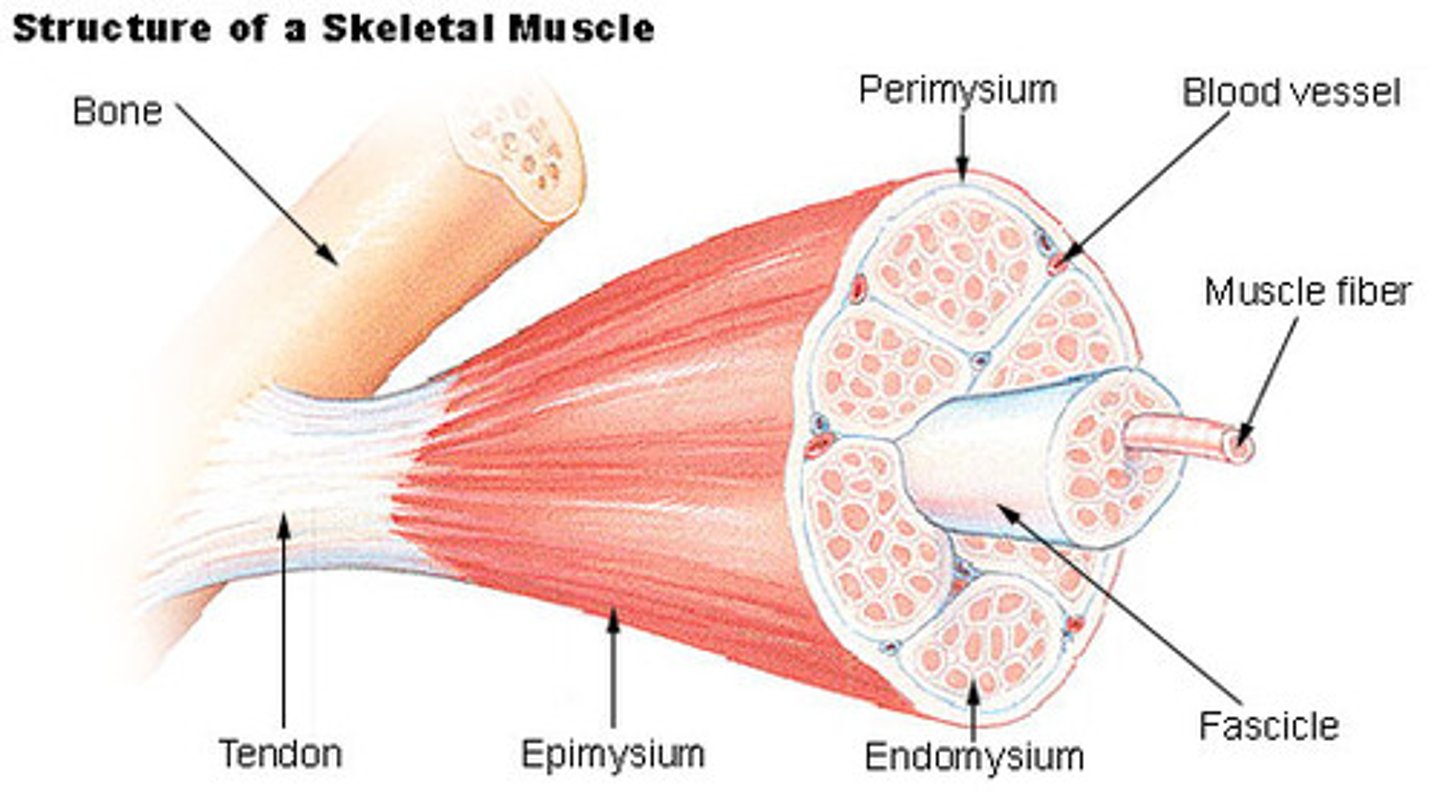
What is the epimysium?
surrounds entire muscle
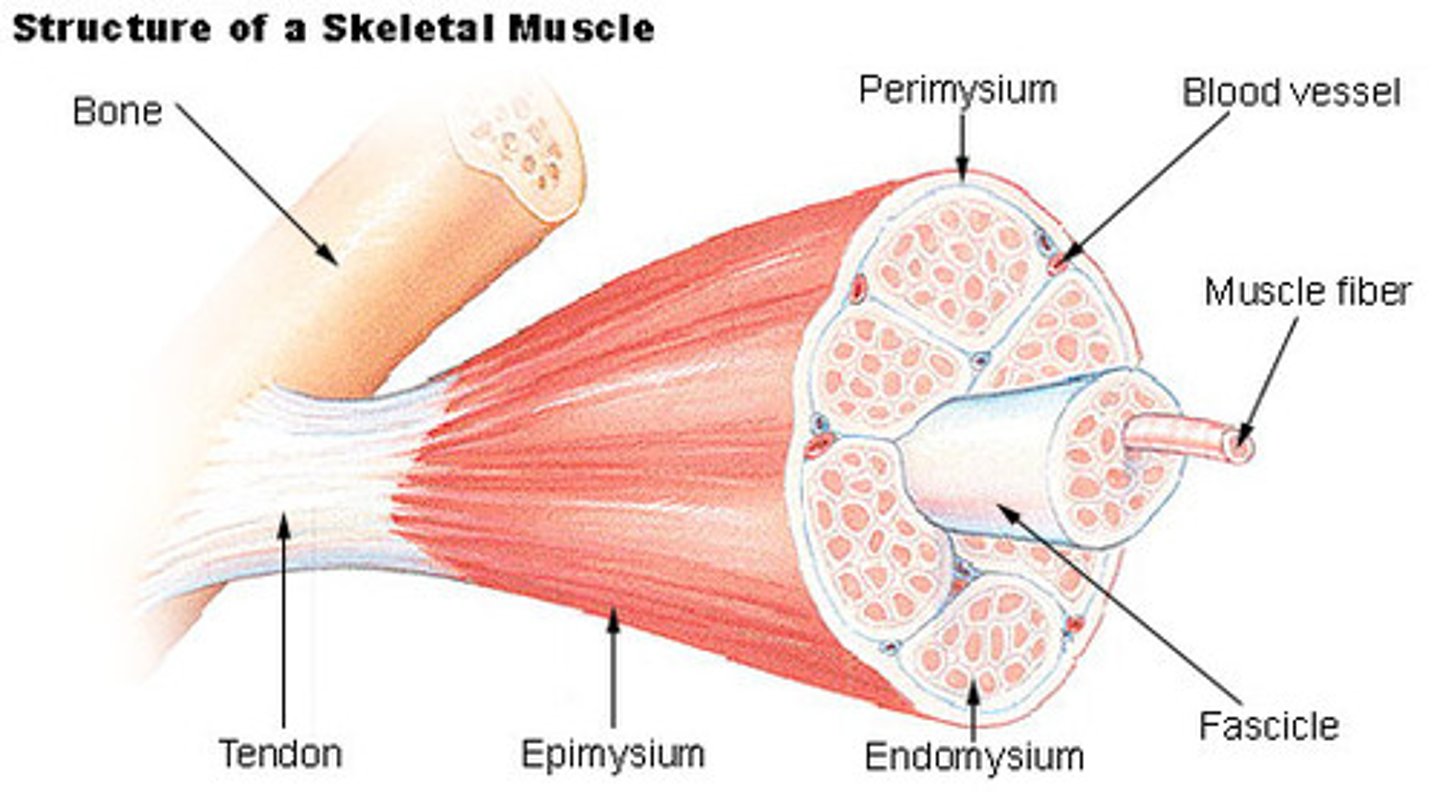
What is a muscle fasicle
bundle of skeletal muscle fibers ( cells )
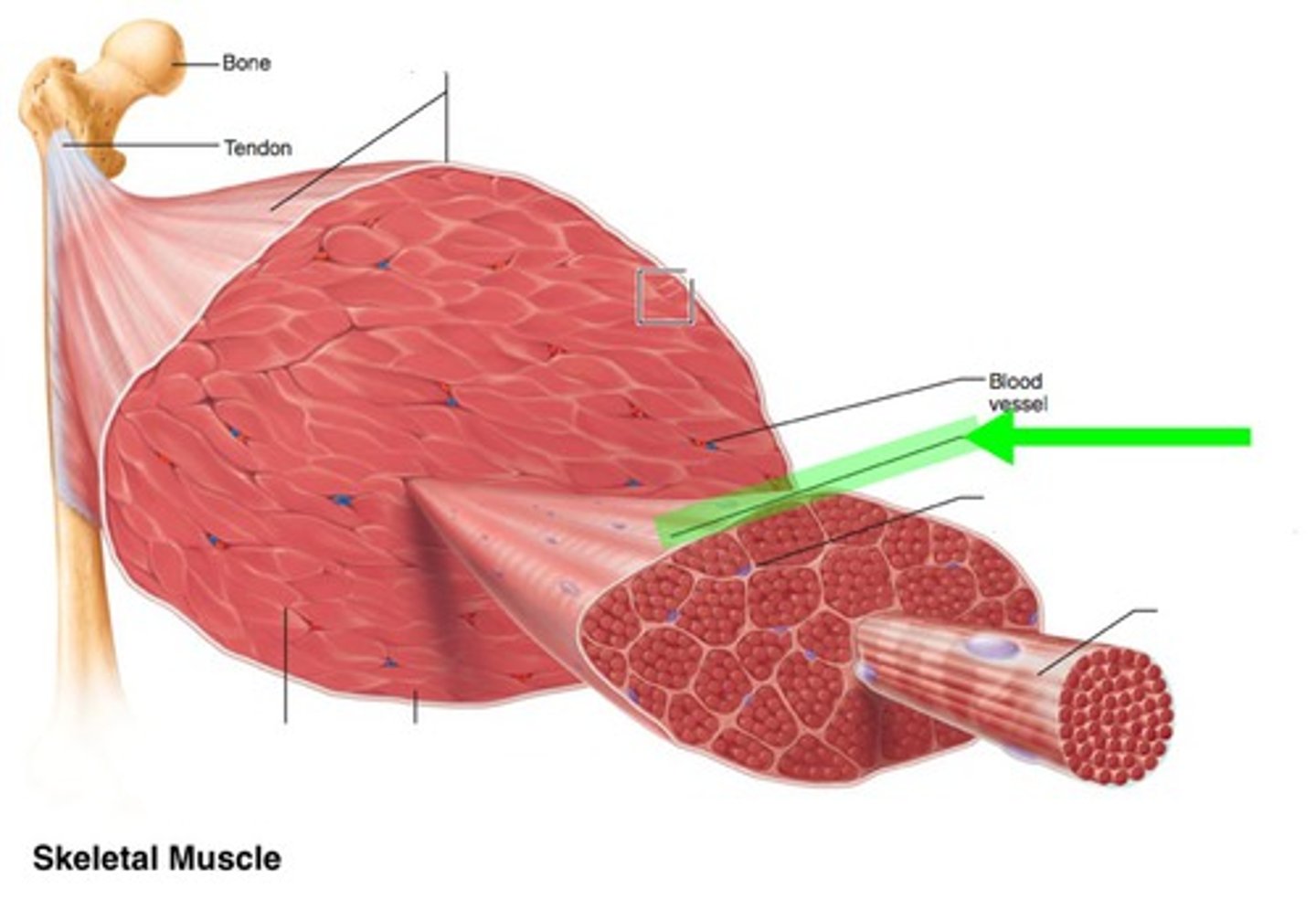
What is the perimysium
The connective tissue that surrounds fascicles.
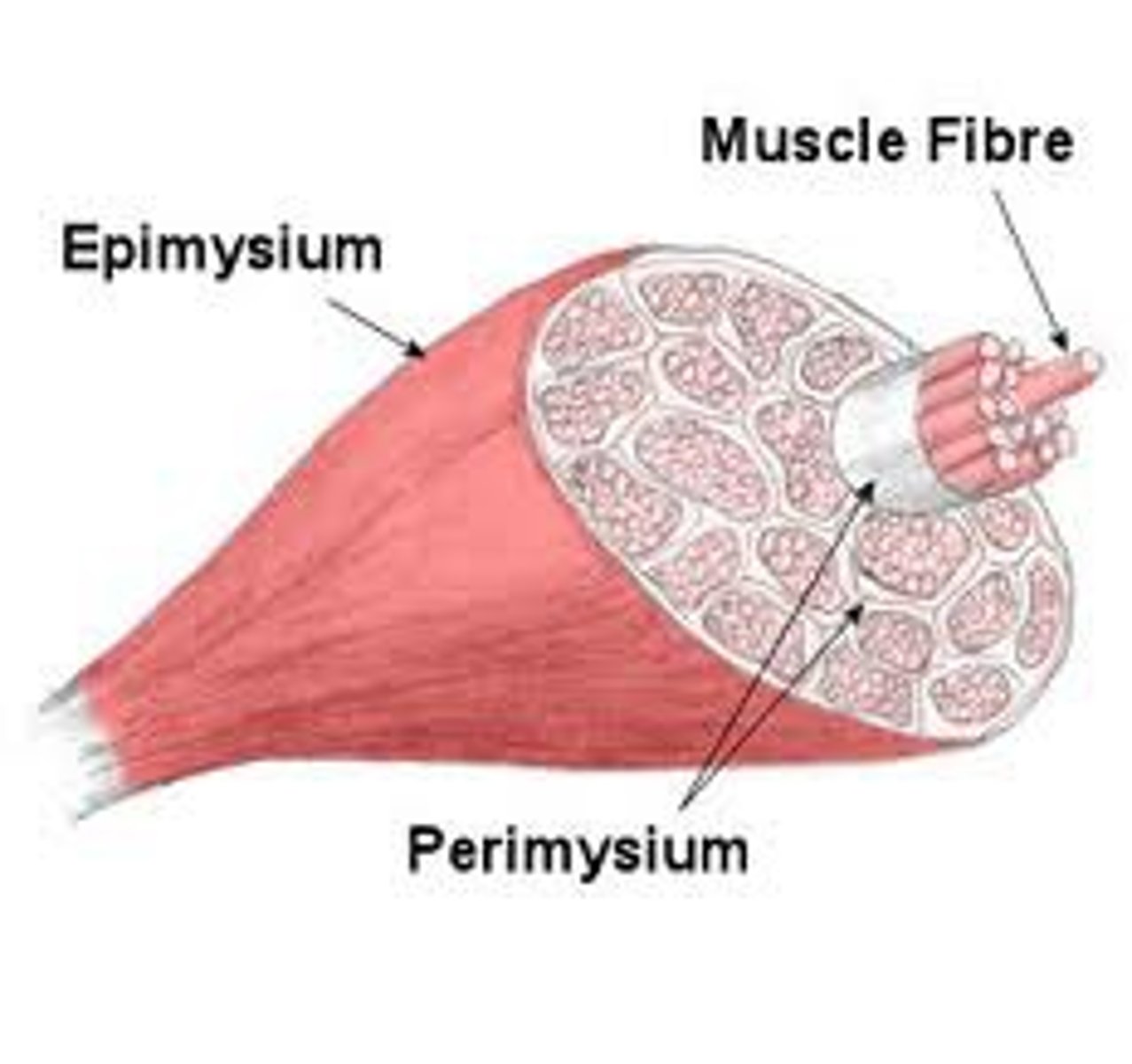
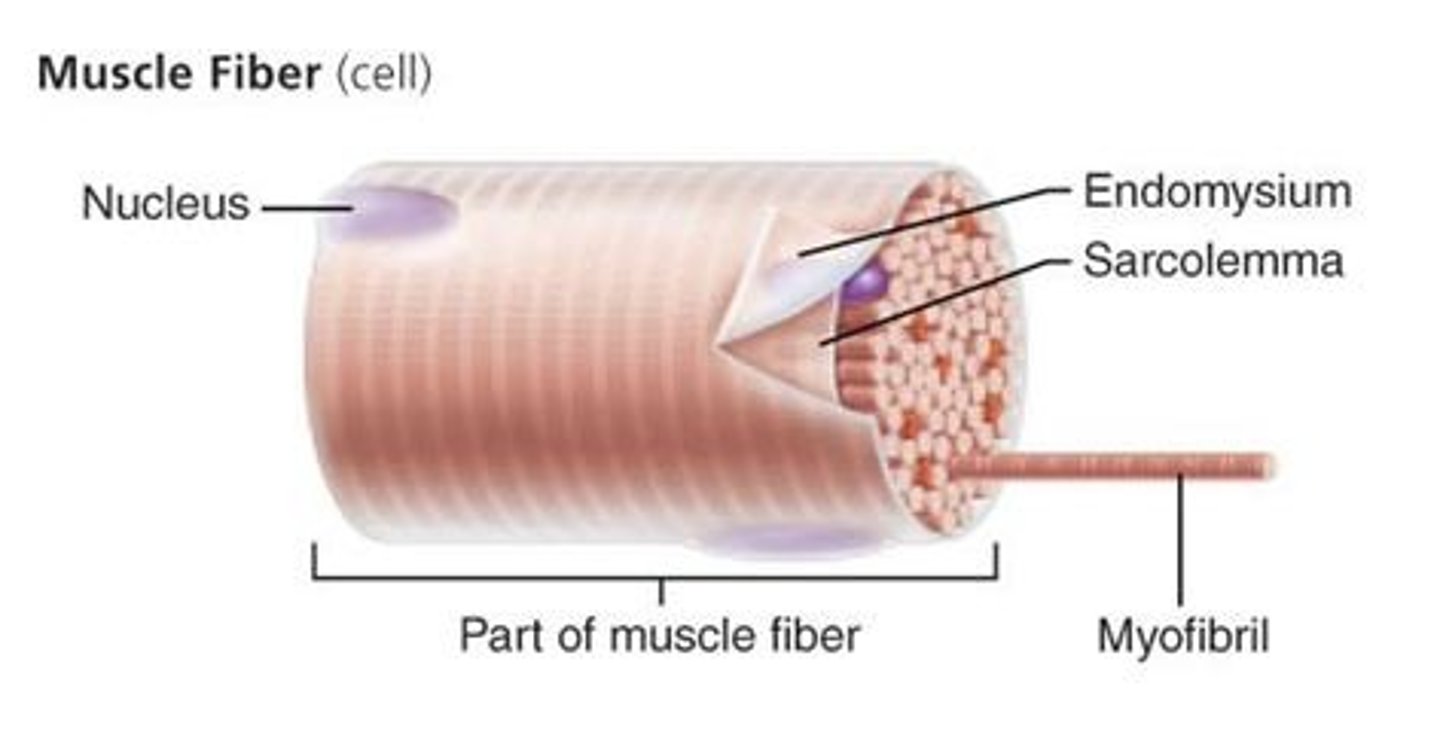
What is a muscle fiber
muscle cell
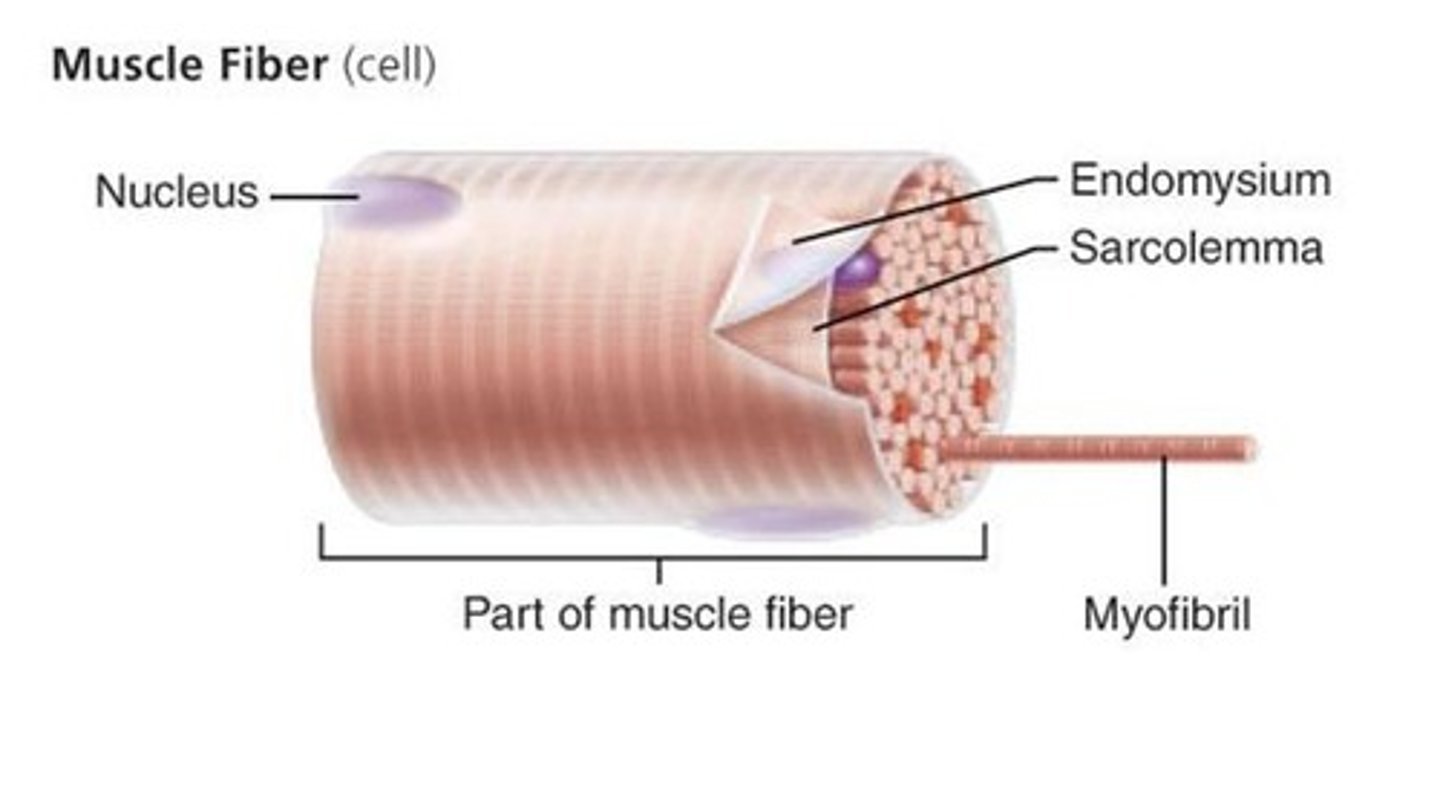
What is a endomysium
a thin layer of connective tissue that surrounds each muscle fiber
What. is a myofibril
Many of these units make up a single muscle fiber. These are made up of sarcomeres.
