Biology: Lab Practical
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
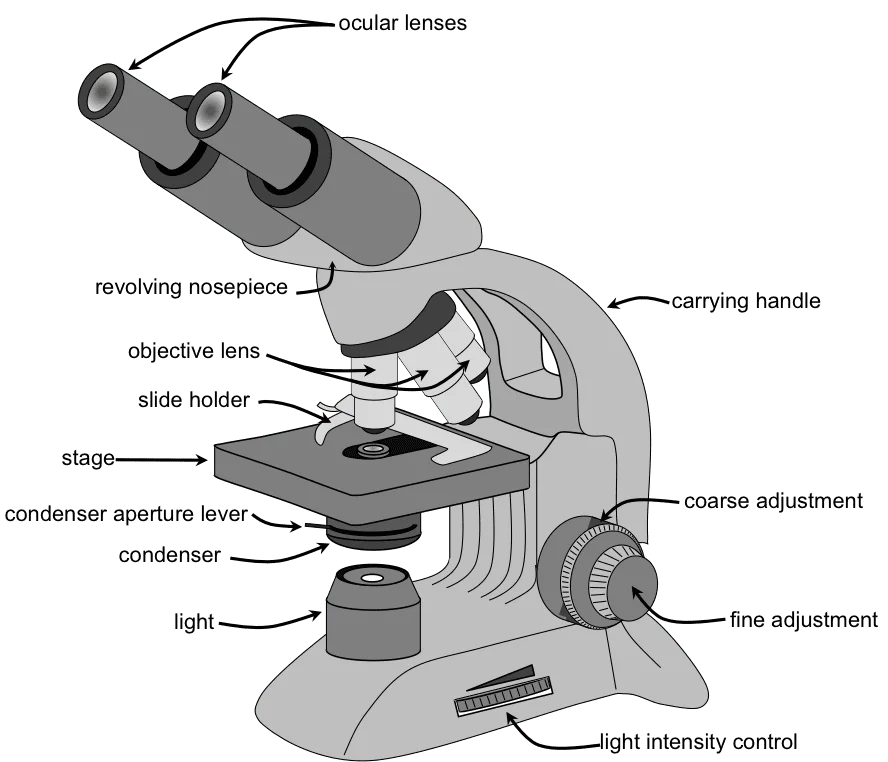
parts
Be able to lable all
magnification of eyepiece x magnification of objective lens (ex: cells being viewed using the 40x objective lens with a microscope that has a 10x ocular lens = 400x magnification)
Total magnification =
decrease in depth of field (and vice versa)
Increase in magnification =
temperature, pH, and salinity
What are some of the factors that may influence enzyme activity?
denature
What would happen if enzymes were exposed to too high of temperatures and the proteins lose structure or function?
amylase
Which type of enzyme digests starch?
1- add Benedict’s solution to the sample
2- Heat in water bath
What are the steps to run a Glucose test?
glucose test
Benedicts solution =
orange/yellow
Positive for glucose =
blue
Negative for glucose =
1- Add iodine to the sample
2- Let sit in room temperature conditions
What are the steps to run a starch test?
starch test
Iodine =
blue/black/purple
Positive for starch=
brown
Negative for starch=
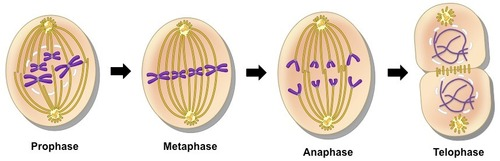
1- Prophase
2- Metaphase
3- Anaphase
4- Telophase
What are the phases of mitosis?
interphase
What occurs before mitosis?
PMAT under a light-microscope
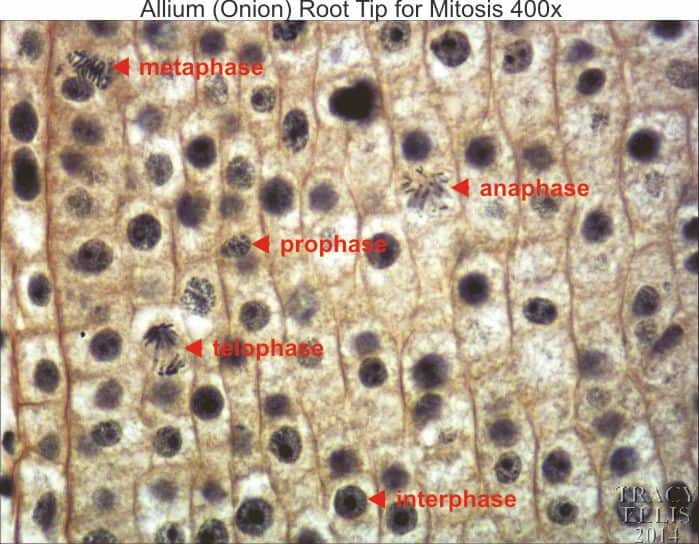
PMAT models
46
If a human somatic cell contains 46 chromosomes before mitosis, how many will it contain after?
diploid (2n)
If a cell is 2n (diploid) before mitosis, will it be diploid (2n) or haploid (n) after mitosis?
binary fission- paramecium, other one-celled organisms
budding- hydra, and many yeasts
tuber- potatoes
bulb- tulips, glads
What are the different modes of asexual reproduction and give an example?
bianary fission
a single organism splits into two equal parts
budding
a small growth forms on the parent and detaches to grow into a new organism
tuber
