1. AQA GCSE Biology: Cell Biology
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Eukaryotic cells
Plant and animal cells
What characterises eukaryotic cells? (3)
Cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus
Prokaryotic cells
Bacterial cells
What characterises prokaryotic cells? (4)
1. much smaller in comparison
2. have a cytoplasm and cell membrane surrounded by cell wall
3. genetic material is a single DNA loop not enclosed in a nucleus
4. may be 1 or more small rings of DNA called plasmids
Millimetre
mm, thousandth of a metre, 10^-3m
Micrometre
μm, millionth of a metre, 10^-6m
Nanometre
nm, billionth of a metre, 10^-9m
Nucleus
Contains genetic information and controls cell's activities
Cell membrane
Controls the passage of substances in and out of the cell e.g. glucose and ions
Cytoplasm
Where most chemical reactions take place
Ribosomes
Where protein synthesis takes place
Mitochondria
Where aerobic respiration takes place
Chloroplasts
Where photosynthesis occurs because contain chlorophyll (in plant cells)
Plasmids
Small rings of DNA which code for very specific features such as antibiotic resistance (in bacterial cells)
Most animal cells have... (5)
1. Nucleus
2. Cytoplasm
3. Cell membrane
4. Mitochondria
5. Ribosomes
In addition to the parts found in animal cells, plant cells often have...
1. Chloroplasts
2. Permanent vacuole filled with cell sap
Plant and algal cells also have...
...a cell wall made of cellulose which strengthens the cell
Equipment for microscopy practical (6)
1. Microscope
2. Onion
3. Scalpel
4. Forceps
5. Slide and cover slip
6. Iodine
What must you remember when you are drawing cells from a microscope? (2)
1. Draw in neat pencil lines
2. Note down what magnification you are using
Microscopy practical
1. Cut a thin sample of onion with the scalpel and place it on the slide
2. Add a few drops of iodine
3. Carefully place a cover slip on top, avoiding air bubbles
4. Place the slide onto the stage
5. Select the lowest-powered objective lens
6. Use the coarse adjustment (/focus?) and then fine adjustment knob to focus your image
7. If necessary, select a higher-powered objective lens and refocus
How are sperm cells adapted for their function? (5)
1. Function: to swim to and fertilise an egg cell
2. Lots of mitochondria in middle section provide energy to tail
3. Tail is long and contains muscle-like proteins for swimming
4. Acrosome (head) stores digestive enzyme for breaking down outer layers of egg
5. Large nucleus contains genetic information to be passed on
How are nerve cells adapted for their function? (4)
1. Function: to transmit messages from one part of the body to another
2. Axon is very long so easier to communicate over further distances
3. Dendrites (branched endings) allow connections with many other neurones
4. Nerve endings contain lots of mitochondria to provide energy to make transmitter chemicals
How are muscle cells adapted for their function? (4)
1. Function: to generate movement
2. Contain many mitochondria to transfer the energy needed
3. Can store glycogen which can be used in respiration to transfer the energy needed
4. Contain special proteins that slide over each other making the fibres contract
How are root hair cells adapted for their function? (4)
1. Function: to absorb minerals and nutrients from the soil
2. Increased surface are for water to move into the cell
3. Large permanent vacuole speeds up the movement of water by osmosis
4. Many mitochondria to transfer the energy needed for active transport
How are xylem cells adapted for their function? (3)
1. Function: to carry water and mineral ions from the roots to the rest of the plant
2. Coated in lignin which kills cells, waterproofs them and creates a long hollow tube
3. Spirals of lignin make them strong to withstand water pressure and support stem
How are phloem cells adapted for their function? (3)
1. Function: to transport sugar from the leaves to the rest of the plant (translocation)
2. Cell walls between cells form sieve plates (tiny holes) which allow dissolved food to move between cells
3. Supported by companion cells which have mitochondria to transfer energy for translocation
Why is cell differentiation important?
So that cells can become specialised for a particular function and carry out this function in the most efficient way
When do most types of animal cells differentiate?
At an early stage
Many types of plant cells...
...retain the ability to differentiate throughout life
How is cell division restricted in mature animals?
Cell division is mainly restricted to repair and replacement
What happens as a cell differentiates?
It acquires different sub-cellular structures to enable it to carry out a certain function. It has become a specialised cell
Light microscopes
1. Use a beam of light and lens to form an image
2. Can magnify up to around 2000 times
3. You can see individual cells and nuclei
Electron microscopes
1. Invented in 1930s
2. Use beams of electrons to form an image
2. Can magnify up to 2,000,000 times - subcellular structures
3. Transmission microscopes give 2D images with high magnification and low resolution
4. Scanning electron microscopes give 3D images but with a lower resolution
Resolution
The ability to distinguish between 2 points
Magnification
How small you can go
Why can an electron microscope be used to study cells in much finer detail than with a light microscope?
