Invertebrate chordates
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
-
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
what are the invertebrate chordates?
invertebrate - animals without backbone
chordates - animals with nerve cord
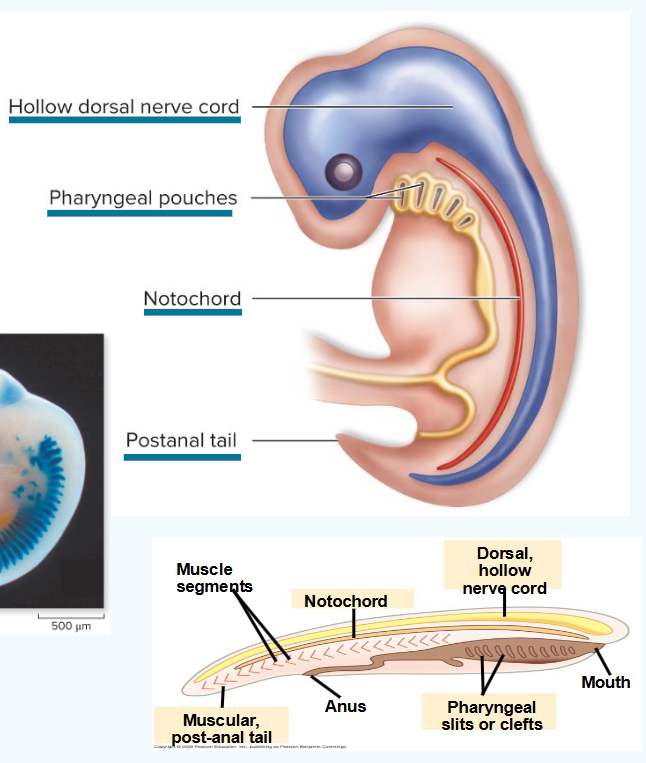
what is the notochord?
longitudinal flexible rod between gut and nerve cord
provides structural support
key for swimming in chordate ancestors
replaced by vertebrae in vertebrates
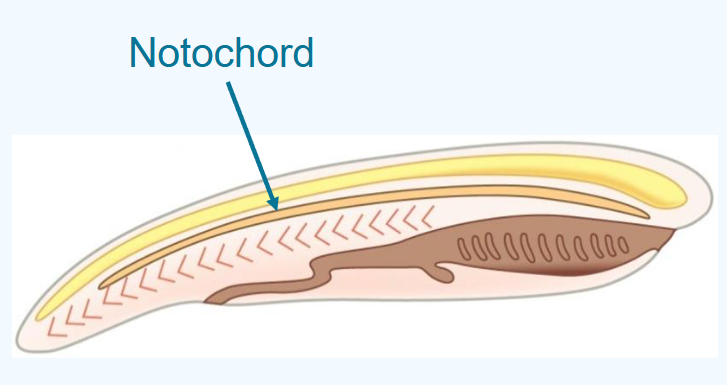
what is the dorsal hollow nerve cord?
lies dorsal to the notochord
develops from rolled ectodermal tissue
develops into the central nervous system
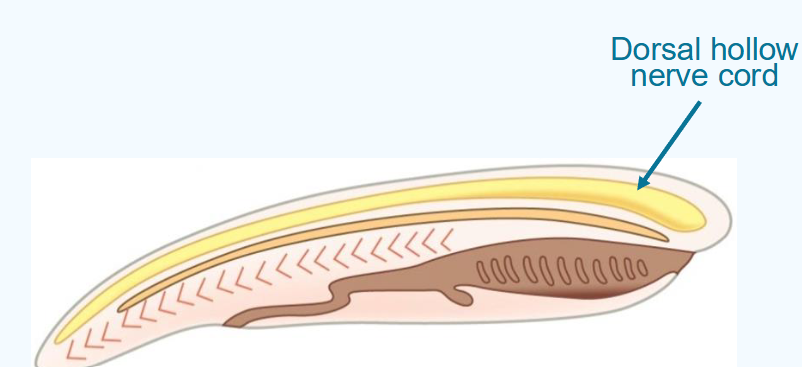
what are the pharyngeal slits?
