Preventive Exam 3 [Periodontal Disease: Association with Diet: Marshall]
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Chronic Diseases
Disease with a slow progression which once developed is slow to resolve
- Systemic: Obesity, hypertension, cardiometabolic disease
- Oral: Periodontal disease
Public health concern of chronic diseases
60% of adults have 1+ chronic diseases
42% of adults have 2+ chronic diseases
12% of adults have 5+ chronic diseases
Prevention is very important
Risk factor definition
An attribute or exposure that increases the chances of an outcome
- Nature: Not modifiable (Age, gender, genetics)
- Nurture: modifiable (smoking, alcohol use, diet etc)
An individuals risk is shaped by
by both nature and nurture
Periodontal disease
Complex chronic inflammatory disease
Initiated by dysbiotic microbial plaque biofilm below gingival margin
Immune-inflammatory response contributes to sequelae of event
- Destruction of connective tissue
- alveolar bone loss
- tooth loss
Etiology of periodontal disease
Interaction between pathogenic bacteria and host immuno-inflammatory response
Predisposing factors:
Host
Environment:
- Diet related
-- Obesity
-- Malnutrition
Obesity is a risk factor for many of our chronic systemic diseases:
- Hypertension
- Cardiometabolic disease
- Cancer
- etc
Disease definition
A condition that impairs physiological function... resulting from causes such as infection, genetics or environmental stress
Social considerations of obesity: A disease or a state of being?
The WHO and AMA have defined obesity as a disease
Consequences of obesity
Premature morbidity and mortality
Psycho-social/emotional consequences
- Discrimination
- Lower wages
- Lower quality of life
- Lower self-esteem
- Increased susceptibility to depression
Memoirs of an Obese Physician: Takeaway
" Physicians also harbor a similar prejudicial view of obese patients. As a medical student and now as an attending physician and as someone who has been obese for much of my life, I have had to face both simmering and overt prejudice from the profession I hold in the highest esteem"
- Joseph Majdan
There is some prejudice in healthcare profession
Main job is to take care of the patient
Patients who feel ostracized by their caregivers don't come back for care
Definition of obesity
Presence of excess body fats
- >22% in young men, >32% in young women
BMI
- Underweight <19
- Expected 19-25
- Overweight >25-30
- Obese >30-40
- Morbid obesity >40
Distribution of body fat (android vs gynoid)
Abdominal/visceral fat is associated with great risk of _____ ______ than subcutaneous fat
metabolic disease
Etiology of obesity
Energy in > energy out
Contributing factors of Etiology of obesity
Genetic predisposition
- 1 parent obese = 40% chance of it yourself
- 2 parents obese = 80%
- 0 parents obese = 20%
Fetal and maternal explanation
- Fetal programming
- Epigenetic mechanism
Thrifty genotype
- Ancestors that survive famine is less suited in our current environment
