Lab #2: Microscope, Cells, and the Cell Cycle
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
How many different kinds of cells are in the human body?
over 200
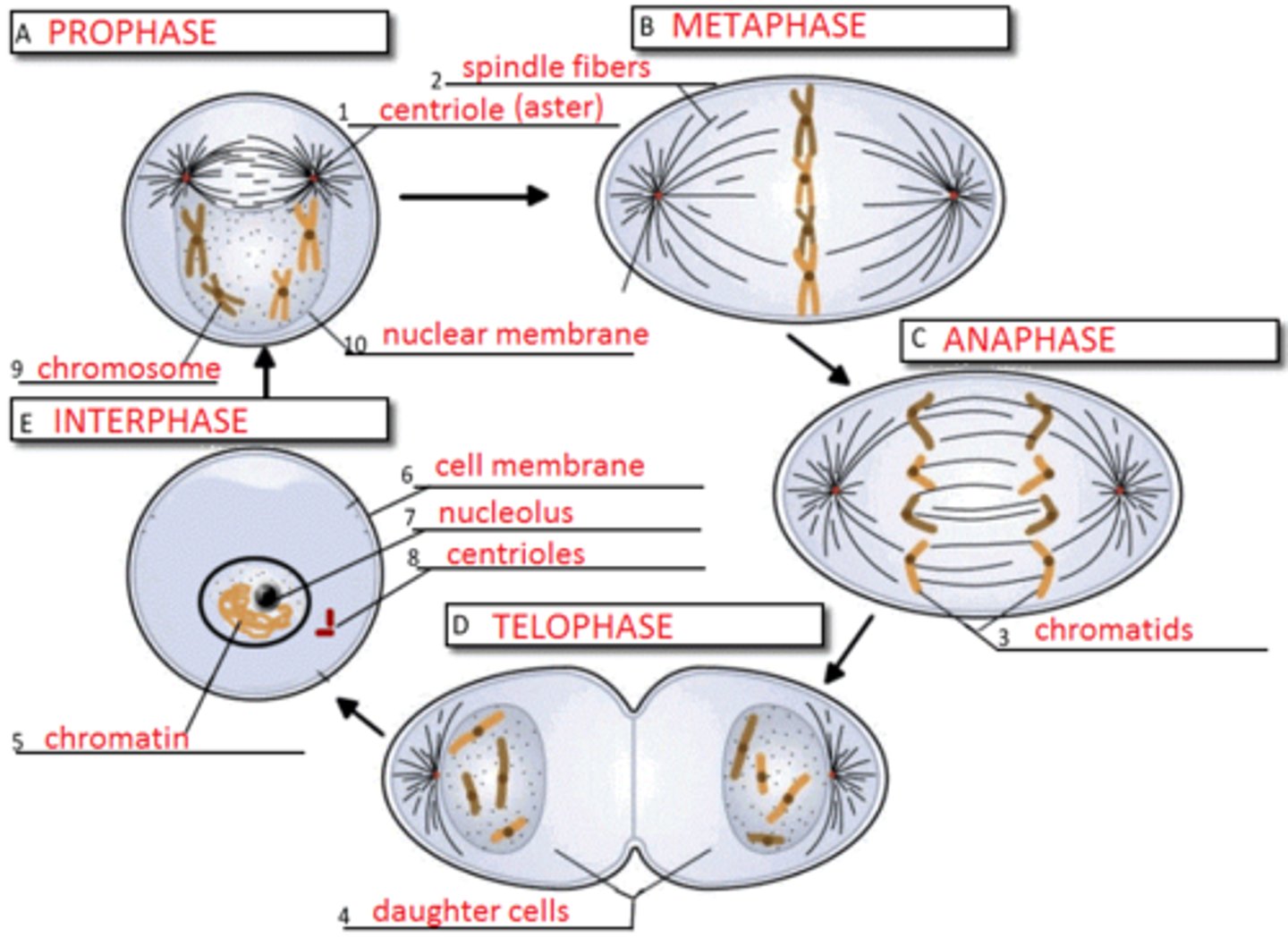
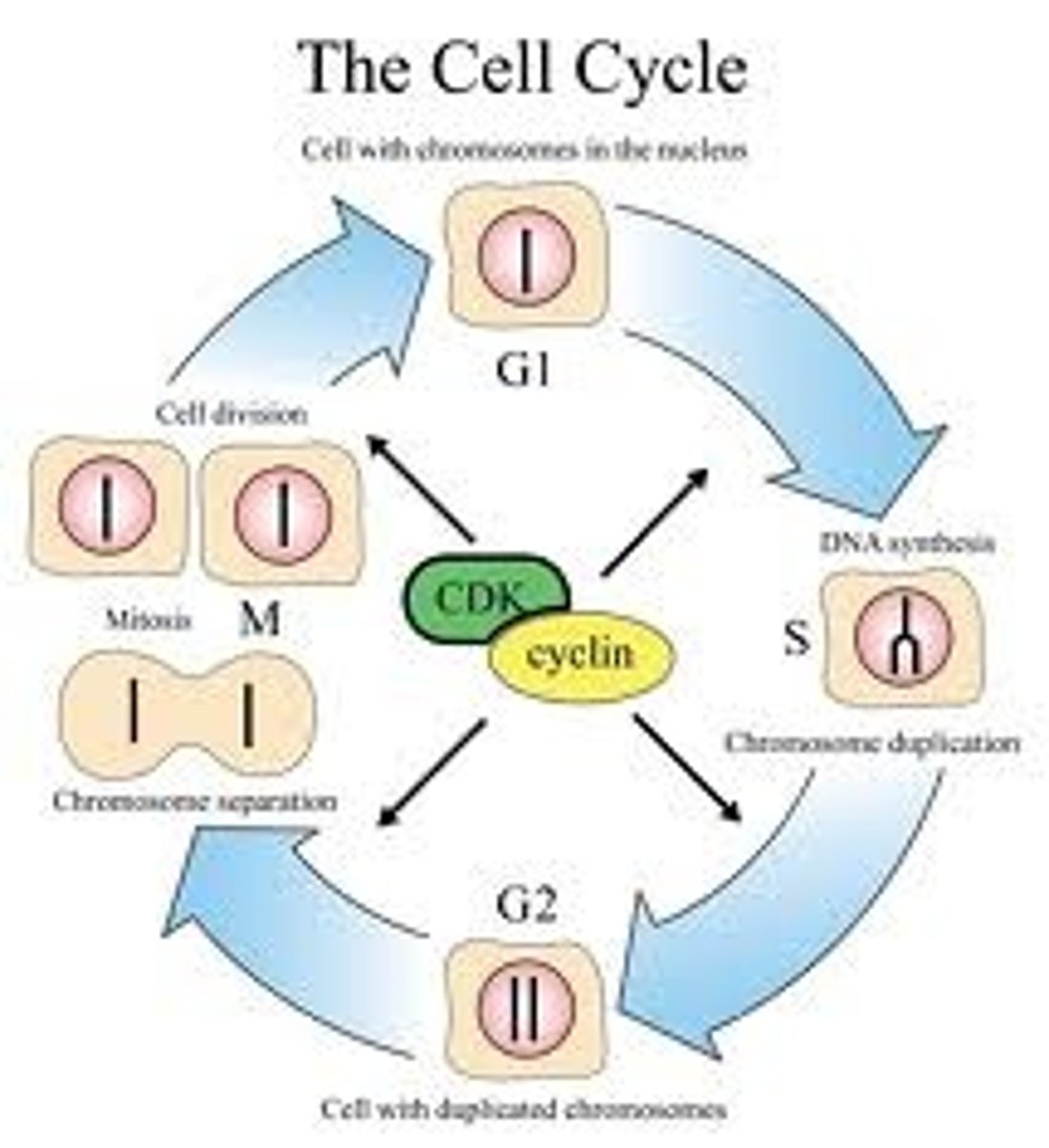
Cell Cycle
all events in the life of a cell from the time the cell forms to the time when it divides and becomes 2 new cells
3 Major Stages:
1. Interphase
2. Mitosis
3. Cytokinesis
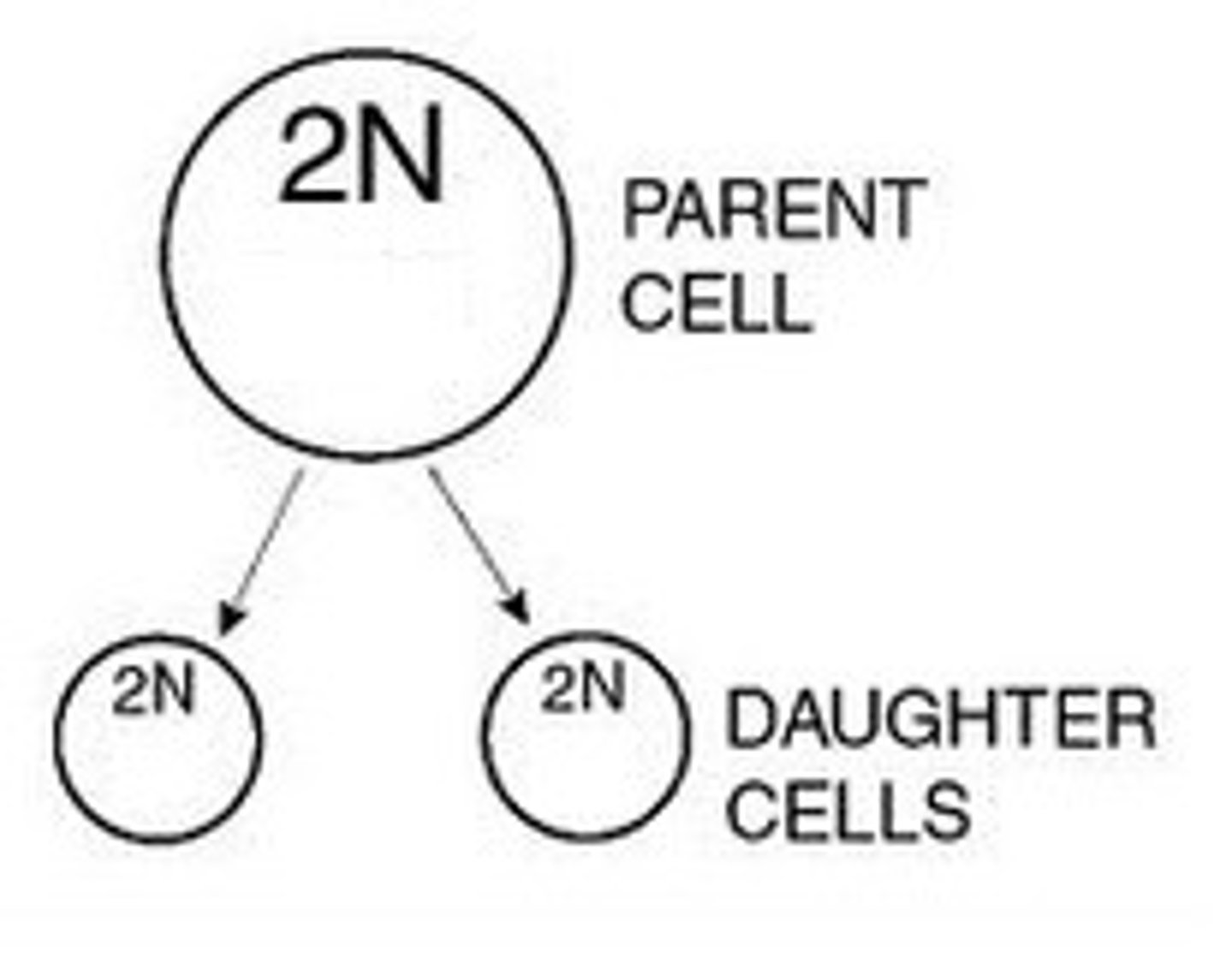
Parent Cell
cell that divides
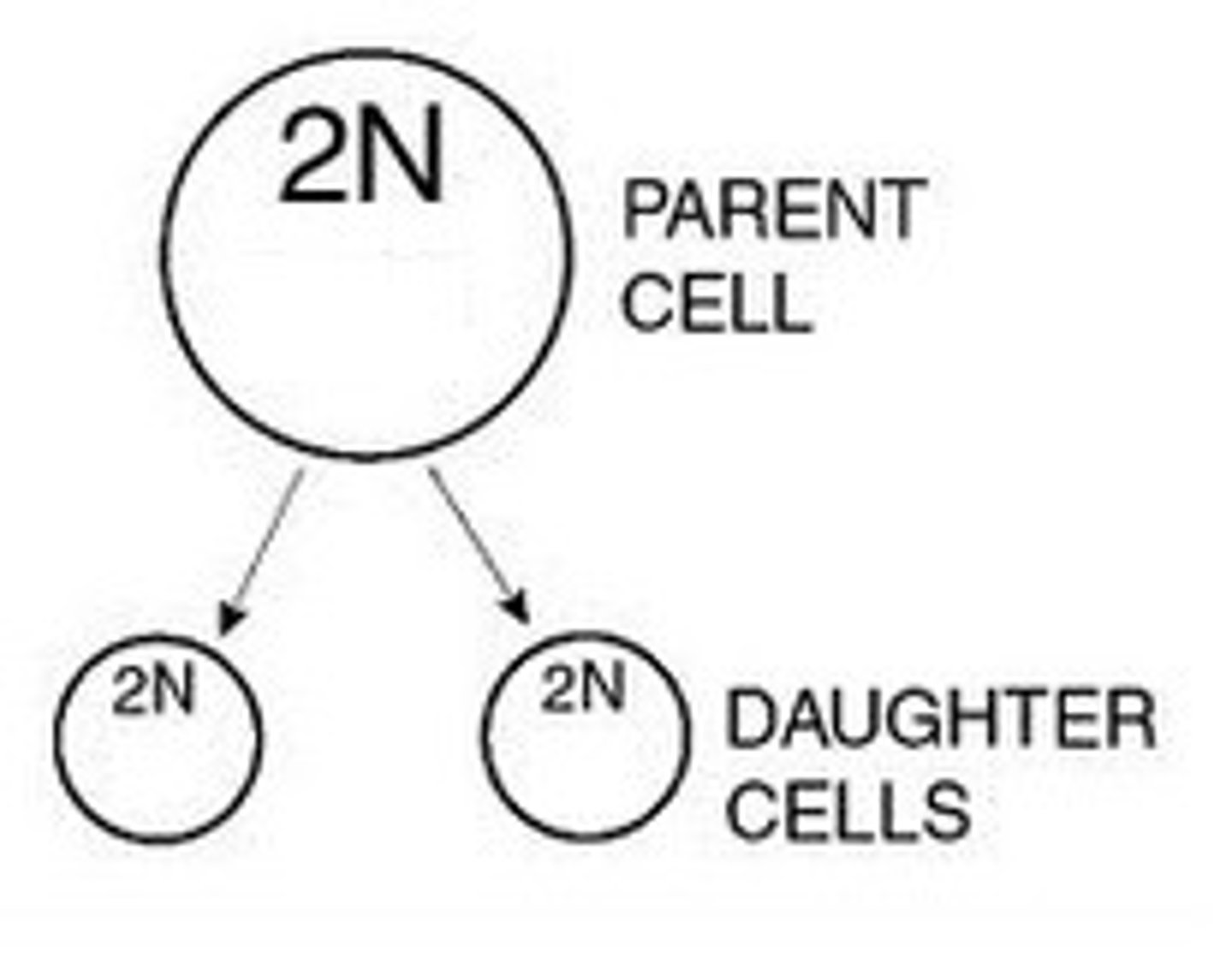
Daughter Cell
the 2 new cells
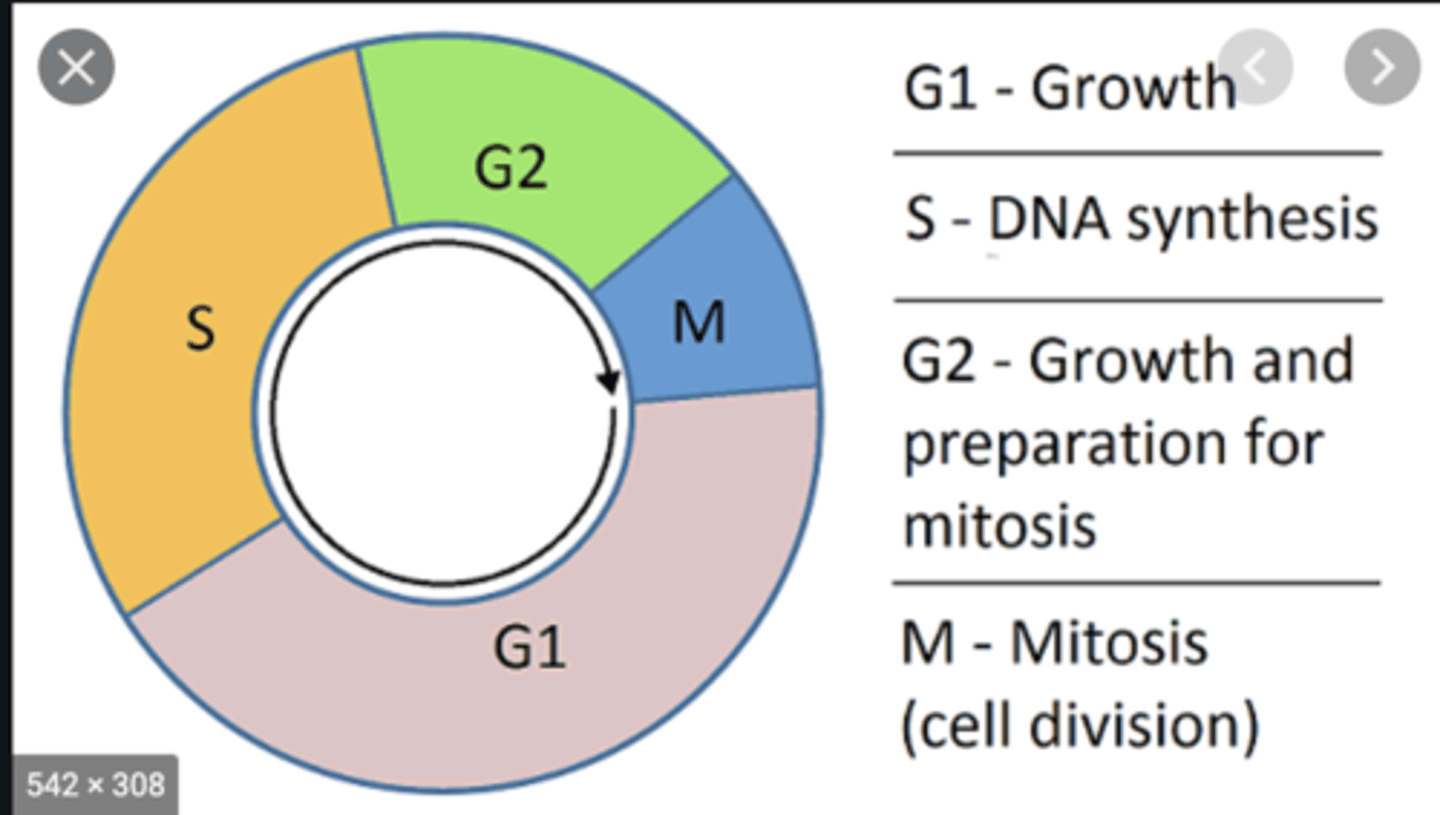
Interphase
