Hematocrit
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
hematocrit
percentage of red blood cells (RBCs) in your blood
tells how much of your blood is made up of RBC
how to measure hematocrit
collect small blood sample
place blood in a thin capillary tube
spin tube in centrifuge to separate blood into layers (plasma, buffy coat, RBCs)
RBC’s layer’s height is compared to total blood height, making a percentage
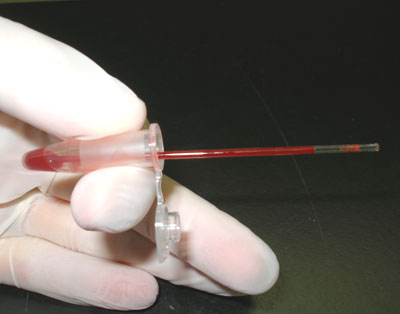
what type of tube is blood put into?
capillary tube
what is used to separate the elements in the blood?
a centrifuge
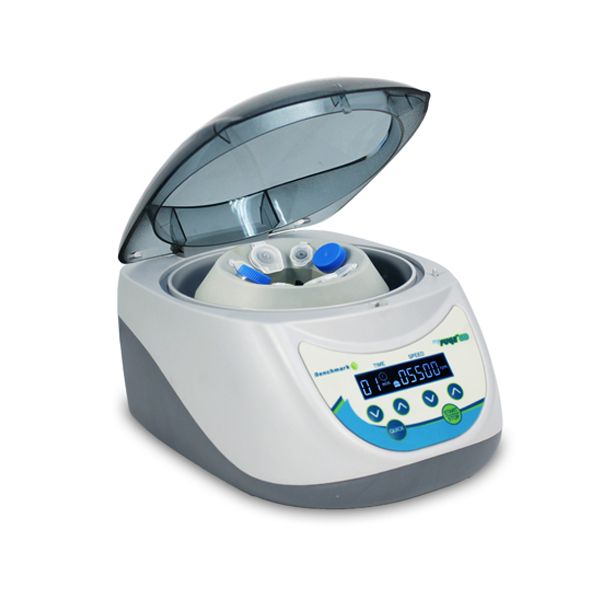
what is the top layer of the tube?
plasma (mostly water and nutrients)
what is the middle layer of the tube?
buffy coat (wbc and platelets)
buffy coat
wbc and platelets
middle layer of tube
what is the bottom layer of the tube?
rbcs
what is calculated to find the hematocrit %?
the RBC layer’s height is compared to the total blood height
normal hematocrit levels in men
40% to 54%
normal hematocrit levels in women
36% to 48%
how to use a hematocrit chart
1. After centrifuging, place the capillary tube on the hematocrit chart.
2. Align the bottom of the RBC column with the “0%” mark.
3. Align the top of the plasma with the “100%” mark.
4. The line where the top of the RBC layer falls gives the hematocrit value.
equipment needed for hematocrit
Capillary tubes
• Centrifuge
• Microhematocrit reader (chart)
• Anticoagulated blood sample
• Gloves & PPE
positive control sample
contains a known hematocrit value within the normal range
importance of a positive control sample
tt ensures that the procedure and equipment are working correctly.
negative control
a sample with no RBCs (like just plasma) to check for errors or contamination
importance of negative control
to check for errors or contamination
blood doping
when athletes artificially increase their RBC count to get more oxygen to their muscles and improve endurance
why is blood doping dangerous?
too many RBCs make blood thicker, which increases the risk of blood clots, heart attacks, and strokes