The nutritional transition
- urbanization and immigration
- Nutrition globalization
- Agriculture and ultra-food processing
Social/cultural perceptions of food/weight
MULTIFACTORIAL ETIOLOGY
Adipocytes expand to
store fat
Excessive adipose tissue
Hypertrophic obesity: enlarged adipocytes
Hyperplastic obesity: increased number of adipocytes
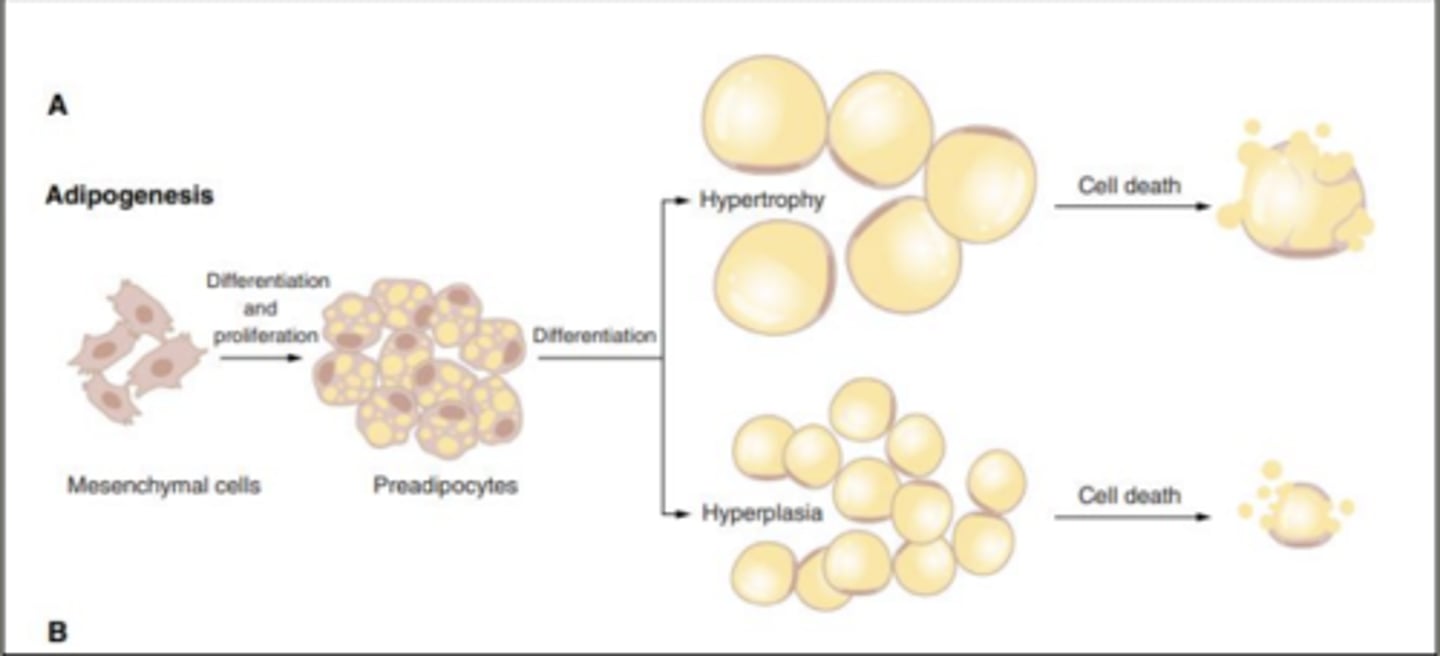
Adipocyte growth
Normal size = 70 microns
Signal to make more when they get to big
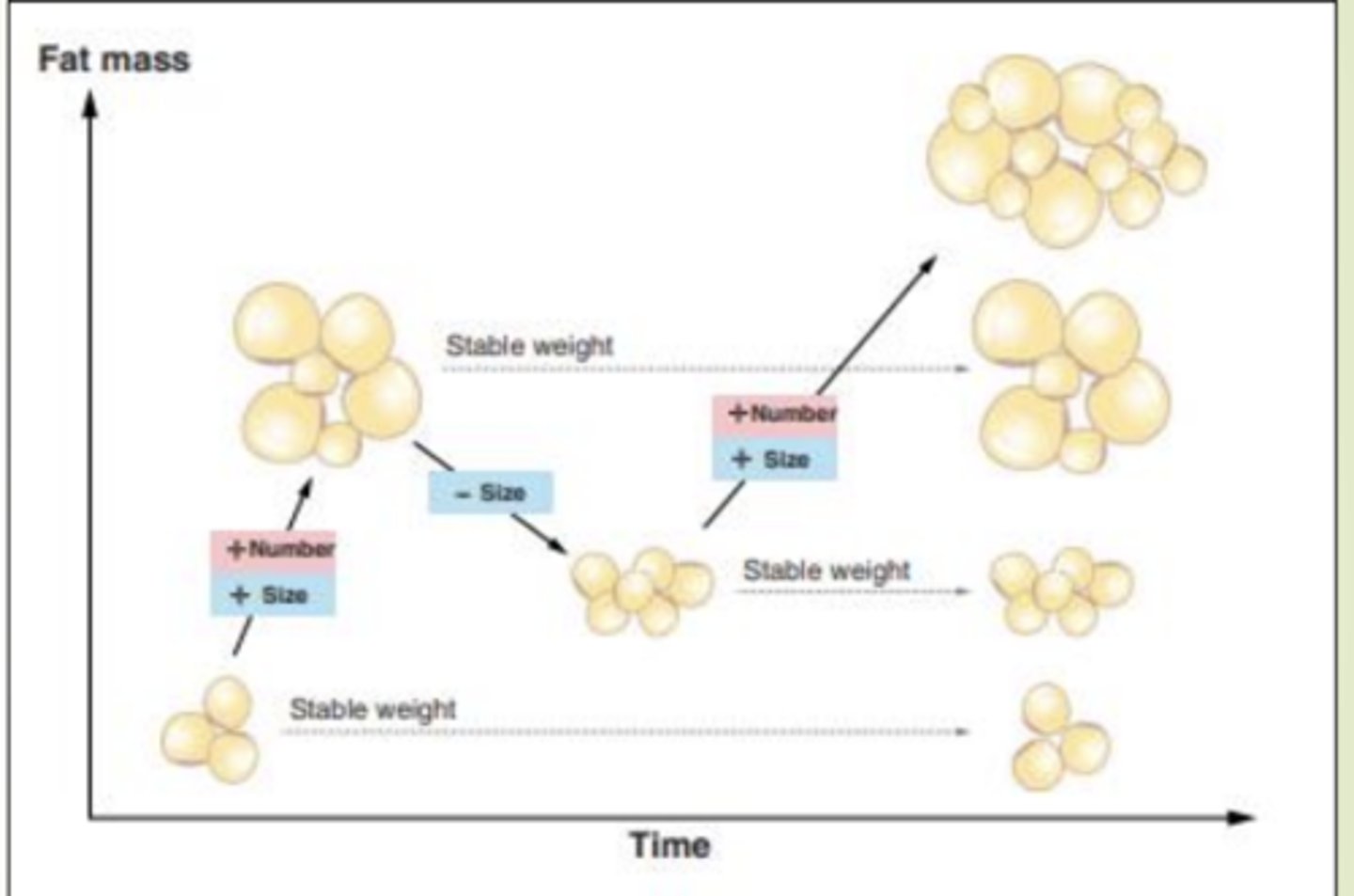
Adipocyte number
generally increases throughout childhood and adolescence
Constant during adulthood unless challenged
Does not decline
Adipose tissue is a blend of adipocytes of different
Sizes
We have a blend of fat cell sizes, some small, some large, and some very large,
Problems begin when the small adipocytes cannot...
And when large and very large adipocytes are...
Expand to hold more lipid
At capacity with limited ability to store more fat
Large and very large fat cells are associated with
impaired insulin response, increased secretion of free fatty acid and proinflammatory cytokins
Small fat cells with impaired ability to expand contribute to
metabolic complications
SUMMARY: Dysfunctional adipocytes IMAGE
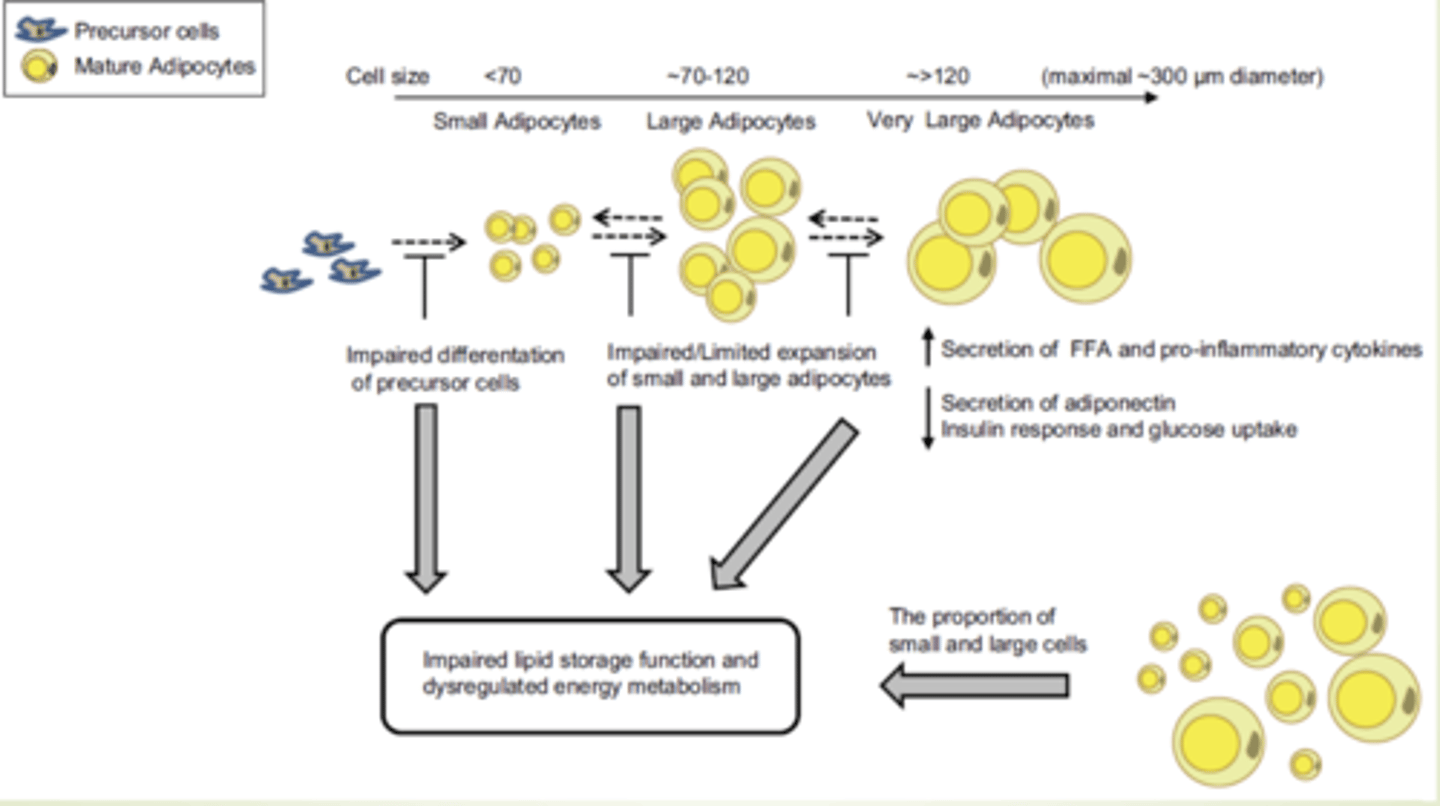
Problems with large adipocytes
Increased risk of
- Inflammation
- Metabolic dysfunction
- Non-obese type 2 diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes
- Cardiovascular disease
- Hypertension
TAKE HOME: The majority of the problem lies with the ______ adipocytes
large
TAKE HOME: The chronic diseases we typically associate with obesity are pretty much thought to be a result of the
Large fat cells
Not the number but the large size
Treatment of obesity
Energy deficit
Fat cells do not
go away
Fat cells can
return to "normal" size
If fat cells are to small
the body perceives starvation state- cascade of events to increase intake and efficiency of storage and to decrease energy expenditure
Normal fat cell size is thought to decrease
metabolic effects associated with obesity
Not all obese have
metabolic complications
Prevention of obesity
Energy balance (intake and activity)
Maintenance of a normal number of normal size adipocytes
Normal intrauterine environment
- Mother's weight WNL
- Expected pregnancy weight gain
- Balanced diet
Obesity and periodontal disease
Obesity:
- State of low grade chronic inflammation
- Impaired immune function
Periodontal disease
- Complex chronic inflammatory disease
- Immune system and inflammatory response contributes to disease process
STUDY: Association between obesity and periodontitis in US adults: NHANES 2011-2014
Objective: to explore association between periodontal disease and BMI and waist circumference in adults
Design:
Cross-sectional; NHANES 2011-2014
Subjects >30 years of age with complete BMI, waist circumference and periodontal data
Independent variable
- BMI
- Waist circumference
Dependent variable
- Periodontitis: mild + moderate + severe