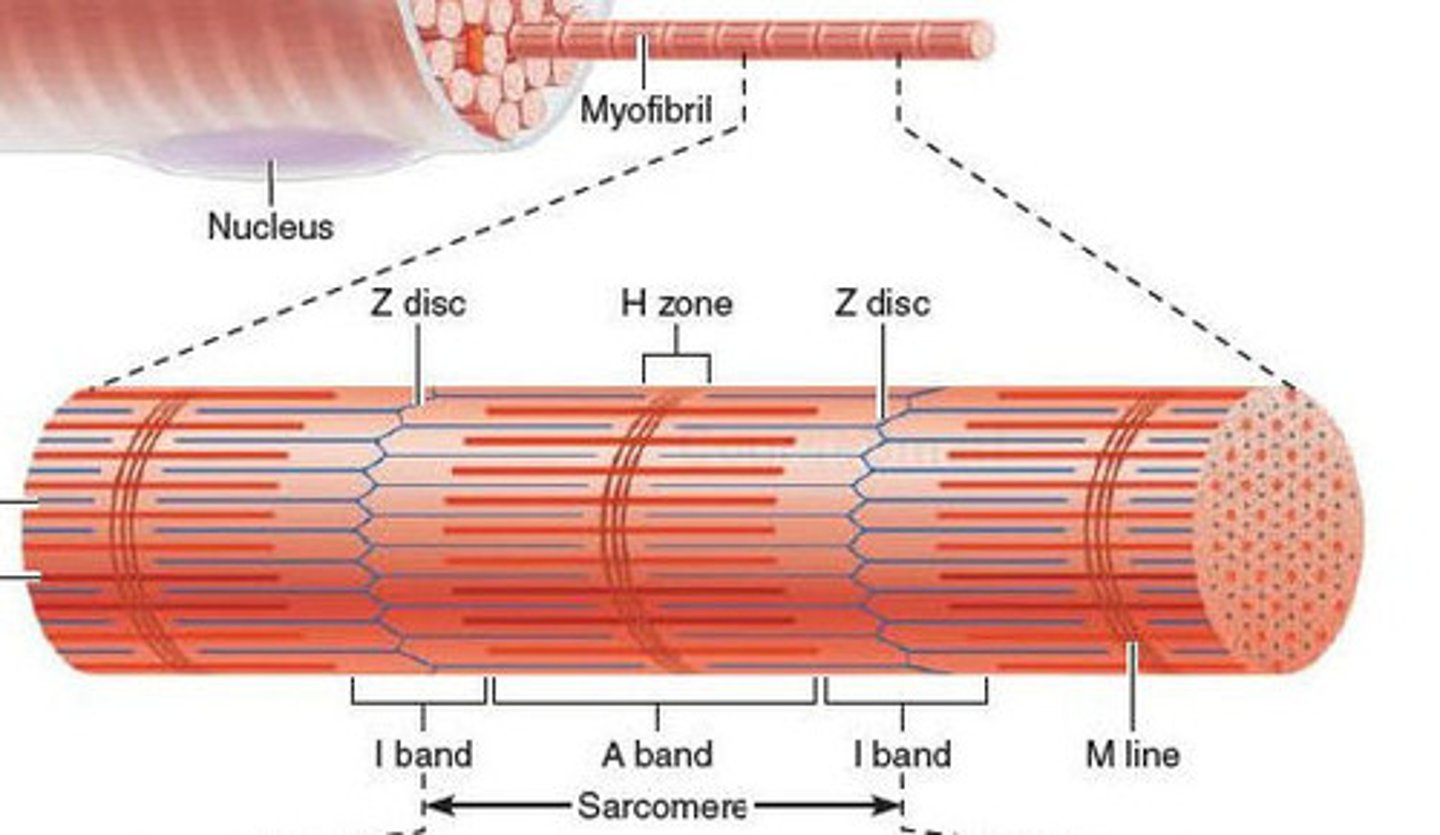
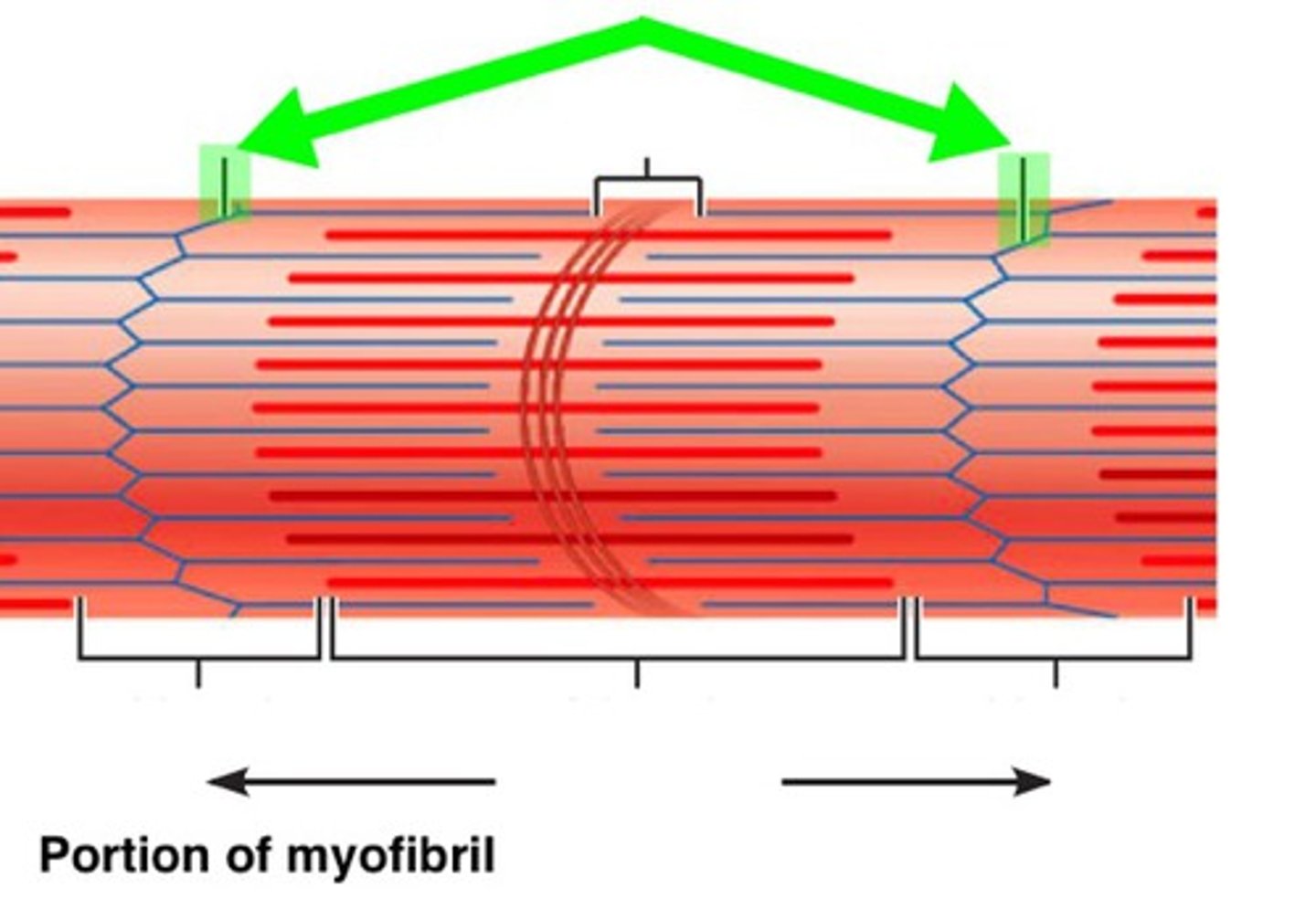
What is a sarcomere
contractile unit of a muscle fiber
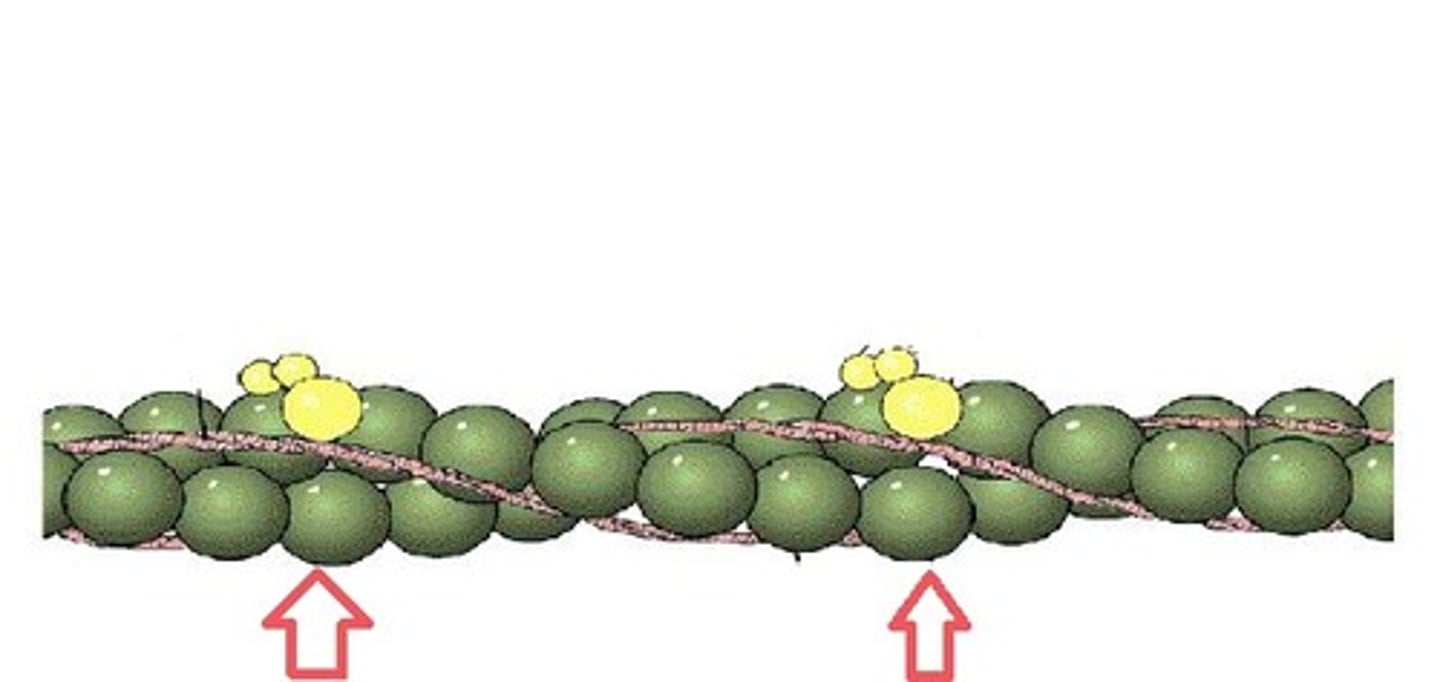
What is actin
This term refers to a thin protein filament that acts with myosin filaments to produce muscle action.
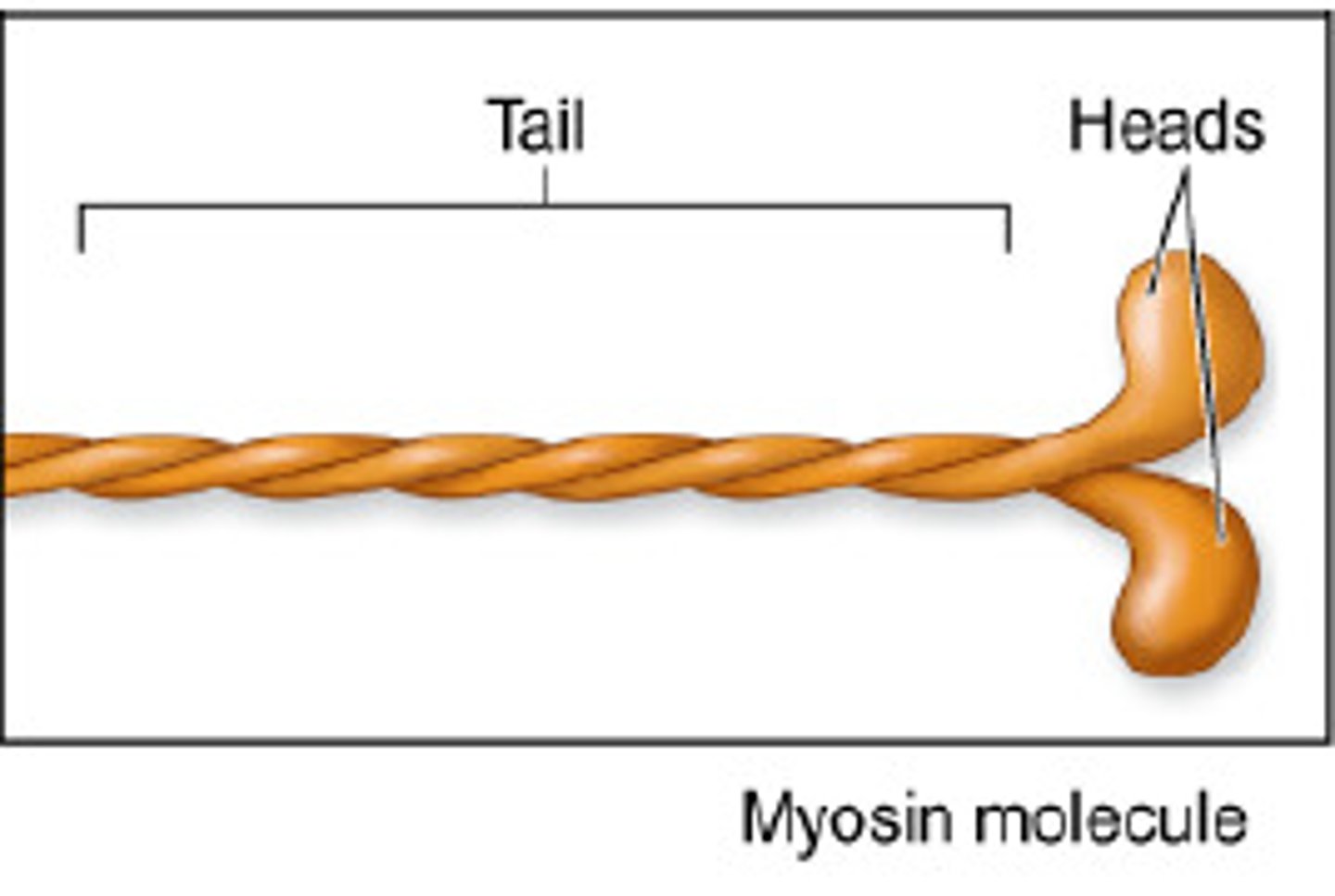
What is myosin
thick filaments
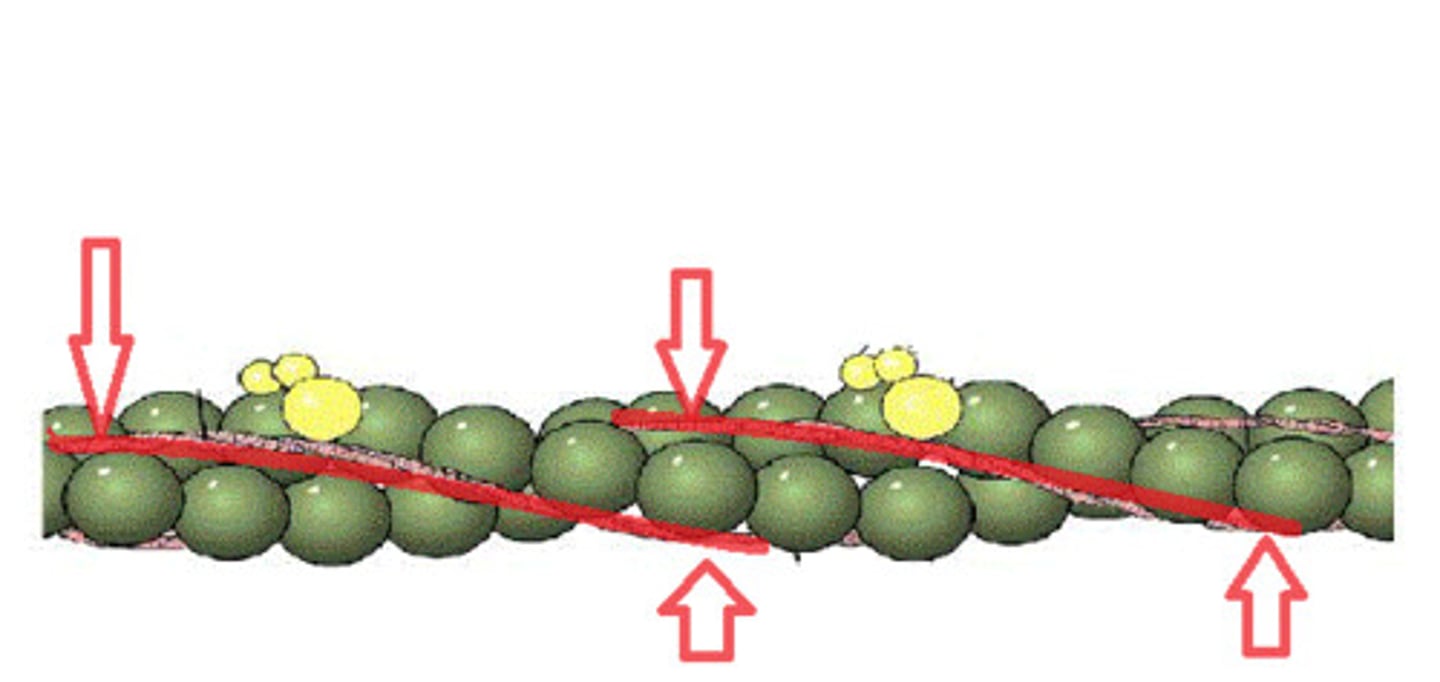
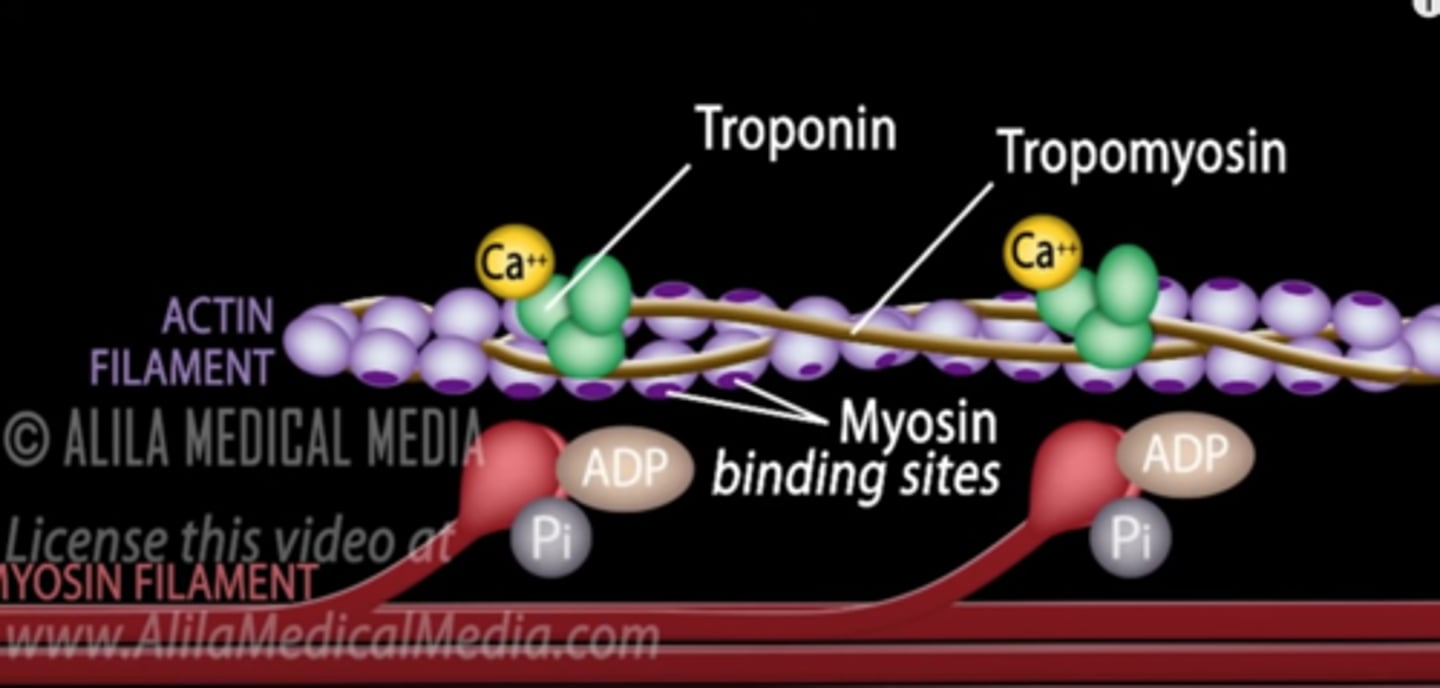
What is tropomyosin?
