Urology Anatomy
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
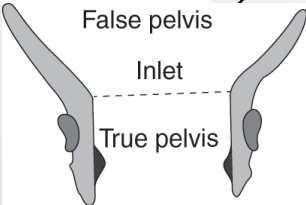
False (greater) pelvis
#3
-Superior region, part of the abdominal cavity
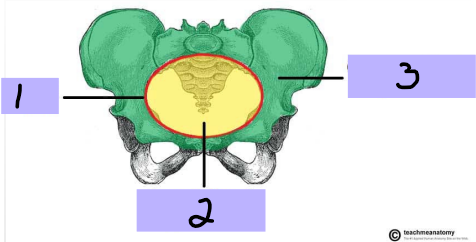
True (lesser) pelvis
#2
-Inferior region, encloses pelvic cavity
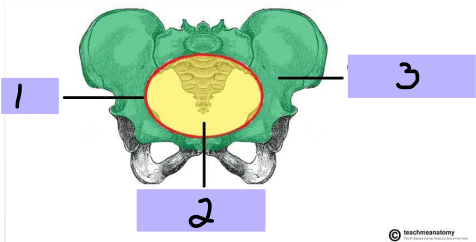
Pelvic brim
#1
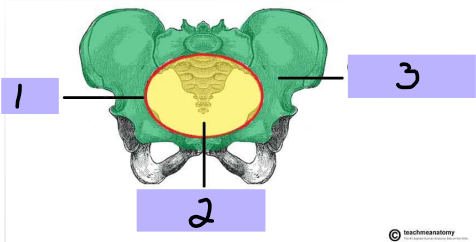
Pelvic cavity
Bowl shaped cavity, continuous with the abdominal cavity
fibromuscular, perineum
Pelvic Floor
-_____________ structure
-Separates the pelvic cavity from __________
inferior, outlet, terminal, urinary, reproductive, external
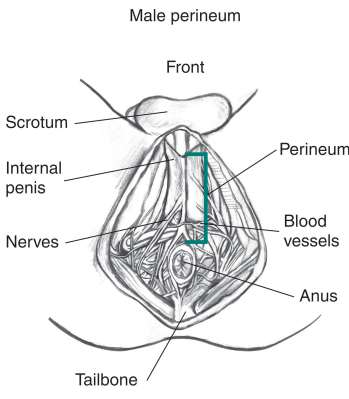
Perineum
-________ to pelvic floor, margin formed by the pelvic ________
-Contains → ________ openings of GI and ________ systems, external opening of _____________ tract, and roots of _________ genitalia
Pelvic inlet
What is being described?
-Rim of pelvic cavity, encircled by bone
-Where the bladder sits
anteriorly, horizontal
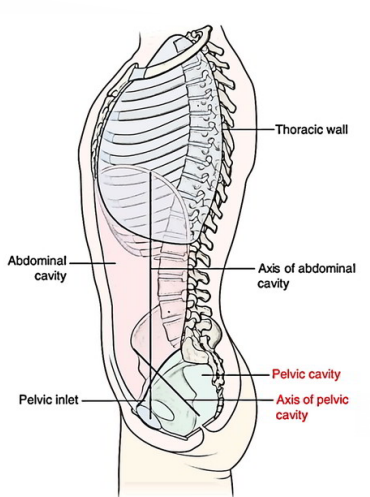
Pelvic Axis
-Top of pubic symphysis and anterior superior iliac spine lie in the same vertical plane
-Pelvic inlet is tilted ____________
-Bodies of pubic bones and pubic arch position in ____________ plan facing ground