Continuous BMI- Higher BMI associated with prevelence of periodontal disease; categorical trends mostly
Continuous WC: Increase in WC association with increase periodontal disease
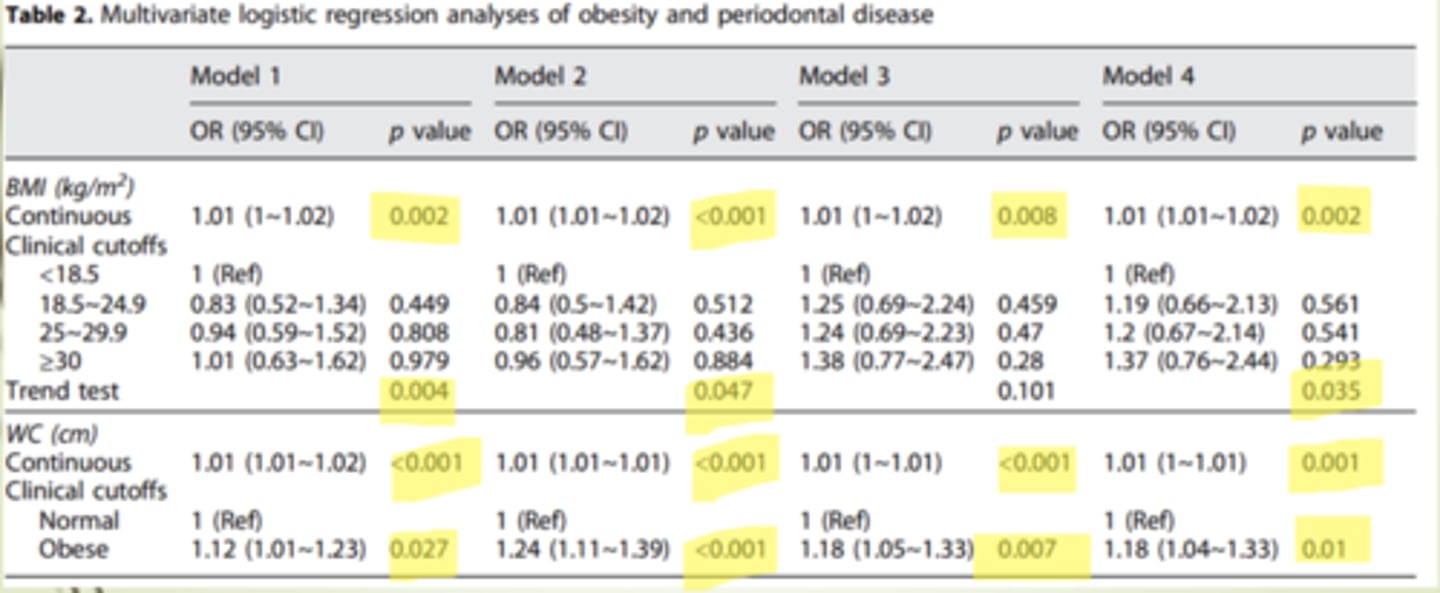
SUMMARIZE: Association between obesity and periodontitis in US adults: NHANES 2011-2014
Both BMI and waist circumference (abdominal adiposity) were associated with periodontal disease in adults
STUDY: Adiposity and periodontal disease
Objective: To investigate associations between obesity and periodontitis
Design: Cross sectional study; NHANES data
Subjects:
- 2452 nonsmokers
-13-21 years
Independent variables
- weight
- waist circumference
- skinfold thickness
- models adjusted for gender, race, poverty, dental visits and calcium intake
Dependent variable
- 1+ sites with both tissue attachment loss of 3MM and probing depth of 3MM
Results:
- Weight (7 kg higher with PD)
- Waist circumference (8cm higher for PD)
Skinfolds
- No association
SUMMARIZE: Adiposity and periodontal disease
Slight association between adiposity and periodontal disease, particularly adiposity
STUDY: Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome and Periodontal Disease
Objective: To determine if metabolic syndrome is an independent risk factor for periodontal disease and to identify which metabolic component contributes most to the association
Design: Cross sectional; NHANES III
Subjects: 7431; 20-90+ years
- 3517 males
- 3914 females
Independent variables: Metabolic syndrome
- abdominal obesity
- high triglycerides
- low HDL cholesterol
- Hypertension
-High fasting plasma glucose
Dependent variables
- Periodontal disease
Results
Metabolic syndrome
- Prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 17.3% and was higher in those who had Periodontal disease
- More pronounced in women than in men
Abdominal obesity:
- Increase risk of periodontal disease with increase abdominal obesity for both men and women
SUMMARIZE: Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Periodontal Disease
Association between periodontal disease and metabolic syndrome was more pronounced in women
Abdominal obesity was primary metabolic factor associated with periodontal disease in both men and women
SUMMARY: Obesity and Periodontal disease
An association exists between obesity and periodontal disease
- Visceral fat is likely more important than total body
- Fat cell size is likely more important than total body fat
Malnutrition
Loss of normal nutrients to function
Loss of normal nutrient function effects
Growth
Maintenance
Repair of damage tissue
Malnutrition can result from either a ________ in energy or nutrients or an _____ in energy or nutrient requirements
decrease, increase
either can lead to a decline in nutritional status leading to a cycle that eventually leads to increased morbidity and mortality
Vicious cycle of malnutrition

Cyril Enwonwu looked at the bacteria present in mouths of individuals who are either well-nourished or severely malnourished.