underground storage stems with buds that grow into new plants
bulb
a rounded underground storage organ with fleshy leaves that con sprout new plants
Prophase I
During what stage of meiosis does crossing over occur?
23
If a primary oocyte contains 46 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will a mature sperm cell contain?
15
If a primary spermatocyte contains 30 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will a mature sperm cell contain?
haploid (n)
If a cell is 2n (diploid) before meiosis, will it be a diploid (2n) or a haploid (n) after meiosis?
Oocytes (egg cells) and sperm cells are haploid (n) to ensure that when they fuse during fertilization, the resulting zygote has the correct diploid (2n) chromosome number (prevents doubling).
Why does it make sense for an oocyte and a sperm cell to be a haploid (n)?
stigma, style, ovule (pistil)
Which parts of the flower are female?
anther, filament (stamen)
Which parts of the flower are male?
dominant allele
Represented by a capitate letter / masks the effect of a recessive allele
recessive allele
Represented by a lowercase letter / only expressed when two copies are present
heterozygous (Aa)
two different alleles for a gene
homozygous (AA or aa)
two identical alleles for a gene
genotype
genetic makeup of an organism
phenotype
the physical expression or appearance of a trait based on the genotype and the environmental factors
gene
a segment of DNA that carries the instructions for making a particular protein or for controlling a specific trait (ex: eye color)
allele
a variant or different form of a gene (ex: allele (B) blue eyes allele (b) brown eyes))
genetic ratio
3:1 is an example of a ___
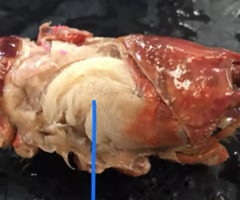
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Crustacea
Order: Decapoda
What is the classification of a crayfish?
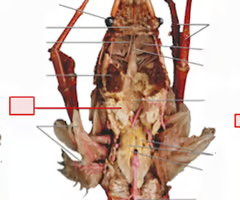
Male crayfish