It is a long, fibrous protein that winds around the actin polymer, blocking all the myosin-binding sites.
What. is troponin
a regulatory protein that moves tropomyosin aside & exposes myosin binding sites when Ca+ is released during muscle contraction
What effect does calcium have on troponin
binds to troponin and removes it from the active site that is covered by tropomyosin
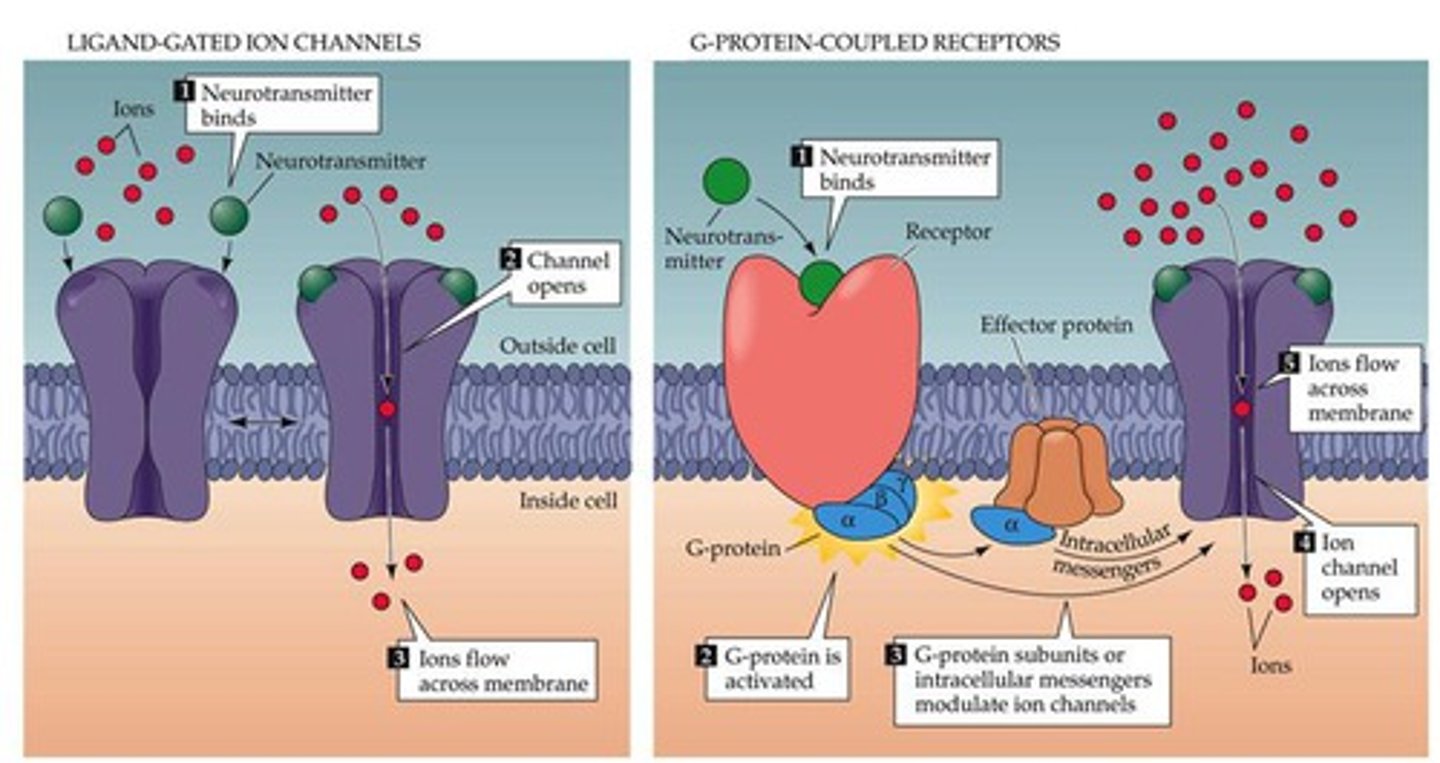
ligand-gated ion channel
Type of membrane receptor that has a region that can act as a "gate" when the receptor changes shape.
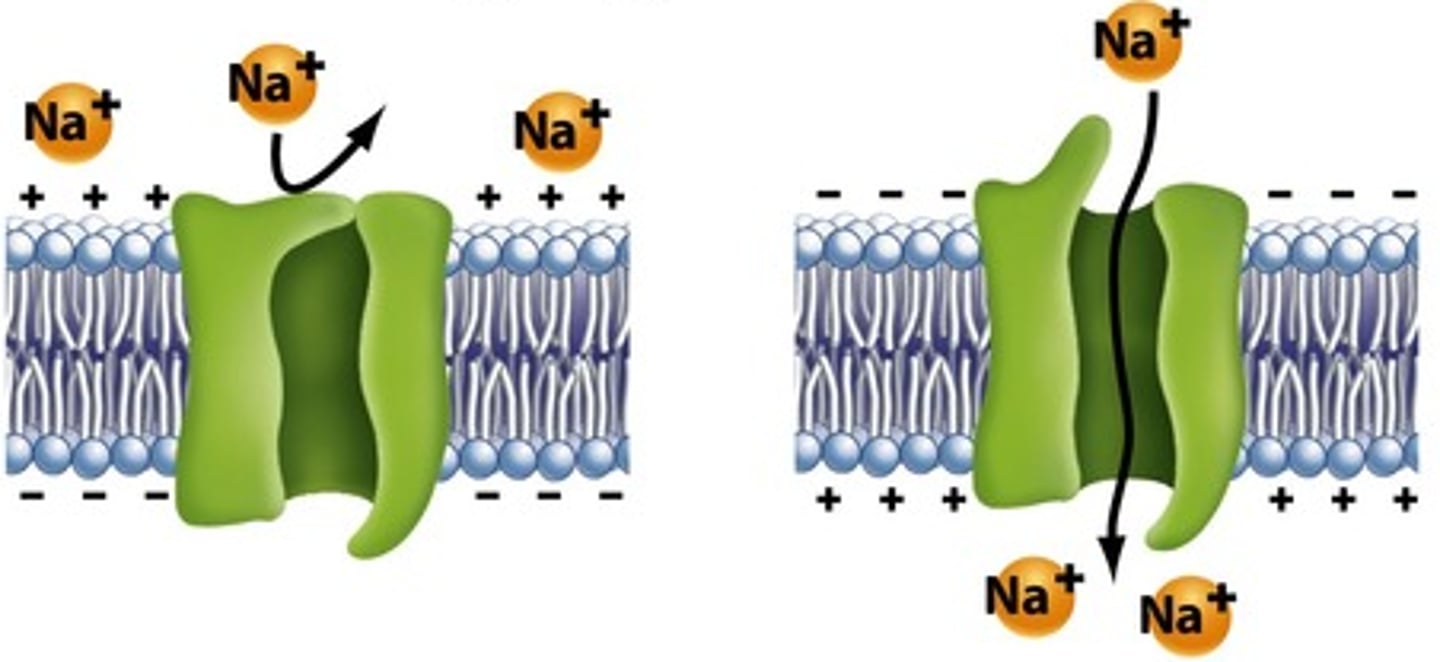
voltage-gated ion channels
Channels that open or close in response to a change in the membrane potential.
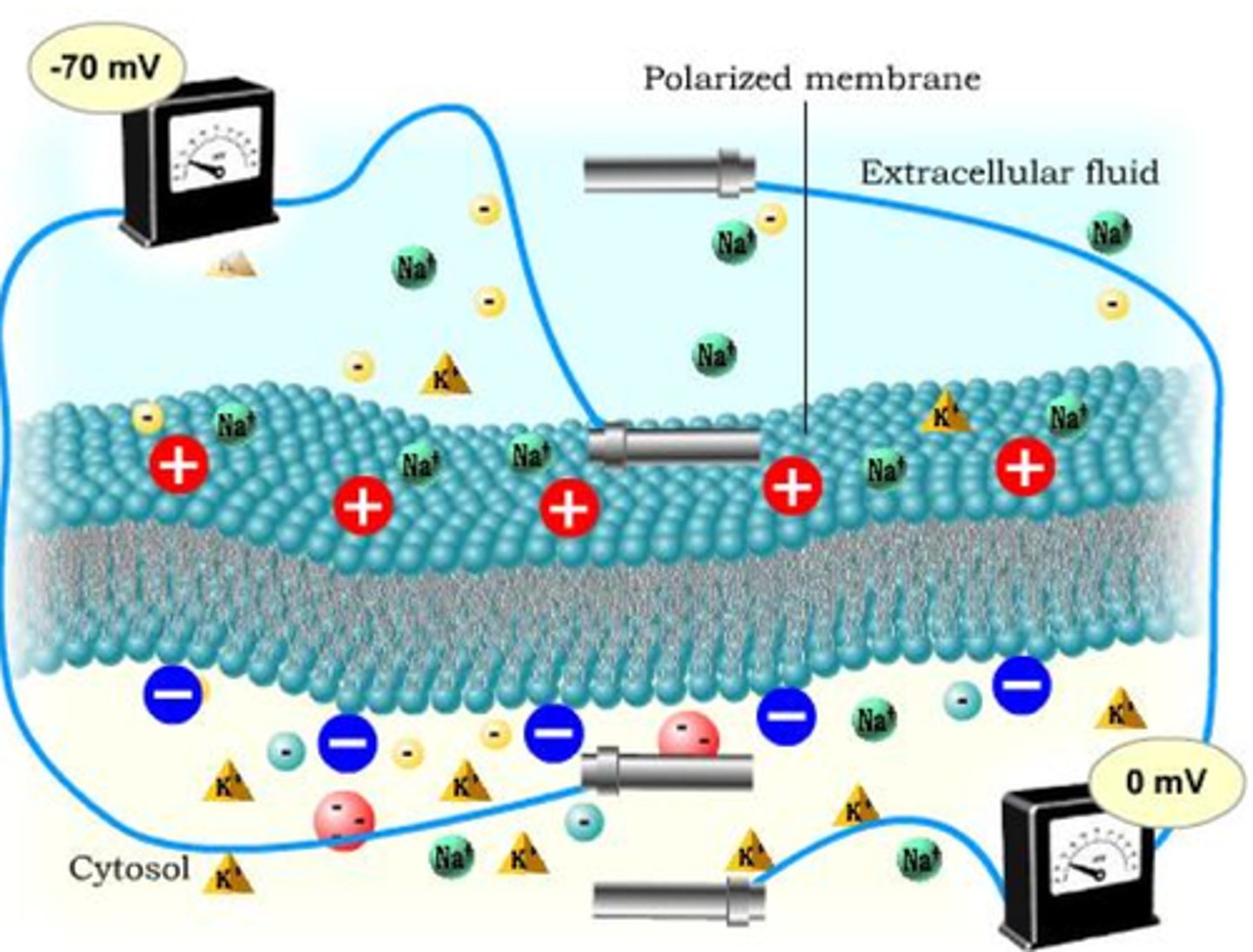
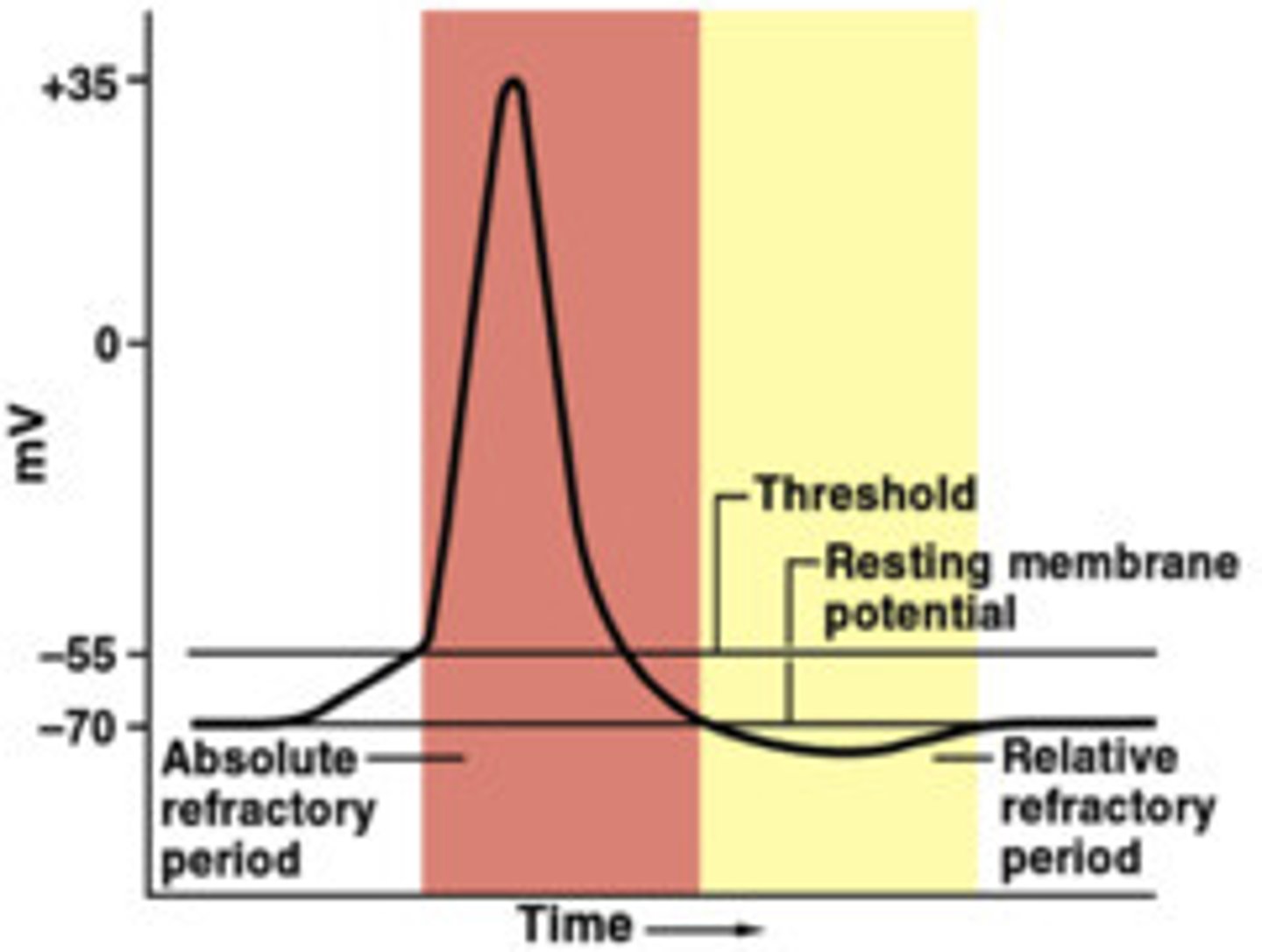
What is a resting membrane potential
Difference in electrical charge across the membrane at rest
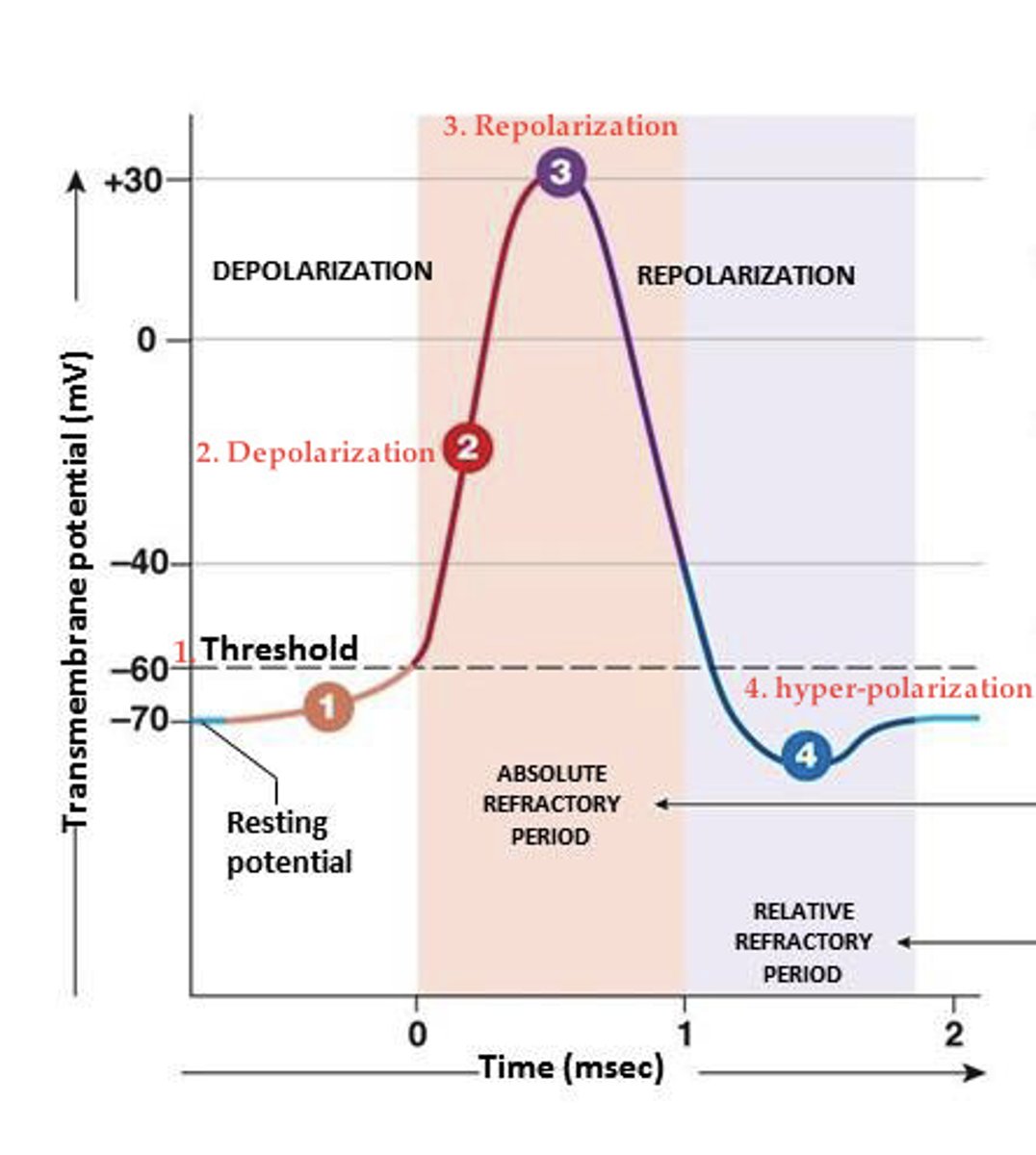
What is the threshold potential?
the critical level to which a membrane potential must be depolarized to initiate an action potential
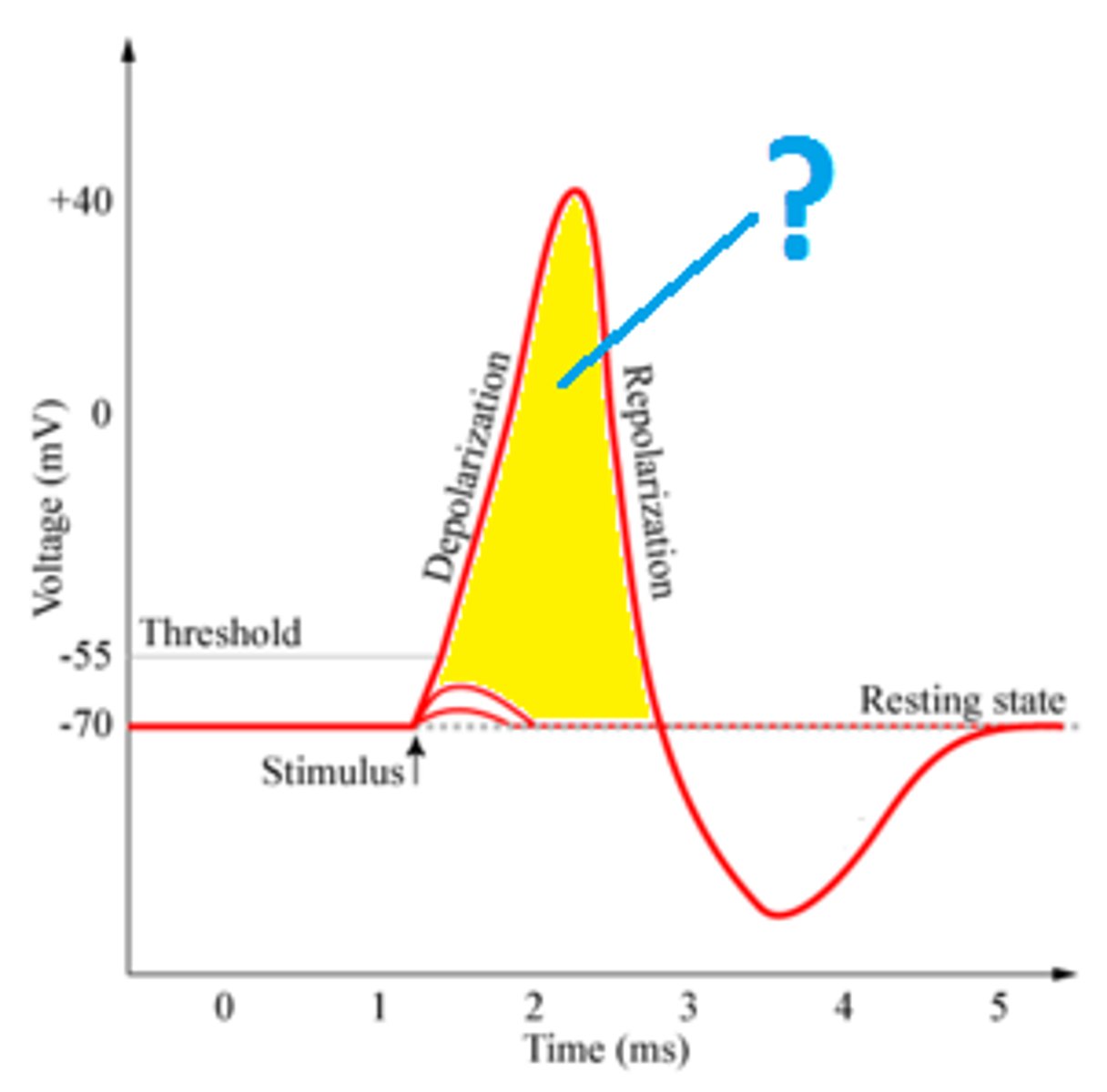
What is depolarization
This term refers to when any time the charge difference becomes more positive than the RPM of - 70mV. moving closer to zero.
