Nucleotides, Nucleic Acids, and Protein Synthesis Overview
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
169 Terms
Gene
segment of DNA that contains the information required for the synthesis of functional biological products, whether protein or RNA.
rRNA
carry out protein synthesis of proteins.
mRNA
intermediaries; carry information for the synthesis of proteins from genes to ribosomes.
tRNA
adapter molecules that translate information in the mRNA into a specific sequence of amino acids.
ncRNA
noncoding RNA.
Nucleotide
consists of a nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine), a pentose sugar, and one or more phosphate groups.
Nucleoside
combination of the pentose sugar and the nitrogenous base when no phosphate is present.
N-β-glycosyl bond
bond formed between the base joined covalently at N-1 of pyrimidines and N-9 of purines to the 1' carbon of the pentose.
Phosphodiester linkage
joins nucleotides together between the 5'-hydroxyl group of one pentose and the 3'-hydroxyl group of the next.
RNA
nucleic acid that contains ribose, with common pyrimidine bases uracil and cytosine.
DNA
nucleic acid that contains 2'-deoxyribose, with common pyrimidine bases thymine and cytosine.
Purines
adenine and guanine.
Pyrimidines
cytosine, thymine, and uracil.
Deoxyribonucleotides
structural units of DNA: A, dA, dAMP - deoxyadenosine; G, dG, dGMP - deoxyguanosine; T, dT, dTMP - deoxythymidine; C, dC, dCMP - deoxycytidine.
Ribonucleotides
structural units of RNA: A, AMP - Adenosine; G, GMP - Guanosine; U, UMP - Uridine; C, CMP - Cytidine.
Tautomers
isomers that interconvert rapidly such that they exist in equilibrium.
Hydrophobic bases
bases that are insoluble in water at neutral pH and stack to minimize contact with water.
Modified bases
found in DNA and RNA, regulating or protecting genetic information.
Exocyclic
not within the ring structure.
Phosphate-group bridges
covalently bind nucleotides where the 5' phosphate group joins to the 3'-hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide.
Oligonucleotide
short nucleic acid (50 or fewer nucleotides).
Polynucleotide
longer nucleic acids.
Avery-MacLeod-McCarty experiment
showed that DNA isolated from one bacterial strain can enter and transform the cells of another strain.
Hershey-Chase experiment
Showed that the DNA of the bacterial virus, but not its protein coat, carries the genetic message for replication of the virus in a host cell.
Primary structure of nucleotides
Covalent structure and nucleotide sequence.
Secondary structure of nucleotides
Regular, stable structure taken up by some or all of the nucleotides in a nucleic acid.
Tertiary structure of nucleotides
Complex folding of large chromosomes within eukaryotic chromatin and bacterial nucleoids; the elaborate folding of large tRNA and rRNA molecules.
Chargaff's Rules
The number of one residue will equal the number of matching residues (example: # of A = # of T and the # of G = # of C), which means that A + G = T + C.
Watson and Crick model
Postulated that native DNA consists of two antiparallel chains in a right-handed double-helical arrangement.
Complementary base pairs
A=T and G=C, formed by hydrogen bonding between chains in the helix.
Base pair stacking
Base pairs are stacked perpendicular to the long axis of the double helix, 3.4 Å apart, with 10.5 base pairs per turn.
Deoxyribose and phosphate groups
Hydrophobic, facing the water on the outside of the DNA structure.
C-2' endo conformation
The furanose ring of each deoxyribose is in this conformation.
G-C bonds
3 bonds can form between G and C, making it stronger than the 2 bonds that can form between A and T.
Stability of DNA
DNA has a higher content of G and C because it's more stable.
B-DNA
The standard form of DNA, most stable structure.
A-DNA
Favored in solutions that don't contain water; wider helix with 11 base pairs rather than 10.5.
Z-DNA
Left-handed helical rotation, 12 base pairs per helical turn, with a zigzag backbone.
Purine conformations
Purine has 2 stable conformations called syn (both groups on the same side) and anti (groups on opposite sides).
Pyrimidine conformation
Pyrimidine is stuck in anti due to steric hindrance between the sugar and the carbonyl oxygen.
Hairpin structure
Complementary parts of a palindromic repeat fold back and pair to form an antiparallel duplex helix closed at one end.