- inter = "between"
- stage of the cell cycle between cell division
3 Specific Phases:
- G1 Phase
- S Phase
- G2 Phase
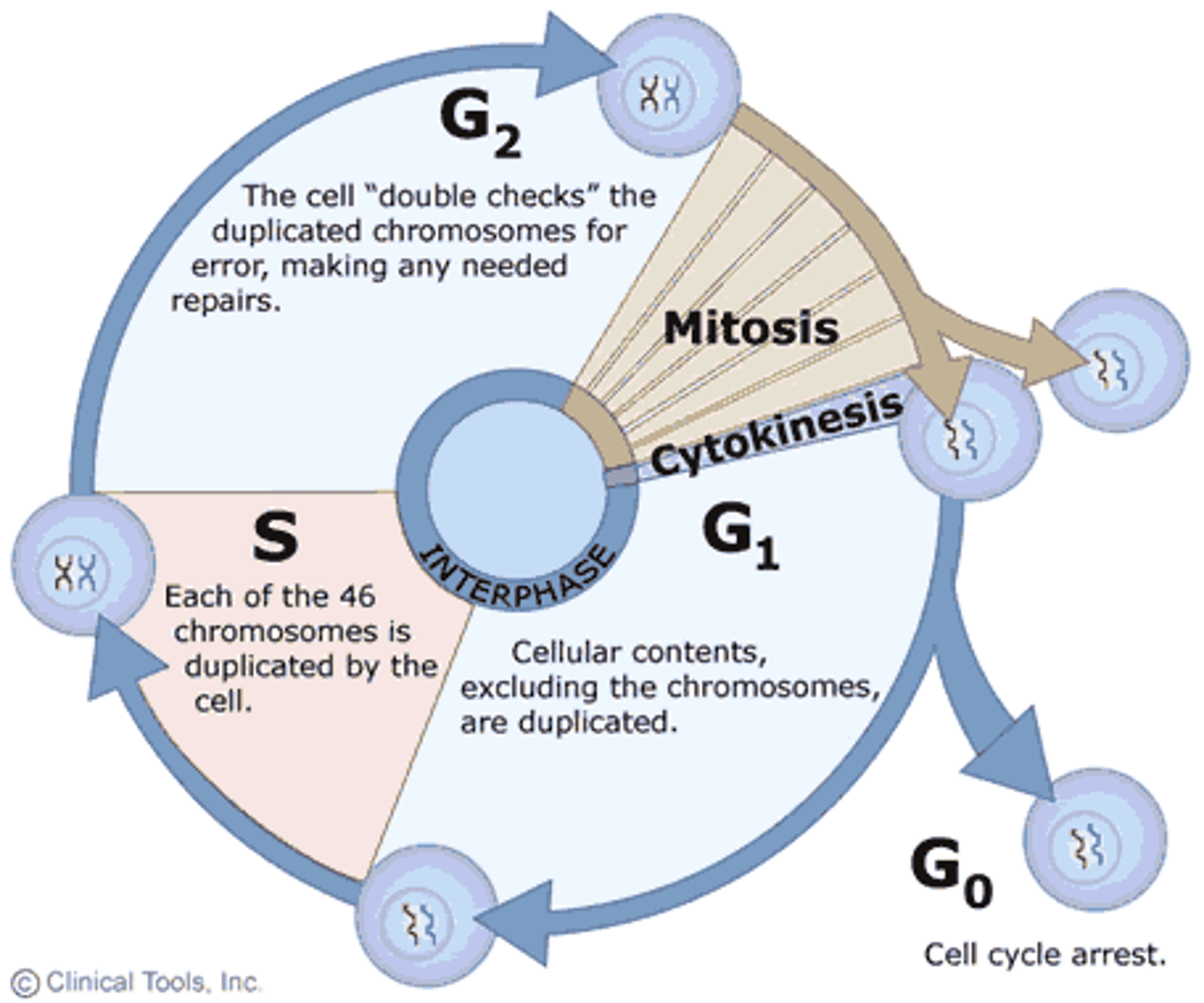
G1 Phase
- 1st gap phase
- cell is carrying out basic metabolic activity
- not preparing to divide
- longest stage
G0 Phase
Some cells (i.e. neurons) do not divide and are stuck in the phase
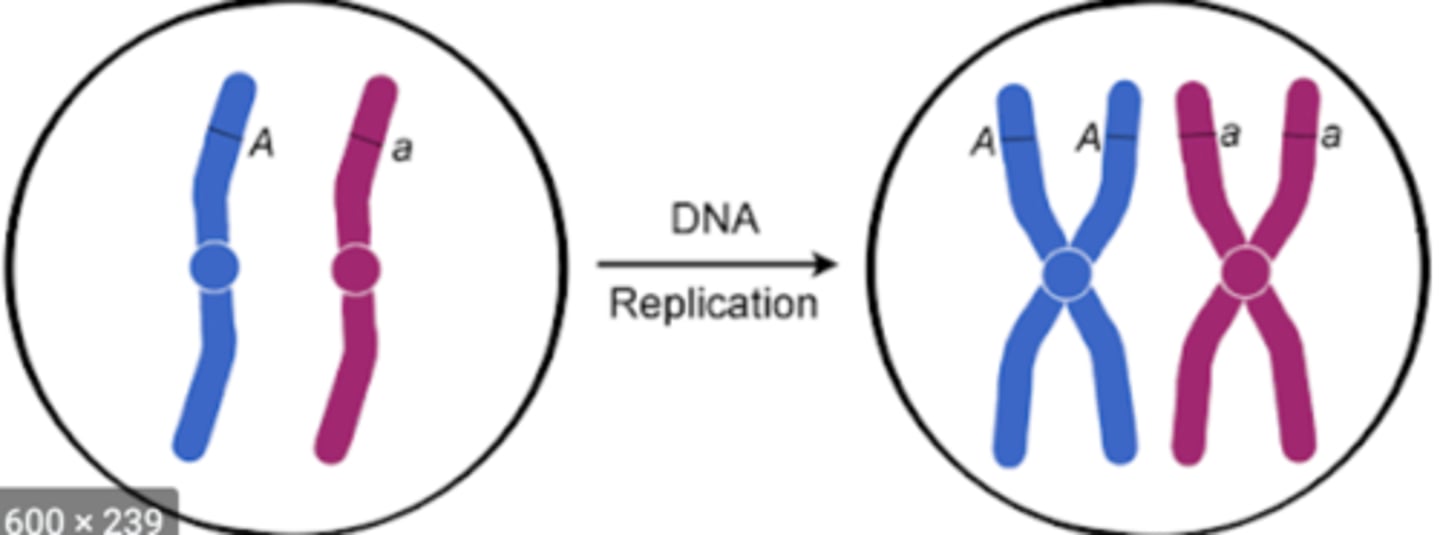
S Phase
- s = synthesis
- cell makes exact copies of its linear DNA molecules (replication/duplication)
Where is linear DNA molecules found?
cell's nucleus
Where is circular DNA found?
inside mitochondria
Chromosome
- chrom ="color"
- some = "body"
