Dentinal hypersensitivity and desensitization
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Histological zones of pulp
Odontoblastic zone
Cell-free zone of Weil
Cell-rich zone
Pulp core
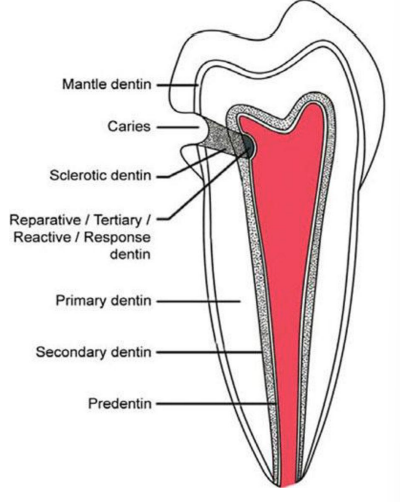
Outer layers of dentine
atubular or has tubules that are bent in loops
less mineralized
mantle dentine in crown
Tomes granule layer and hyalin Hopewell-Smith’s layer in root
Primary dentine
forms during initial tooth development
has organized tubules
Secondary dentine
forms after completion of tooth development
less structured than primary
slowly reduces pulp cavity size in tooth
Reactionary dentine
produced in response to pathological event
less structured than primary or secondary dentine
shields and protects pulp from noxious stimuli
Sclerotic dentine
forms to cover dentinal tubules
Label the basic layers of dentine
Dentinogenesis
Odontoblasts secrete predentine made of:
type I collagen
Non-collagen ECM molecules
Dynamic properties of dentine
Dentine goes from opaque to translucent with age
increase mineralization and loss of organic matter makes dentine more glassy
Increase in sclerotic dentine with age
covering of dentine tubules
increase mineralization of peritubular dentine
Decrease mechanical properties of dentine
increase risk of fracture
potential decreased hypersensitivity
What are common triggers of dentinal hypersensitivity
cold/heat
acid
sweet
air flow
Prevalence of dentinal hypersensitivity
4-57%
may affect eating, drinking, speaking, hygiene
can cause chronic dental pain (rare)
common in periodontal patients and people in 30s-50s
Mechanism of dentinal hypersensitivity
Dentine becomes exposed (local lesion)
hard/soft tissue damage
Localized lesion has to be initiated to become hypersensitive
smear layer or tubular plugs are removed
acid erosion (prominent factor)
Dentine smear
layer of debris, saliva proteins, cementum fragments that cover dentinal tubules
can plug openings of dentinal tubules
can be removed by acid = increase sensitivity
Theories to describe pain transduction through dentine
Dentine innervation theory
Odontoblast transduction theory
Hydrodynamic theory
Dentine innervation theory
C fibers and A fibers terminate in pulp and dentine
Odontoblast transduction theory
odontoblasts may have mechanosensory function
fluid movement in tubules is detected by odontoblasts — transmit signal to neurons in pulp
Hydrodynamic theory
External stimuli causes increased rate of outflow of tubular fluid from open dentine tubules
sensory nerves in pulp are activated by fluid outflow == short, sharp pain
In-office desensitizing agents
fluoride
sealants
adhesive
laser treatment
At-home desensitizing agents
toothpaste
mouthwash
Mechanical/chemical desensitizing agents
Focus on blocking/covering the dentinal tubules
salts
fluoride
oxalate
arganine/calcium
high output laser treatment
Pulpal nerve desensitizing agents
Focus on directly desensitizing pulpal nerves
pharmacological action
low output laser treatment
Invasive treatments for desensitization
For hypersensitivity related to abrasion/erosion
restoration with CR or GI
crowns/veneers
Related to periodontal disease/root exposure
tissue regeneration
flap surgery
tissue grafting