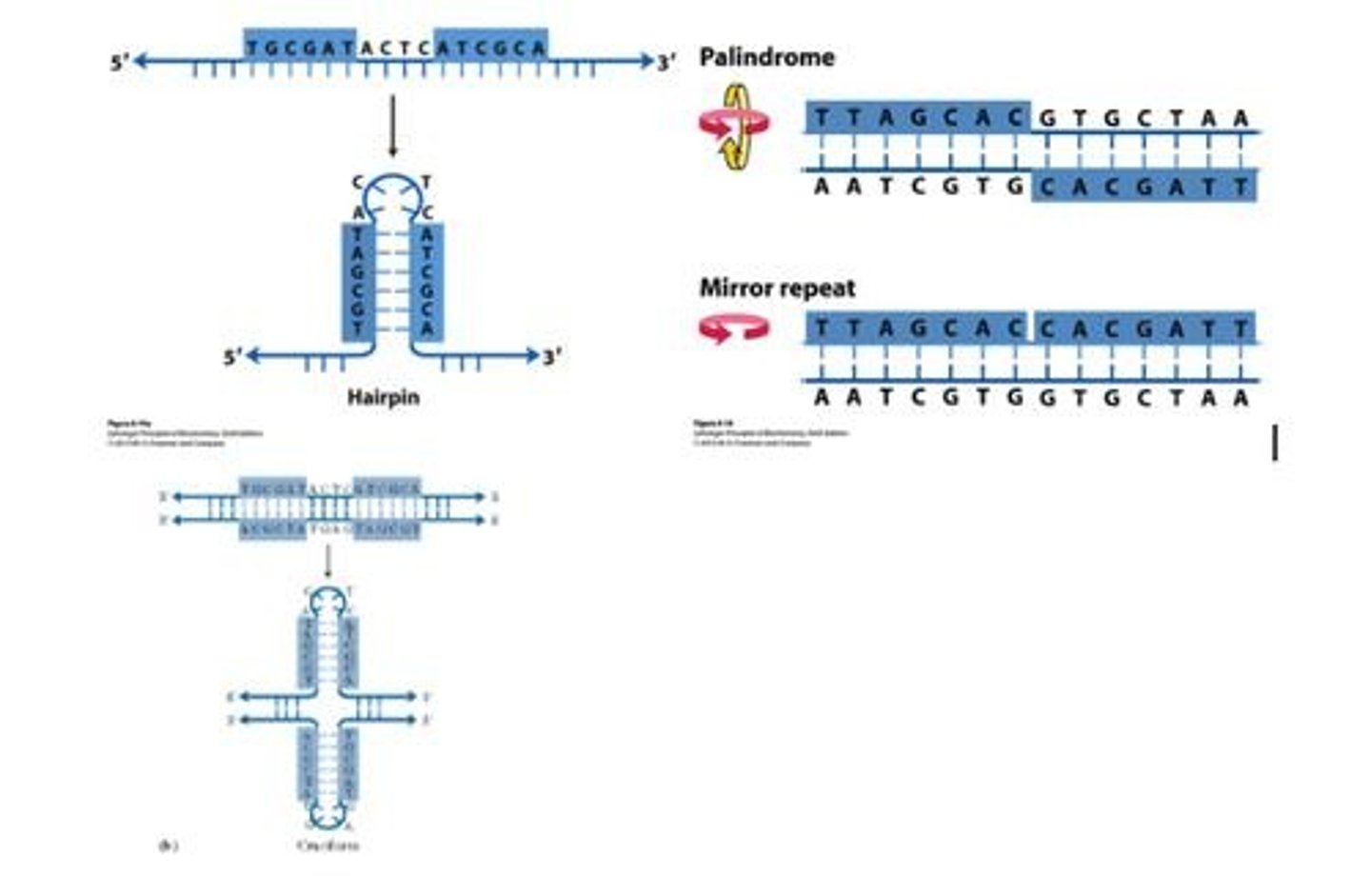
Cruciform structure
Each separated strand is paired internally to form opposing hairpin structures.
Mirror repeats
Inverted repeat occurs within each individual strand of DNA; cannot form hairpin or cruciform structures.
mRNA
Transfers genetic information to DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis.
Transcription
mRNA is formed on a DNA template by using the genetic information contained on one strand of DNA to specify a complementary sequence of bases in an mRNA.
Ribosome function
Once mRNA reaches the ribosome, it gives the template to the amino acid in the polypeptide chain.
