draft part one c dietics 1
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What is 1 meter in cm?
100cm
What is 1 foot in cm?
30.48cm
What is 1 inch in cm?
2.54cm
What does the A, B, C, D, E, F mean in a full dietetic assessment?
A (Anthropometric), B (Biochemical), C (Clinical), D (Dietary), and E (Environmental). F stands for Functional assessments.
What is a PASS statement in Dietetics?
Problem, Aetiology/Cause, Signs/Symptoms
BMI= in kg and meters
BMI = mass (kg) / height m2
What 2 fortisip products have 11.9g of protein per serving?
Forticreme Complete (semi-solid) & Fortisip Compact Fibre
What 2 fortisip products have 12g of protein per serving?
Fortisip CompactFortisip & PlantBased 1.5kcal
What fortisip products have 125 ml as a serving size?
Fortisip Compact Protein, Fortisip Compact, Forticreme Complete (semi-solid) & Fortisip Compact Fibre
What 2 fortisip products have the most kcal per serving of 400kcals?
Fortisip 2kcal & Fortisip PlantBased 2kcal
For renal disease what medications are used for Blood thinning / dialysis access commonly?
Aspirin, Clopidogrel, Dipyridamole
For renal disease what medications are used for BItching (pruritus)?
Gabapentin, Pregabalin, Antidepressants, Chlorphenamine, Difelikefalin, Phosphate binders
For renal disease what medications are used for Stomach protection?
Lansoprazole, Omeprazole
For renal disease what medications are used for Cholesterol lowering?
Simvastatin, Pravastatin, Atorvastatin
For renal disease what medications are used for Constipation relief?
Lactulose, Macrogols (Laxido, Movicol), Docusate, Senna
For renal disease what medications are used for slowing kidney disease?
Dapagliflozin, Other SGLT2 inhibitors (“-flozins”), Finerenone
For renal disease what medications are used for Vitamin replacement (dialysis)?
Ketovite, Dalavit, Renavit
For renal disease what medications are used for Reducing acid in the blood?
Sodium bicarbonate
Types of Oral iron tablets.
Ferrous Sulfate, Ferrous Fumarate, Ferrous Gluconate, Carbonyl Iron, Brand names include, Ferric Maltol.
Iron Sucrose (Venofer), Ferric Carboxymaltose (Injectafer), Ferumoxytol (Feraheme), Iron Dextran (INFeD), Ferric Derisomaltose (Monoferric).
For renal disease what medications are used for Anaemia treatment – iron?
Oral iron tablets, Intravenous iron infusion
For renal disease what medications are used for Anaemia treatment – ESA injections?
Eprex, Neo-Recormon, Retacrit, Aranesp, Mircera
For renal disease what medications are used for Anaemia treatment – oral alternative?
HIF stabilisers
For renal disease what medications are used for Bone disease / phosphate control?
Calcichew, Phosex, Renacet, Osvaren, Renagel, Renvela, Fosrenol, Velphoro
For renal disease what medications are used for Vitamin D?
Alfacalcidol
For renal disease what medications are used for Medications paused during illness (sick-day guidance)?
Bendroflumethiazide, Furosemide, Indapamide, Spironolactone, Finerenone, ACE inhibitors (e.g. lisinopril, ramipril), Angiotensin receptor blockers (e.g. losartan, valsartan), Metformin, SGLT2 inhibitors (e.g. dapagliflozin, empagliflozin, canagliflozin)
For COPD what medications are used for Inhalers – bronchodilators?
Salbutamol, Terbutaline, Ipratropium
For COPD what medications are used for Long-acting inhalers?
LAMA inhalers, LABA inhalers, LAMA/LABA combination inhalers
Steroid inhalers
Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS)
Tablets – steroids
Salbutamol, Terbutaline, Ipratropium
Examples of Beta-blockers
Atenolol, Bisoprolol, Carvedilol, Metoprolol, Propranolol
Calcium Channel Blockers examples
Amlodipine, Felodipine, Nifedipine, Diltiazem, Verapamil
How do Beta-blockers work?
Slow the heart rate and reduce the force of heart contractions, which lowers blood pressure and the heart's oxygen demand.
What do Calcium Channel Blockers do?
Relax and widen blood vessels, which lowers blood pressure and increases blood/oxygen supply to the heart.
High blood pressure (hypertension) is
a consistent, excessive force of blood against artery walls, forcing the heart to work harder
Impact of High blood pressure (hypertension)?
Damaged arteries, potential for heart attacks, strokes, and kidney disease.
For Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus what medications are used for Biguanides (oral meds for T2D)?
Metformin
For Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus what medications are used for SGLT2 Inhibitors?