It has a much higher magnification and resolving power
What have electron microscopes enabled biologists to see and understand?
Many more sub-cellular structures
Magnification =
size of image/size of real object
How do bacteria multiply?
Simple cell division (binary fission)
How often do bacteria multiply?
Up to every 20 minutes, if they have enough nutrients and a suitable temperature
How can bacteria be grown? (2)
1. Nutrient broth solution
2. As colonies on an agar gel plate
What is required for investigating the action of disinfectants and antibiotics?
Uncontaminated cultures of microorganisms
What is aseptic technique used for?
To prevent contamination of unwanted microorganisms
Describe the aseptic technique required to prepare an uncontaminated culture (4)
1. Sterilise petri dishes and culture media (usually by heating)
2. Sterilise inoculating loop by passing through flame
3. Lid of petri dish secured with tape and stored upside down
4. Incubated at 25 degrees C (in school laboratories)
Culture medium
A liquid or gel containing nutrients for bacteria
Why must the Petri dishes and culture be sterilised before use?
To ensure no microbes are present before the experiement
Why must the inoculating loop be sterilised before use?
To ensure no microbes are present and prevent contamination from previous uses
Why must the lid of the Petri dish be secured with adhesive tape and stored upside down?
Tape - so bacteria cannot escape but oxygen is still able to get in for aerobic respiration
Stored upside down - to stop condensation (and other microbes?) falling onto the agar jelly from the lid
Why should cultures be incubated at 25 degrees C in school laboratories?
To encourage bacterial growth but not be so high as to encourage pathogenic bacteria to grow
Area of a circle
πr^2
Zone of inhibition
A clear area of agar gel indicating the bacteria have been killed
Reproducible
Same method but by a different individual
Difference in antiseptic effectiveness =
diameter of largest zone of inhibition/diameter of smallest zone of inhibition
Why should you include a piece of filter paper with nothing added to the agar jelly?