Female crayfish
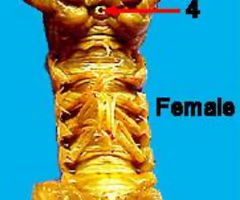
Antennae

Antennules

Cheliped

Cephalothorax

Abdomen
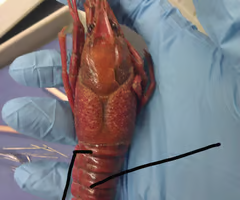
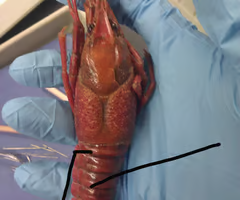
Abdomen
Uropods
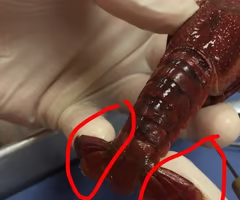
Walking legs

Swimmers

Stomach
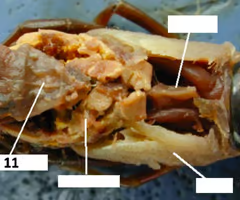
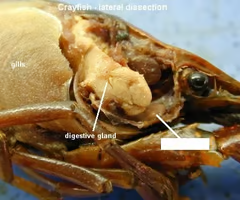
Gills
Digestive gland
Heart
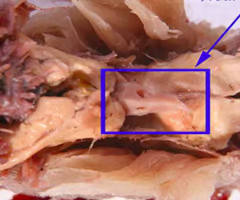
Intestine
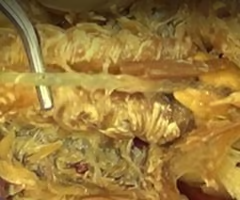
Nerve cord

Green gland
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Amphibia
What is the classification of the frog?
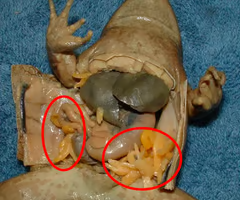
Male frog
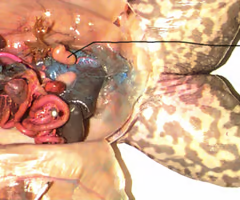
Female frog
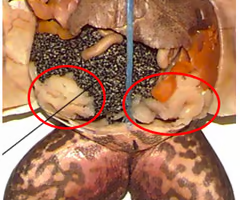
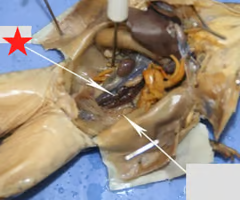
external nares

eye

maxillary teeth
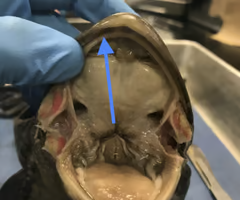
cloaca
vomerine teeth
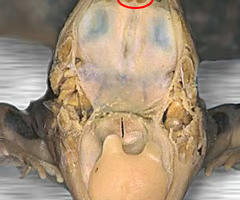
heart
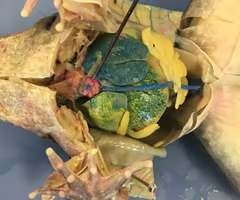
liver
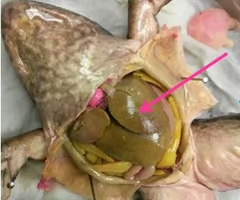
gallbladder

stomach
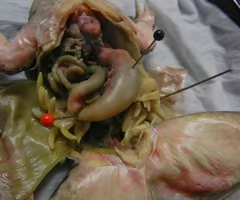
small intestine
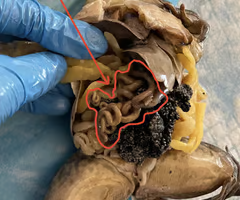
large intestine

spleen
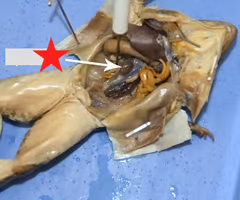
lungs
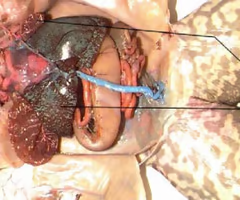
ovaries
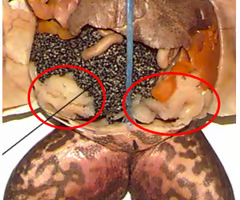
fat body
kidneys
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Aves
What is the classification of a Barn owl?
count the skulls and multiply by pellets per day/week/month/year
How do you calculate how many prey items an owl consumes per week/month/year?
predator
an organism that hunts and eats other animals (prey)
heterotroph
An organism that cannot make its own food and must consume other organisms for energy
autotroph
an organism that makes its own food, usually through photosynthesis
producer
makes energy-rich compounds from sunlight or chemicals
consumer
organisms that eat other organisms to gain energy
sharp talons, good eye site and hearing
Why are owls good hunters?
cardinal

Canada goose

Crow

American robin

Blue jay

Turkey vulture

Goldfinch

Red bellied woodpecker

Red-headed woodpecker

Black-capped chickadee

simple leaf
one leaf per axillary bud
compound leaf
multiple leaflets per auxiliary bud
Alternate leaf