What is repolarization
the membrane returns to its resting membrane potential
What is an action potential
electrical impulse that travels down the axon triggering the release of neurotransmitters
What are the T tubules in skeletal muscle
invaginations (folded in sections) of cell membrane that dive into the core to carry the action potential of the cell membrane internally to contact the terminal cisternae of 2 adjacent lengths of sacroplasmic reticulum - this creates a TRIAD
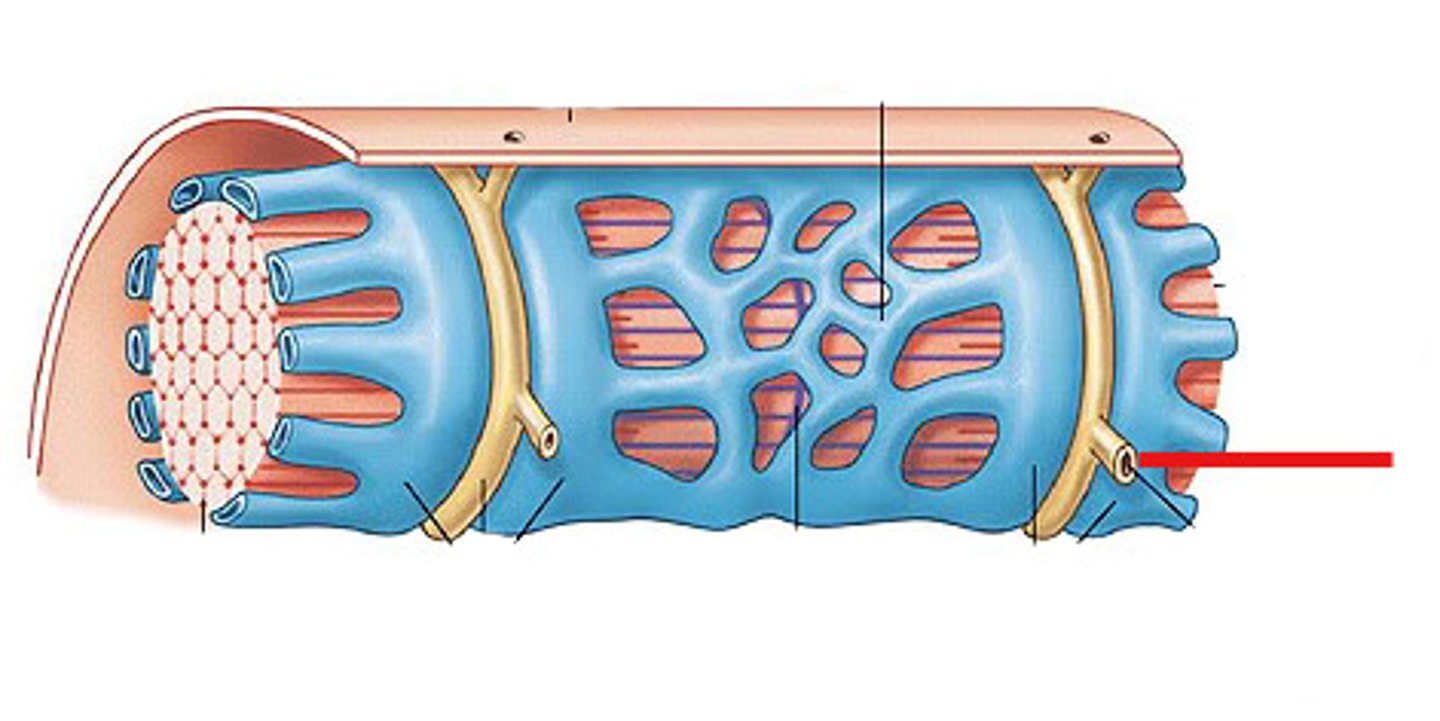
What is stored in the Cisternae
Calcium
What causes the globubar head to go into a cock position
hydrolysis of ATP , ADP AND. P attach to the globular head
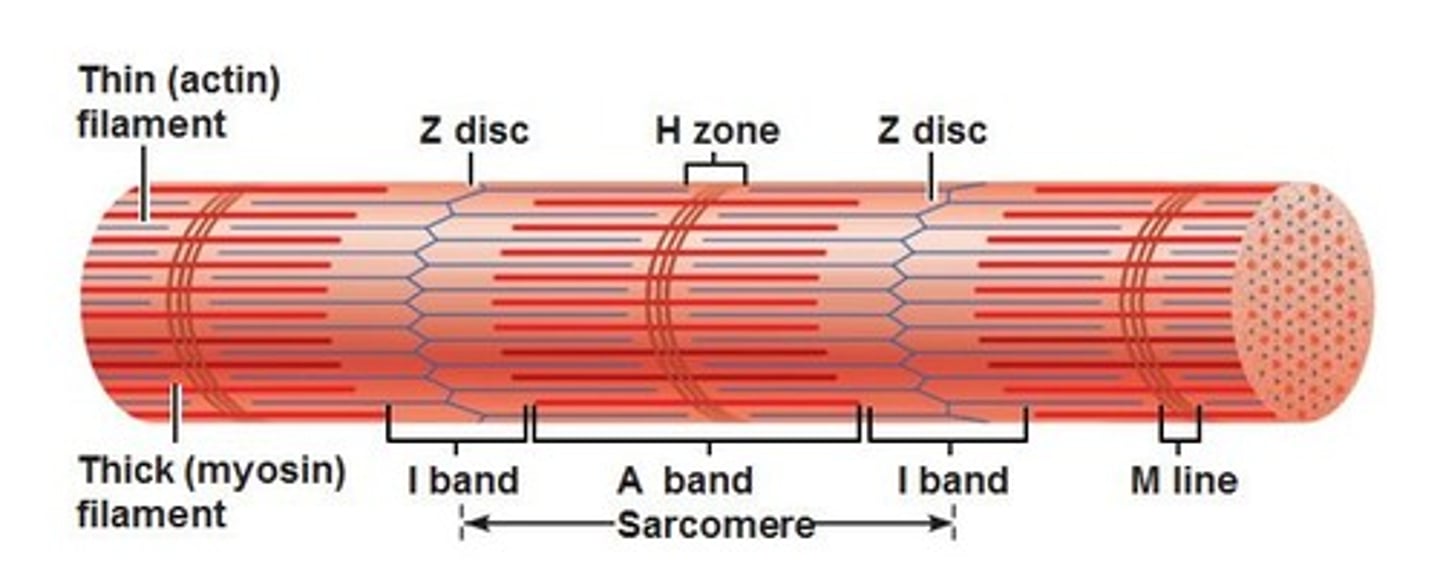
What is the H zone
myosin only
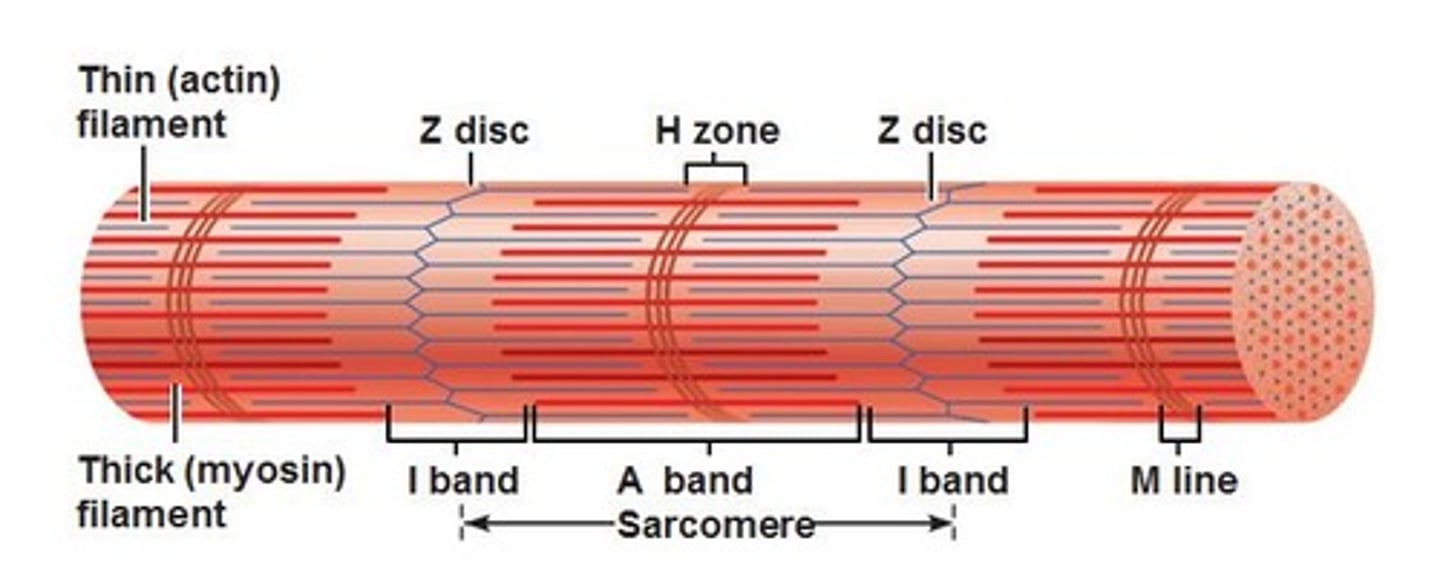
