GBIO Final (Eva Hillmann; Southeastern Louisiana University)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Binary Fission
A form of asexual reproduction in single-celled organisms (in this case, bacteria) by which one cell divides into two cells of the same size
Steps of bacteria replication
1) starts at the bacteria
2) splits in two directions (opposite, typically)
3) Septum (cell wall) is formed, causing a termination of replication
Eukaryotic organisms have how many chromosomes...
10-50 chromosomes (chromatid pairs)
How many chromosomes do humans have?
46 (23 pairs)
Diploids
(2N) Humans; 46 chromosomes
Haploid
(N) Sperm/egg; 23 chromosomes
Homologue
a chromosome pair; each chromosome pair is alike in size and trait (eye color, hair color, etc)
Chromatin
mixture of DNA and proteins
Chromatin mixture ratio
DNA -- 40%
Protein -- 60%
Chromosome replication (beginning)
each chromosome has 1 DNA molecule
Chromosome replication (ending)
each chromosome has 2 identical DNA molecules (sister chromatids)
G1 (gap 1)
growth and development
what phase does DNA replication happen
G2 (gap 2)
preparation for division
M-phase (mitotic)
5 subphrases (PMAT-C)
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm into 2 cells
(end of m-phase)
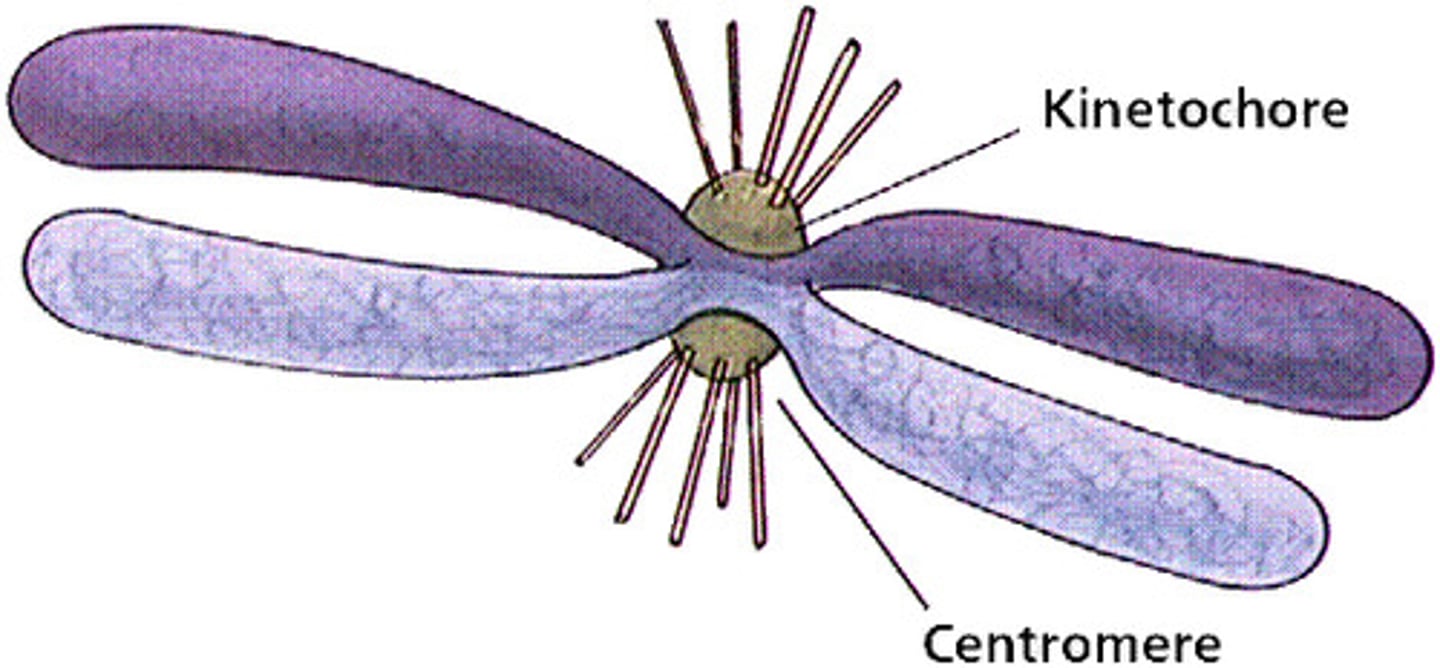
Centromeres
point of constriction
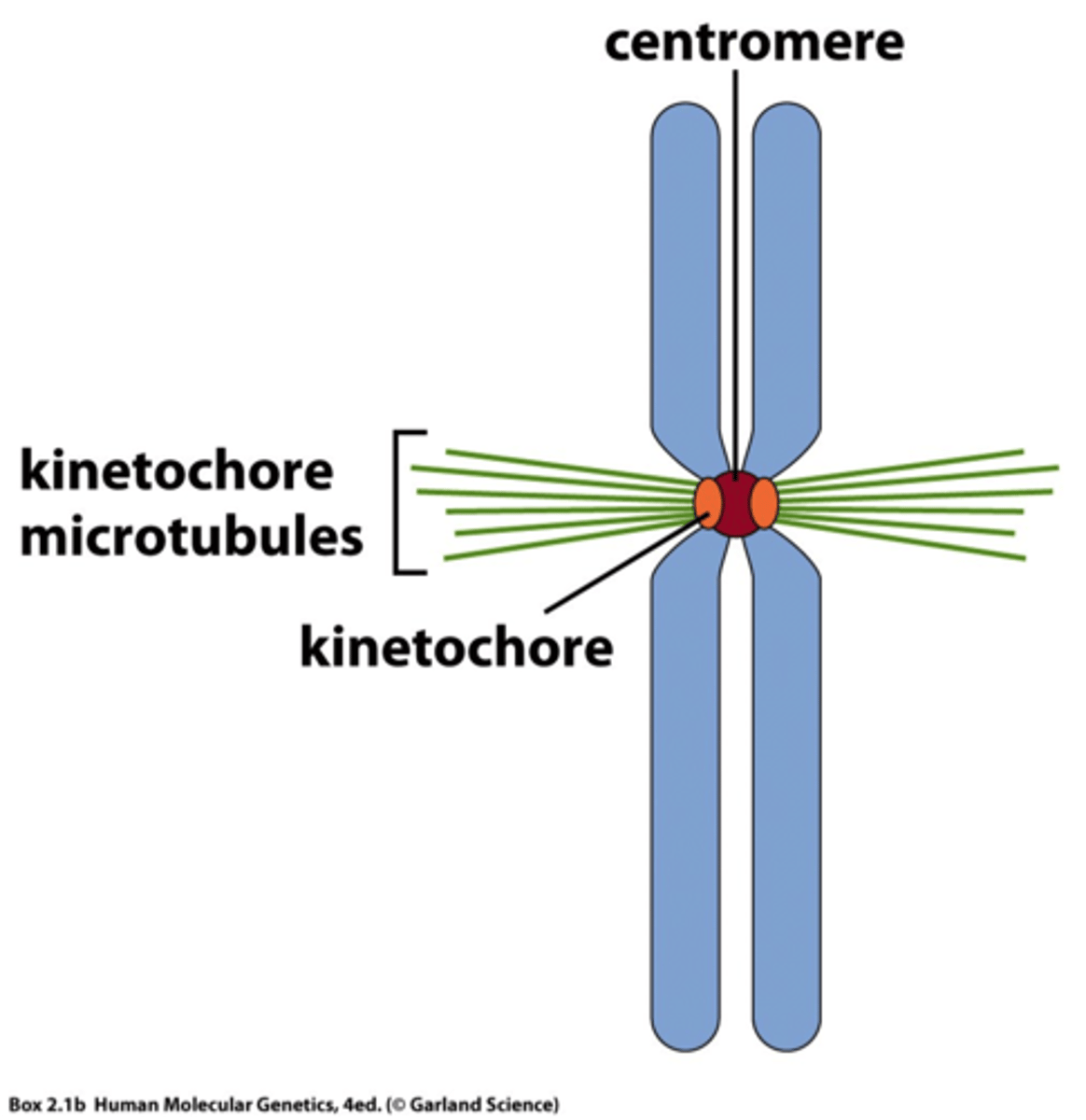
Kinetochore
point of attachment for microtubules
Steps of Interphase
1) G1
2) S
3) G2
Prophase
Chromosomes become visable, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle forms
Prometaphase
The second stage of mitosis, where MICROTUBULES attach to the KINETOCHORES
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase
sister chromatids (DNA copies) are pulled apart to opposite sides of the cell
Telophase
Nuclear envelope reforms; cell starts to pinch
Cytokinesis
Cell splits in half
(Animal cells: furrow)
(Plant cells: cell plate/wall)
Meiosis
sexual life cycles
Diploid cells
A cell containing two sets of chromosomes (2n), one set inherited from each parent.
Haploid cells
gametes, containing a single set of 23 chromosomes
