Quiz 2: Bacterial Structures and Light Microscopy
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Label the parts of the microscope and describe the function of each one
Arm of microscope: where the microscope is held when relocating it
Coarse focus knob: moves the lens for coarse focus
Fine focus knob: moves the lens for fine focus
Stage knobs: moves the stage
Base of microscope
Light knob: adjusts light intensity
Light switch: turns on the lamp
Light source (lamp): provides light for specimen analysis
Iris diaphragm: adjusts light intensity
Condenser Lens: a focused light beam passes through the specimen
Specimen: item being analyzed
Objective lenses: 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x
Ocular lens: where the eyes are placed on to see the specimen
Provides an additional 10x magnification
Purpose of Gram staining:
differentiates bacteria based on the properties of their cell wall
Steps for Gram Staining:
Heat: application of heat to fixate the sample (specimen smear)
Crystal violet: application of primary stains to specimen smear to form a colorful complex (CVI) which is trapped inside the cell wall
Followed by a water rinse
Gram iodine: application of primary stains to specimen smear to form a colorful complex (CVI) which is trapped inside the cell wall
Followed by water rinse
Alcohol: decolonization of the same with alcohol (decolorizer)
Gram-negative cells lose the CVI complex, while Gram-positive cells retain it
Followed by water rinse
Safranin: application of counterstain to the sample
Followed by water rinse
Reveals color to determine whether specimen is gram positive or negative
What color would indicate Gram-positive and Gram-negative?
Gram-positive bacteria: purple or dark blue
have a thick cell wall outside their plasma (cell) membrane composed of many layers of peptidoglycan
Gram-negative bacteria: pink or reddish
have a very different composition outside of the plasma membrane.
Identify accurately the shape and cell arrangement of cells on a microscope slide.
Two main categories of bacterial shape:
Cocci: sphere-shaped
Bacilli: rod-shaped
Other shapes:
Curved rods: comma-shaped
Spirochete-shaped bacteria: spiral-shaped
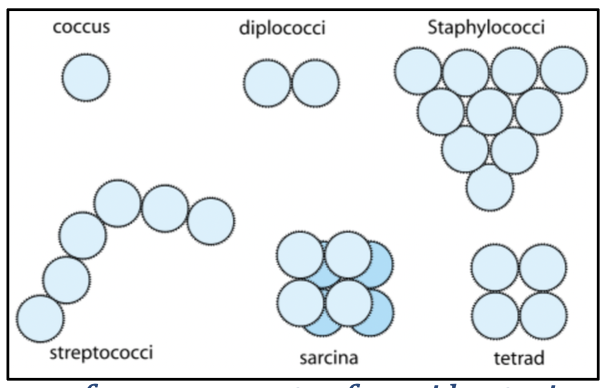
Arrangement of bacterial cells can indicate their speicies:
coccus: single bacterial cell
diplococci: double
staphylococci: a bunch of grapes
Streptococci: long chain
Sarcina: eight cells clumped together
tetrad: four cells arranged together in the same plane
Purpose of immersion oil
has the same refractive index as glass and will minimize the loss of light and light refraction creating a crystal-clear image of the cells.
a drop of immersion oil is added on top of the slide to replace the air in the working distance.
List of PPE
personal protective equipment:
Blue lab coat since it is fire resistant
Gloves
Goggles
describe the proper handling of food, drinks and cosmetics in the lab
No food, drinks, or gum are allowed in lab
No putting on any sort of cosmetics during lab, not even chapstick
describe the proper clothing to wear in the lab as well as the safe ways to wear your hair and jewelry
Long pants
Closed-toe shoes
Tie back hair and tuck under lab coat if necessary
Take off any loose jewelry that might possible get in the way of the lab procedure
describe when you need to disinfect the benches
Disinfect lab benches before and after use
which structure does the gram-stain stain and how do we get two different results based on the cell structure?
the cell wall is stained with a gram-stain
we get two different results depending on the thickness of the peptidoglycan layer in the cell wall and its capability to trap the CVI complex