- term used for linear DNA in different stages of the cell cycle for the circular DNA in the mitochondria
- form in single, double helix DNA in G1 phase, anaphase, telophase
- 2 identical DNA molecules during G2 phase, prophase, metaphase
Replicated Chromosome
after replication, each linear chromosome exists as this consisting of 2 double-stranded DNA molecules
Sister Chromatids
2 complete DNA molecules within a replicated chromosome
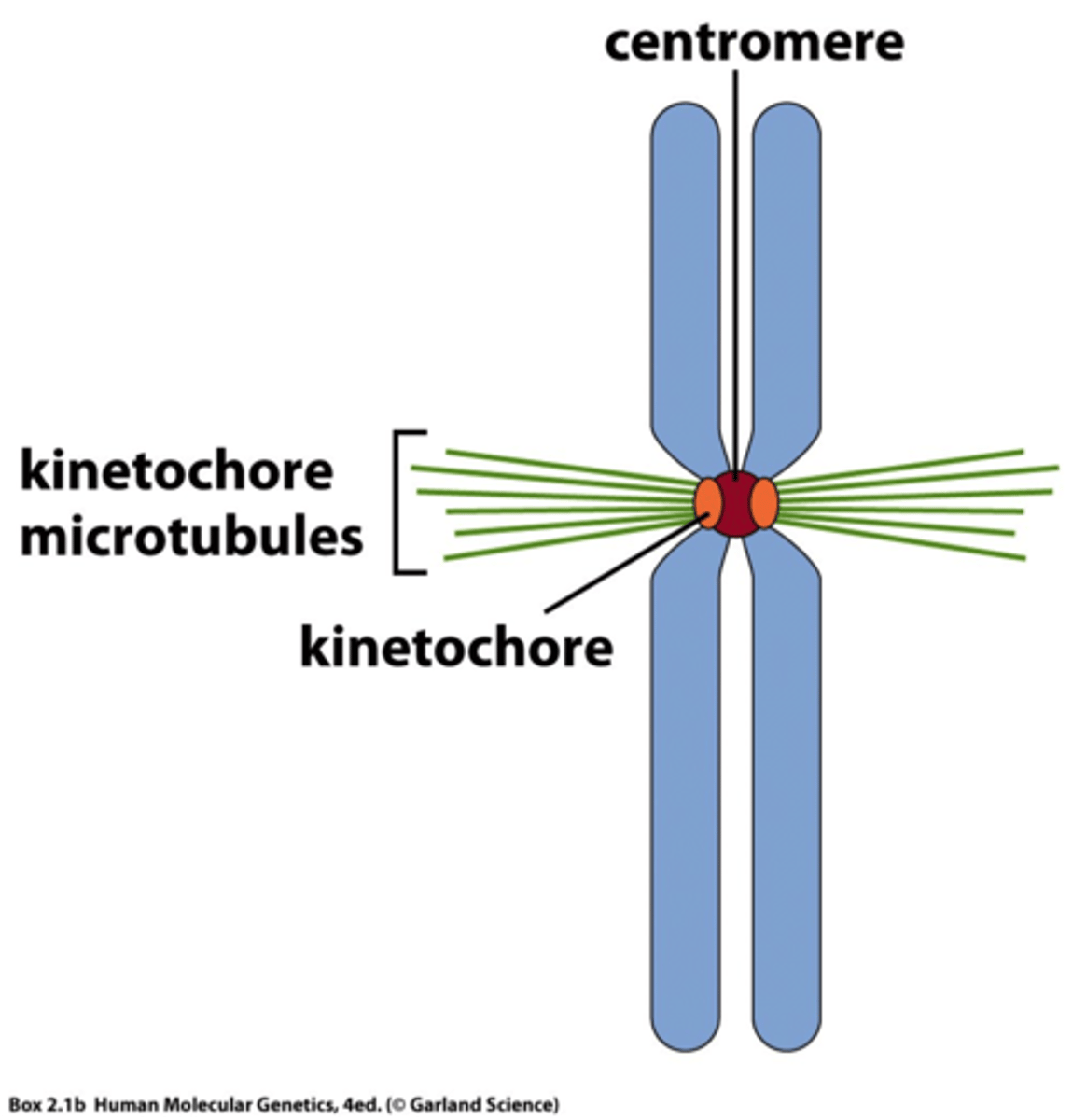
Centromere
- centro = "center"
- mere = "part"
- temporarily hold together chromatids
Karyotype
- karyo = "kernel"
- photograph of an organism's linear chromosomes