As an experimental control so the results can be compared
What 2 hazards could you control in the experiment on the effectiveness of antiseptics?
1. Prevent pathogenic bacteria from growing by not incubating at more than 25 degrees C
2. Stop disinfectant touching skin by using forceps to pick up the disinfectant disks
Calculating bacterial populations equation
Bacteria at the end of the growth period = bacteria at the beginning of the growth period x 2^number of divisions
The mean division time for a population of bacteria is 30 mins. How many bacteria will result from one bacterium after 8 hours?
How many divisions:
2 x 8 = 16
Number of bacteria at start x 2^16 = 65,536
= 65,536 bacteria
Chromosome
A structure made up of DNA molecules. Each chromosome carries a large number of genes. In body cells these are normally found in pairs.
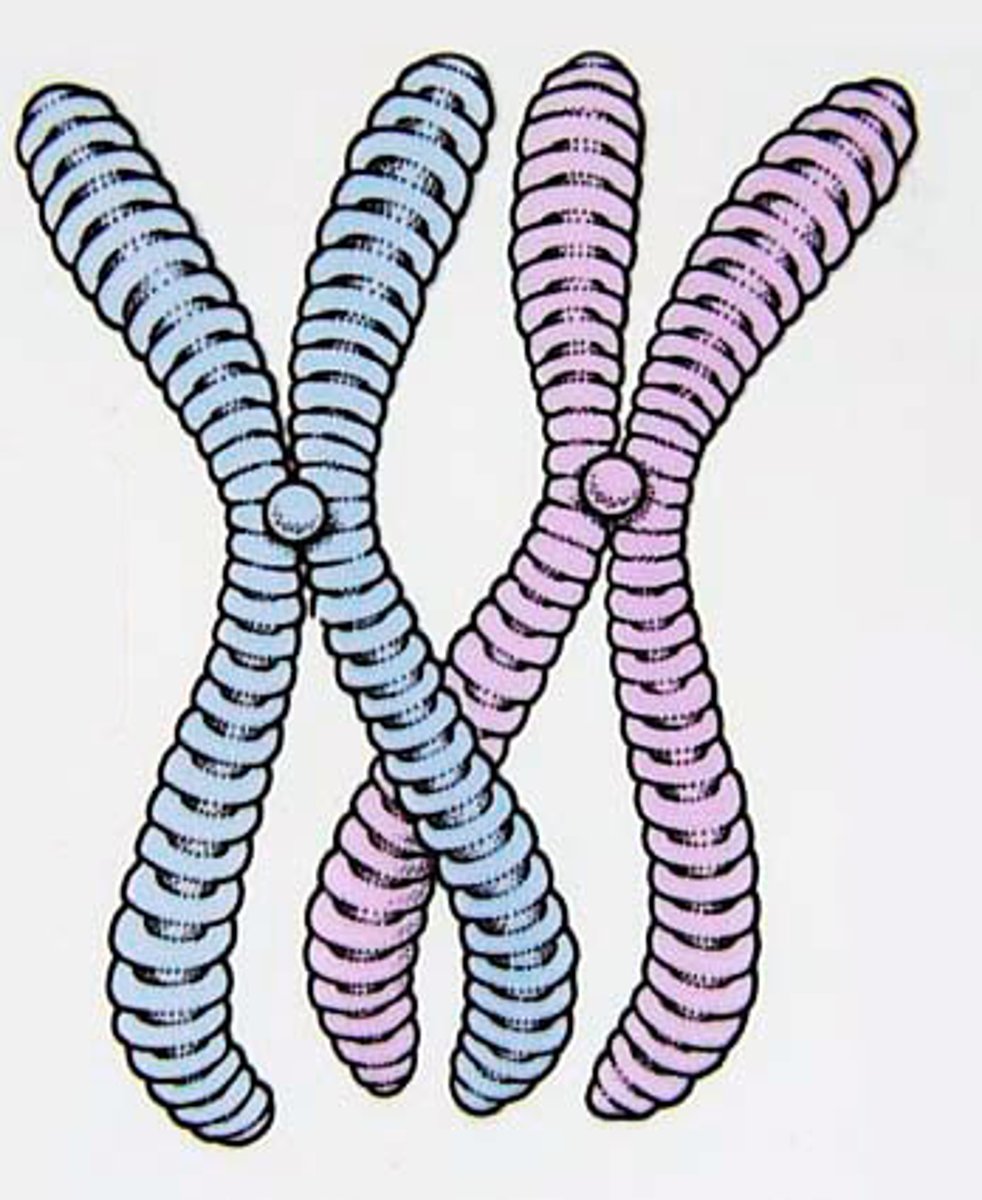
Where are chromosomes found?
The nucleus of a cell
What are the 3 stages of the cell cycle?
Interphase, cell division and cytokinesis
Interphase
Longest part of cell cycle; cell grows, develops and functions in parts of our body. Almost at the end of interphase, genetic material is doubled
Cytokinesis
When the cell cytoplasm divides to form the daughter cells
What must happen before a cell can divide?
1. It needs to grow and increase the number of sub-cellular structures such as ribosomes and mitochondria
2. The DNA replicate to form 2 copies of each chromosome
What happens during mitosis?
1. One set of chromosomes is pulled to each end of the cell and the nucleus divides
(2. The cytoplasm and cell membrane divide to form 2 identical cells)
During the cell cycle, the genetic material...
...is doubled and then divided into two identical cells
Cell division by mitosis is important in...
...the growth and development of multicellular organisms
Further cell division, stem cells, monoclonal antibodies and therapeutic cloning
See this quizlet set: https://quizlet.com/240906580/gcse-aqa-biology-cell-division-monoclonal-antibodies-flash-cards/
How do substances move into and out of cells across the cell membrane?
