Coordination and response
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Tropism
A growth response by a plant, in which the direction of the growth is affected by the direction of the stimulus.
Auxin
Type of plant hormone that promotes cell growth or elongation
Gravitropism/Geotropism
A response in which a plant grows towards or away from gravity
Phototropism
A response in which a plant grows towards or away from the direction from which light is coming
Stimulus
A change in an organism's surroundings that causes the organism to react
Receptors
Special structures that allow living organisms to sense the conditions of their internal or external environment.
Effectors
Causes responses that alter conditions in the internal environment
Examples of effectors
Muscles and glands
Nervous system
The body's communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells (receptors, nerves) of the peripheral and central nervous systems
Nerve impulses
Electrical signals from other neurones
Endocrine system
The body's chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
Neurones
Basic cells of the nervous system that carry minute electrical impulses around the body
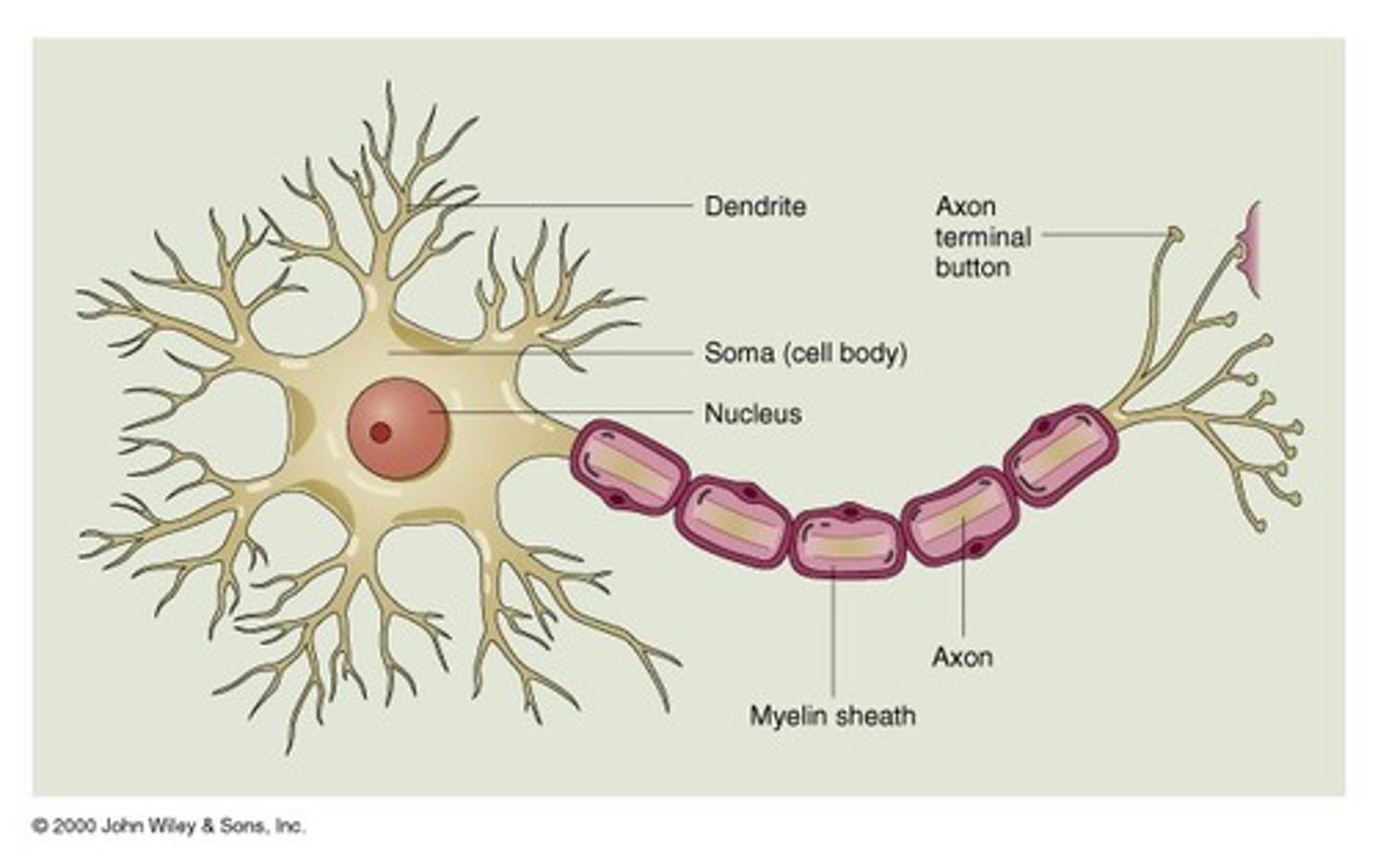
Structure of neuron
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Consists of the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
All of the parts of the nervous system except for the brain and the spinal cord, made up of nerves and receptors
Reflex Arc
- stimulus detected by receptors
- sensory neurones carry impulses to relay neurones in CNS
- relay neurones carry impulses to motor neurones
- motor neurones carry impulses to effectors
- effectors carry out response
Sensory Neurone
A neurone that sends impulses (from a sensory receptor) to a relay neurone in the spinal cord/CNS
Relay Neurone
Carries impulses from sensory neurone to motor neurone
Motor Neurone
Sends impulses from the spinal cord/CNS to the effector (muscle or gland)
Reflex action
An immediate response to a specific stimulus without conscious control
Synapse
A junction between two nerve cells, consisting of a minute gap across which impulses pass by diffusion of a neurotransmitter
Retina
The part of the eye that contains the receptor cells, and is therefore the part that is sensitive to light
Sclera
A very tough coat surrounding the part of the eye inside the orbit, in order to protect this part of the eye
Fovea
Part of the retina where light is focused
Blind spot
A spot near where the optic nerve leaves the retina where there are no receptor cells
Choroid
Jelly-like liquid which nourishes eye
Rod cells
A type of receptor cell that is sensitive to dim light, but doesn't respond to colour, found in the retina
Cone cells
A type of receptor cell that is able to distinguish between different colours of light, found in fovea
Iris
A circular piece of tissue in front of the lens, contains muscles to control diameter of the pupil
Pupil
A gap in the middle of the iris which lets light in
Circular muscles
When they contract, they make the pupil constrict, or get smaller
Radial muscles
When they contract, they make the pupil dilate, or get larger
Cornea
The clear tissue that covers the front of the eye and is responsible for most of the bending of the light
Lens
The transparent structure behind the pupil that changes shape to help focus images on the retina
Accomodation
The process by which the eye's lens changes shape to focus/adjust near or far objects on the retina
Suspensory ligaments
A fibrous membrane that holds the lens of the eye in place
Ciliary muscle
A smooth muscle portion of the ciliary body, which contracts to assist in near vision
Object far away
- relaxed ciliary muscles
- tightened suspensory ligaments
- thinner lens
Objects close by
- contracted ciliary muscles
- slack suspensory ligaments
- thicker lens
Hormones
A chemical substance produced by a gland, carried by the blood, which alters the activity of one or more specific target organs
Adrenaline
A hormone released into the bloodstream in response to a situation where the body may be in danger, 'fight or flight'