What is the A band a sarcomere
The entire length of the myosin filament. Contains myosin and actin
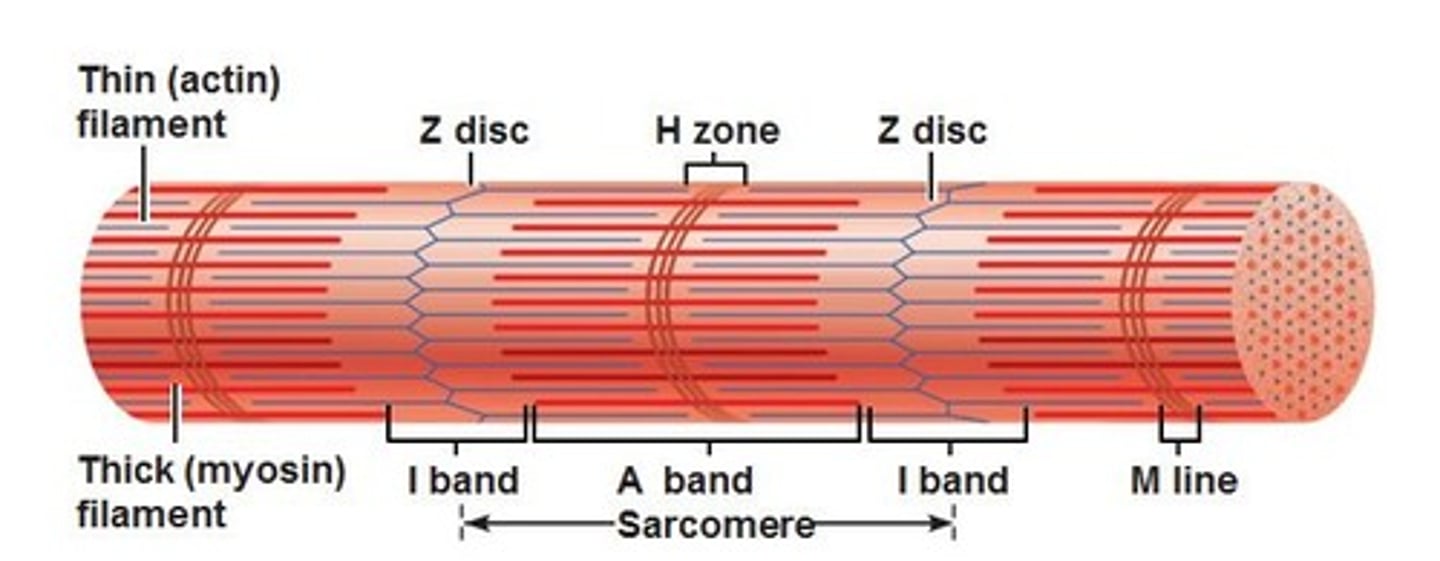
'what is the I band
actin only
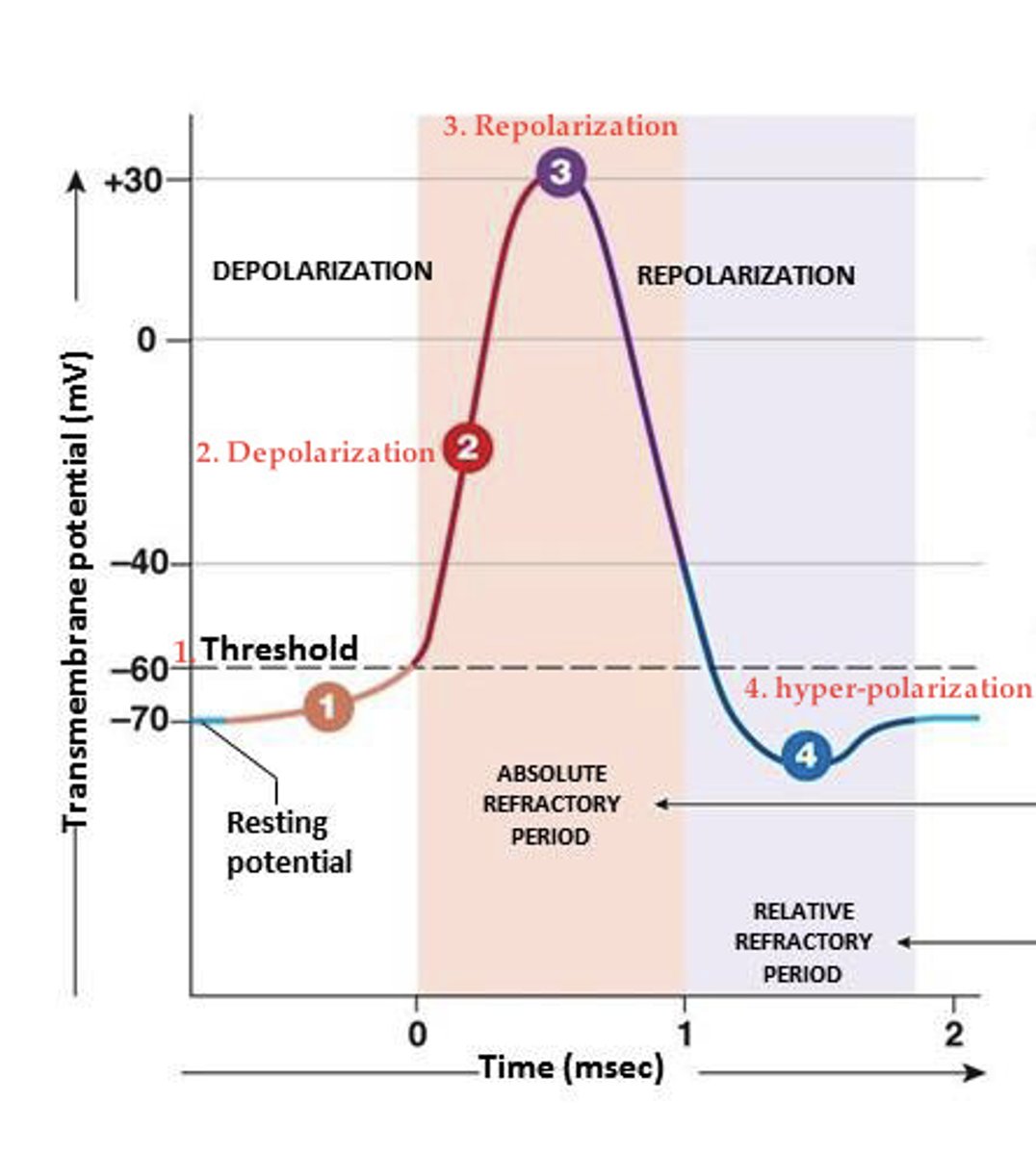
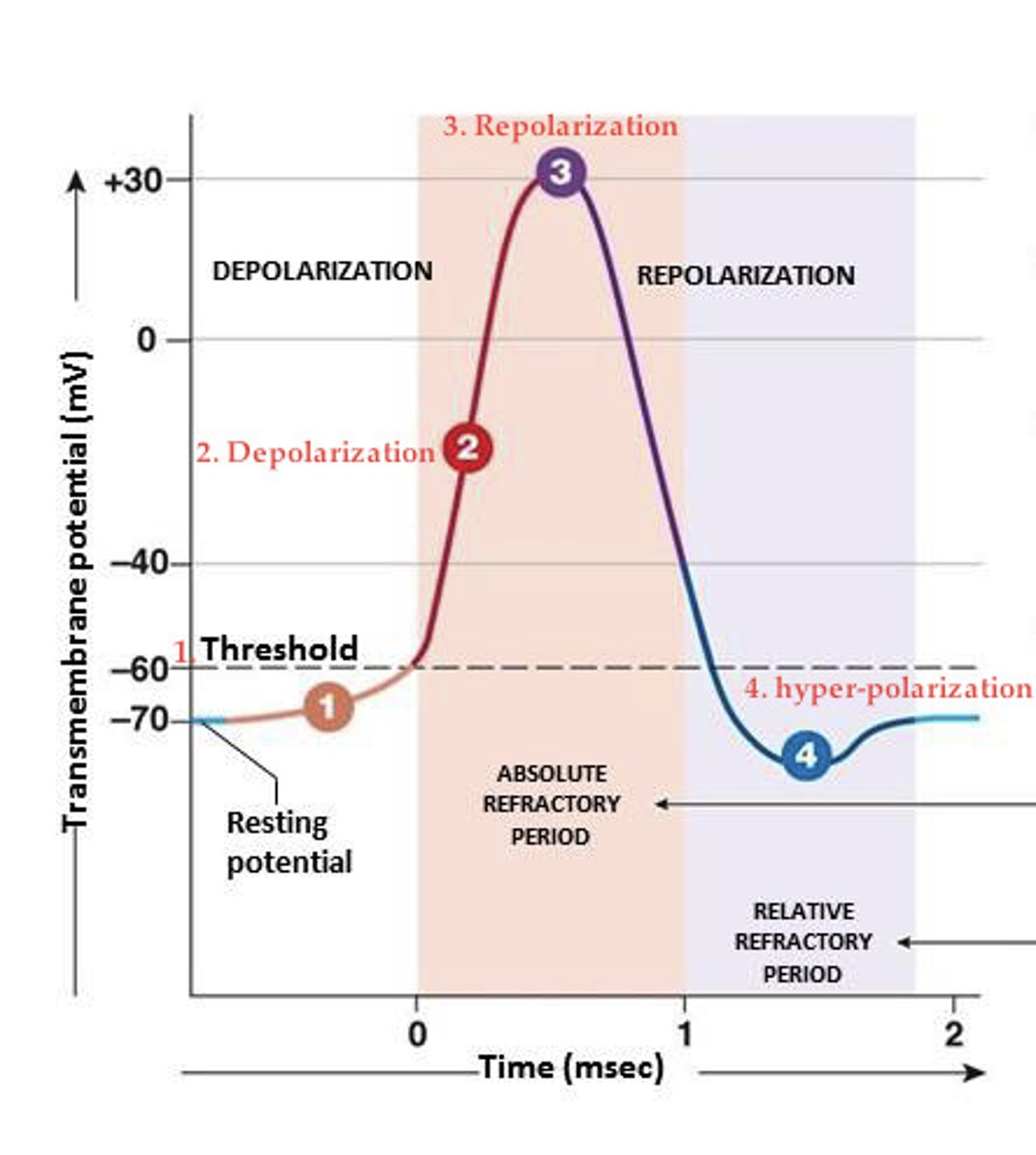
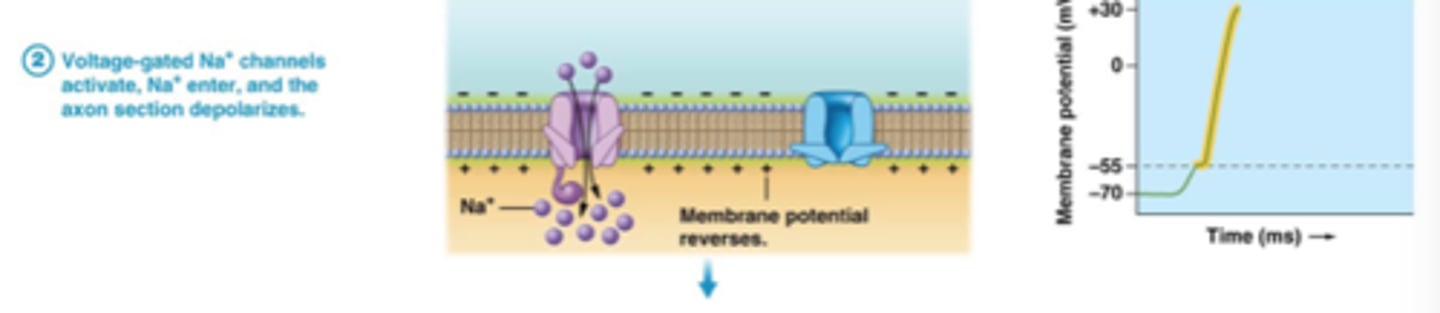
depolarization phase
sodium channels open
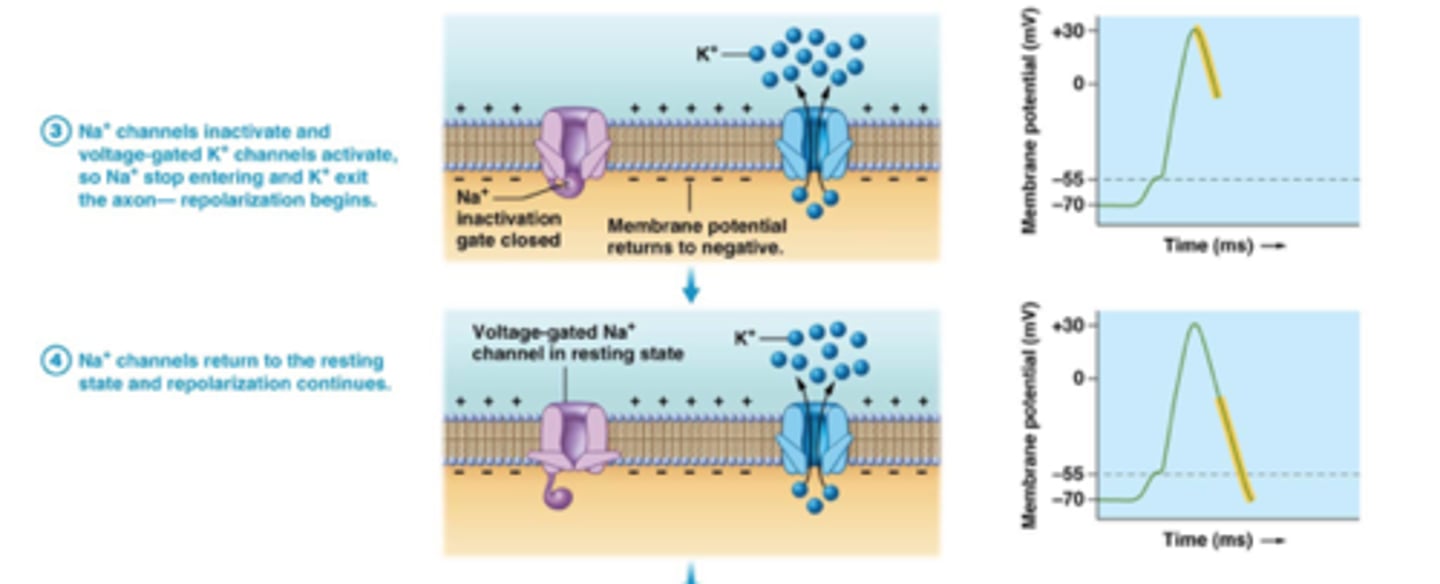
repolarization phase
sodium channels close and potassium channels open
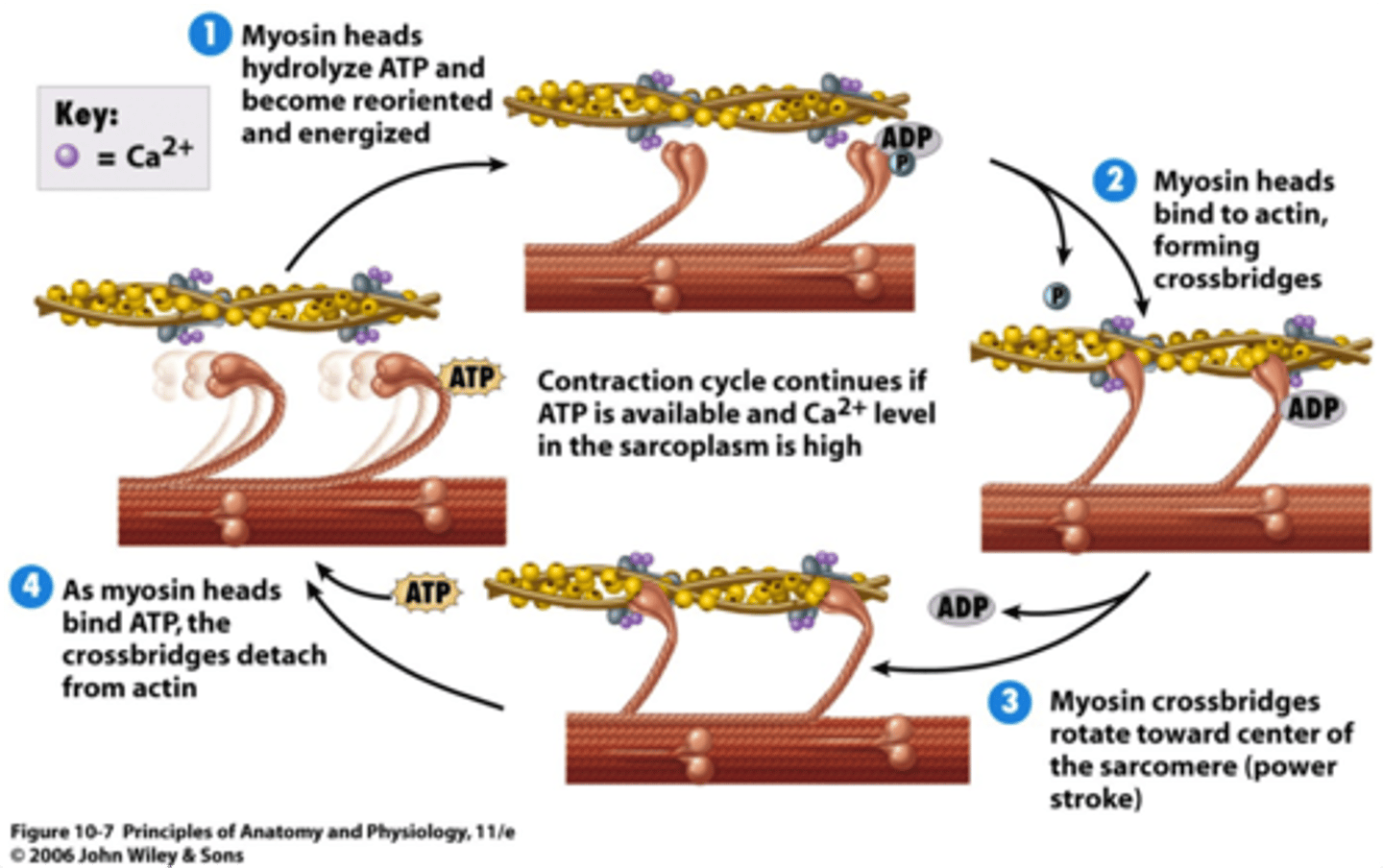
muscle contraction in sarcomere
letter. a
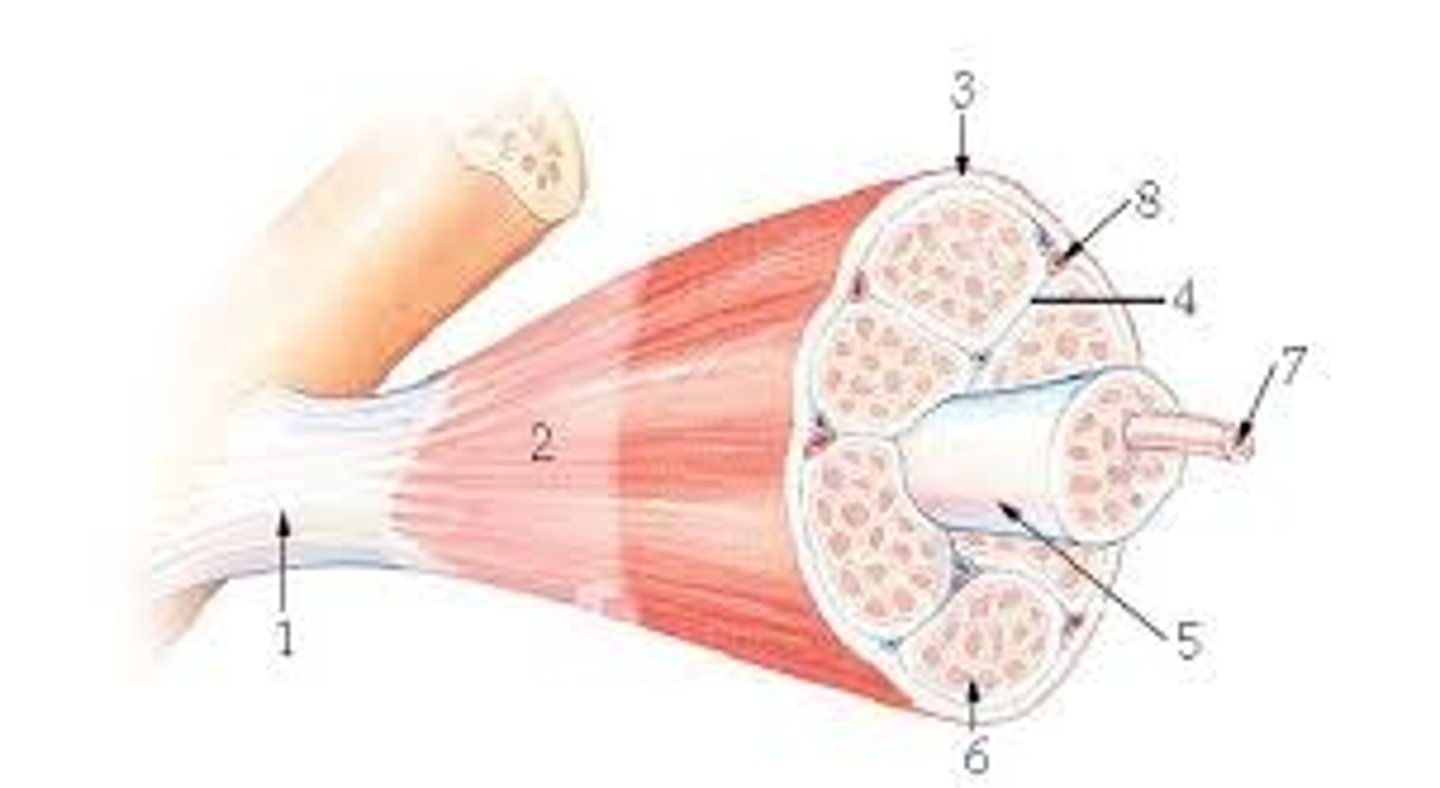
What letter is the muscle facia
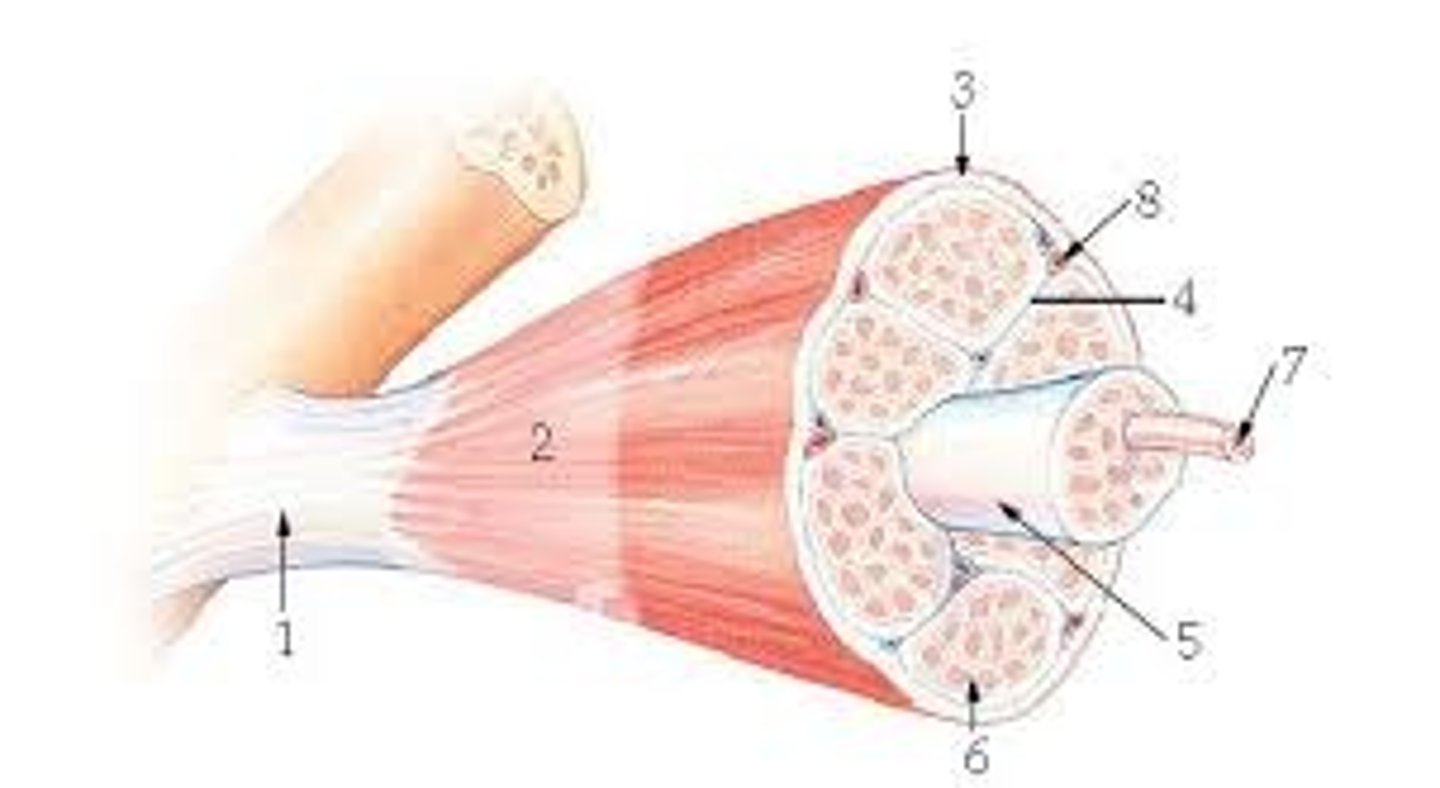
What letter is the muscle fascicle?
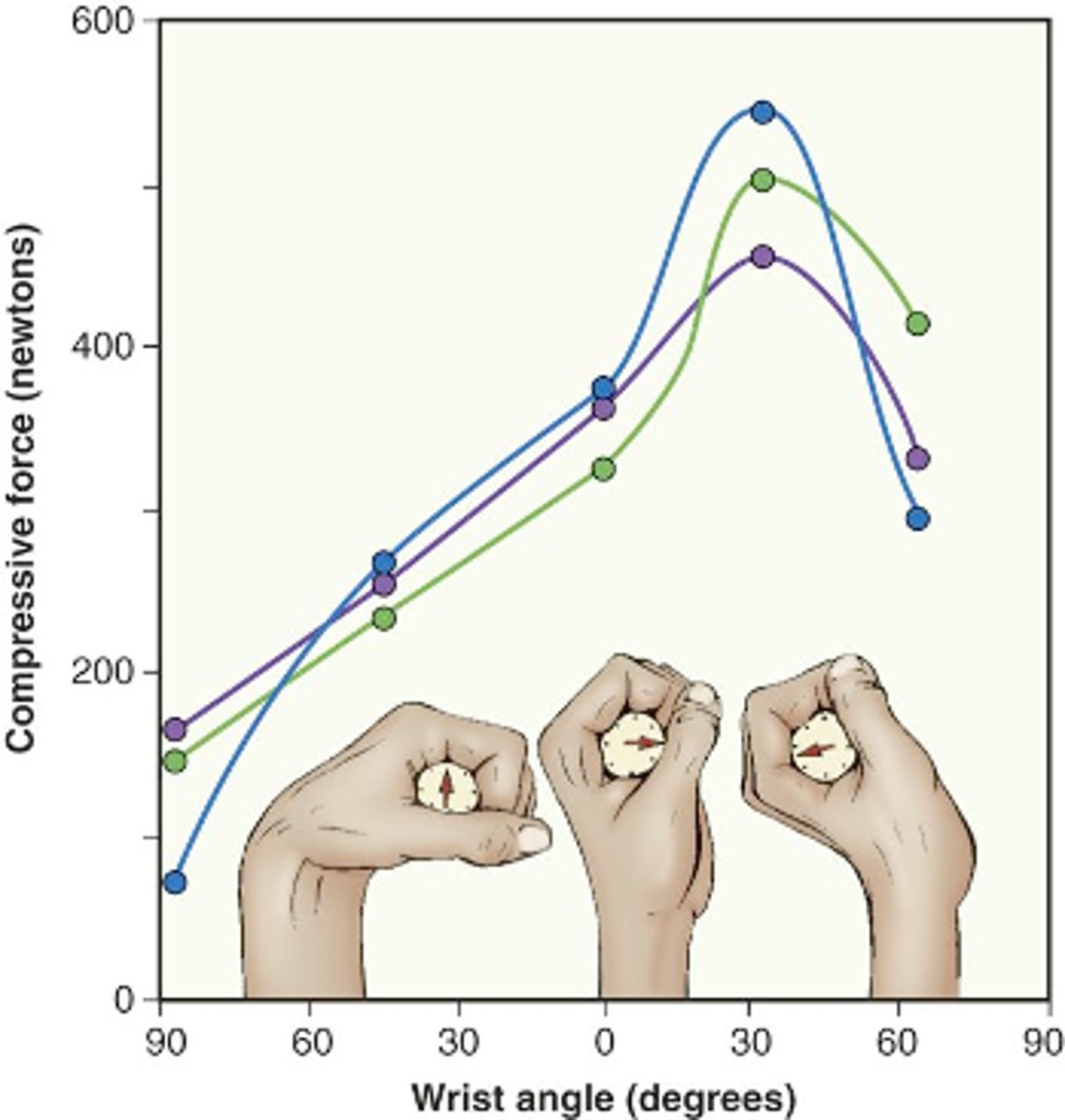
Grip Strength
Force exerted by hand during gripping.