Shows: Percent of individuals in each group who have the bacteria present in the mouth
Facultative and aerobic flora were present in both the well-nourished and the malnourished individuals
Nonsporing anaerobes and Spirochetes only 20% of the well-nourished had the gram negative rods where most all the malnourished had them
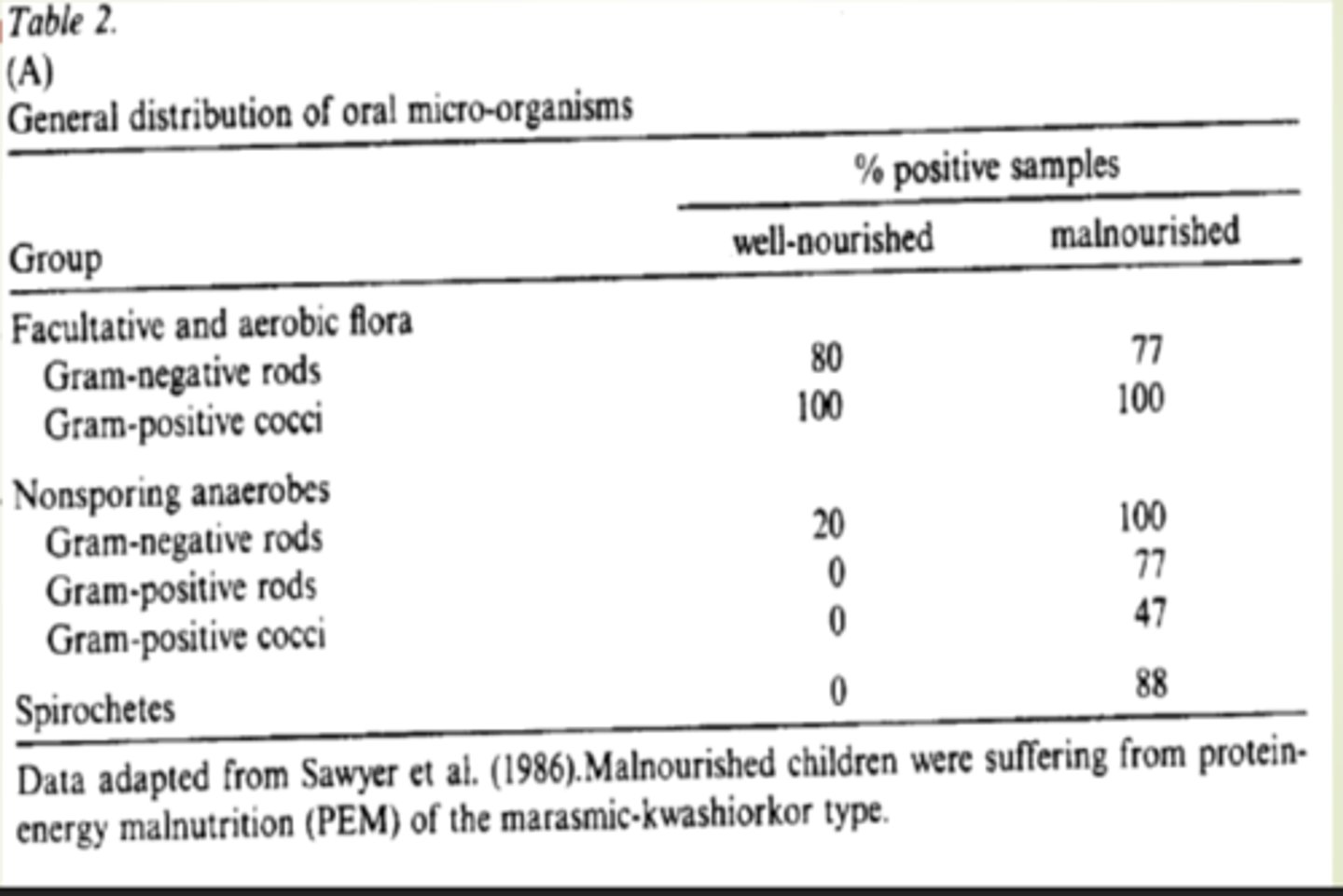
Anaerobic cocci and rods are present in more subjects with _____ than in _____
malnourishment than in well nourished

SUMMARY of Nourishment and bacteria
The distribution of oral bacteria differs between individuals with PEM and without
The different distribution has the potential to alter susceptibility to periodontal disease
Dietary intakes
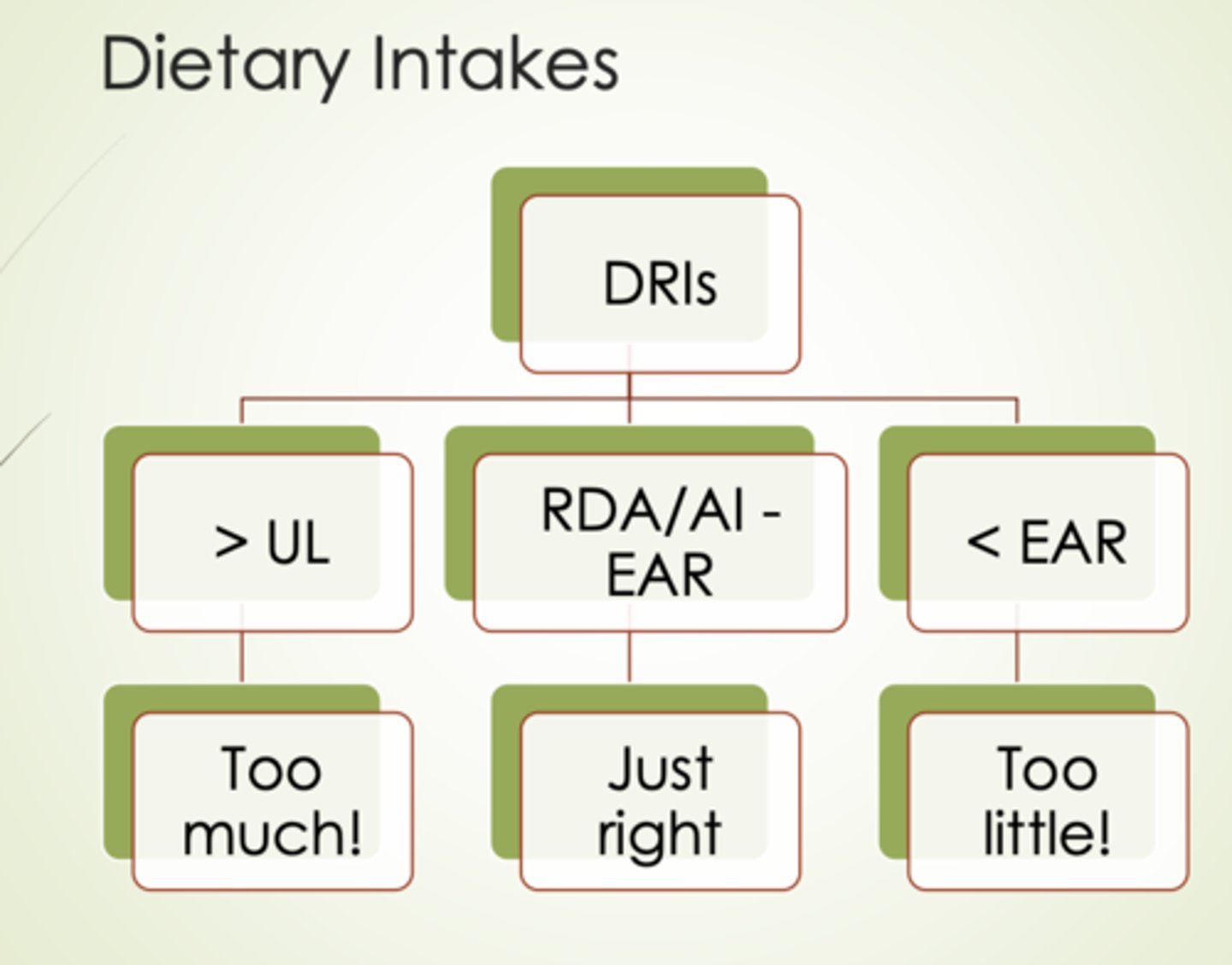
Serum/Tissue levels
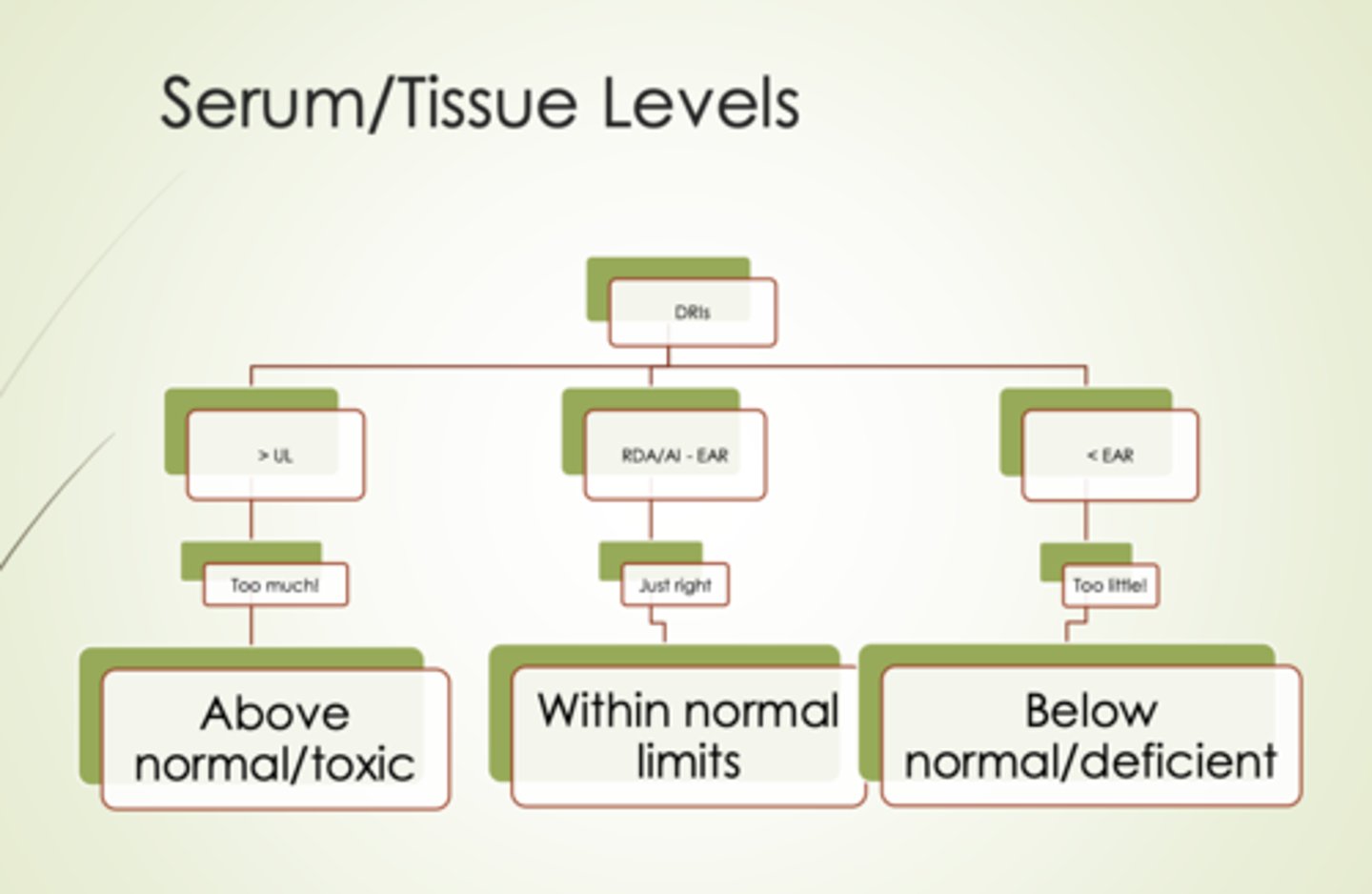
Supplement intakes
If you are at a above normal or toxic rate then taking supplements are likely to do harm and if you are adequately nourished its pointless
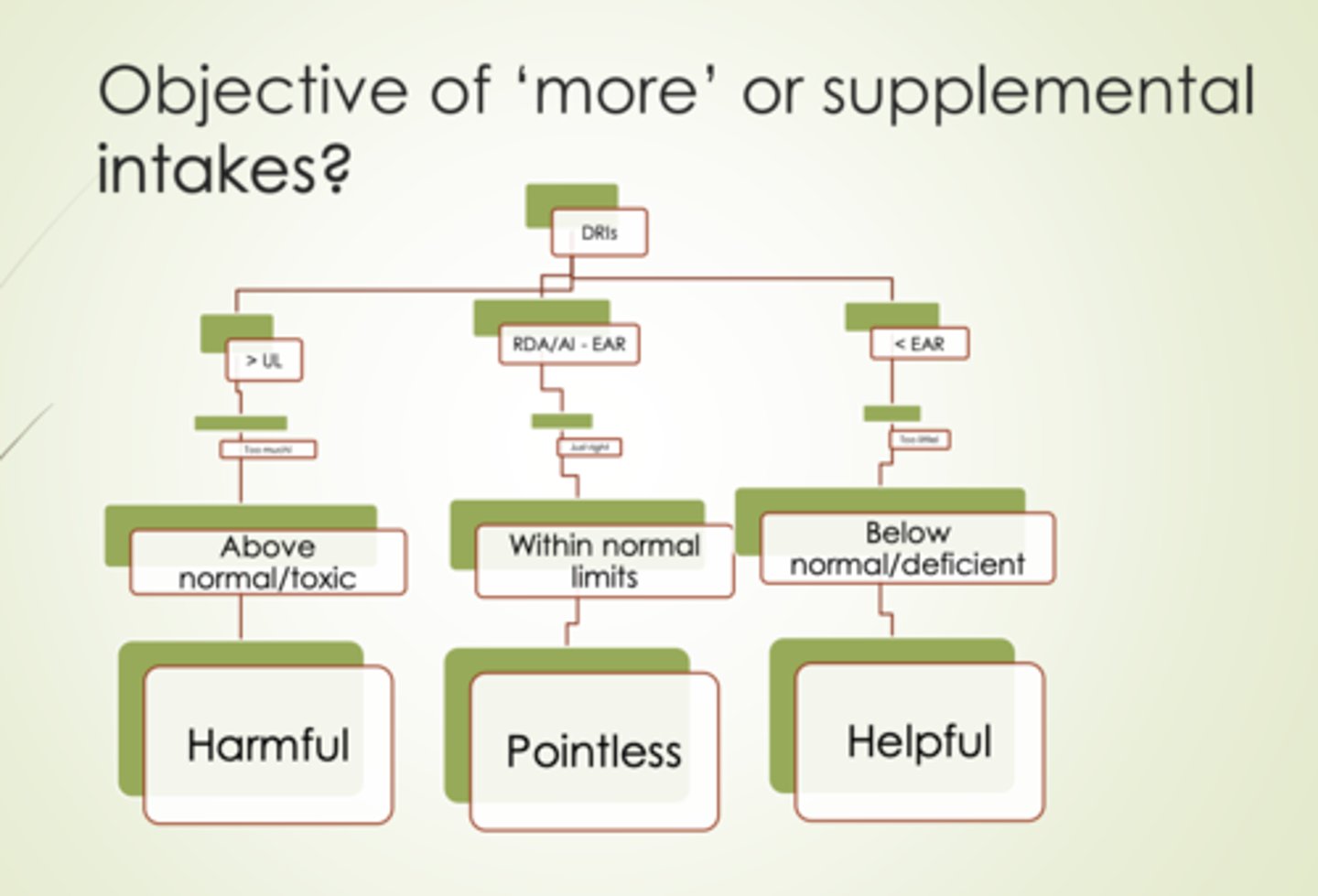
Supplements: Clinical pracitce
Do no harm
Want to make sure total intake is within broad normal limits