Dapagliflozin, empagliflozin, canagliflozin
For Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus what medications are used for DPP-4 Inhibitors?
Sitagliptin, linagliptin
For Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus what medications are used for Sulfonylureas (a class of oral medications primarily used to treat Type 2 diabetes by stimulating the pancreas to release more insulin)?
Gliclazide, glimepiride
For Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus what medications are used for Meglitinides/Prandial Glucose Regulators?
Nateglinide, repaglinide
For Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus what medications are used for Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)?
Pioglitazone
For Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus what medications are used for Dopamine-2 Agonists?
Bromocriptine
For Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, what medications are used for Injectable Medications (Non-Insulin & Insulin)?
Semaglutide, liraglutide, tirzepatide & Insulin
When someone has a Acute Stroke Treatment (Immediate) and has a Ischemic Stroke (Clot-Based) what medication is required?
Thrombolytics ("Clot-Busters"): Alteplase (tPA) and Tenecteplase (TNKase) Blood Pressure Management: Nicardipine, Labetalol, or Clevidipine
What BMI is classed as underweight?
Below 18.5
What BMI is classed as Healthy Weight?
18.5 – 24.9
What BMI is classed as Overweight?
25.0 – 29.9
What BMI is classed as Obesity?
30.0 and above
Obesity BMI categories is classed as
Class 1 Obesity: 30.0 – 34.9 Class 2 Obesity: 35.0 – 39.9 Severe/Class 3 Obesity: 40.0 or higher
What could high blood pressure mean for someone with type 2 diabetes?
Increased risk for health issues, including damaging blood vessels, raising likelihood of heart attack, stroke kidney disease, vision loss and foot problems leading to amputation
What is the primary biochemical cause of respiratory acidosis in COPD?
Carbon dioxide retention due to hypoventilation
Why is a pH of 7.29 clinically important in COPD?
It reflects acidemia that may impair enzyme and cardiac function
What does an albumin level of 35 g/L suggest in this patient with COPD?
Low–normal nutritional and inflammatory status
Which combination of biochemical findings best reflects the chronic physiological adaptation seen in stable, long-standing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)?
Persistently elevated PaCO₂ with renal bicarbonate retention, near-normal pH, chronic hypoxaemia, and raised systemic inflammatory markers
Why must oxygen therapy be used cautiously in COPD patients with these blood gases?
excessive oxygen can lead to worsening hypercapnia (dangerously high blood carbon dioxide levels) and respiratory acidosis
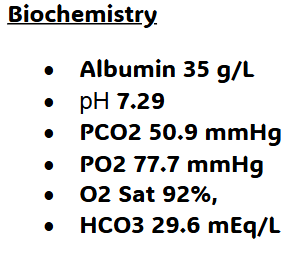
Based on the biochemical and arterial blood gas results below, which option best describes the overall biochemical picture in this patient with COPD?
Partially compensated respiratory acidosis characterised by low pH, elevated PaCO₂, raised bicarbonate, mild hypoxaemia, and low-normal albumin
Why are patients with advanced COPD at increased risk of abnormal renal biochemistry?
Chronic hypoxaemia, hypercapnia, and systemic inflammation reduce renal perfusion and function
In a COPD patient with co-existing chronic kidney disease, which biochemical pattern is most likely raised?
Urea, creatinine, Potassium, Phosphate, Protein/Albumin (in urine), Parathyroid Hormone (PTH), possibly Ferritin/Iron stores and possibly White Blood Cell (WBC) count/Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
In a COPD patient with co-existing chronic kidney disease, which biochemical pattern is most likely low?
Calcium, Bicarbonate, eGFR (Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate), Albumin (in blood), Haemoglobin (Hb), Haematocrit, possibly Ferritin/Iron stores and possibly White Blood Cell (WBC) count/Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
In renal disease, these levels increase because the kidneys can no longer filter waste products or because the body is compensating for internal imbalances.- Renal
Creatinine, Urea (BUN), Potassium, Phosphate, Protein/Albumin (Urine), Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
These levels decrease because the kidneys are failing to perform vital functions, such as producing hormones or maintaining filtration rates.- Renal
eGFR, Haemoglobin (Hb), Haematocrit, Calcium, Bicarbonate, Albumin (Blood)
These markers may fluctuate or show abnormal ratios based on the presence of inflammation or the specific stage of disease.- Renal
Ferritin/Iron Stores, White Blood Cell (WBC) count/Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
In a type 2 diabetes patient, which biochemical pattern is most likely raised?