Monocistronic
carries the code for one polypeptide (most eukaryotic cells are this)
Polycistronic
carries the code for 2 or more polypeptides
Amino acid coding
Each amino acid is coded by at least 3 nucleotides therefore it's a 1:3 ratio
tRNA
pairs with mRNA to grow polypeptide in the correct sequence.
rRNA
are component of ribosomes.
Noncoding RNA (ribozymes)
have enzymatic activity.
RNA structure
RNA is structurally complex; single RNA strands can fold into hairpins, double-stranded regions, or complex loops.
Base pairing in RNA
Base pairing between G and U is allowed when two single strands of RNA pair with each other.
A-form helix
When perfectly complementary, the helix is an A-form (uncommon).
Z-form helix
Z-form has been made in a lab.
B-form helix
B-form has not been observed.
Melting of DNA
Native DNA undergoes reversible unwinding and separation of strands (melting) upon heating or at extreme pH.
Melting point and base pairs
DNAs rich in pairs have higher melting points than DNAs rich in pairs.
Hyperchromic effect
increase in absorption.
RNA stability
RNA is more stable though so it takes more heat to denature.
DNA mutations
permanent changes in genetic material.
AP site
Base is lost, creating a DNA lesion called an AP site or abasic site.
Deaminating agents
cause damage.
Alkylating agents
methylate guanine to make methylguanine, which can't base pair.
Oxidative damage
is the most common alteration made.
Oligonucleotides
of known sequence can be synthesized rapidly and accurately.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
provides convenient and rapid method for amplifying segments of DNA if the sequences of the ends of the targeted DNA segment are known.
Requirements for PCR
Requires DNA sample, synthetic oligonucleotide primer, pool of deoxynucleoside triphosphates, and a DNA polymerase.
Sanger dideoxy sequencing
Routine DNA sequencing of genes or short DNA segments is carried out using an automated variation of Sanger dideoxy sequencing.
Phosphite linkage
A bond formed during the reaction with immobilized nucleotide, leading to the elimination of the diisopropylamino group.
Next-gen sequencing technologies
Commercial methods that allow for the efficient determination of DNA sequences, including entire genomes, in hours or days.
Sanger sequencing
A method of DNA sequencing that uses dideoxy chain termination to stop DNA strand extension.
dNTPs
Normal nucleotides used in DNA polymerase reactions.
ddNTPs
Modified nucleotides that stop DNA strand extension and are fluorescently labeled for identification.
ATP
The central carrier of chemical energy in cells.
Cyclic AMP
A common second messenger formed from ATP in a reaction catalyzed by adenylyl cyclase.
DNA cloning
The process of generating a DNA fragment of interest, inserting it into a cloning vector, and transferring it into a host cell for replication.
Recombinant DNA
Composite DNA formed by the assembly of DNA segments in new combinations.
Restriction endonucleases
Enzymes that cleave DNA into smaller fragments at specific sequences.
DNA ligase
An enzyme that links the cloning vector to the DNA fragments to be cloned.
Reverse transcriptase
An enzyme that makes a DNA copy of an RNA molecule.
Polynucleotide kinase
An enzyme that adds a phosphate to the 5'-OH end of DNA to label it or permit ligation.
Terminal transferase
An enzyme that adds homopolymer tails to the 3'-OH end of DNA.
Exonuclease III
An enzyme that removes nucleotide residues from the 3' ends of DNA.
Sticky ends
Staggered cuts on the two DNA strands, leaving 4 unpaired strands.
Blunt ends
Cuts that cleave the DNA straight across, leaving no unpaired bases on the ends.
Cloning vectors
DNA molecules used to transport foreign genetic material into another cell.
Plasmids
Circular DNA that replicates separately from the host chromosome.
BACs
Bacterial artificial chromosomes that can clone large segments of DNA.
YACs
Yeast artificial chromosomes used to clone very long segments of DNA.
Shuttle vectors
Plasmids that can propagate in cells of two or more species.
Expression vectors
Vectors that incorporate cloned genes with the sequence signals needed for transcription and translation.
Expression systems
Systems used to express proteins in different types of cells, including bacteria, yeast, insects, and mammalian cells.
Genetic engineering techniques
Methods that can alter cloned genes as required by the investigator.
Fusion protein
Proteins or peptides can be attached to a protein of interest by altering its cloned gene.
Affinity chromatography
Methods used to purify proteins by utilizing additional peptide segments.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Permits the amplification of chosen segments of DNA or RNA for cloning.
RT-PCR
Can be used to derive sequences from living cells instead of dead ones.
qPCR
Estimates the relative copy numbers of particular sequences in samples.