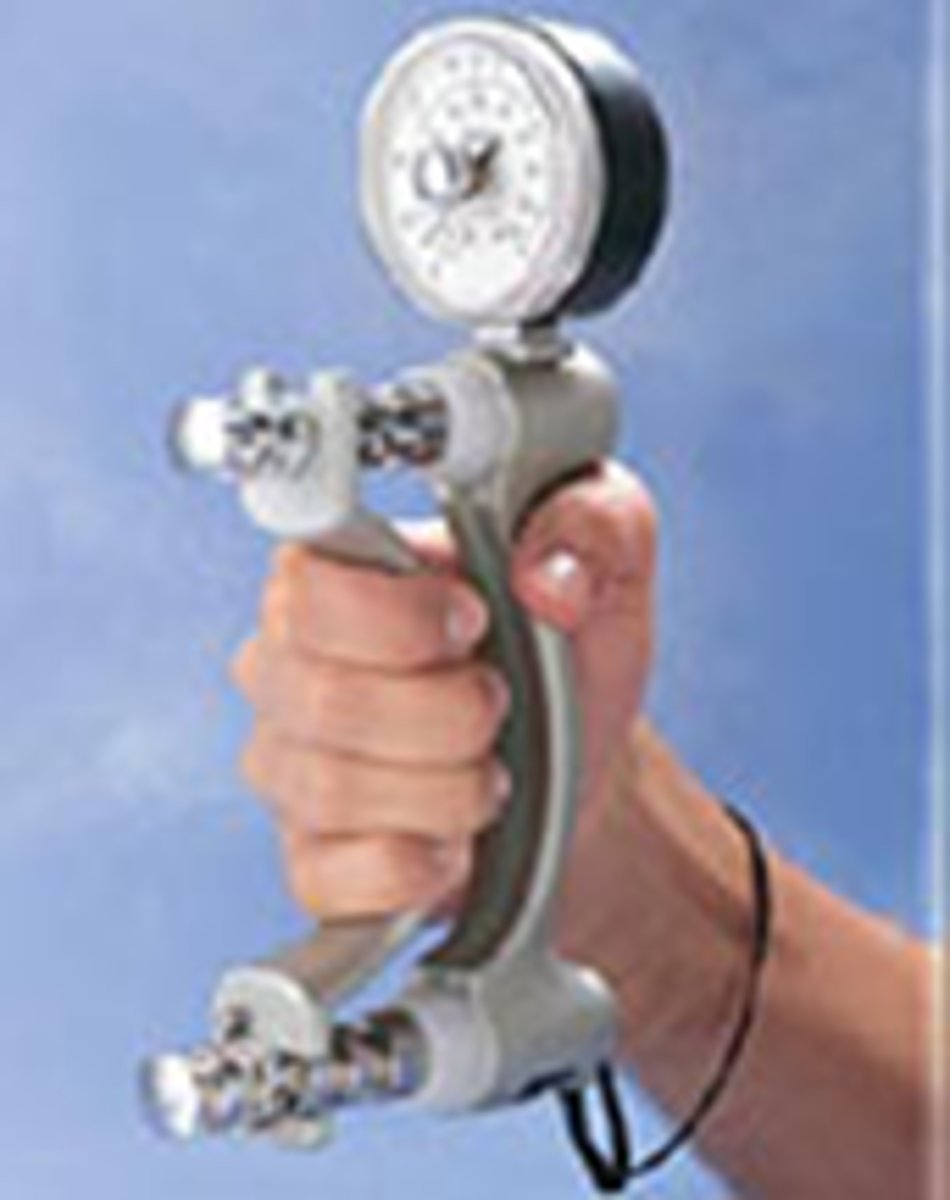

Grip strength
C7, C8, T1
muscle twitch
a motor unit's response to a single action potential of its motor neuron
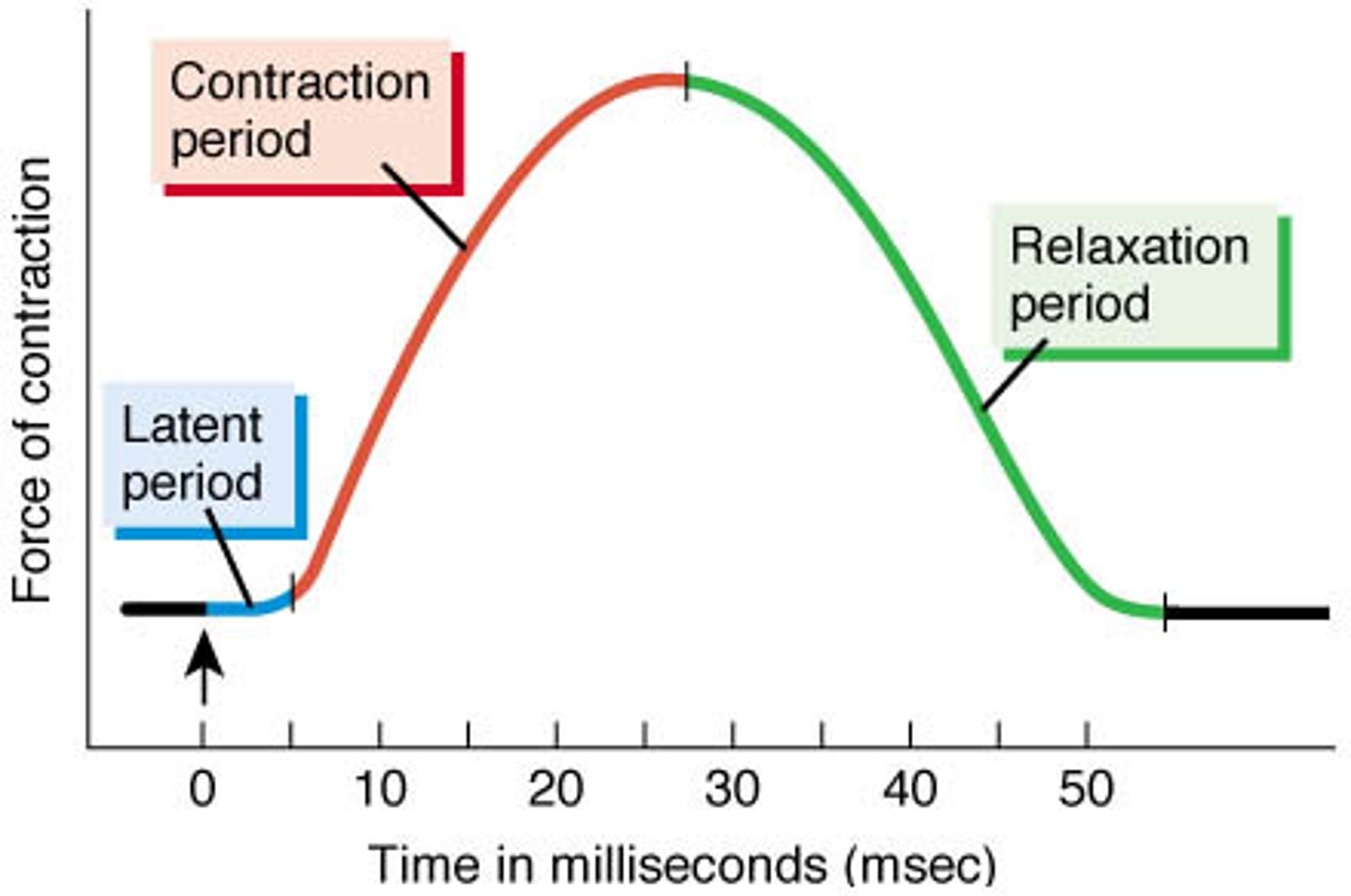
latent period
time between application of a stimulus and the beginning of a response in a muscle fiber
relaxation period
during this time, calcium ions are actively transported back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, myosin-binding sites are covered by tropomyosin, myosin heads detach from actin, and tension in the muscle fiber decreases
What is the role of ATP in muscle contraction
ATP attaches to myosin which allows the cross bridge cycle to begin which allows muscle contraction to occur
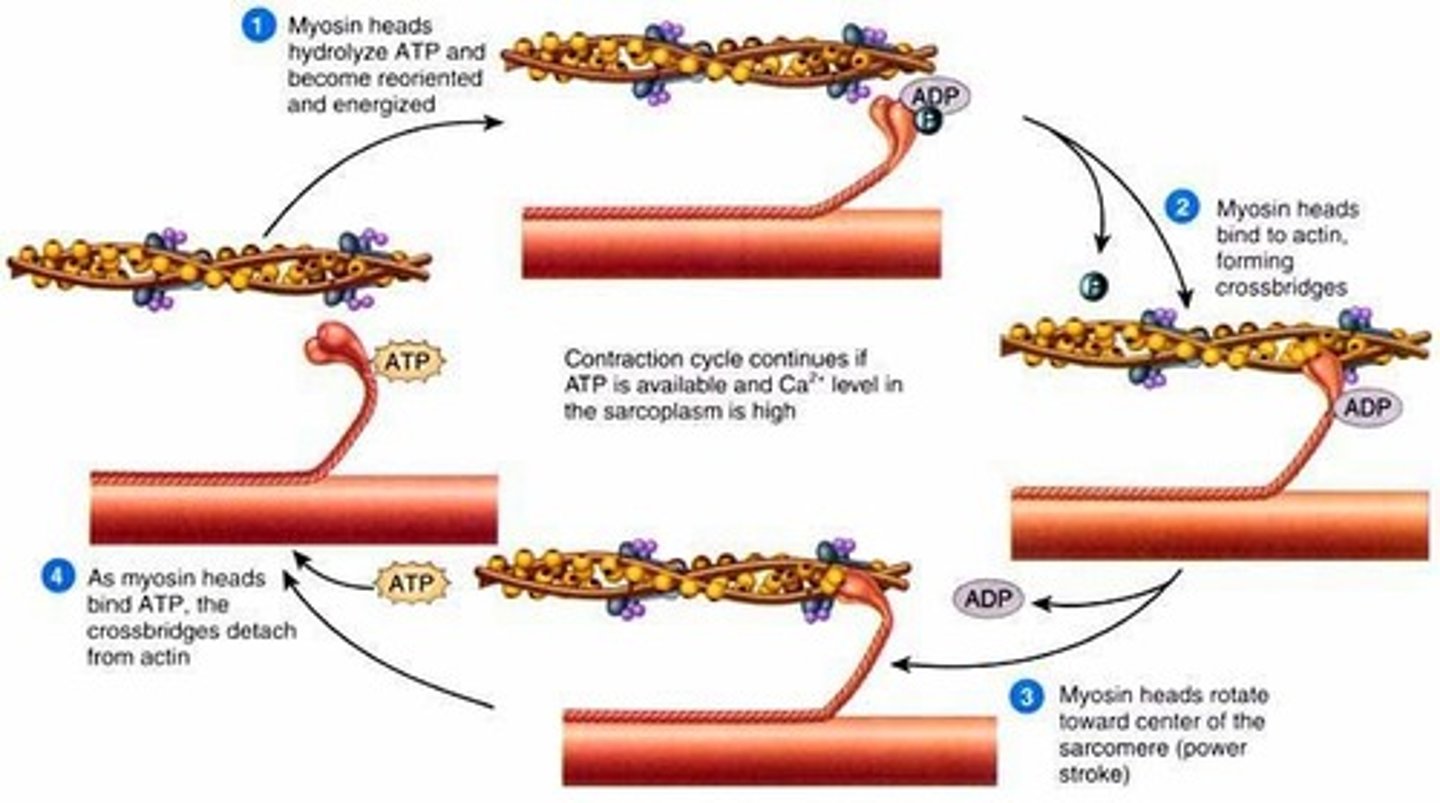
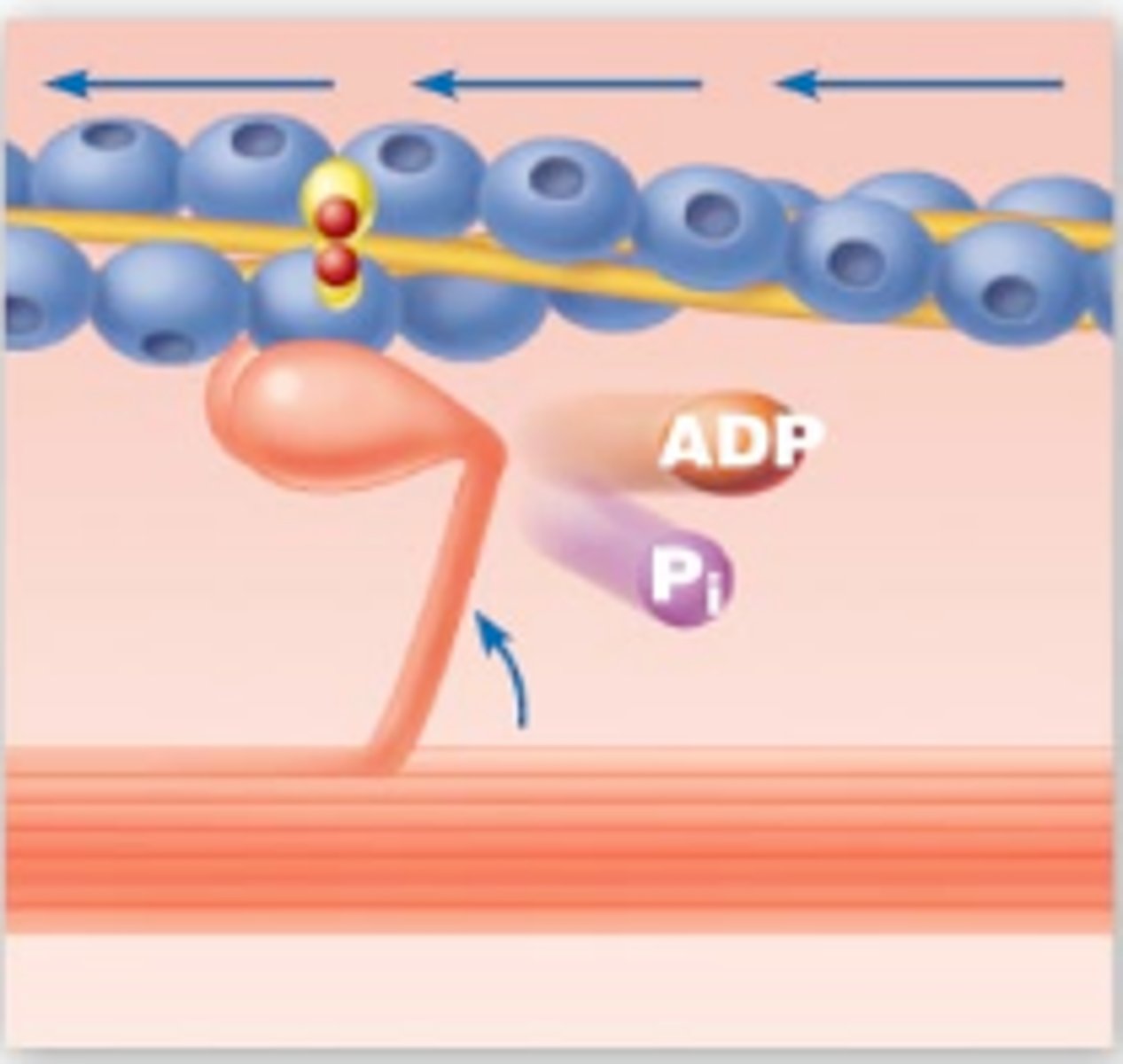
What causes the power stroke
release of ADP and Pi
(the hydrolysis of ATP provides the energy for the power stroke. Energy is transferred from ATP to the myosin head.)
What is the refractory period
a period immediately following stimulation during which a nerve or muscle is unresponsive to further stimulation.
muscle tension
Force exerted by a contracting muscle.
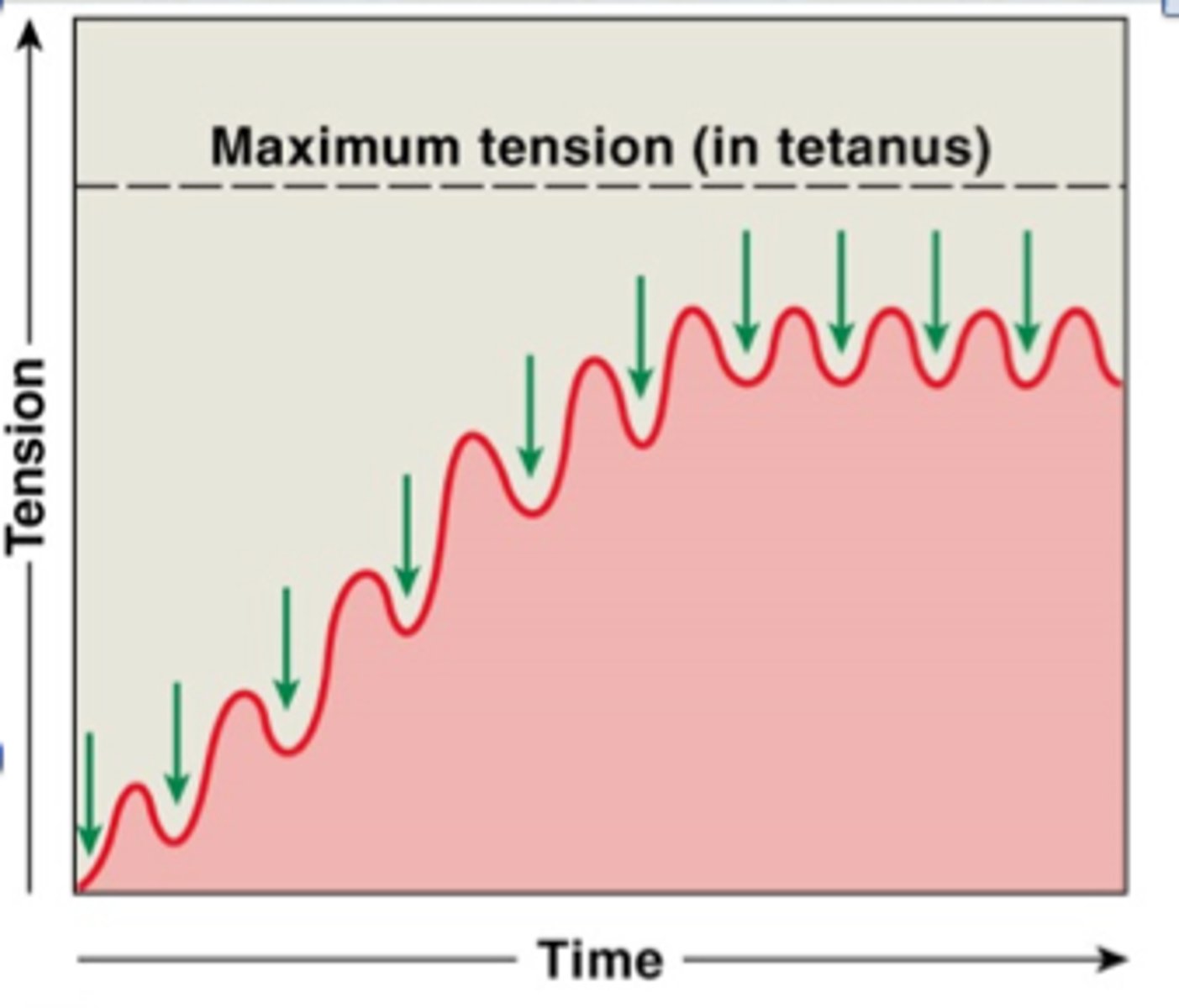
what is wave summation
When a muscle receives a 2nd stimulus before the 1st is complete,
the contraction will be stronger.
