Chapter 6: Sequential Valuation
How do we value companies?
Using Discounted Cash Flows (DCF)
What is paid first and considered least risky in terms of claims?
Secured Creditors
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
How do we value companies?
Using Discounted Cash Flows (DCF)
What is paid first and considered least risky in terms of claims?
Secured Creditors
What is paid last and considered most risky in terms of claims?
Common Stock
What is Firm Value equal to?
Equity Value + Debt Value
What are the steps to valuing the firm and the equity?
Determine how big the bucket is
The aggregate value of the firm = PV of the Unlevered Free Cash Flow
Determine how much leaks out to Creditors
They get paid first
Lower risk = lower price
Subtract the PV of Debt
What remains when you subtract Firm Value by PV of Debt?
PV of Equity
How do we divide the firm’s life?
Into the Non-Constant Growth Period and the Constant Growth Period
What happens to growth rates during the Non-Constant Growth Phase?
There are different growth rates during this period because the firm may go through many different growth cycles
When does the Non-Constant Growth Phase end?
Only when we can assume that growth is stable and will remain unchanged
What do we need to value cash flows in the Non-Constant Growth Phase?
Estimate cash flows for all years
Discount cash flows (growing perpetuity)
What NPV formula do we use in a Non-Constant Growth Phase?
NPV = CF/r-g
What do you have to calculate to value the firm during the Constant Growth Period?
Terminal Value
How do you calculate the Terminal Value?
If you estimate the constant growth rate, use the growing perpetuity formula
PV to the start of the Constant Growth Phase
PV that to get to t=0
Otherwise, use an exit multiple
What are the rules for Valuing Cash Flows?
Rule 1: Be consistent in your treatment of inflation
Rule 2: Consider the timing of cash flows
How do we adhere to the first rule of “be consistent in treatment of inflation”?
Discount nominal cash flows using nominal discount rate
Discount real cash flows using a real discount rate
When are are CFs relating to sales, COGS, etc. paid and received?
Throughout the year
If cash flows are paid and received throughout the year, how should they then be discounted?
As mid-year cash flows
What is the formula for mid-year discounting?
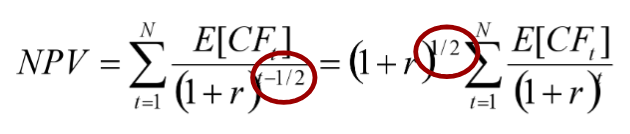
What gives us the Asset Value?
Applying the TVM principles to the expected cash flows from the asset
How are Bonds valued?
As an annuity (coupon payments) and a lump-sum (principal payment) at the due date
How are Stocks (common and preferred) often valued?
With the dividend discount model
What are Bonds?
A debt obligation sold to investors
How are Bonds sold?
In $1,000 increments (AKA Face Value or Par Value)
How often are interest payments for Bonds?
Semi-Annual (also called coupon payments)
What is a Coupon Rate?
A combination of the Risk-Free Rate, plus a Credit Spread based on the default risk of the borrower
When is the Face Value of a Bond due?
At maturity (a lump sum)
What is the Default Risk of a Bond based on?
Ratings
Where do Bonds trade?
On the open market
How does the price of a Bond change?
With interest rates
What is Yield-to-Maturity (YTM)?
The discount rate at which the present value of all future cash flows (coupon payments and the face value) of a bond equals its current market price
What is the current Bond Price equal to?
= PV of the coupons + Face Value at the current interest rate
What happens if rates RISE?
Bond Prices FALL
What will a bond trade at if the Coupon Rate > Market Rate?
Premium
What will a bond trade at if the Coupon Rate < Market Rate?
Discount
What does it mean the longer until the maturity date?
The more the price changes with interest rates
What does the effect of the rate change adversely affect?
Duration
Who does the rate change (and duration) affect more?
Investors more than issuers
What remains constant in corporate finance?
The need to issue new bonds to refinance old ones
What kind of opportunities are Issuers and Bankers on the lookout for?
Extend maturities
Reduce coupons
What do you need to solve for YTM (or any part of the current bond price equation)?
Current Price (the PV)
FV (face value due at maturity)
Periodic Payments (annuity/coupons)
How can we use market values to determine equity?
Value of the Firm - Market Value of Debt = Value of Equity
What does the Dividend Discount Model help find?
The present value of project dividends
What formula do we use for constant dividend growth?
Gordon Growth Model: P = DIV (t+1)/r - g
What’s important to know about Preferred Stock Dividends?
Go on forever (perpetuities)
Dividend payouts are fixed at issuance
What’s important to know about Common Stock Dividends?
Discretionary