pelvic, coccyx, L5, sacrum, pelvic
Pelvis Bones and Joints
Bones
-Right and left _____ bones
-Sacrum
-_________
Joints
-Lumbosacral (LS) joint → sacrum and __
-Sacroiliac (SI) joints → pelvic bones and _______ (posterior)
-Pubic symphysis → right and left _______ bones (anterior)
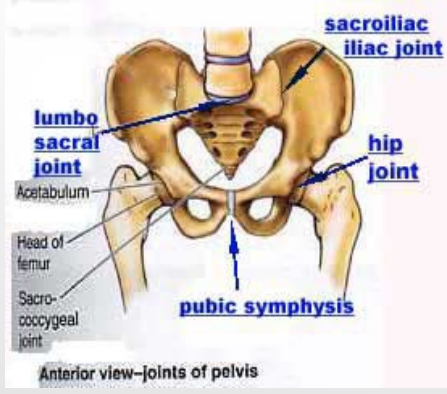
ilium, pubis, ischium
Label the parts of the pelvic bone (#1-3)
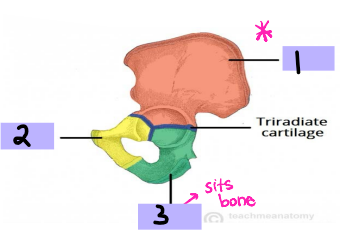
ridge, ilium, lateral, true, margin, inlet
Ilium: Arcuate Line
-_______ that separates _______ into upper and lower parts
Upper = _______ wall of false pelvis, part of abdominal cavity
Lower = lateral wall of ____ pelvis, part of pelvic cavity
-Linea terminalis (lower 2/3rds of the arcuate line), contributes to _______ of pelvic ____
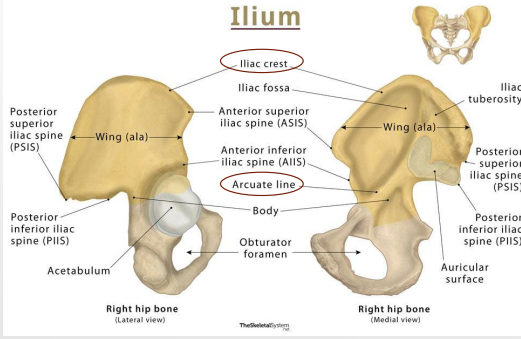
muscle, fascia, back
Ilium: Iliac Crest
-Site for _______ and _______ attachment of abdomen, _____, and lower limb
Anteriorly = anterior superior iliac spine
Posteriorly = posterior superior iliac spine
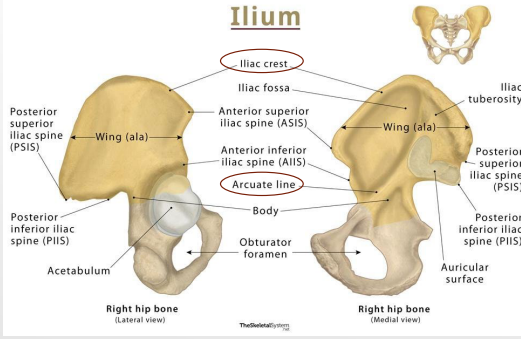
Iliac crest
#1
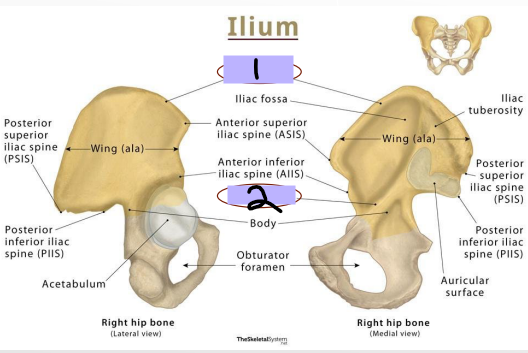
Arcuate Line
#2
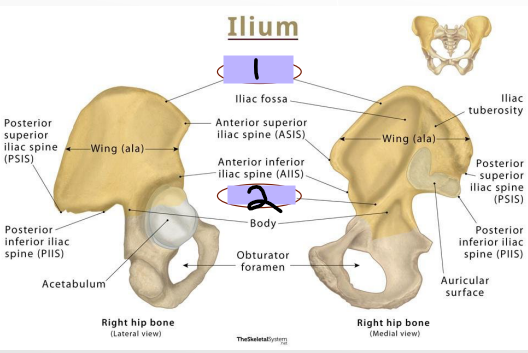
Body
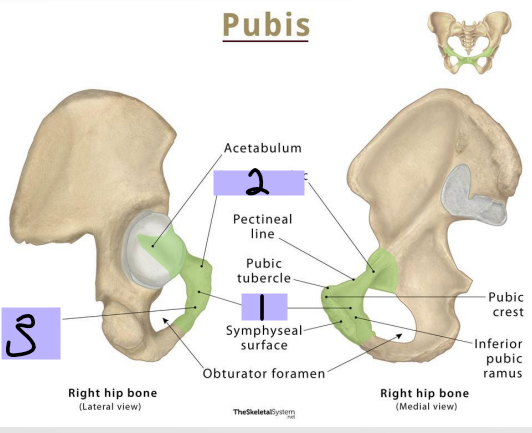
Pubis: _______ (#1)