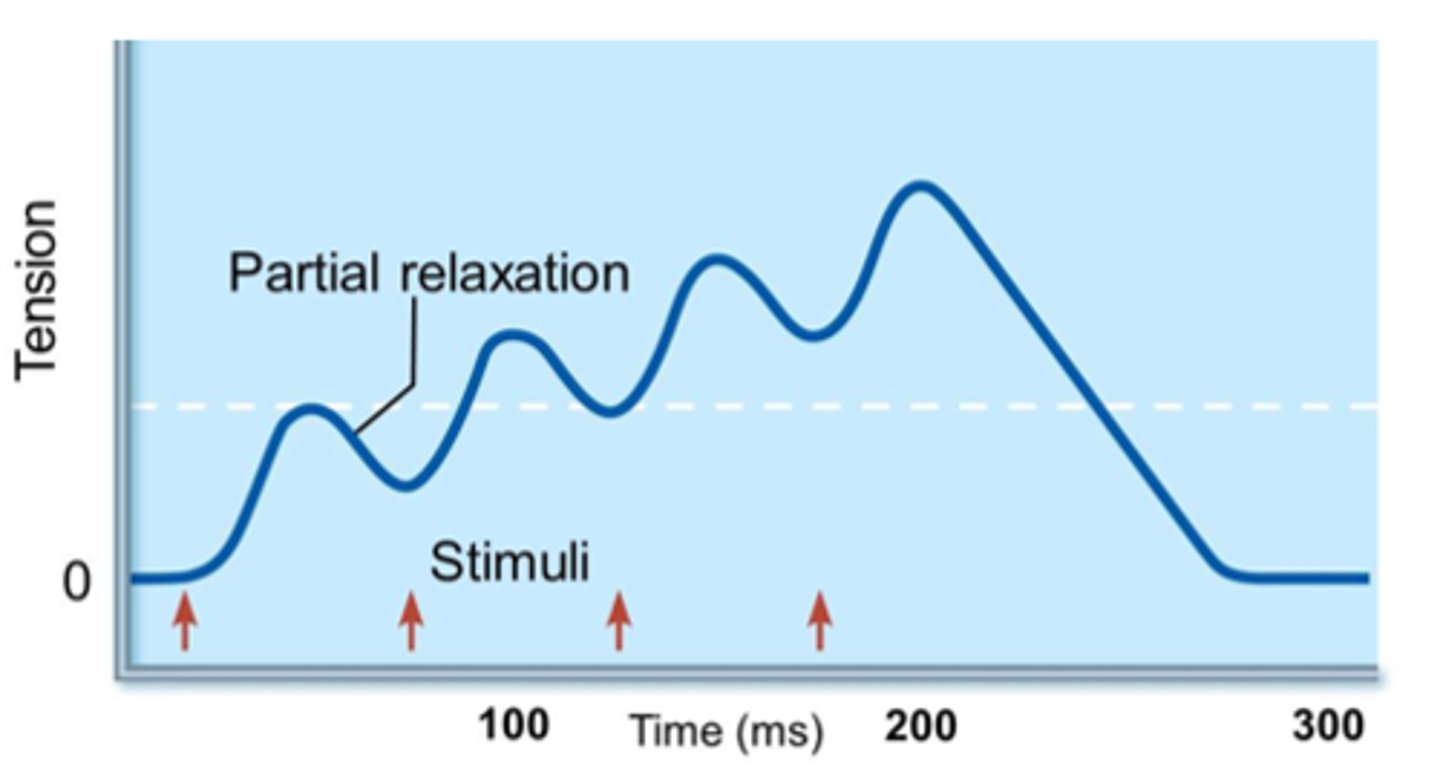
unfused tetanus
type of wave summation with partial relaxation observed between twitches
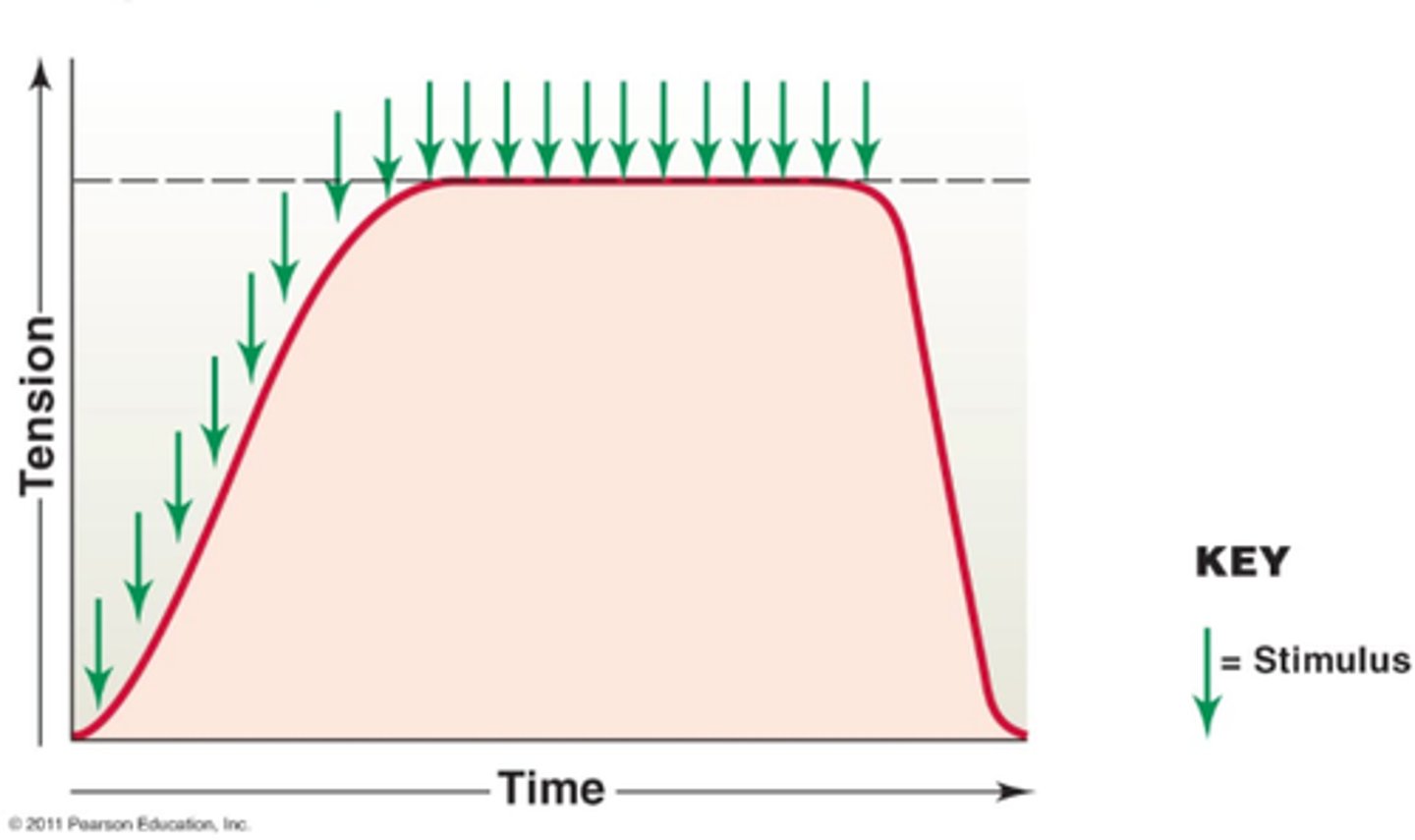
fused tetanus
when stimulus frequency is so high that no muscle relaxation takes place between stimuli
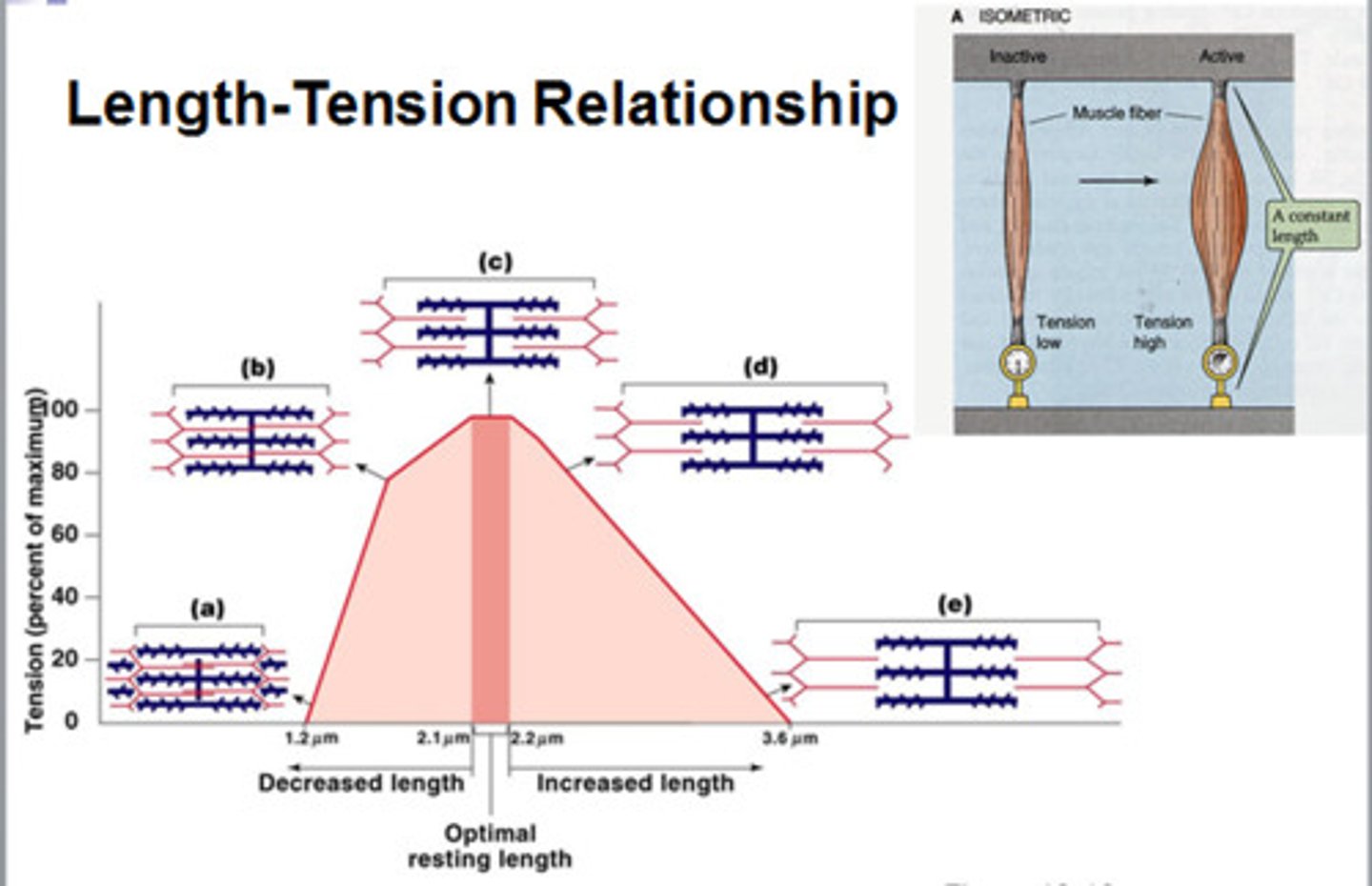
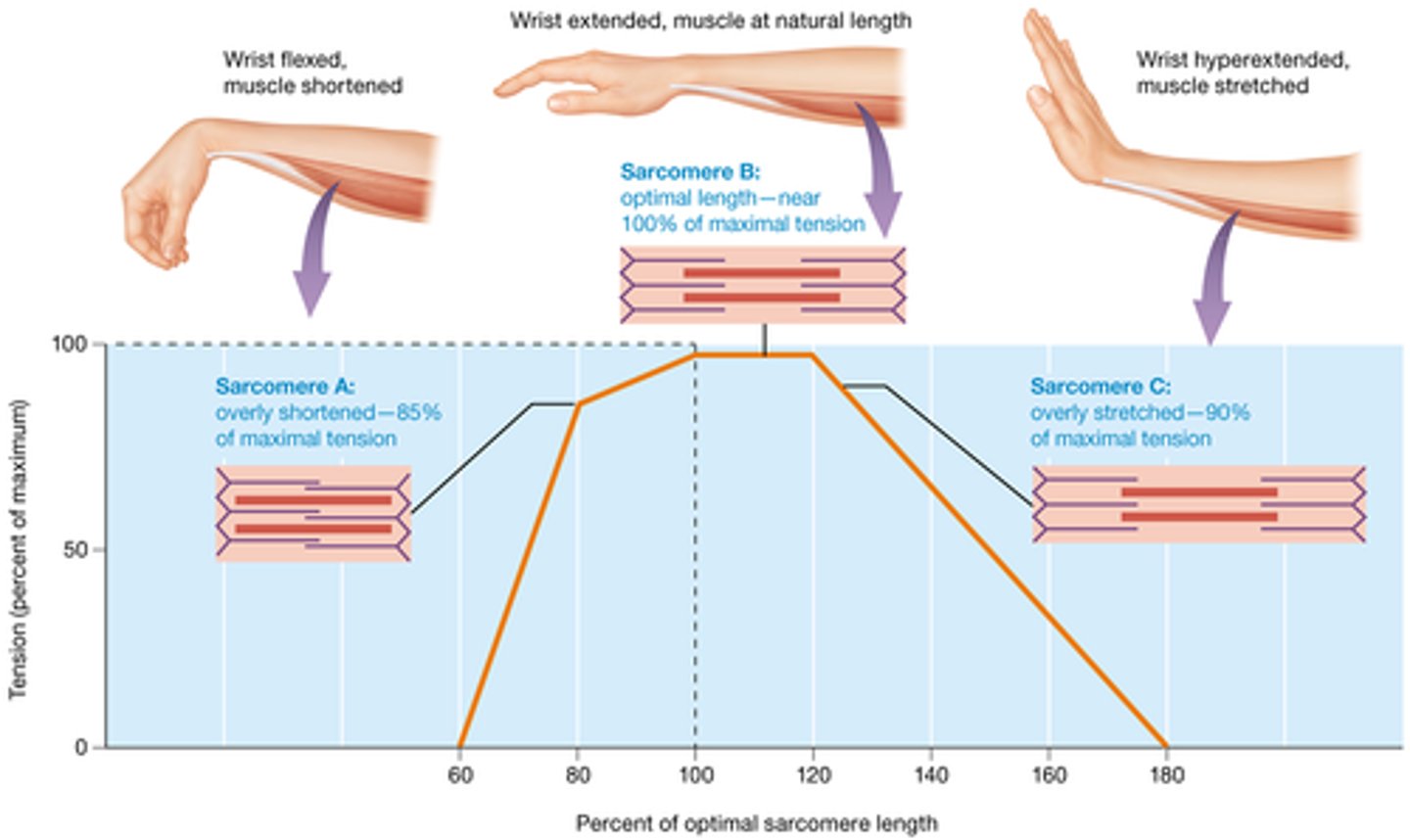
optimal length of a sarcomere
lots of actin-myosin overlap and plenty of room to slide
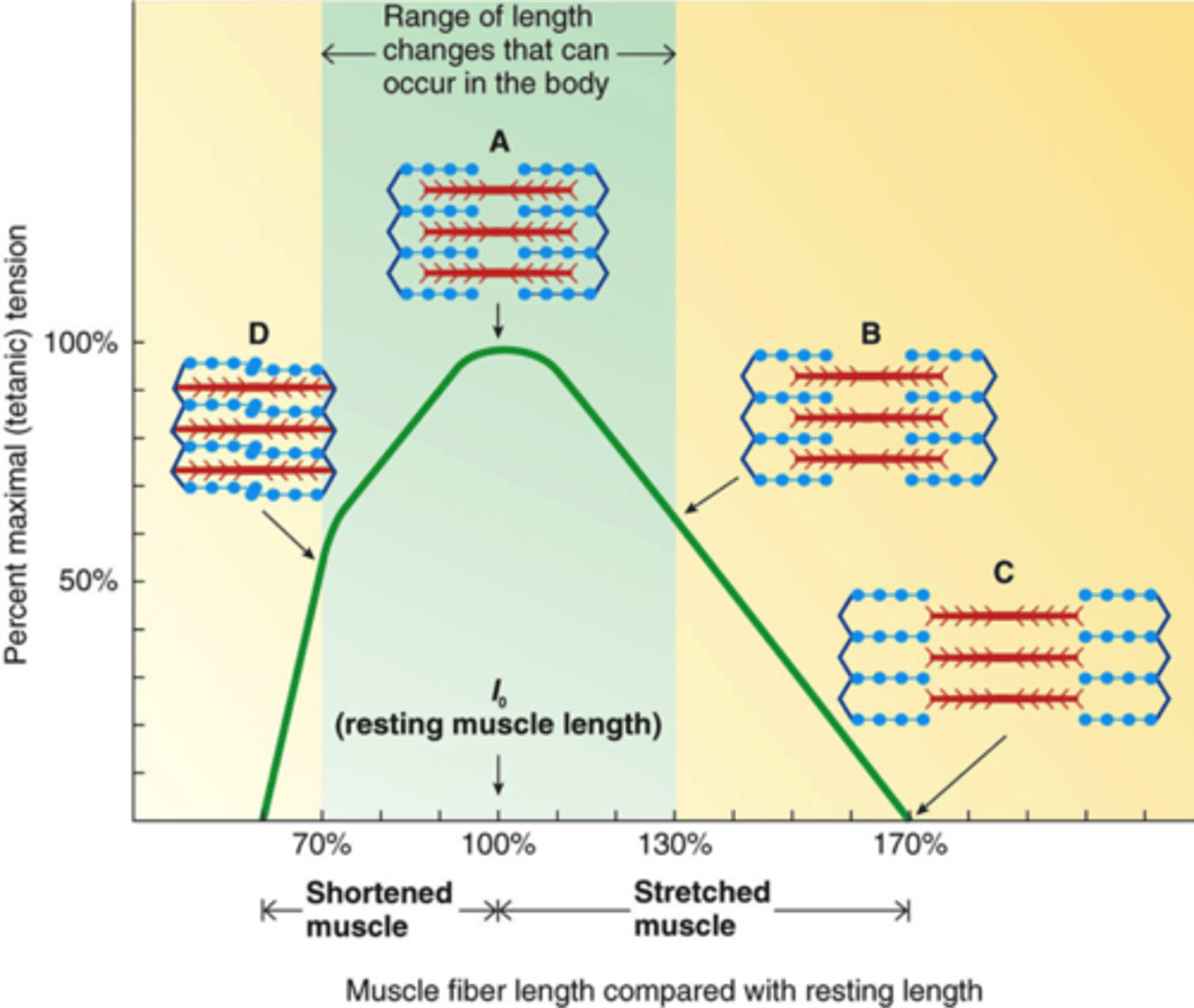
length - tension relationship
resting length of a muscle and the tension it can produce at that length
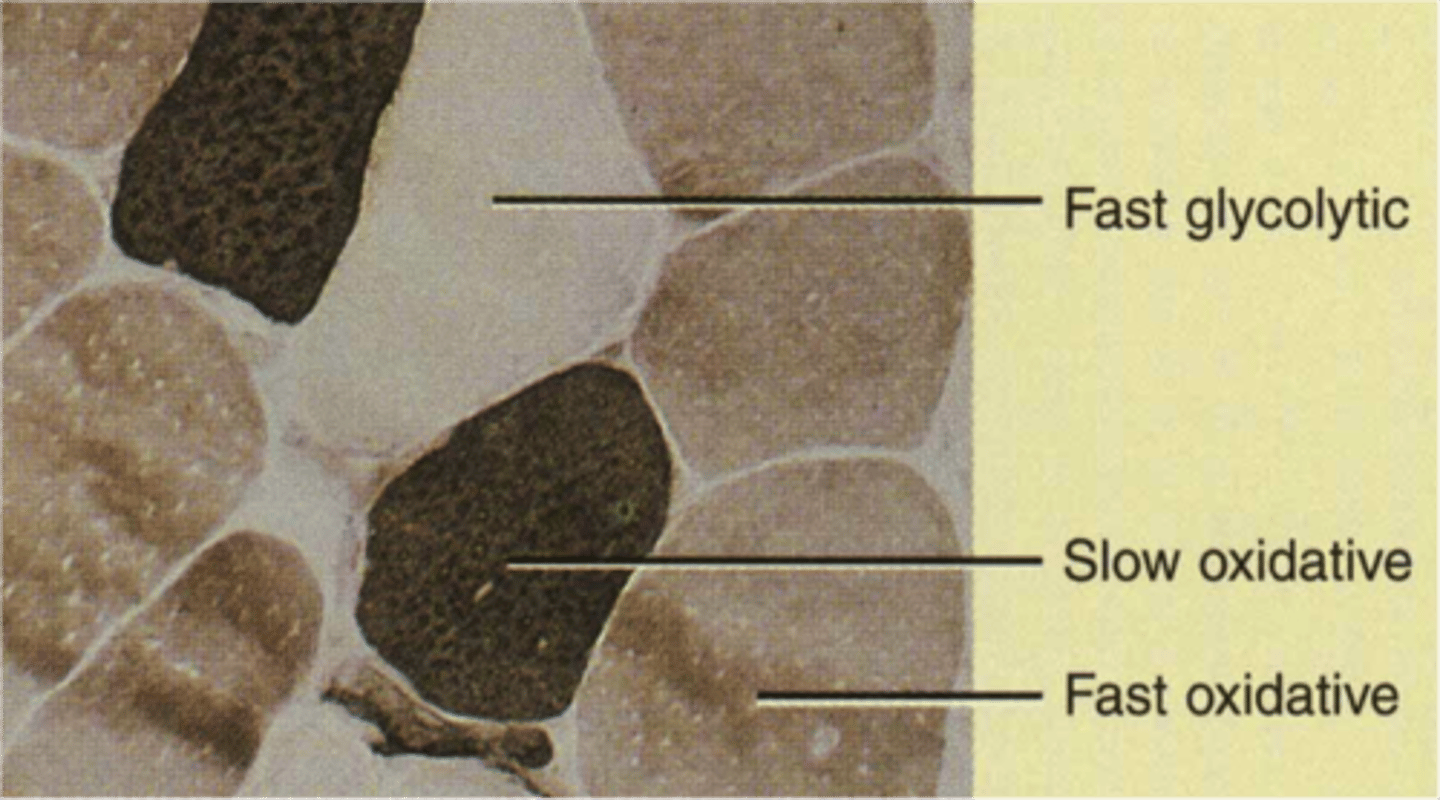
type I muscle
Slow twitch muscle fibers that are efficient at using oxygen to generate fuel (Aerobic). Continuous contractions for longer sustainable exercise, such as cycling, hiking, distance running.