G2 Phase
- 2nd gap phase
- cell is making final preparations for division
- chromosome condensing, shorter, thicker due to excessive coiling of chromatids
- centrioles replicate and move to opposite ends of the cell
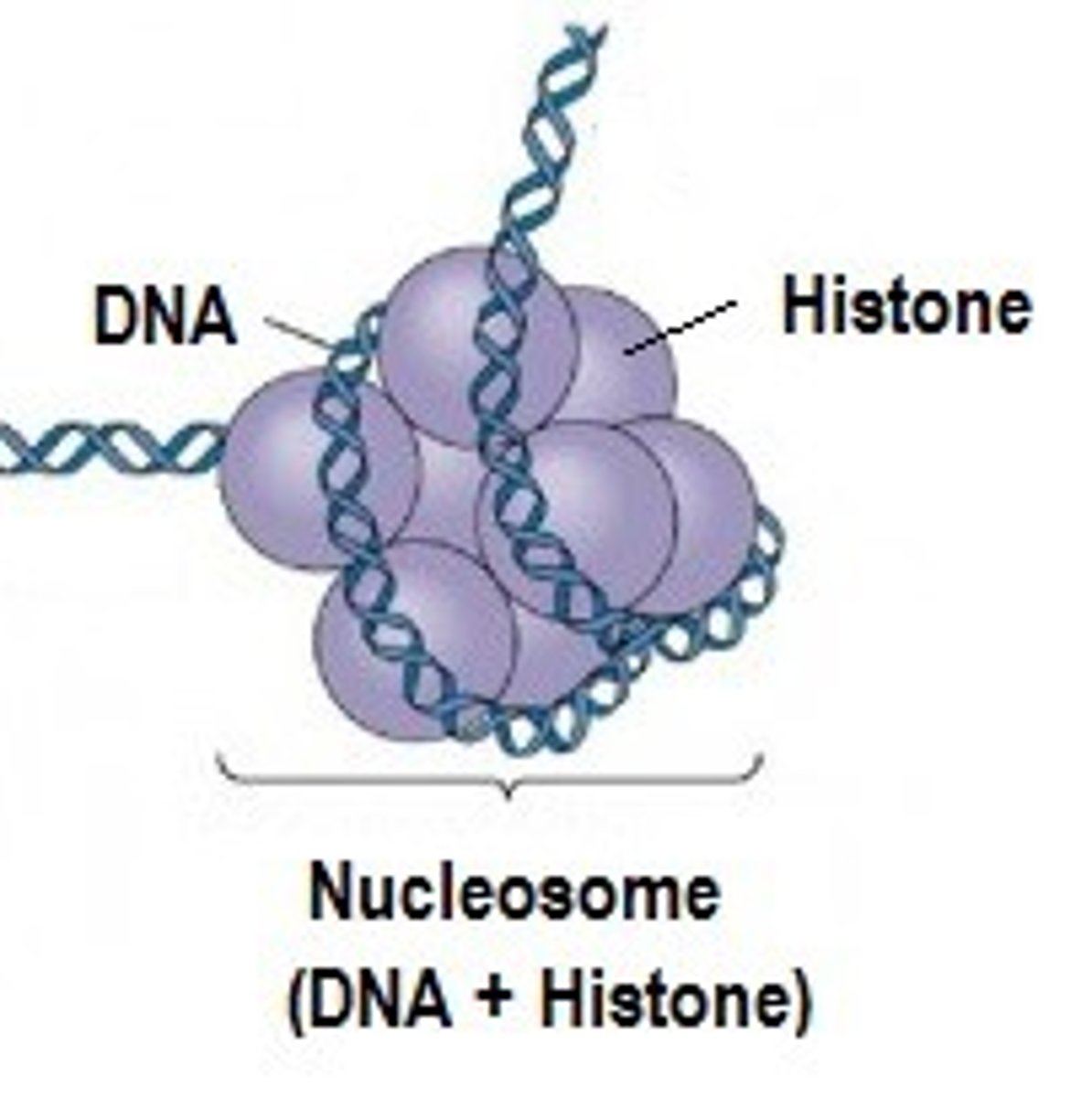
Histones
- proteins around which linear DNA molecules wrap prior to mitosis
- allows linear chromosomes to condense and visible during mitosis
- not present in mitochondrial DNA
Kinetochores
sites on chromatids; spindle fibers radiate out from centrioles and attach to this
Mitosis
- mito = "thread"
- osis = "condition"