slits that open to the outside of the body
develop from grooves in the pharynx called pharyngeal clefts
functions:
suspension feeding
gas exchange in vertebrates
repurposed - ear structures and tonsils
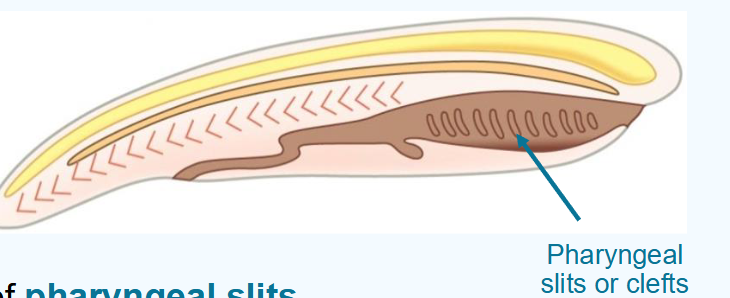
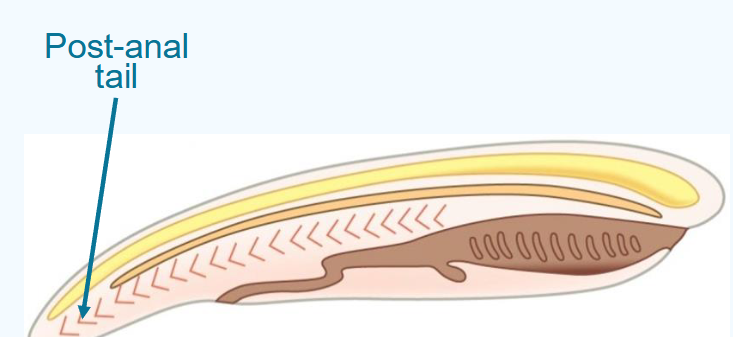
what is the post anal tail?
chordates have a tail posterior to the anus
contains skeletal elements and muscles
provides propulsion in many aquatic species
reduced or lost in many species
Why are they not quite vertebrates?
two invertebrate lineages: tunicata and cephalochordata
both closer to vertebrates than other invertebrates
differences:
no vertebrae (backbone)
no true head
use of pharyngeal slits for feeding not respiration
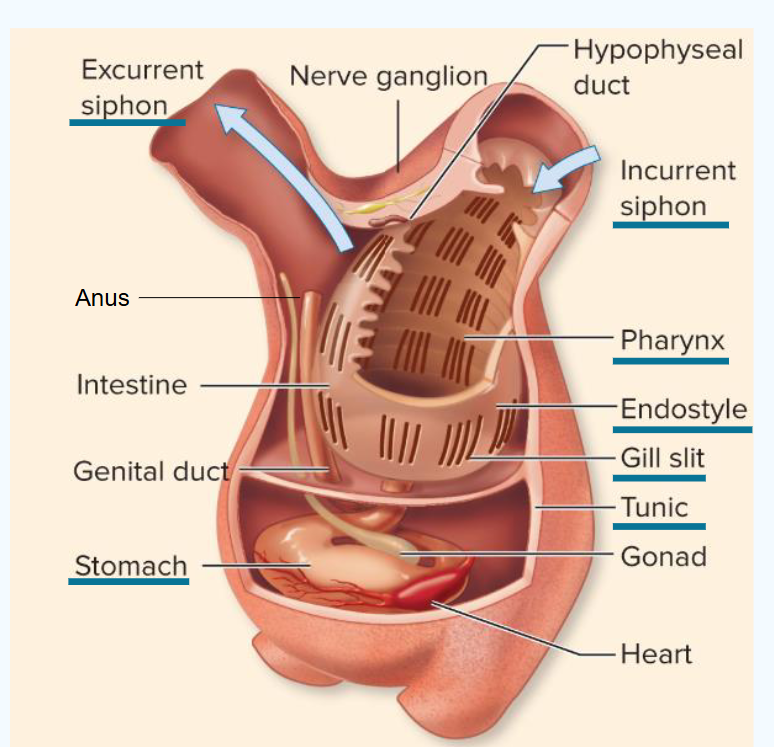
What are features of class ascidians?
common in coastal habitats
known as sea squirts
filter feeders
could be confused with sponges
bluebell sea squirts: solitary, clumped or colonial growth forms
What is ascidian reproduction like?