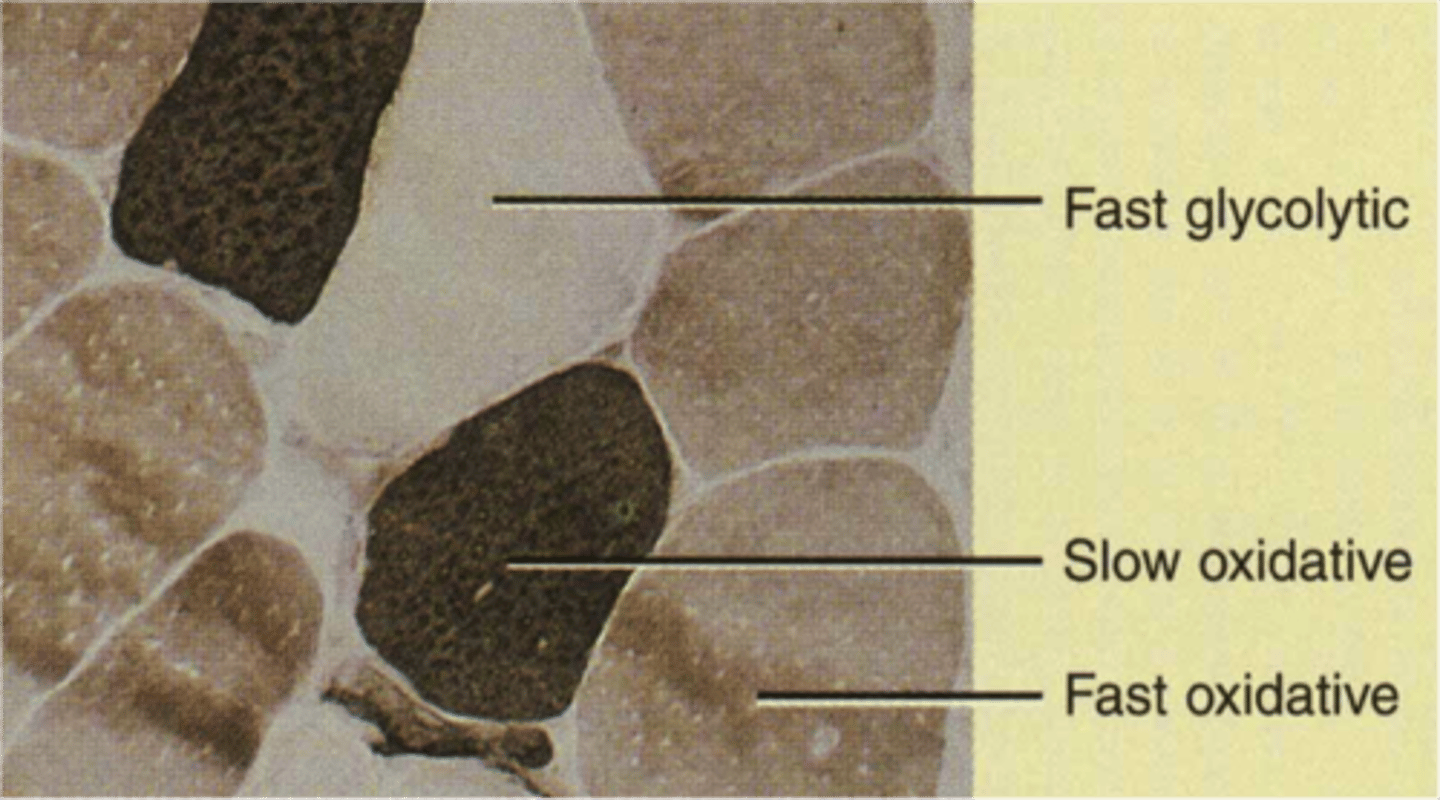
Type II muscle fibers
Muscle fibers that are larger in size, generate higher amounts of force, and are faster to fatigue.
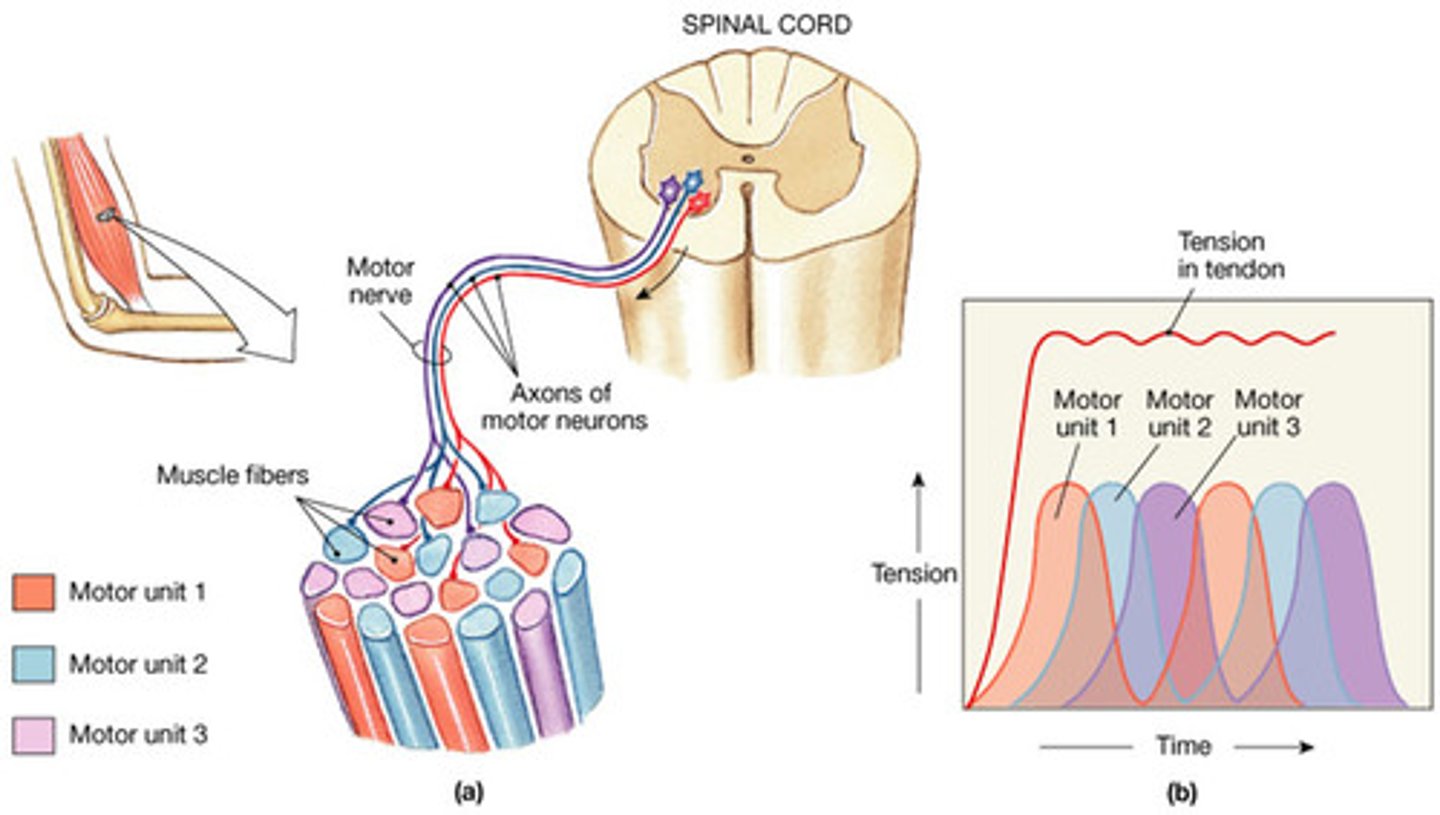
muscle recruitment
increase in the # of motor units being used to increase strength of contraction
muscle tone
the state of balanced muscle tension that makes normal posture, coordination, and movement possible
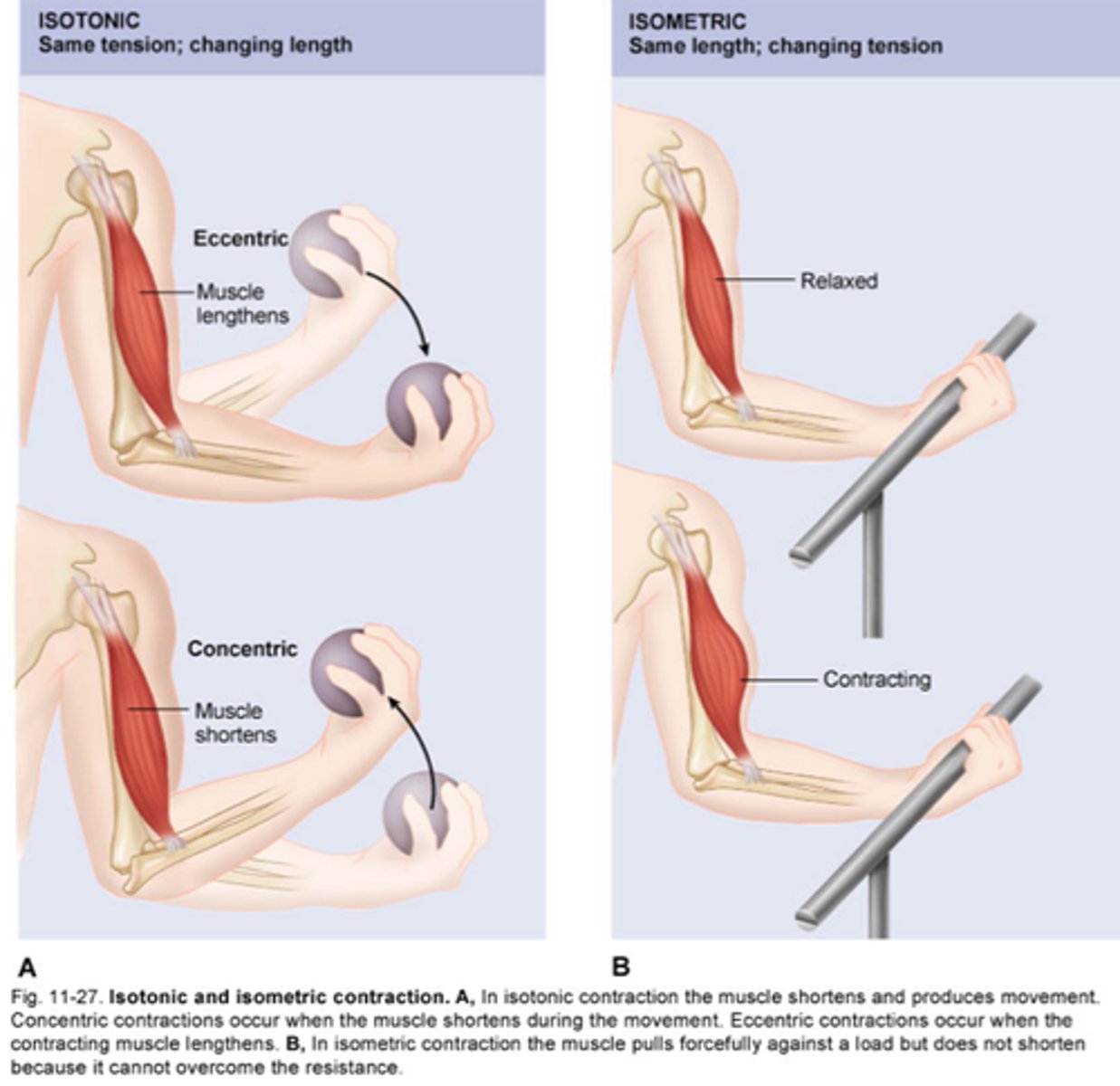
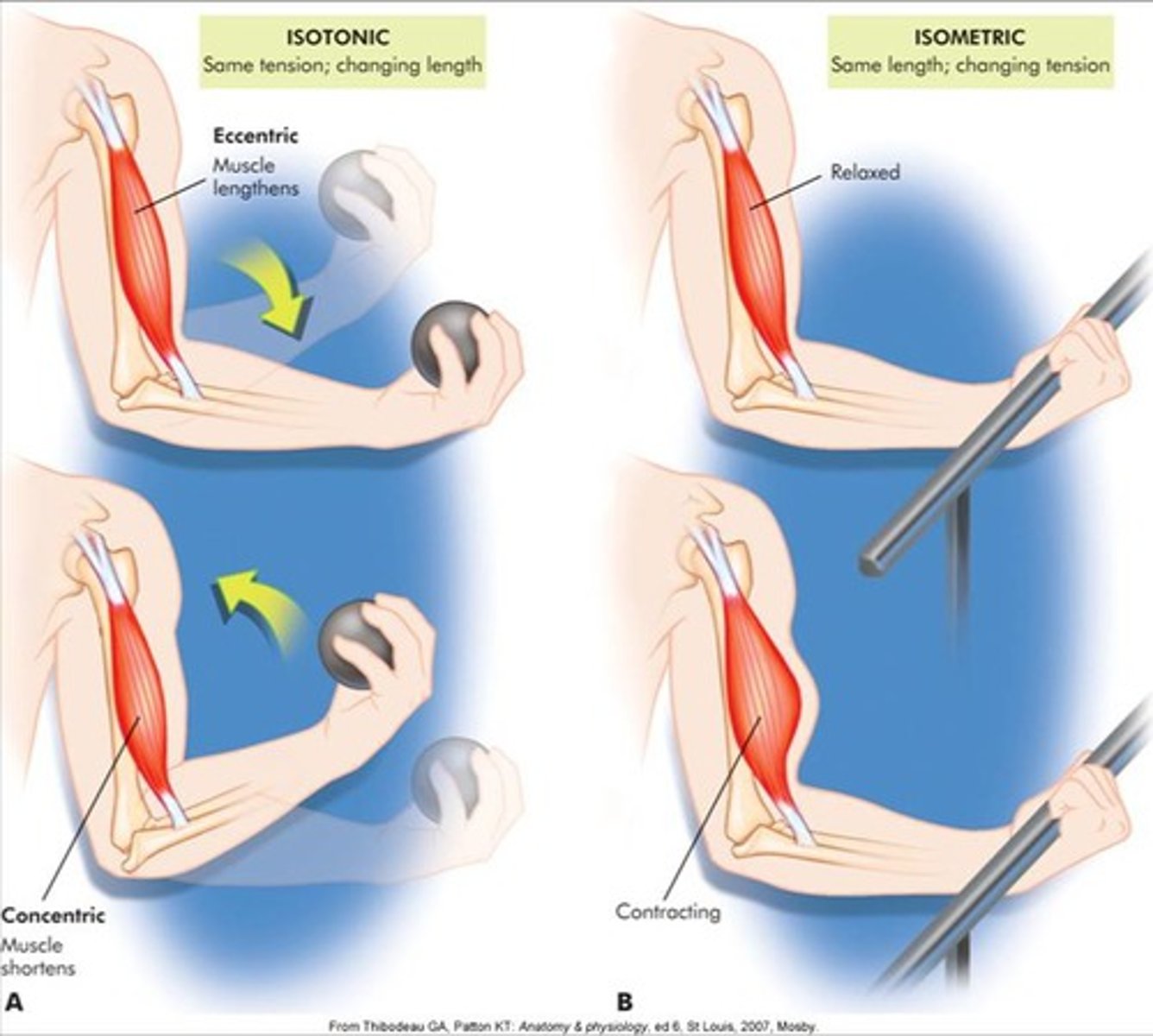
isometric
same length, changing tension
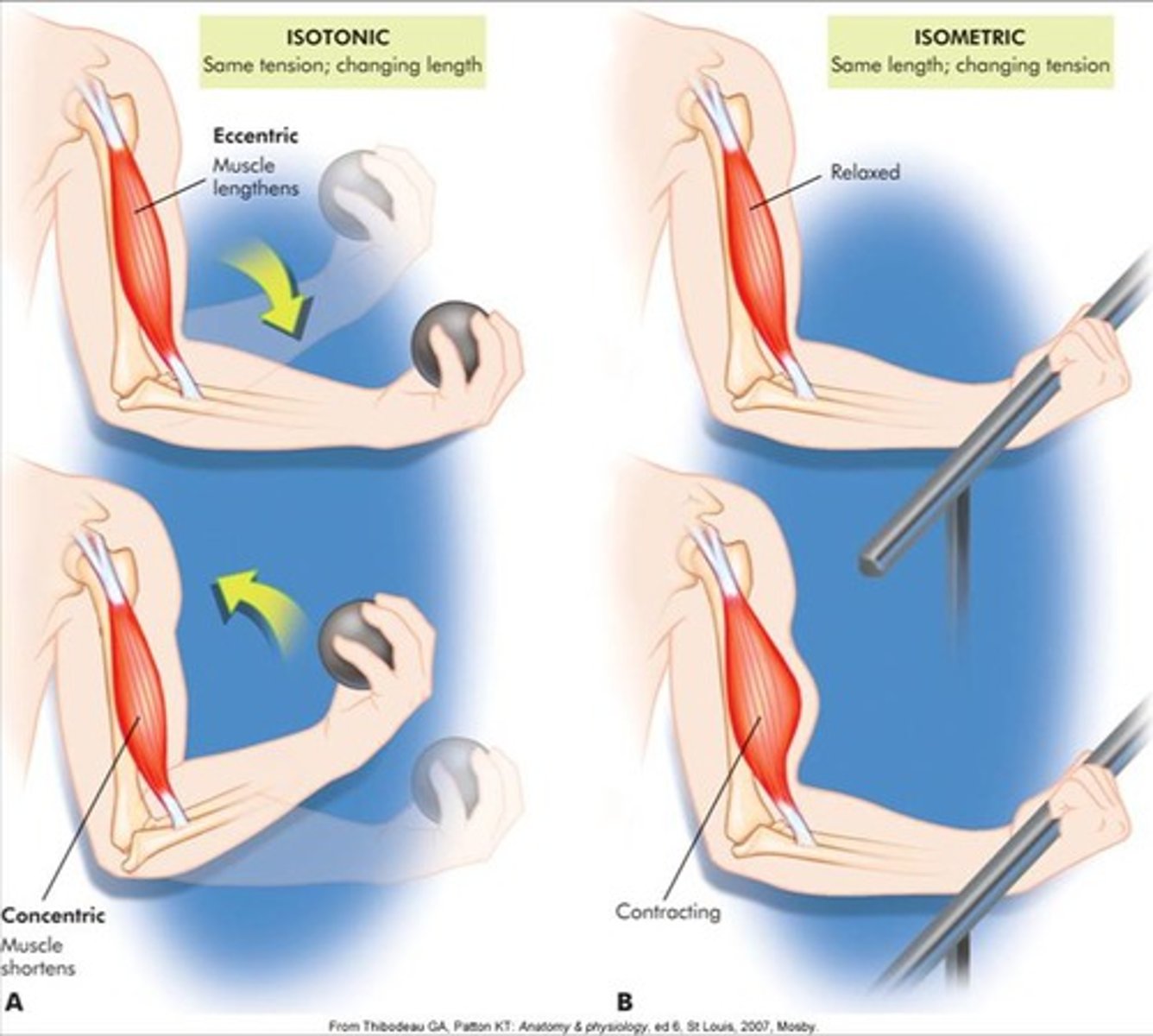
isotonic muscle contraction
muscle changes in length with no change in tension
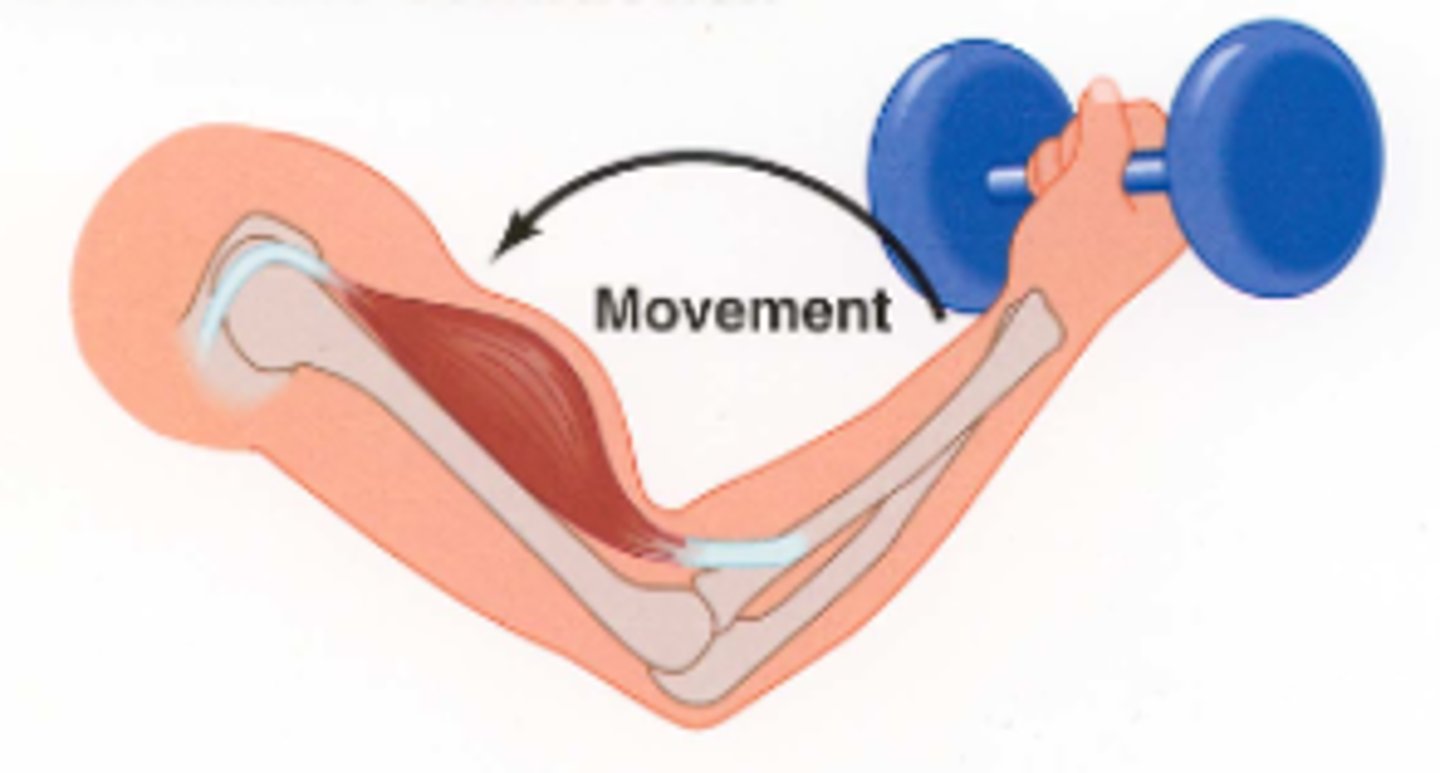
isokinetic muscle movement
Muscle contractions without resistance. Resistance is provided at a constant rate by an external devise.
Ex: Rehabilitative exercises for knee and elbow injuries and lifting weights.