-Articulates anteriorly with the body of the opposite pubis at the pubic symphysis
-Pubic tubercle has an anterior and superior surface
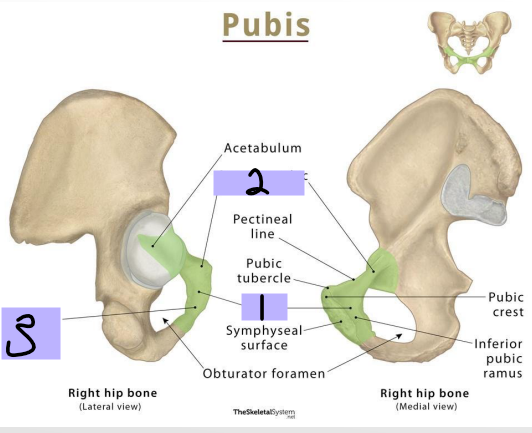
Superior pubic ramus
Pubis: __________ _____ _____ (#2)
-Projects posterolateral from body
-Joins with ilium and ischium
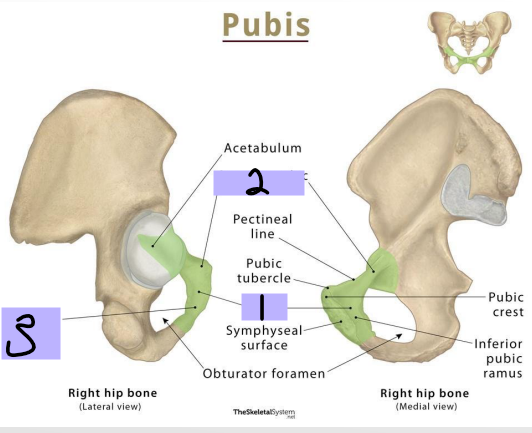
Inferior Pubic Ramus
Pubis: _________ _____ _______ (#3)
-Projects laterally and inferiorly
-Joins with ramus ischium
Body
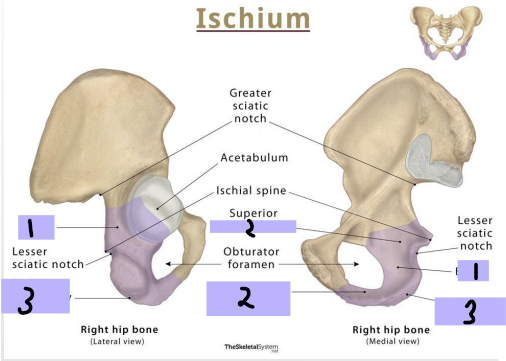
Ischium: ____ (#1)
-Projects superiorly to join the ilium and superior pubic ramus
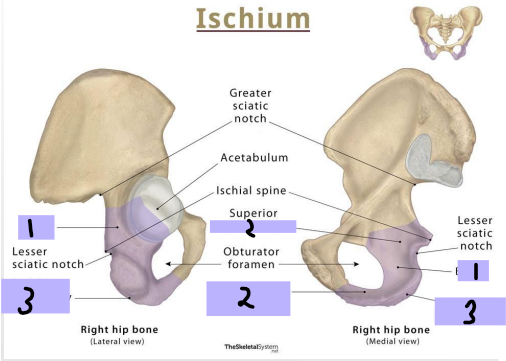
Ischial Ramus
Ischium: ________ _____ (#2)
-Projects anteriorly to join the inferior pubic ramus
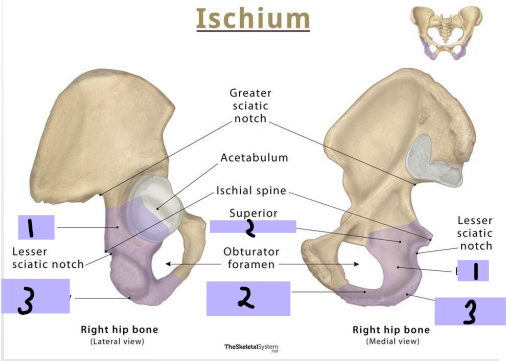
Ischial tuberosity
Ischium: _______ _________
-Posteroinferior aspect of the bone
-Site of attachment of lower limb muscles
-Supports body when sitting
abdominal, pelvic
Pelvic Inlet
-Opening between the __________ and ______ cavities
-Margins → sacral promotory midline posteriorly, sacral ala posterior/laterally, linea terminalis
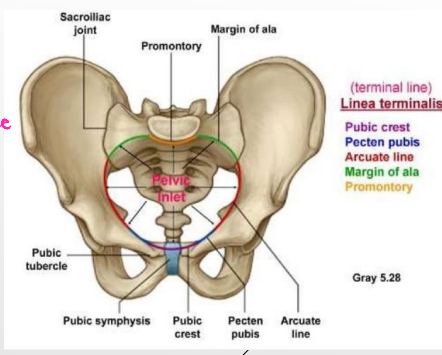
sacrospinous, sacrotuberous, obturator
Pelvic Wall
-Bones → sacrum, coccyx, pelvic bones