Meiosis features
-- 2 rounds of division
-- synapsis (homogonous pairing)
-- chiasmata (crossing over)
-- NO DNA REPLICATION (unlike mitosis)
Interphase process
G1
S
G2
Meiosis 1
PMAT-1
(prophase 1)
(metaphase 1)
(anaphase 1)
(telophase 1)
Meiosis 2
PMAT-2
(prophase 2)
(metaphase 2)
(anaphase 2)
(telophase 2)
Josef Kolreuter (1760)
crossed tobacco strains to produce hybrids that differed from both parents
T.A. Knight (1823)
-crossed 2 varieties of garden pea, Pisum sativa
~ crossed 2 true-breeding strains
~ 1st generation resembled only 1 parent strain
~ 2nd generation resembled both
Gregor Mendel
applied science to his work with pea plants
Mendel steps
1) produce true breeding strains for each trait
2) cross fertilize treu breeding plants to create alt. forms of a trait
Monohybrid crosses
study 2 variations of a single trait
P
parent generation
F1
first filial generation
F2
second filial generation
F1 generation (ratio)
1:1 (100%)
F2 generation (ratio)
3:1 (75% -- 25%)
Mendel discovered
1 dominant trait
1 recessive trait
(for each genetic trait)
Mendel's model
1) Trait variation is due to alternative versions (alleles) of heritable factors (genes)
2) For each character an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent
3) Dominant alleles mask recessive alleles
4) Two alleles for a heritable character segregate (separate) during gamete formation and end up in different gametes (= Law of Segregation)
List of expressions
Dominant allele
Recessive allele
Phenotype
Genotype
Allele
alternative forms of a gene
Homozygous
2 of the same allele
Heterozygous
1 of each allele
Homorozygous Dominant
two same genes that are dominant; AA
Factors affecting phenotypes
1) environment
2) continuous variation (gradients, such as skin color or hair color)
3) Pleiotropy (diseases or disfigures that are almost impossible to predict)
4) Multiple alleles (blood type most commonly)
5) Co-dominance (mixture of 2 traits of the same gene that show together, such as light brown skin when mixed with white and brown)
6) Incomplete dominance (one trait is dominant over the other dominant trait)