- process leading to parent cell's replicating, nuclear DNA molecules become equally distributed at opposite ends
- ensure daughter and parent cells have same genetic material
- nuclear division
4 Major Stages:
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
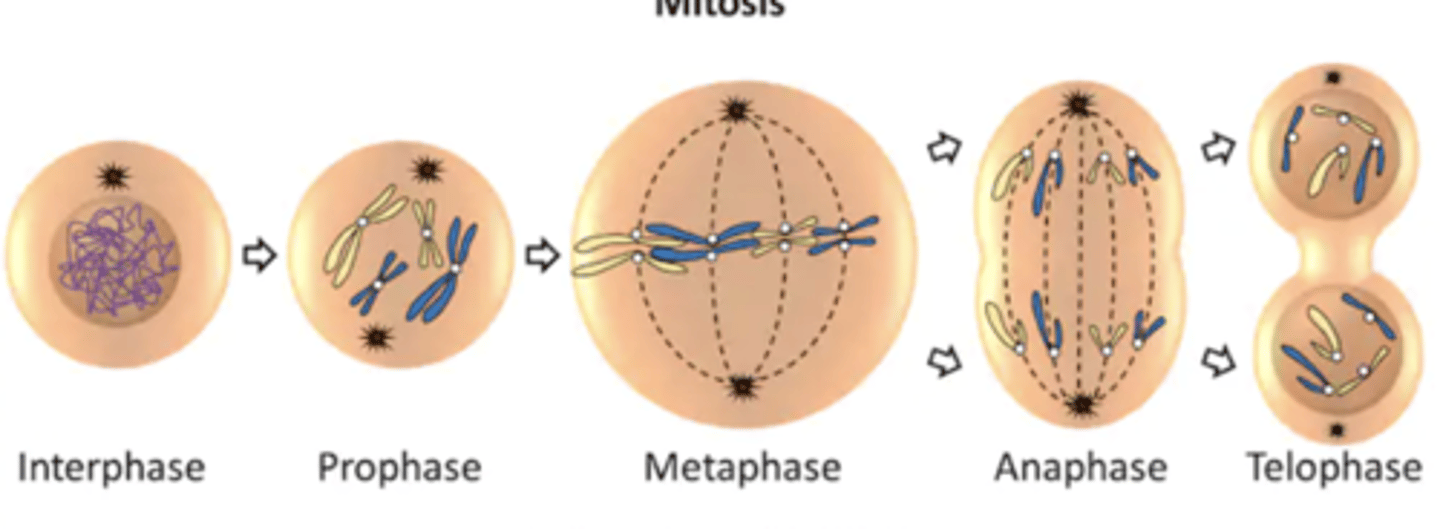
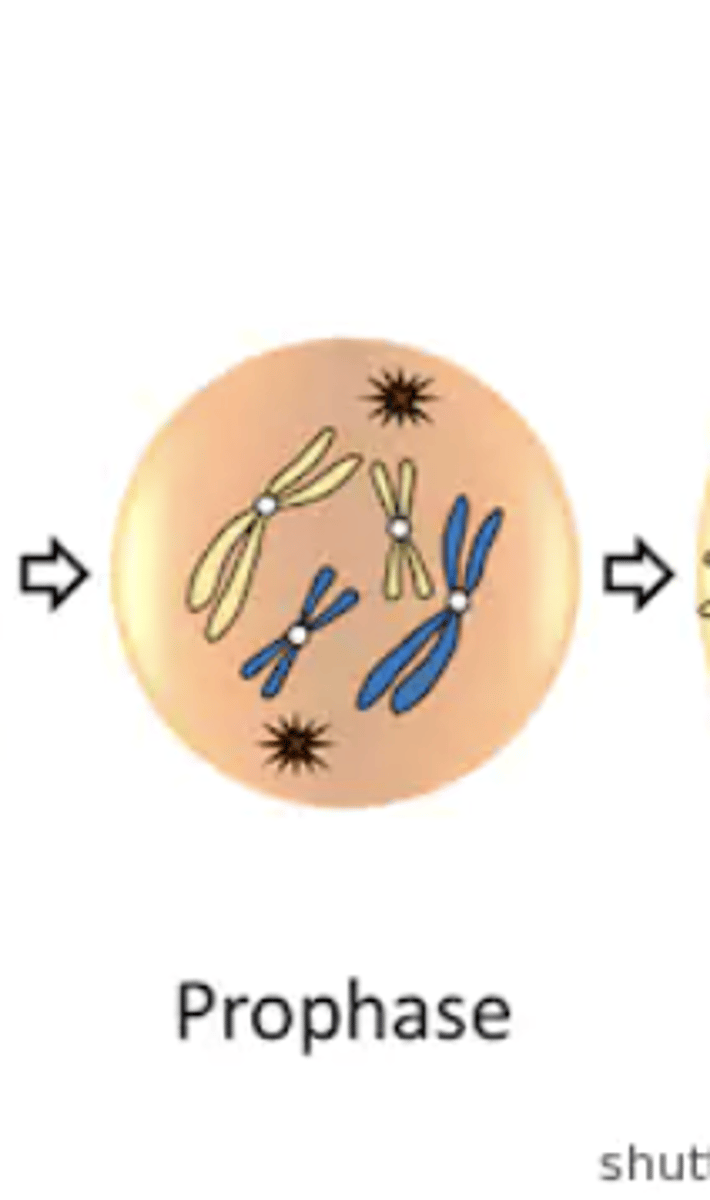
Prophase
- pro = "before"
- each chromatid is fully condensed & has a spindle fiber attached to kinetochore
- replicated chromosomes are randomly distributed
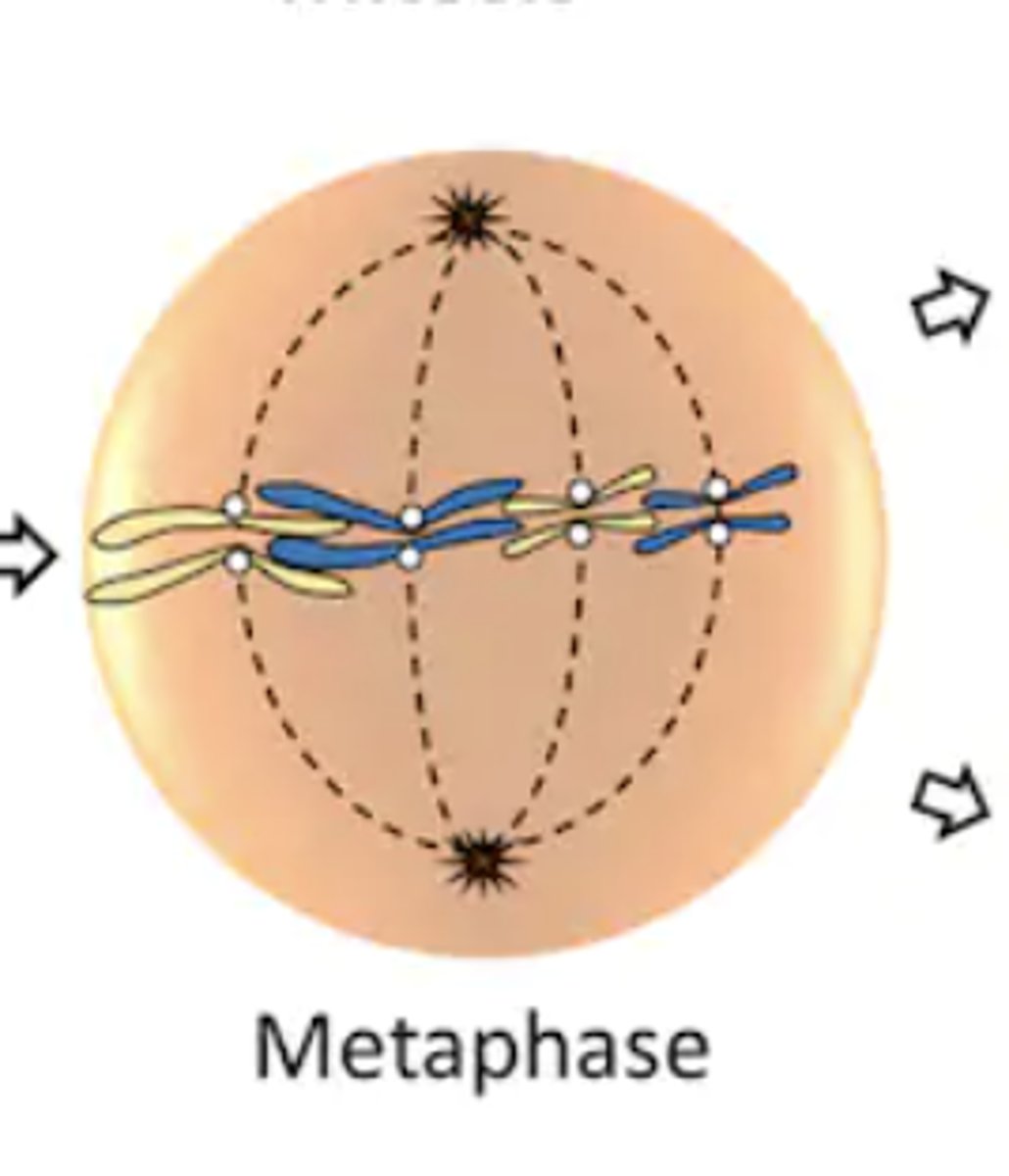
Metaphase
- meta = "between"
- replicated chromosomes align themselves along the parent cell's equator
Anaphase
- ana = "apart"