-Ligaments → _____________ ligament (#1), ___________ ligament (#2), stabilize the sacrum on the pelvic bones, and creates foramina from greater and lesser sciatic notches
-Muscles → _________ internus (#3), piriformis (#4), which both aid in hip joint movement
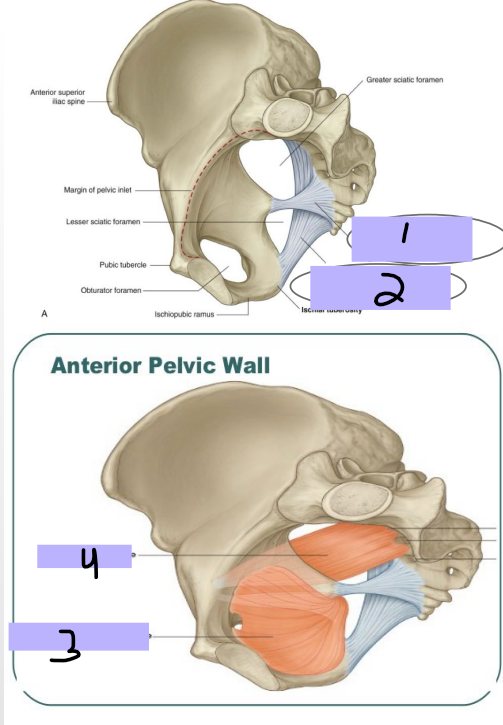
midline, laterally
Pelvic Outlet
-Pubic symphysis → ________ anteriorly
-Body of pubis/inferior pubic ramus/ramus of ischium/ischial tuberosity → ________
-Sacrotuberous ligament and coccyx → posteriorly
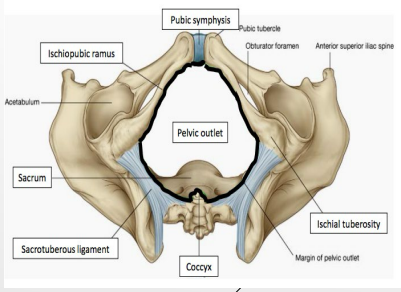
muscular, levator, pelvic, hiatus, urethra
Pelvic Floor: Pelvic Diaphragm
-Pelvic Diaphragm → __________ portion shaped like a bowl or funnel
-Muscles
_______ ani (#1) and coccygeus muscles (#2)
Originates at ______ bones and comes together midline and around the anal aperture
Posterior to anal aperture, the coccygeus muscle comes together as the ligament or raphe called the anococcygeal ligament and attaches to coccyx
-Urogenital _______
U-shaped gap allowing _______ in both sexes and vagina in women to pass through the diaphragm
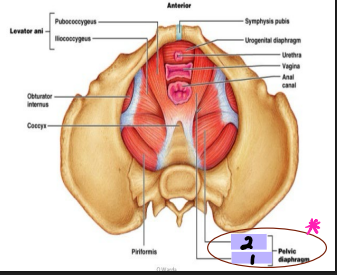
external, muscles, perineal, urethral, position
Pelvic Floor: Perineal Membrane and Deep Perineal Pouch/Space
Perineal Membrane (#1)
