HBS 2.1.1 and 2.1.2 The Brain
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is the PNS
Peripheral Nervous System
voluntary actions
involuntary actions
consists of nerves outside of CNS
sensory division
motor division
somatic (voluntary movement)
autonomic (ivoluntary)
parasympathetic (rest & digest)
sympathetic (fight or flight)
What is the somatic in the motor division
controls voluntary movement
what is the autonomic in the motor division
controls involuntary movement
what is parasympathetic in the autonomic
rest and digest
what is sympathetic in the autonomic
fight or flight
What is the CNS
consists of brain and spinal cord
sensory input
processes information
initiates commands
controls thought and emotion
cerebrum
thought
memory
senses
language
emotion
voluntary movement
cerebellum
maintains posture, balance
motor learning
timing
brain stem
breathing
heart rate
blood pressure
conscienceness
pathway for signals from spinal cord to brain
pons
breathing
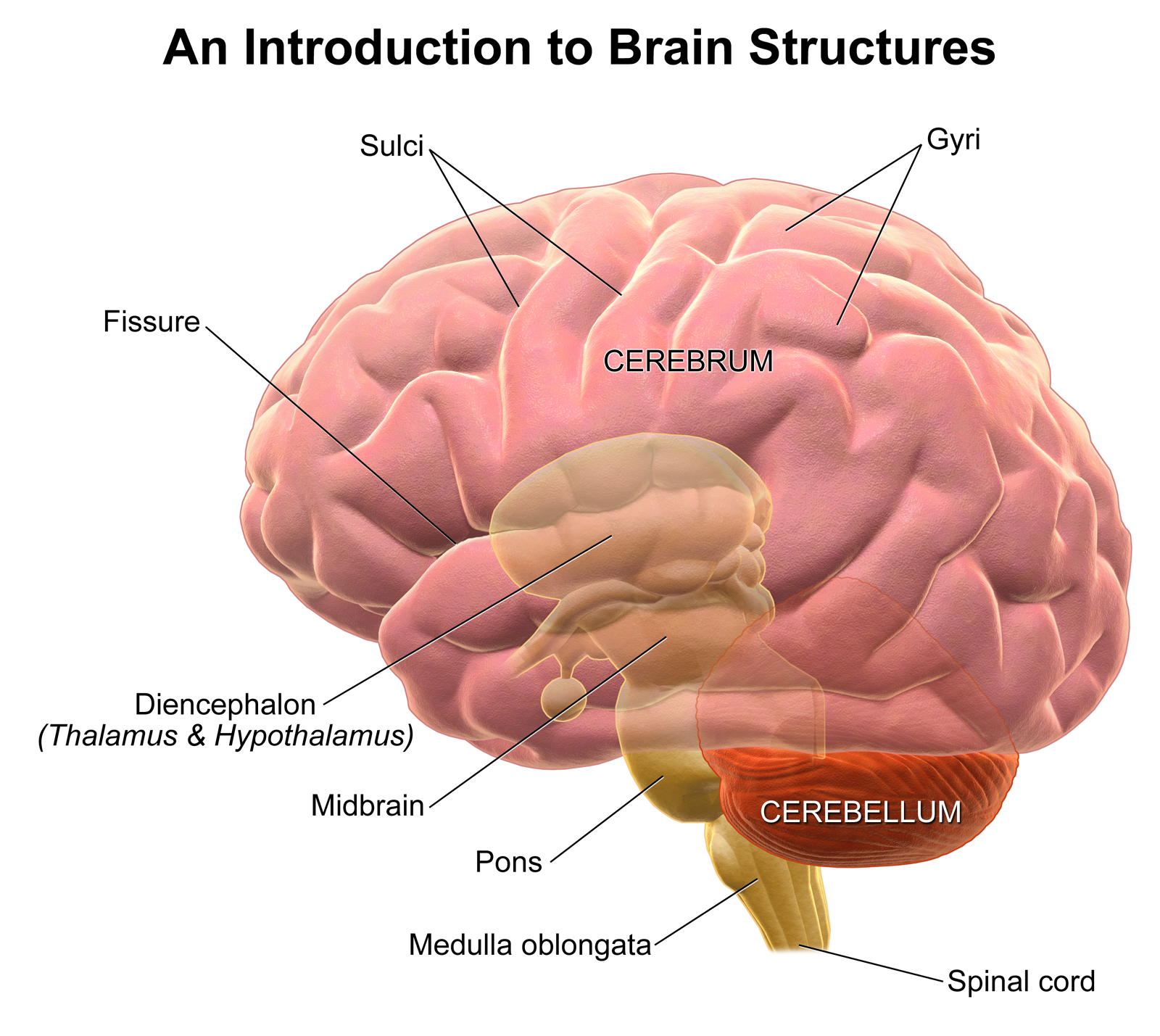
medulla oblongata
heart rate
blood pressure
breathing
swallowing
vomitting
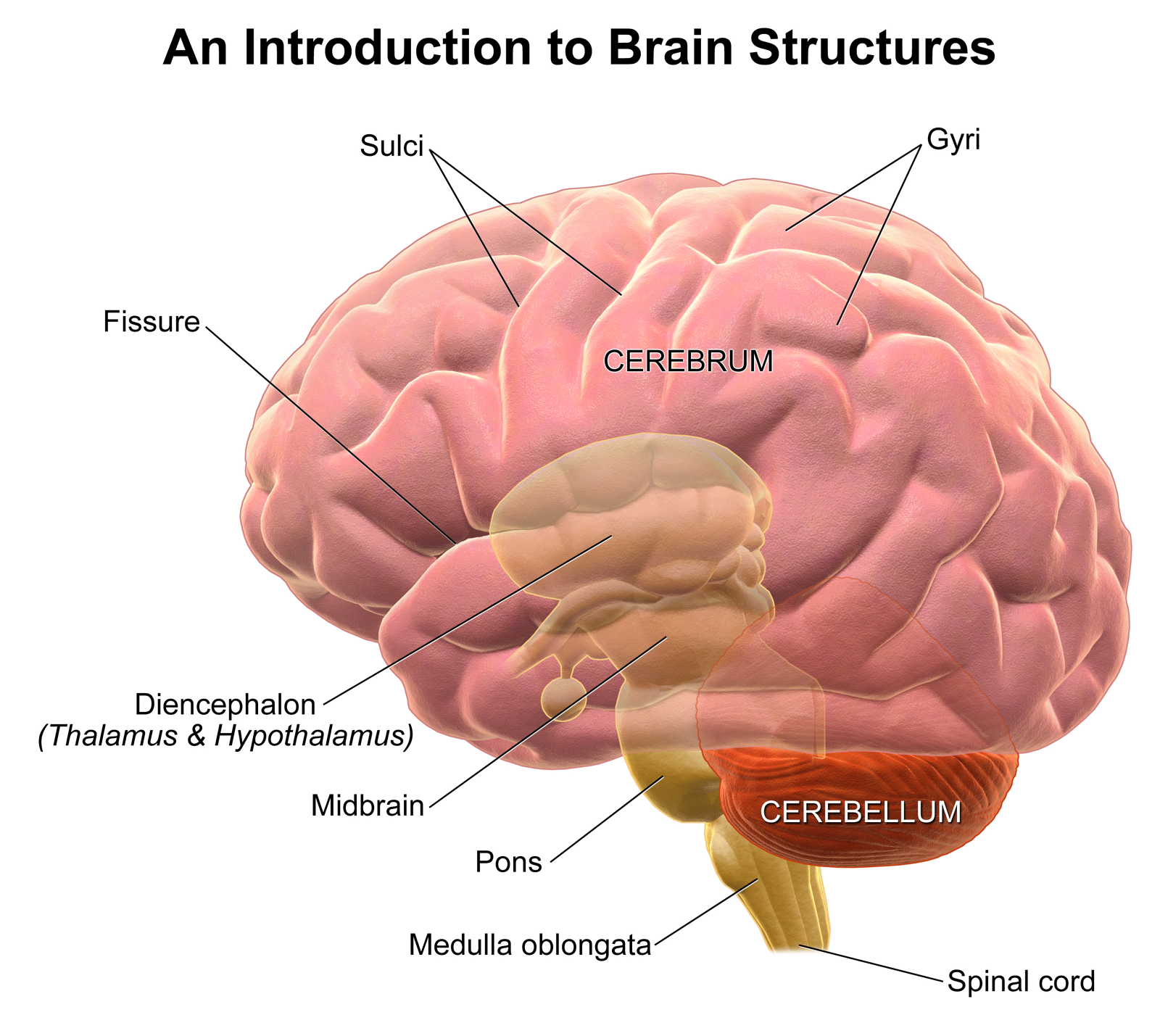
parietal lobe
taste
touch
pain
temperature
learning
memory
occipital lobe
takes vision and interprets it
visual memories
sends signals for response
frontal lobe
movement
thought
personality
decision-making
problem-solving
voluntary movement
speech production
temporal lobe
auditory
taste
form and retrieve memories
manage emotions
motor cortex
in the back of the frontal lobe
muscle movement
sensory cortex
front of parietal lobe
senses
pituitary gland
hormone production
growth
metabolism
tiny ball by pons
thalamus
routes sensory information and takes it to the proper cortex
big ball above pons
hypothalamus