- sister chromatids separate from one another and move toward opposite poles of the cell
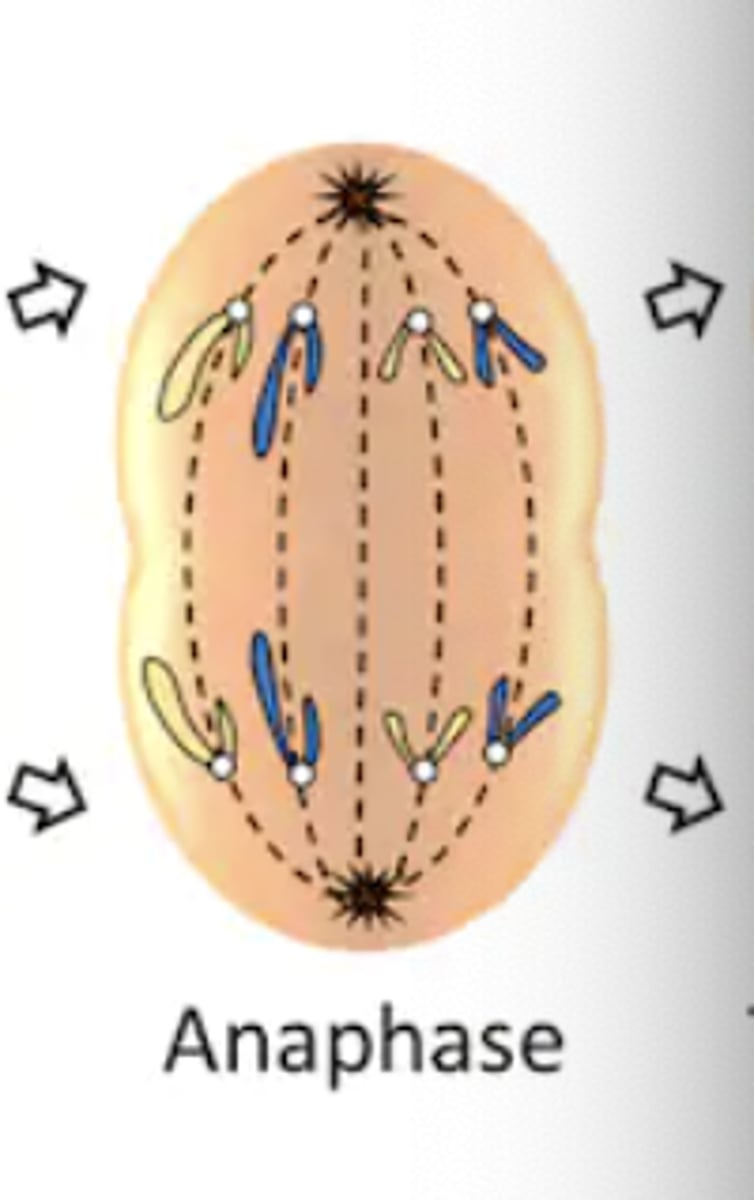
Sister Chromosomes
separated chromatids
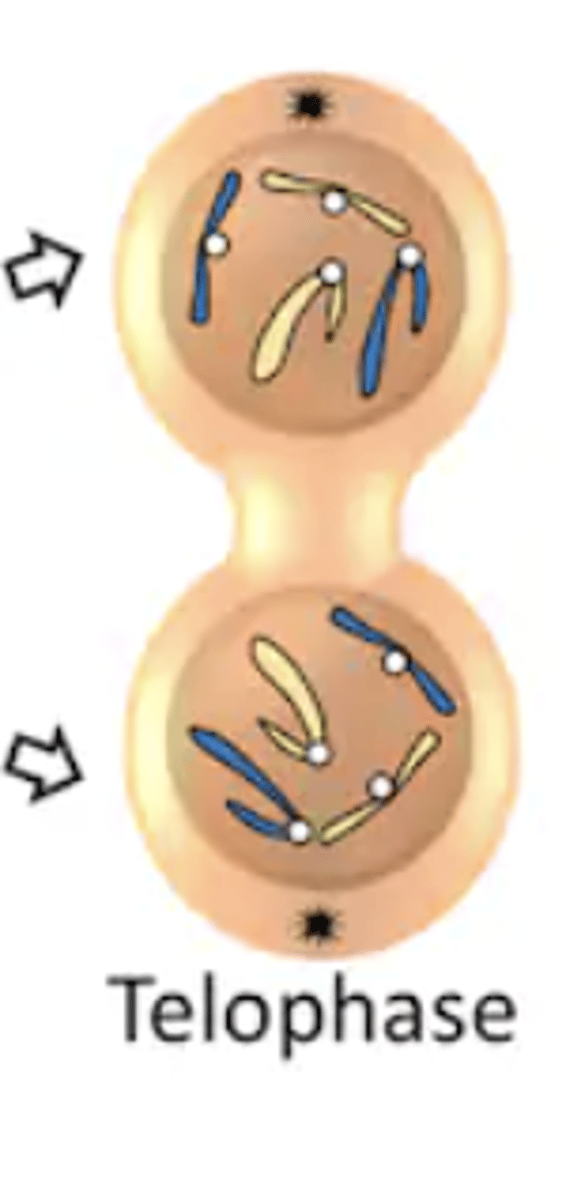
Telophase
- telo = end
- last stage of mitosis
- condensed chromosomes reach opposite poles of parent cell and uncoil
- a new nuclear membrane forms around elongating strands of chromatin
Cytokinesis
- final stage
- parent cell divides to form 2 daughter cells
- begins with contraction ring
- parent cell splits into 2 daughter cells
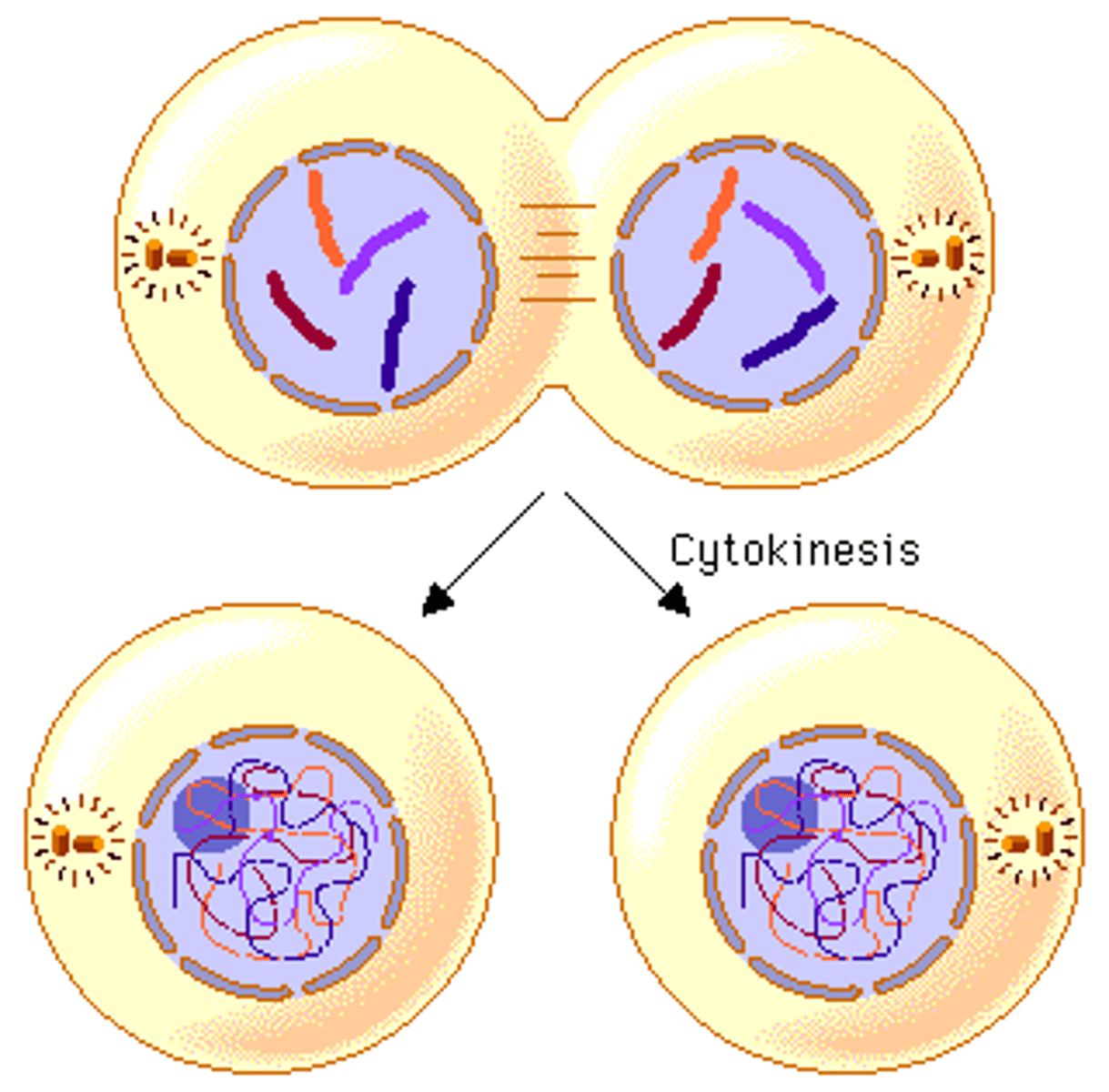
Contraction Ring
- made of microfilaments