-Thick fascial, triangular structure
-Attached to pubic arch with free posterior edge
-Provides attachment for roots of _________ genitalia and genitalia ________
Deep Perineal Pouch/Space (#2)
-Above _________ membrane, contains layer of skeletal muscle
-External ________ sphincter → in both sexes, closes urethra
-Deep transverse perineal muscle → in both sexes, stabilizes the ___________ of the perineal body
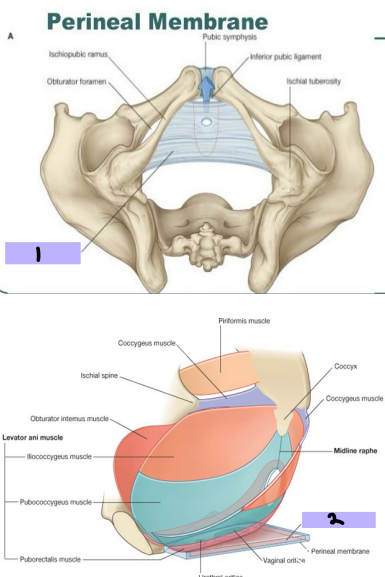
inferior, urinary, reproductive, genitalia, anus, sphincter, pudendal
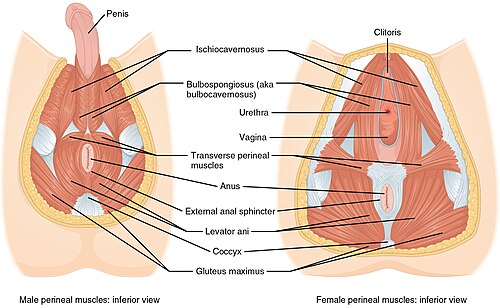
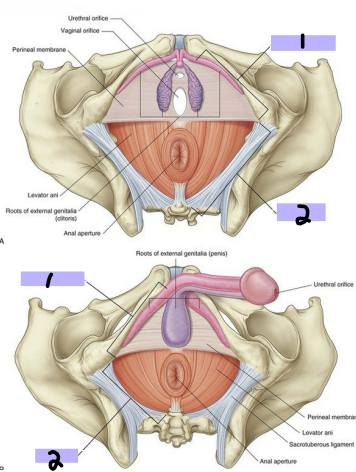
Perineum
-Diamond shaped region _______ to pelvic floor
-Boundaries → pelvic outlet, pelvic diaphragm, walls of pelvic cavity
-Urogenital triangle (#1) → anterior, associated with openings of the _______ and ___________ system, anchors external _________
-Anal triangle (#2) → posterior, contains the ____ and external anal _________
-_________ nerve and internal pudendal artery are the major nerve and artery of the region
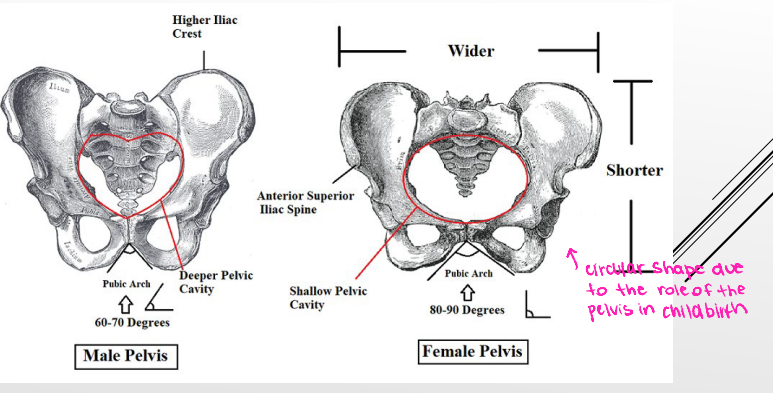
wider, shorter, round
The female pelvis is _______, _________, and ______. This is in stark contrast to the male pelvis, which has a deeper pelvic cavity and is heart shaped.