Fasting Plasma Glucose, Random Plasma Glucose, Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), Triglycerides, LDL Cholesterol, Creatinine/Urine Albumin (in later stages), Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW), Total White Blood Cell Count (WBC), Neutrophil and Basophil Counts, Platelet Count (sometimes), Mean Platelet Volume (MPV)
In a type 2 diabetes patient, which biochemical pattern is most likely low?
HDL Cholesterol, Hemoglobin (Hb), RBC Count (sometimes)
Larger ____ are more reactive and common in poorly controlled diabetes, increasing vascular risk. ____ counts can be elevated, indicating increased ____ activity and a higher risk of blood clots (thrombosis).
platelet(s)
___: Value might be High (≥ 6.5%); this indicates high average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. Higher levels correlate with increased risk of complications.
HbA1c
T2DM is considered a pro-inflammatory state, and elevated ____ is a marker of inflammation.
C-reactive Protein (CRP)
Which of the following best describes the physiological link between nutrition and fall risk in older adults?
Malnutrition and low protein/calcium intake weaken muscles and bones, while dehydration impairs balance through dizziness and low blood pressure.
How would you test a BMI with a stooped posture?
Mid-Upper Arm Circumference (MUAC), Waist-to-Height Ratio (*mabey)
Examples of Calcium channel blockers
Amlodipine (Istin), Diltiazem (Adizem), Nifedipine (Procardia), Verapamil (Calan, Isoptin)
Examples of Statins
Atorvastatin (Lipitor), Simvastatin (Zocor), Rosuvastatin (Crestor), and Pravastatin (Pravachol).
What are calcium channel blockers used for?
medicines that relax and open blood vessels, making it easier for blood to flow, used primarily for high blood pressure (hypertension), angina (chest pain), and certain heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias) by controlling calcium entry into heart and vessel cells
For strokes, what medications are used for Ischemic Stroke (Clot)?
Thrombolytics (Clot-Busters), Antiplatelets, Dual Antiplatelet Therapy (DAPT), Alteplase (tPA), Tenecteplase, Aspirin, Clopidogrel, Atorvastatin, Simvastatin, Rosuvastatin, atrial fibrillation, Warfarin, Apixaban (Eliquis), (ACE inhibitors, Beta-blockers, etc., to manage hypertension)
For strokes, what medications are used for Hemorrhagic Stroke (Bleed)?
Labetalol, nicardipine, enalapril, hydralazine, Nitroprusside (can raise intracranial pressure), Vitamin K, Prothrombin Complex Concentrate (PCC), Nimodipine to prevent blood vessel narrowing, Anticonvulsants (if seizures occur, not usually preventative), Osmotic diuretics (e.g., mannitol) and possibly corticosteroids (like dexamethasone, though evidence varies), Painkillers
For strokes, what medications are used for long-term Prevention & Management (Hemorrhagic Stroke (Bleed) and Ischemic Stroke (Clot))?
Clopidogrel (Plavix), Aspirin, dipyridamole (Aggrenox), apixaban (Eliquis), dabigatran (Pradaxa), edoxaban (Savaysa), rivaroxaban (Xarelto), warfarin, Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, Calcium channel blockers, Thiazide-like diuretics, Statins
For strokes, what medications are used for maintain a target BP of <130/80 mmHg in stokes
ACE Inhibitors (ACEi): Lisinopril, Ramipril, Perindopril.
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs): Losartan, candesartan, Telmisartan.
Thiazide-like Diuretics: Indapamide, Chlorthalidone, Hydrochlorothiazide.
Calcium Channel Blockers (CCBs): Amlodipine, Nifedipine, Felodipine.
ACE Inhibitors (ACEi):
Relax blood vessels to improve flow.
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs): are/do…
Often used if ACE inhibitors cause a dry cough.
Thiazide-like Diuretics:
Help the body eliminate excess salt and water.
In patients with dysphagia, which group of nutrients is most likely to be deficient due to the lower energy density and poor palatability of texture-modified diets?- Stroke
Energy and Vitamins B1, B9, B12, C, and D
Why are texture-modified diets often associated with nutritional deficiencies in dysphagia patients?- Stroke
Texture-modified foods have lower energy density and reduced palatability, leading to lower overall intake.
Which of the following are common barriers to meeting nutritional requirements on a pureed diet and thickened fluid plan?
Lack of visual appeal and meal satisfaction. Feelings of embarrassment while eating. Difficulty managing thin fluids or a reduced desire for thickened fluids.
Which of the following lifestyle changes are recommended for long-term prevention and management of stroke?
Healthy Diet, Reduce Salt, Limit Fats and Sugars, Increase Potassium, Regular Physical Activity, Stop Smoking, Limit Alcohol, Maintain a Healthy Weight, Manage Stress, Monitor Medical Conditions.