- <5x RDA/AI
-
- /= EAR
Supplements: Research
Results of supplemental intakes are pretty much meaningless unless need for more is documented
- correct dietary deficiencies
- Low serum/tissue levels
STUDY: Vitamin C and Periodontal Health
Objective: To investigate effects of Vitamin C deficiency on periodontal disease
Design:
- clinical trail vs case series
- All received some treatment (no control)
Subjects:
- 12 healthy men
- 25-43
- nonsmokers
Independent variable: vitamin C
- Baseline: 250
- Depleted: 5
- repletion: gradual for 56 days
Dependent variable
- Plasma and leukocyte ascorbate levels
- Plaque index
- gingival index
- probing depth
- attachment level
- subgingival plaque samples
Results
Vitamin C depletion did not alter:
- Plaque index
- Probing depths
- Attachment level
- Subgingival plaque samples (microbes)
Vitamin C depletion did alter:
- Gingival index
There are some graphs from this study but are kind of pointless if you just know the results
SUMMARIZE: Vitamin C and Periodontal health
Vitamin C deficiency is associated with increased bleeding, likely due to increased capillary fragility. In periodontal tissue- but not with altered microflora or loss of periodontal integrity
Experimental conditions: adequate oral hygiene, remaining dietary variables unchanged
Referring to this study because running out of lecture time:
STUDY: Vitamin C and periodontal Disease #2
Chapple et al [NHANES III data]
Observational: cross sectional
Results:
High vitamin C serum levels is associated with decreased periodontitis in smokers and nonsmokers
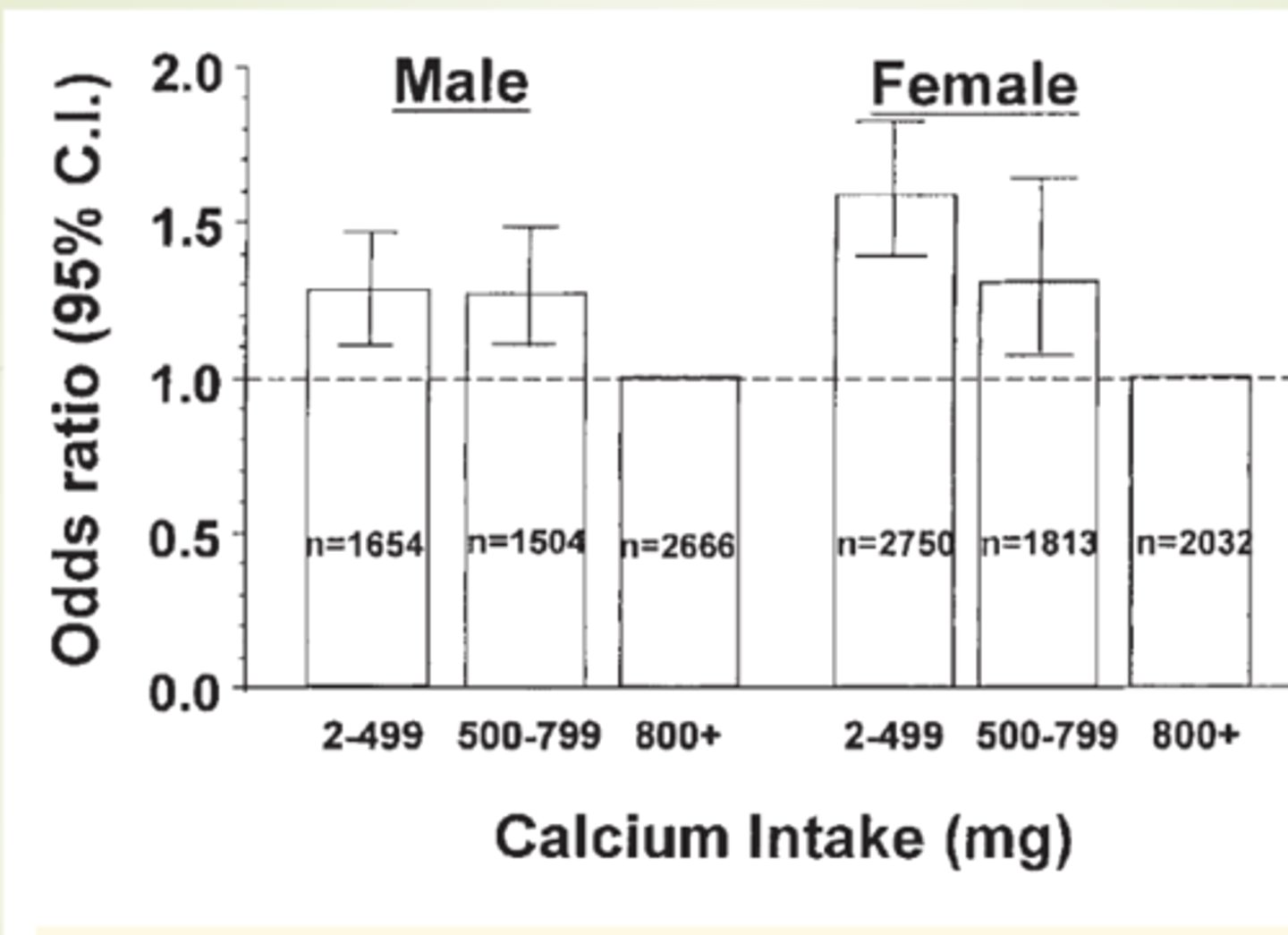
STUDY: Calcium and Periodontal Disease
Objective: Investigate association between dietary calcium and periodontal disease
Subjects: NHANES III
- Observational cross-sectional
Independent variable
- 24 hour recall: calcium intake
Dependent
- Dental exams: attachement loss, gingival bleeding
Results:
Low dietary intakes of calcium were associated with more severe periodontal disease
STUDY: Diet quality and Periodontal Disease
Objective: examine association between diet quality and severe periodontal disease
Design: cross sectional
Subjects: 13920 US hispanic/latinos (aged 18-74)