- ring squeezes inward causing the split
Cleavage Furrow
groove formed by contraction ring tightening around the cell's periphery
Basal Body
- microtubule organizing center
- forms microtubules
- give rise to a 9+2 arrangement of microtubules
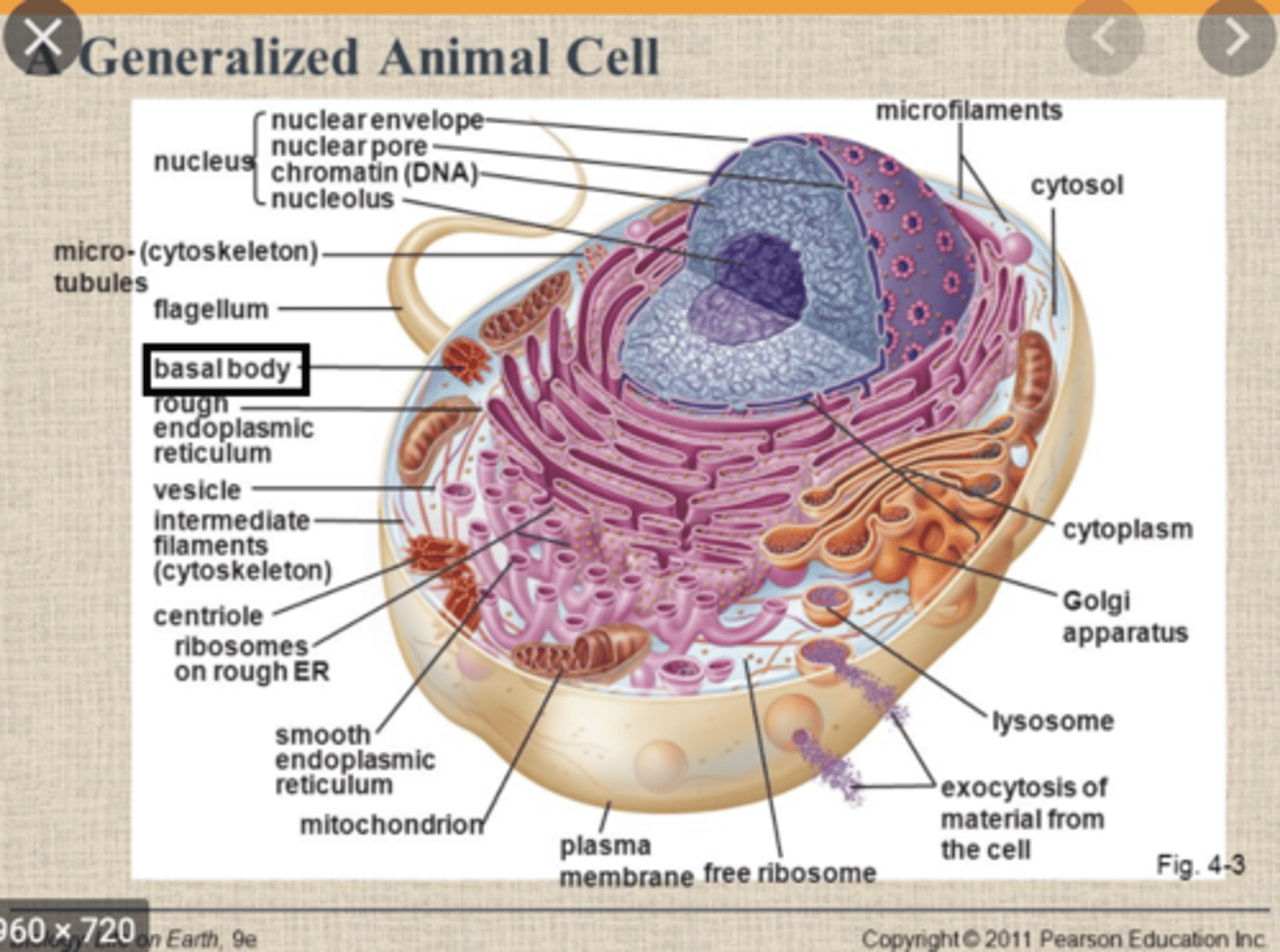
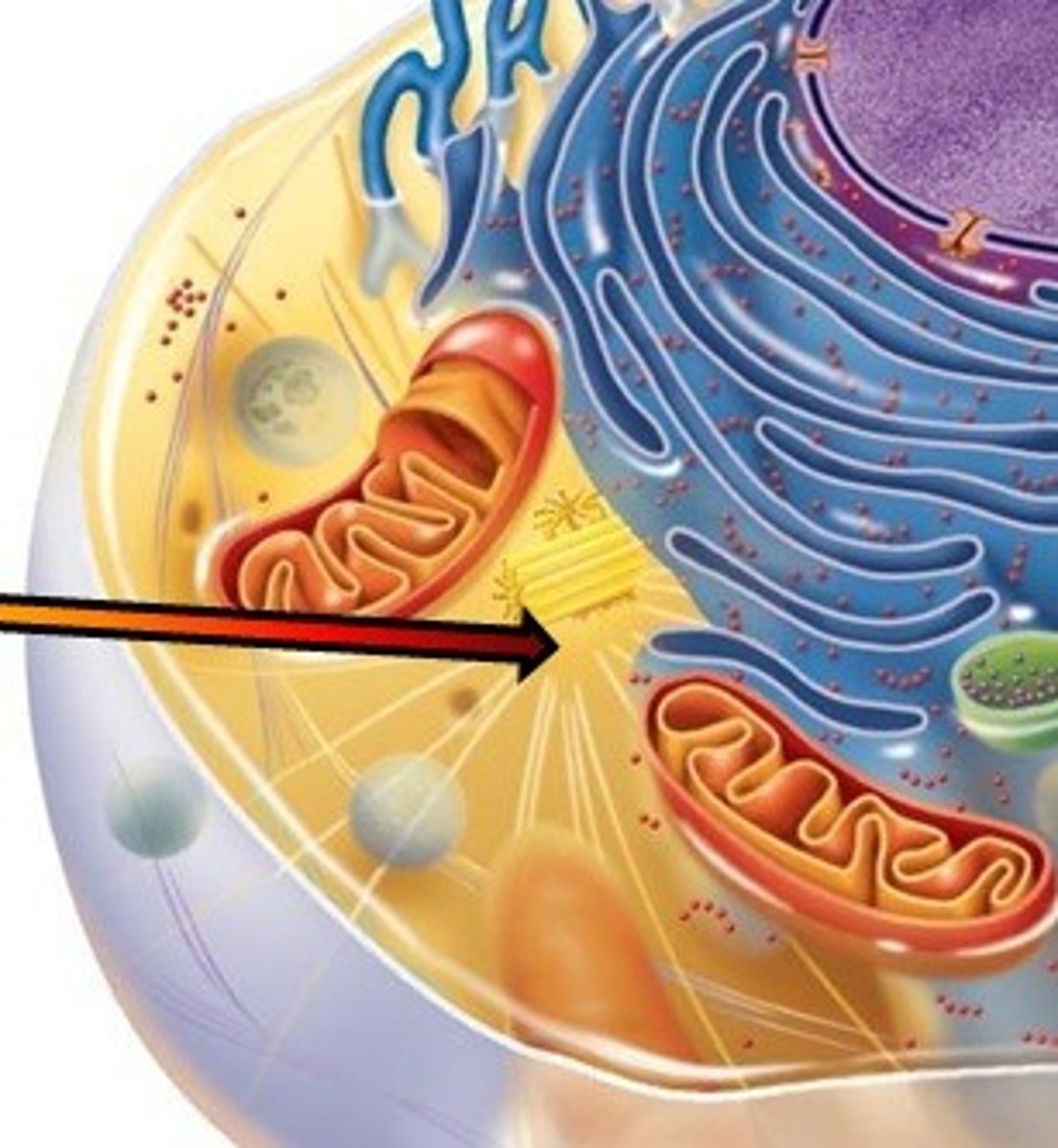
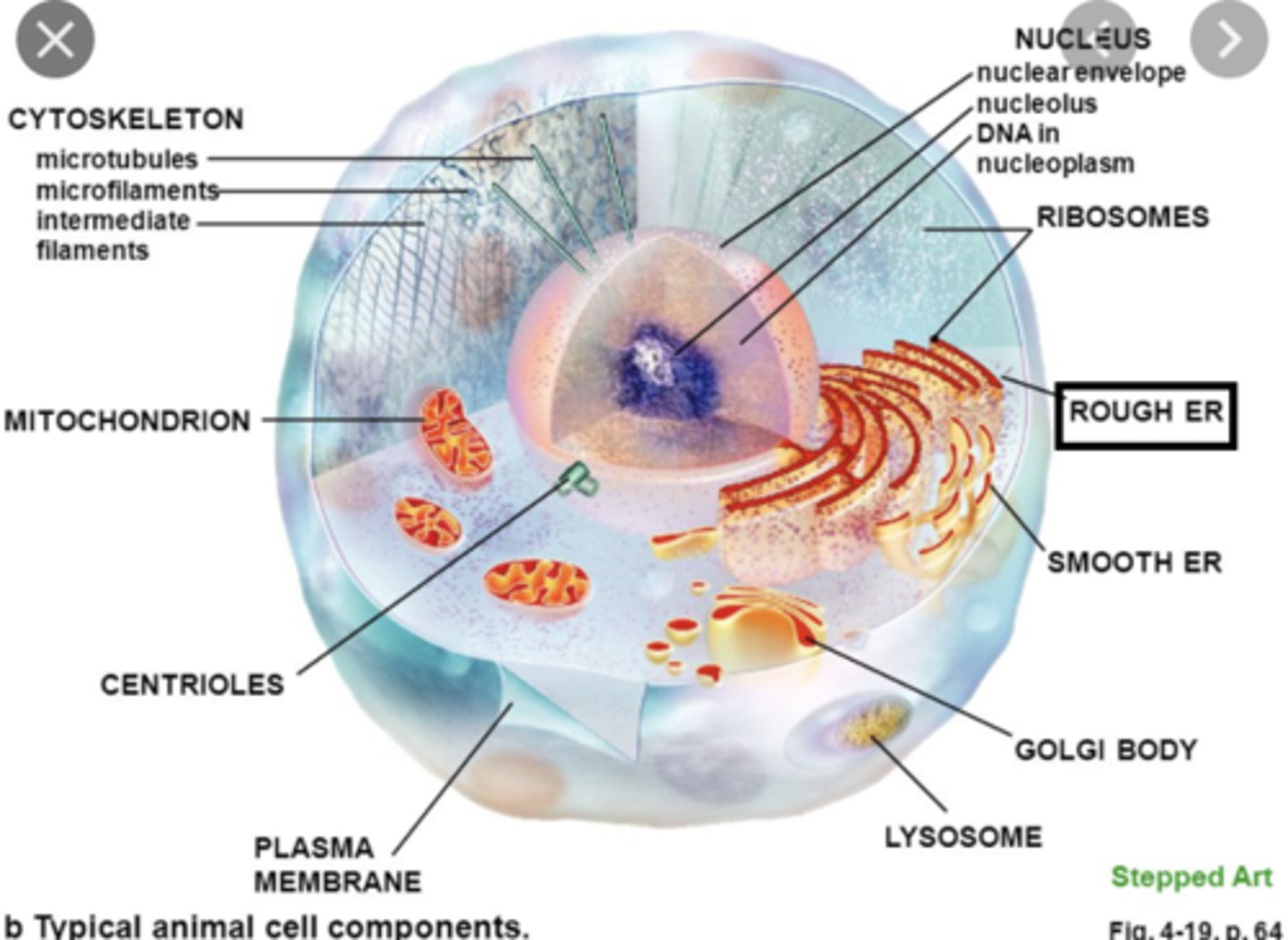
Centriole
- within a centrosome
- contains 27 microtubules arranged in 9 triplets
- plays role in cell division by giving rise to a spindle fibers that attach to kinetochores on chromatids
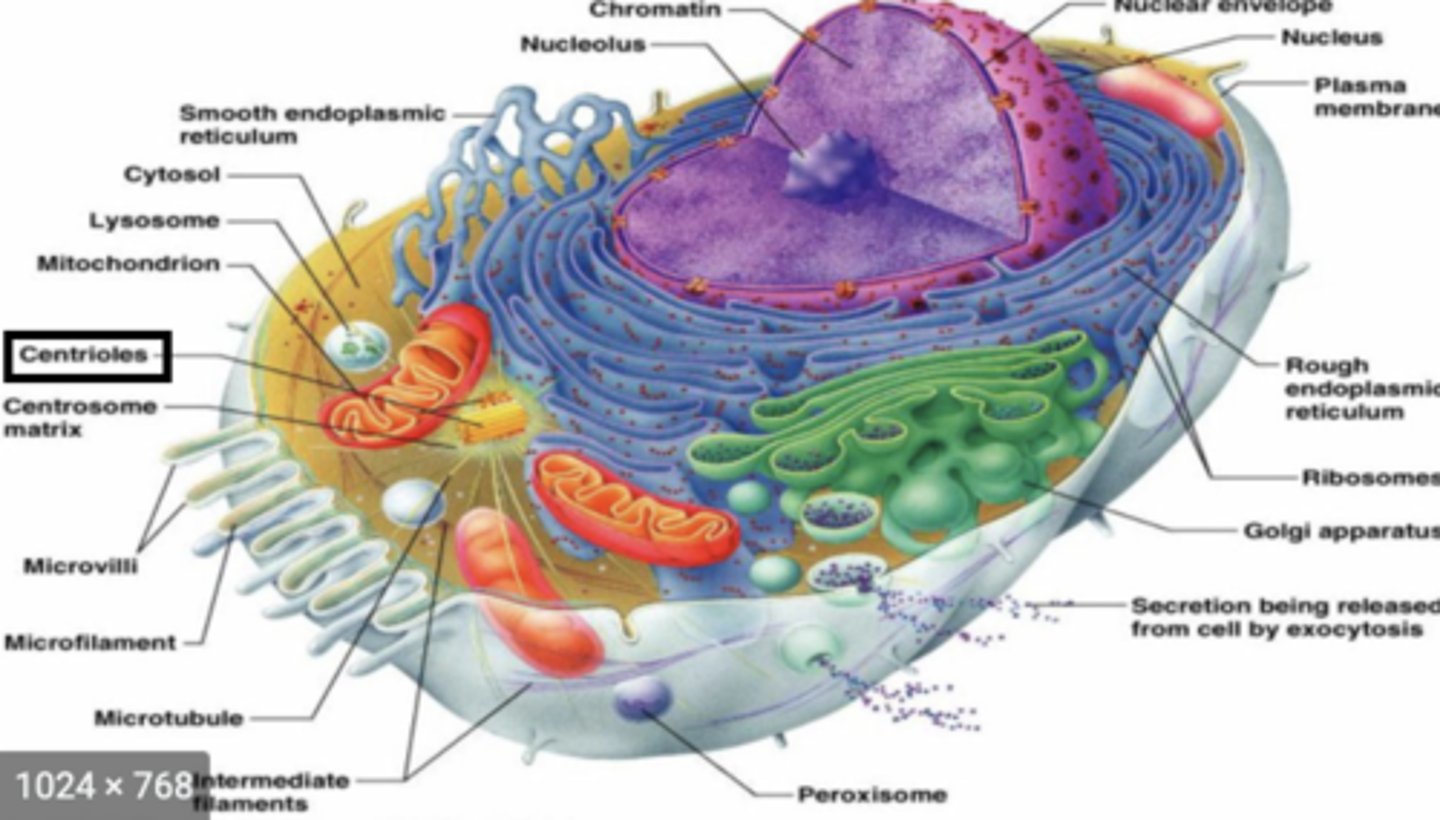
Centrosome
region that contains centrioles and located near the nucleus