most are hermaphrodites
gametes released into water collumn
develop into free swimming tadpole larvae
larvae last a few minutes to days
settle and metamorphosise into sessile adult form - losing notochord, dorsal nerve chord and tail
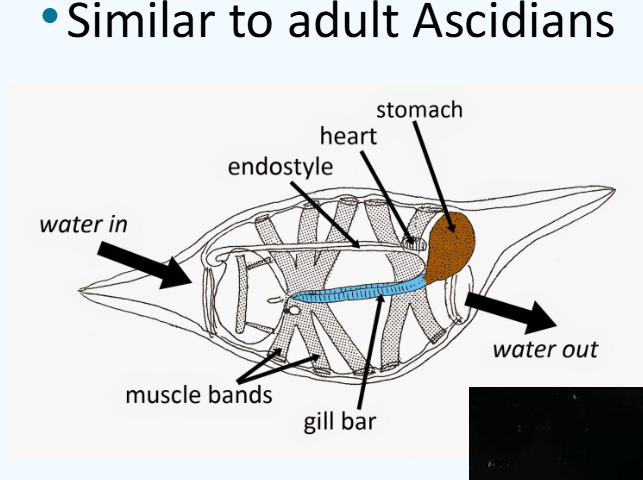
What are the features of thaliacea (salps)?
similar to adult ascideans
not as sessile
free swimming tunicates
solitary and colonial forms
morphology adapted for jet propulsion

what is the role of salps?
salps are food for many marine animals
they filter large amounts of water
they produce heavy carbon rich pellets
much about their ecology still unknown
what are the majestic colonial salps?
pyrosomes
long gelatinous colonies
many zooids embedded in a shared tunic
zooids orientated in same direction - water pumped into the atrial chamber
often biolumiscent
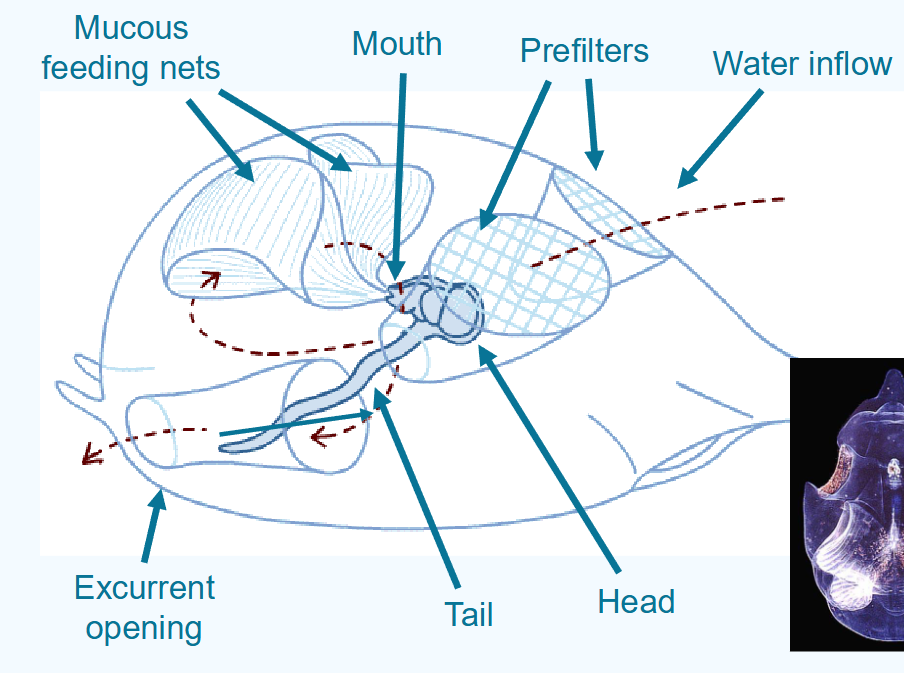
what are the features of appendicularia?
larvaceans
have a mucus house
mucus house typically lasts three hours
larvaceans very common
mucus house is major pathway for moving carbon and nutrients to deep waters
what are the features of cephalochordates?
small fish like invertebrate chordates
bury in shallow marine sediments
found globally
feeding:
water enters mouth into pharynx
mucus from endostyle traps food
water exits via pharyngeal gill slits
movement:
myotomes provide swimming movement
notochord resists compression and prevents body shortening
tail fin aids propulsion
some cephalisaion present

what are the risks to invertebrate chordates?
habitat loss from coastal development and pollution
impacts of climate change - acidification etc
bycatch and overfishing
invasive species altering community structure
What are the invertebrate chordate classes?
ascidiacea (ascideans)
thaliacea (salps)
appendicularia ( larvaceans)
sub phylum cephalochordata