Independent: diet quality
- 2X24 hour recalls
- alternative healthy eating index
Dependent: Periodontal disease
- Clinical exams
- Severe periodontal disease
Results:
As you move from a low diet quality to a high diet quality you see a decrease risk of periodontal disease
High quality = Less PD
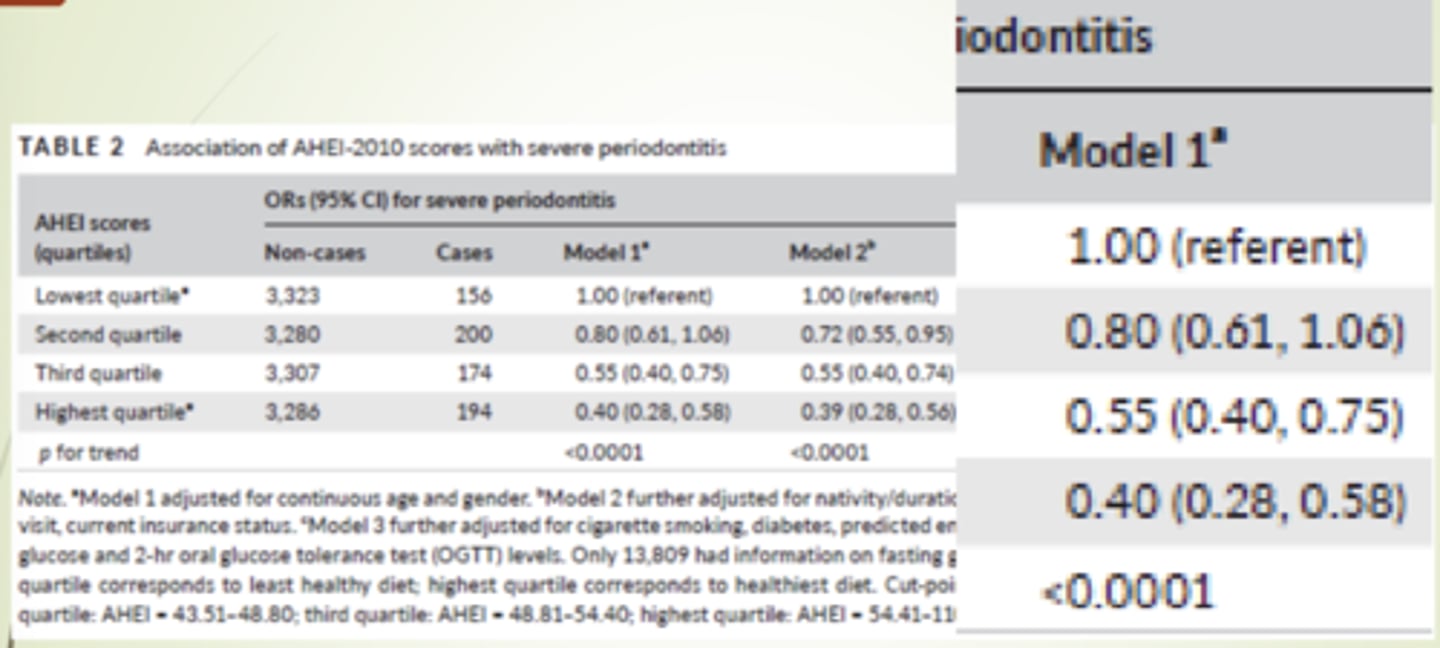
SUMMARIZE: Diet quality and periodontal disease
Higher diet quality was associated with lower odds of severe periodontal disease
STUDY: Investigating oral and systemic pathways between unhealthy and healthy dietary patterns to periodontitis in adolescents; a population-based study
Objective: To investigate direct and indirect pathways by which unhealthy and healthy diets might impact periodontal disease
Design:
Cross sectional analysis of birth cohort: Brazil
Subjects
2515 adolescents (high school)
52% female
Not obese
Independent:
Unhealthy diet
Healthy diet
Dependent:
Periodontal disease
Results:
Unhealthy positively associated with PD
Healthy negatively associated with PD
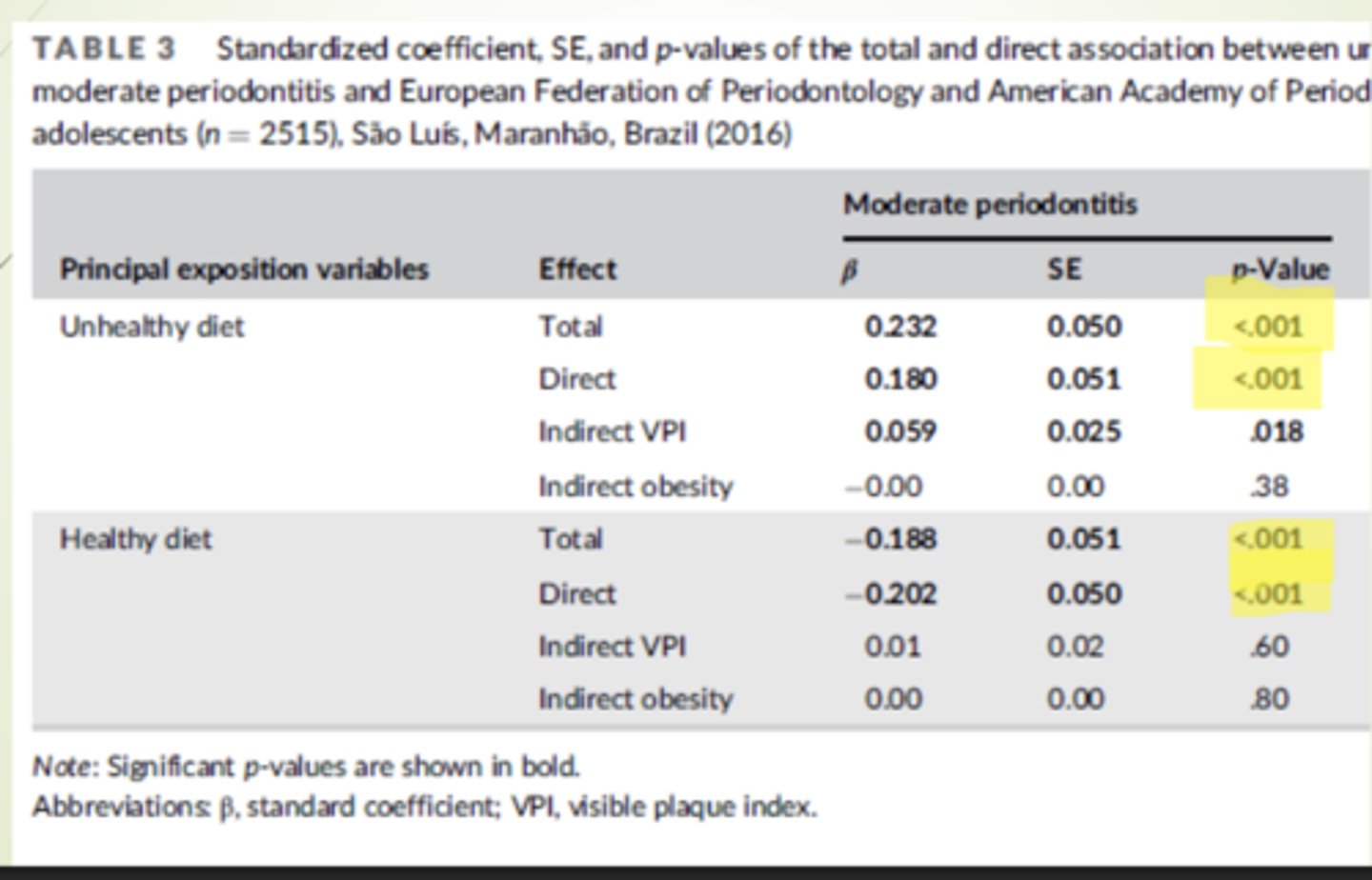
SUMMARIZE: nvestigating oral and systemic pathways between unhealthy and healthy dietary patterns to periodontitis in adolescents; a population-based study
Healthy diets composed of fruits, vegetables, fiber and dairy products are associated with a reduced risk of periodontitis
Unhealthy diets high in nutrient poor ultra-processed food are associated with an increased risk of periodontitis
Neither deficiencies nor toxicities of energy, protein or other nutrients cause
periodontal disease
"I never said a bad diet is going to cause periodontal disease"
- We have no direct causal effect
- It predisposes one to periodontal disease
Nutrition via diet maintains
tissue health, a functional immune system and repairs damaged tissue
Inadequate nutritions =
inadequate energy, protein or other nutrients and is likely increase susceptibility to disease
NON-compliance with MyPlate
Increase of oral or systemic diseases
Optimal diet to prevent PD
My plate
Oral Health clinician's responsibility in regards to diet
Assess patient's nutritional status
Assess diet
Counsel patient relative to MyPlate
Refer patient to registered dietitian