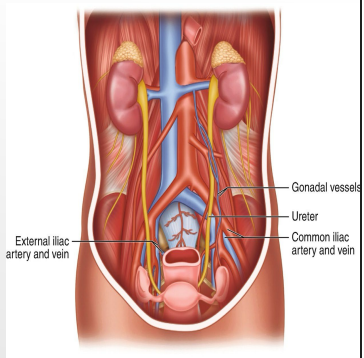
inlet, iliac, bifurcation, bladder, deferens, uterine
Ureters
-Enter pelvic cavity from the abdomen by passing through the pelvic _____
-Enters in the area anterior to the common _____ artery ___________, continues along pelvic wall and floor to join the base of the _________
-In pelvis, crossed by the ductus ________ in men and ________ artery in women
apex, trigone, ureters, urethra, detrusor, neck
Bladder
-_____ → directed towards top of pubic symphysis
-Base → shaped like inverted triangle, faces posterior inferior
_______ → smooth, triangular area firmly attached to wall. Between openings of the ________ and _______
-Bladder wall → _________ muscle, except in the bladder _____
-Superior surface → slightly domed when empty and balloons upward when full
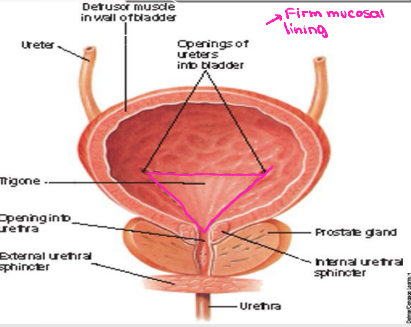
urethra, inferior, fixed, fibromuscular, puboprostatic
Neck of Bladder
-Surrounds the origins of ________ where the two inferolateral surfaces and base intersect
-Most _______ and ______ part of bladder, anchored by pair of ___________ bands
_______________ ligament in males
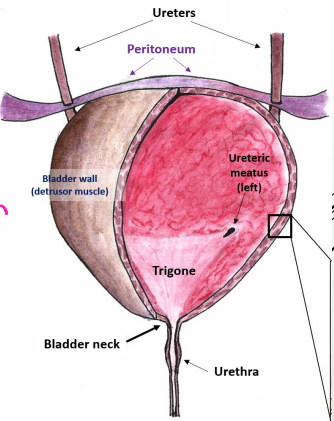
short, Skene’s
Female Urethra
-______ (4 cm long)
-Travels a slightly curved course passing inferiorly through pelvic floor before opening in the vestibule that lies between labia minora and anterior to vaginal opening
-_______’_ glands = paraurethral mucous glands, keep the area moist
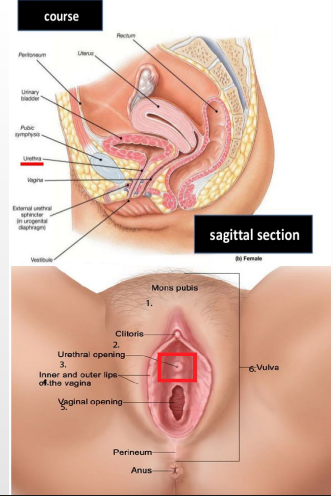
long, base, prostate, internal, retrograde, semen, prostate, ducts, narrow, skeletal, erectile, penis, slit
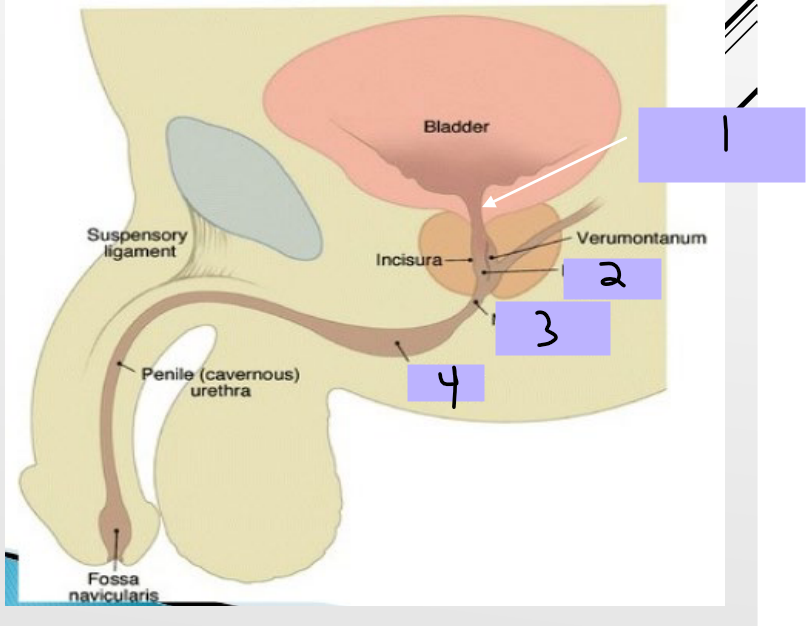
Male Urethra
-____ (20 cm)
-Preprostatic Urethra (#1)
Extends from _____ of bladder to the ________
Associated with cuff of smooth muscle fibers called the ________ urethral sphincter
Prevents _________ movement of _______ into bladder during ejaculation
-Prostatic Urethra (#2)
Surrounded by _________
Prostate gland and ejaculatory _______ open up into this portion
-Membranous Urethra (#3)
__________ and passes through the deep perineal pouch
Surrounded by _________ muscle (external urethral sphincter)
-Bulbar/Penile/Spongy Urethra (#4)
Surrounded by ________ tissue (corpus spongiosum) of penis
Enlarged at base and end of _______
Exits penis through sagittal ____ (external urethral orifice)