via diffusion
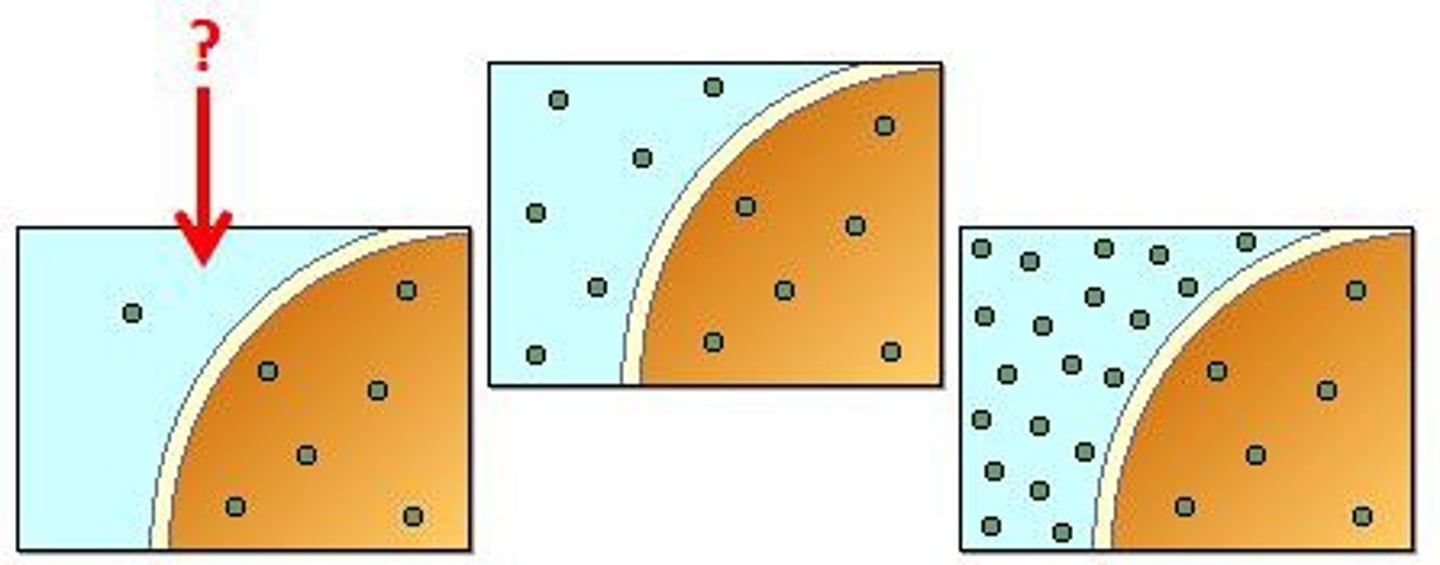
Diffusion
The spreading out of the particles of any substance in solution, or particles of a gas. resulting in a net movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
What are some substances transported in and out of cells by diffusion? (2)
1. Oxygen and carbon dioxide in gas exchange
2. Waste product urea from cells into the blood plasma for excretion in the kidney
What 3 factors affect the rate of diffusion?
1. Temperature
2. Surface area of membrane
3. Steepness of concentration gradient (difference in concentrations)
How does temperature affect diffusion? (2)
1. If temperature is increased, particles have more kinetic energy
2. Diffusion takes place more rapidly as the random movement of particles speeds up
How does concentration gradient affect diffusion? (2)
1. If the difference between the concentration of two areas is greater, the rate of diffusion will be faster
2. The particles will be close together if they are concentrated and will collide together often so will spread rapidly to the less concentrated area
How does the surface area of the membrane affect the rate of diffusion?
As the surface area increases, there is more space for particles to pass through the membrane, therefore more particles will diffuse across it
The large surface area to volume ratio of a single celled organism allows...
...sufficient transport of molecules into and out of the cell to meet the needs of the organism
Why do multi-cellular organisms need exchange surfaces?
As organisms get bigger and more complex, their SA:vol ratio gets smaller, making it increasingly difficult to exchange materials quickly enough with the outside world without a specialised surface
How is the small intestine in mammals adapted for exchanging materials?
Villi provide large surface area, short diffusion paths and rich blood supply
How are the lungs in mammals adapted for exchanging materials?
Alveoli have an enormous surface area and rich blood supply
How are gills in fish adapted for exchanging materials? (3)
1. Many gill filaments increase surface area
2. Gills have a rich blood supply - lots of capillaries
3. Pump water needed to maintain concentration gradient over gills with a flap called the operculum
How are roots in plants adapted for exchanging materials? (2)
1. Large surface area, increased by root hair cells
2. Water moves constantly away from roots in transpiration stream, maintaining concentration gradient
How are leaves in plants adapted for exchanging materials?
Flat, thin leaves, presence of air spaces and stomata help provide a big surface area and maintain a steep concentration gradient
What is the effectiveness of an exchange surface increased by? (4)
1. Large surface area
2. Thin membrane to provide a short diffusion path
3. (in animals) efficient blood supply
4. (in animals for gaseous exchange) being ventilated
Osmosis
The diffusion of water from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a partially permeable membrane
Isotonic
External concentration of solutes is the same as internal concentration
Hypertonic
External concentration of solutes is greater than internal concentration

Hypotonic
External concentration of solutes is lower than internal concentration
Describe an investigation into the effects of osmosis on plant tissue.
