Pesticides
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Mechanism of action of glyphosate
Blocks amino acid pathways /Protein synthesis e.g tryptophan
Shikimic acid pathway
EPSPS enzyme inhibitor
LD50
Lethal dose 50%. Dose that kills 50% of test population.
Measures Acute toxicity only
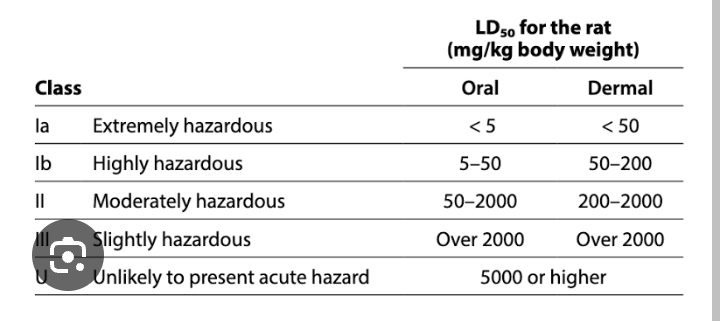
WHO LD 50 classification for pesticides acute toxicity
WHO LD 50 classification for pesticides acute toxicity
1a = extremely hazardous, < 5mg/kg
1b = highly hazardous, 5-50mg/kg
2 - moderate 50-2000mg/kg
3- slightly hazardous 2000-5000
U - unlikely - more than 5000
WHO classification does not take chronic low dose into account.
True
Classification system of pesticides
Type e.g. insecticide, herbicide
Toxicity - LD 50
Chemical composition e.g. organophosphate, carbamate, pyrethroid
Inert and active ingredients must be reviewed
True
Chronic health effects of pesticides
Neuro - parkinson's
Pysch- ADHD, anxiety
Resp - Asthma
Malignancy - leukemia
Pesticides are Neurotoxic, carcinogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic, respiratory and endocrine disruptors
True
A highly toxic pesticide with low exposure may pose less risk than a low-toxicity pesticide with chronic exposure.
True
Low toxicity glycophoshate chronic exposure is possibly higher risk than acute exposure to parathion
True
Who are the vulnerable groups
Pregnant
Breastfeeding
Children
Organophosphates have minimal bioaccumulation and environmental persistence
True
Paraquat
Oxidative Stress/ROS/Redox cycling
Ground water contamination
Bio-accumulation
Paraquat lung fibrosis,hepatotoxic, renal toxic
No antidote
Organophosphates: mechanism of human toxicity
Inhibits acetylcholinesterase enzyme at synapes
Phosphorylation of serine hydroxyl groups of the enzyme forming and OP-ACHe complex. Loss of an alkyl group(ageing) with time leads to irreversibility against oxime reactivation
Accumulation of acetylcholinesterase in the autonomic nervous system and central nervous system synapses
Overstimulation of acetylcholine receptors.
Exhaustion at synapses
Paralysis
Key elements of pesticide risk assement
Type of pesticides including it's chemical composition and active and inert ingredients
Concentration, frequency, duration of exposure
Individual susceptibility such as age, genetics
Symptoms of chronic OP exposure
Anorexia, malaise,weight loss
Neurobehavioral
Dermatitis
Cancer
Glyphosate health effects
Low acute toxicity
Chronic toxicity is a concern - IARC 2A - probably carcinogenic in humans , sufficient evidence in animals
**GENOTOXIN/DIRECT DNA DAMAGE
**ENDOCRINE DISRUPTOR
associated with increased risk.
Hepatic, renal, endocrine disruptor, non Hodgkin's lymphoma and breast ca
Muscurinic effects
Salivation
Lacrimation
Urination
Defecation
Gastrointestinal distress Emesis
Miosis
** Parasympathetic effects
Nicotinic effects
Cardiac Para and sympathetic effects - tachycardia, high BP
NMJ:
Skeletal somatic motor effects - fasciculations, tremors, muscle weakness paralysis
CNS ACH receptor effects
Confusion, headaches, seziures, coma and respiratory depression.
