Crossing Over and Independent Assortment
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
DE Bio Unit 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
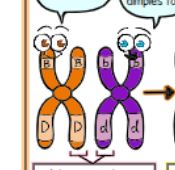
What kind of chromatids are shown?
non-sister
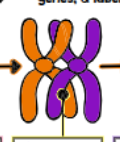
What kind of chromatids are shown?
chiasma
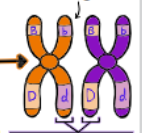
What kind of chromatids are shown?
recombinant
when homologous chromosomes pair up during prophase 1, they form a _____
tetrad
when the non-sister chromatids overlap, they form ______
chiasmata (singular - chiasma)
when the chiasmata are formed, parts of the chromatids _______ and reanneal on the other chromatid
break off
when chromatids break and reanneal on the other chromatid, alleles are exchanged forming new _______________
genetic combinations
what is the benefit of crossing over and independent assortment?
offspring have genetic variation, increasing change of survival and ability to adapt
in species that carry out sexual reproduction, where to the chromosomes in a body cell come from?
½ Parent One, ½ Parent Two
each chromosomes has a corresponding chromosome that contains the same genes
homologous pair of chromosomes
when a diploid cell divides it forms ______
two Haploid daughter cells
every gamete is _____
unique
During Metaphase 1, homologous pairs are randomly lined up which means each daughter cell ends up with a random combination of ______
chromosomes