water balance (hydration, dehydration)
body temperature
watery looking area in between thalamus and pituitary gland
hippocampus
long term memories
learning
below corpus callosum (second ring)
epitalamus
spinal fluid
gyri
brain’s ridges
sulci
shallow grooves in brain
fissures
large grooves separating major parts of the brain aka lobes
grey matter
contains neruon cell bodies (where processing happens)
white matter
myelinted axons that transmit signals between brain areas
reticular formation
running through brain steam (moves organs)
Where is vision processed
occipital lobe
where is muscle coordination processed
cerebellum
where is breathing processed
medulla oblongata and pons
where is language understanding processed
Broca’s area (frontal lobe) and Wernicke’s area (temporal lobe)
where is thirst and hunger processed
hypothalamus
where is speech production processed
broca’s area (frontal lobe)
where is movement processed
motor cortex in frontal lobe
where is smell processed
olfactory bulb in frontal lobe
where is hearing processed
temporal lobe
where are bodily sensations (temperature, pain, etc.) processed
sensory cortex in the parietal lobe
where is taste processed
temporal and frontal
where is blood pressure regulation processed
medulla oblongata
where is sleeping and waking processed
brainstem
where is balance processed
cerebellum
What is occuring on Broca’s area
brain plans and produces what it wants to say through motor movements
what is occurring in the Wernicke’s area
processes spoken and written words
what is an aphasia
language disorder caused by brain damage
what is occurring with broca’s aphasia
can’t physically say what they know they want to say
what is occurring with wernicke’s aphasia
can speak but no words make sense to any context