1. Cut potato chips using a cork borer, use scalpel to trim to same size
2. Find the mass and length of each chip
3. Pour 5cm3 water into test tube
4. Add 5cm3 of salt solutions of different concentrations
5. Leave for 30 mins
6. Remove chips and blot
7. Record masses and length of chip
Percentage change
Percentage change = change in value/original value x 100
Crenation
When an animal cell is put into a hypertonic solution - water has travelled out by osmosis

Lysis
When an animal cell bursts because it has been put into a hypotonic solution - water has travelled in by osmosis

Flaccid
When a plant cell is put into a hypertonic solution - the cell membrane becomes plasmolysed
Turgid
When a plant cell is put into a hypotonic solution and it swells
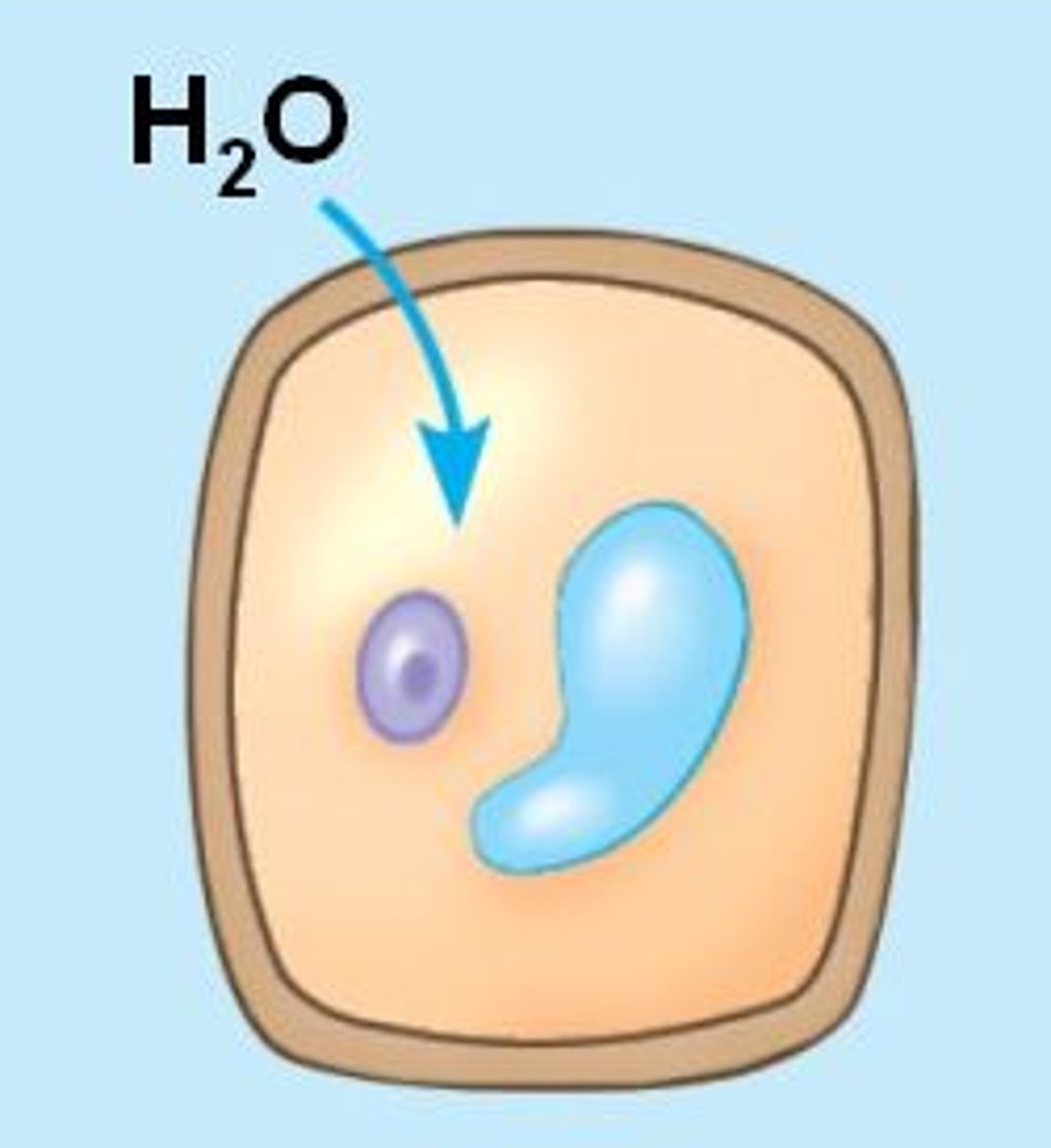
Active transport
Move substances from a more dilute solution to a more concentrated solution (against a concentration gradient). This requires energy from respiration.
What does active transport allow in plants?
Mineral ions to be absorbed into plant root hairs from very dilute solutions
What do plants require mineral ions for?
Healthy growth
What does active transport allow in humans?
Sugar molecules to be asborbed from lower concentrations in the gut into the blood, which has a higher sugar concentration
What are sugar molecules used for?
Cell respiration
How are molecules moved by active transport into cells?
By carrier proteins which use energy from respiration to transport molecules against a concentration gradient