Respiratory muscurinic effects
Bronchospasm, wheeze,secretions
10 GHS TOXICITY HEALTH HAZARD
ACUTE TOXICITY
SKIN CORROSION/IRRITATION
EYE IRRITATION/INJURY
RESPIRATORY AND SKIN SENSITISATION
GERM CELL MUTAGENICITY
CARCINOGENICTY
REPRODUCTIVE TOXICITY
STOT - SINGLE
STOT- REPEATED
ASPIRATION
ENVIRONMENTAL PATHWAYS
SOIL, WATER, AIR POLLUTION
BIOACCUMULATION
GROUND WATER CONTAMINATION
IMPACT ON BEES, NON TARGET ORGAN SPECIES
BIOLOGICAL EXPOSURE MONITORING
MONITORING THE INTACT CHEMICAL OR METABOLITE IN BODY TISSUE OR FLUIDS
BIOLOGICAL EFFECT MONITORING
MONITORING THE BIOCHEMICAL OR PHYSIOLGICAL(intensity)EFFECT WITHIN THE HUMAN BODY
(EARLY REVERSIBLE ADVERSE EFFECTS)
EXPOSURE MONITORING STEPS
AMBIENT/AIR MONITORING
BIOLOGICAL EXPOSURE MONITORING
BIOLOGICAL EFFECT MONITORING
DIAGNOSIS OF OCCUPATIONAL DISEASE AND SCREENING
Cholinesterase monitoring conditions
Plasma vs Whole blood vs Red Cell
Valid Baseline
2-3 months no exposure
2 tests, three days to 2 weeks apart
Agree within 15-20%
Cholinesterase interpretation (Biological effect monitoring)
HCS regulations > 30% drop from baseline significant exposure
Cholinesterase decline: Actions to take
if > 20% drop from baseline for plasma or rbc — reassess work activities
if > 30% drop from baseline for red cell — remove from exposure, > 40% drop in plasma —remove from work
**REMOVAL INCLUDES NO EXPOSURE TO CATEGORY 1 AND 2 PESTCIDES!!
AND RETURN ONLY IF AT 80% OF BASELINE
BIOLOGICAL SAMPLE FOR PARAQUAT
URINE
Cholinesterase interpretation
Valid individual baseline
Red Cell - Chronic exposure, red cells, nerve endings/ nervous system effects, interindividual variability, genetics, anemia
plasma(pseudo/butyryl) - recent or acute exposure, liver synthesis, liver disease, alcohol, pregnancy, genetics
Whole is the composite of both
Carbamates
reversible inhibition of acetylcholinesterase.
Can be assessed with both rbc and plasma cholinesterase. Note the quick recovery of bche even during transport of sample
Don't use pralidoxime
Copper containing Pestcides
Molluscs, fungi, algae, bacteria
Boats, sewers
Human teratogen
Dermal effects(WEAK SENSITISER)
Pyrethoids
Common houselhold
Unknown effects - ? neurodevelop, reproductive and cardiovascular disease, parkinsons
Mechanism of Actions
Glycophosphate - protein/amino acids, shimikate pathway
Dicamba(auxin) - growth hormones
Atrazine - Photosynthesis, endocrine disruptors
Paraquat- ROS, mitochondria
Organophosphates chronic
Weight loss, anorexia, vision, neurobehavioral
Other subacute: neuropathy, intermediate syndrome
WHO LD 50 CLASSIFICATION ALIGNS WITH GHS ACUTE TOXICITY, BUT NOT CHRONIC HEALTH EFFECTS OF LOW DOSE EXPOSURE
TRUE
PESTICIDE CLASSIFICATION
TYPE OF PEST E.G. INSECT, RODENT, HERB/WEED
TOXICITY - LD 50 CLASSES (EXTREME- SLIGHYLY HAZARDOUS)
1A,B - EXTREME, HIGH <5, 5-50
2- MODERATE - 50- 2000
3- SLIGHT >2000
CHEMICAL HERBICIDES - ORGANOPHOSPHOROUS VS TRIAZINE VS QUAT VS AROMATIC E.G. PARAQUAT, DICAMBA
Organophosphate poisoning
Cholinergic syndrome
Plasma cholinesterase in Emergency department
Decontamination, abc, atropine and pralidoxime
Ageing
Time dependent irreversibility of the organophosphate acetylcholinesterase complex