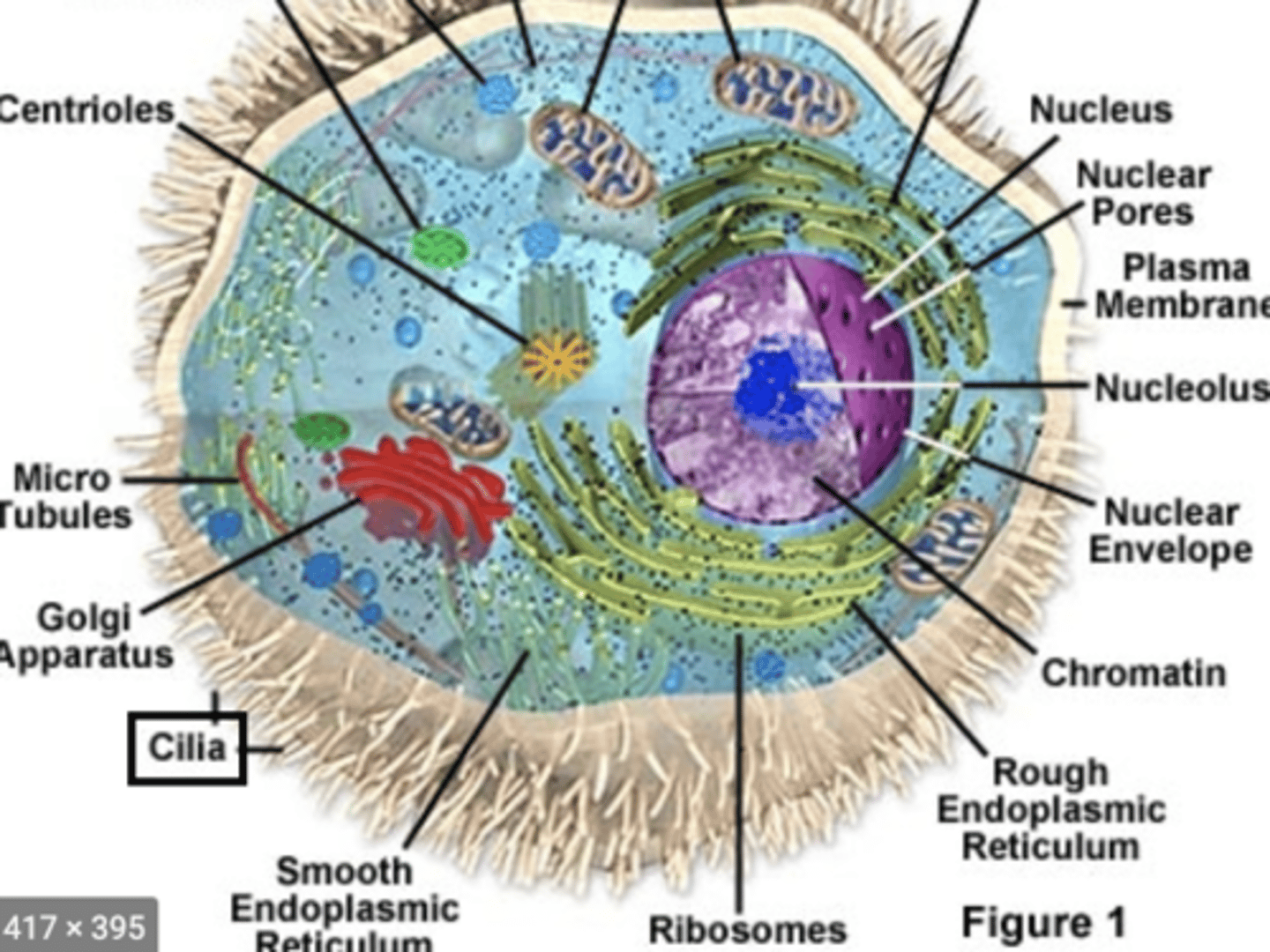
Cilia
- short, hair like projections w/ a 9+2 arrangement of microtubules
- arise from basal bodies
- propels mucus on mucous membranes
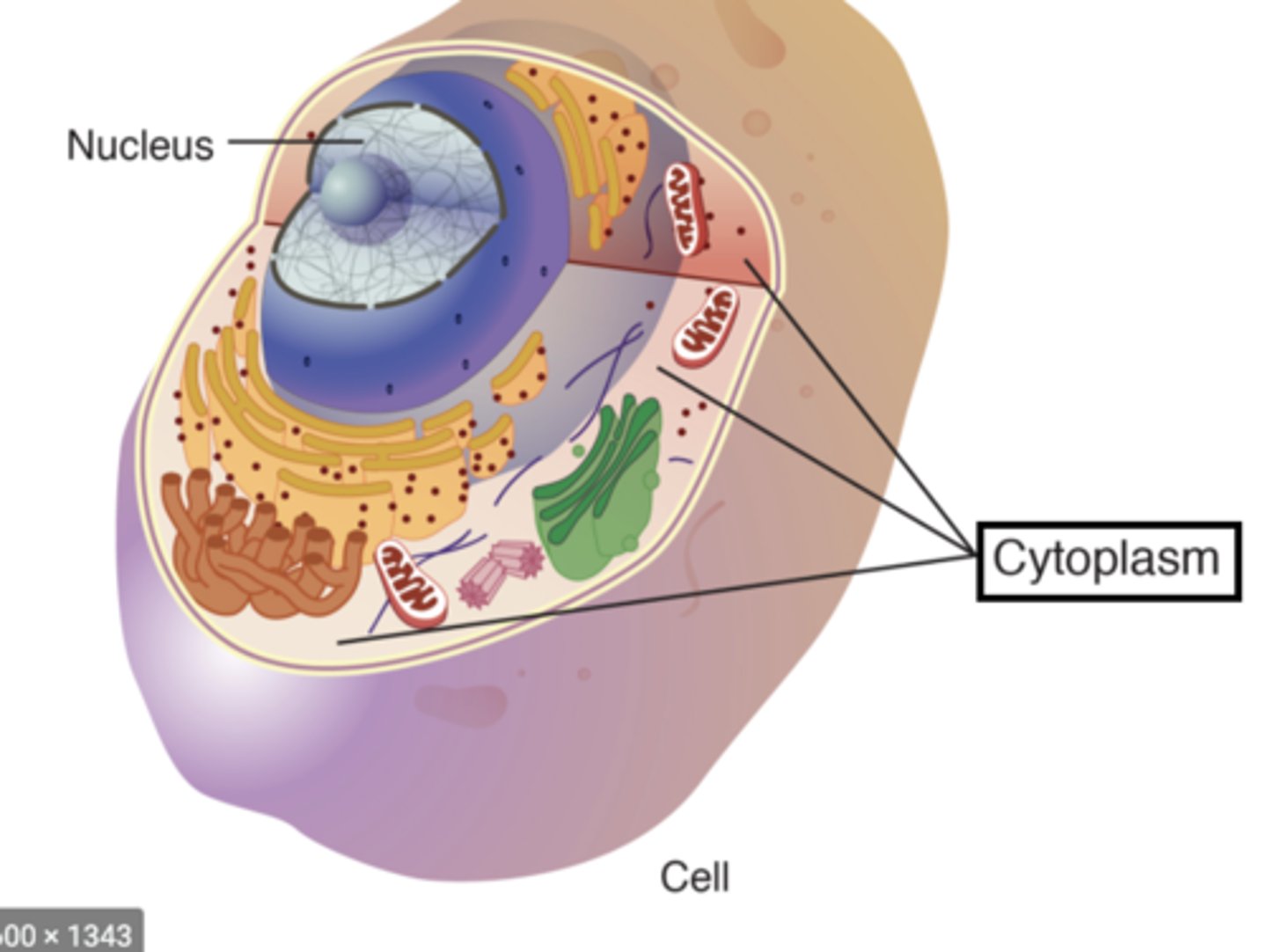
Cytoplasm
all material between the cell membrane and nucleus; includes cytosol & cytoplasmic organelles
Cytoskeleton
- network of microfilaments, microtubules, & intermediate filaments
- forms internal framework of cell
- keeps organelles in place
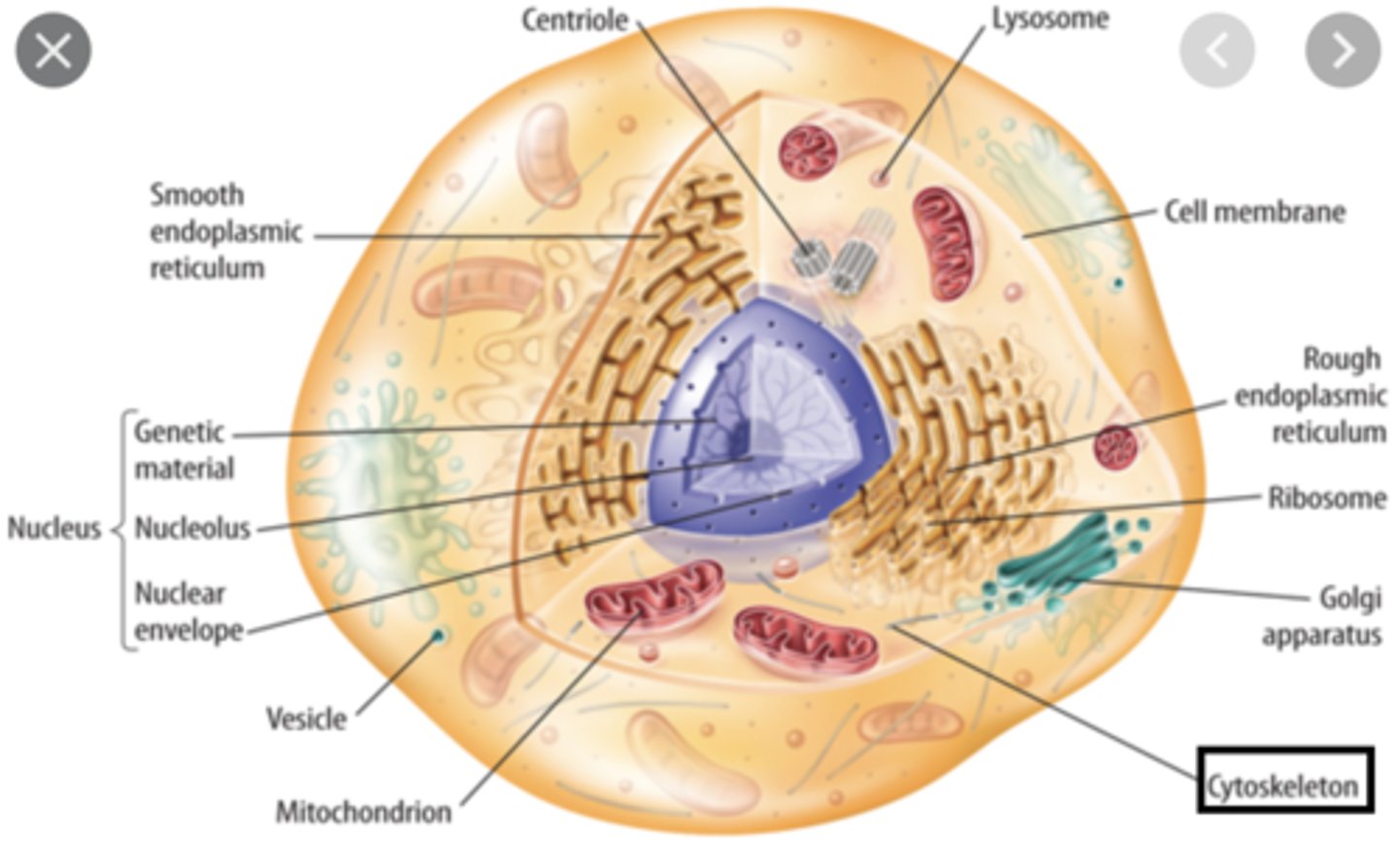
Cytosol
intracellular fluid out of the nucleus; contains mostly water with a colloid consistency
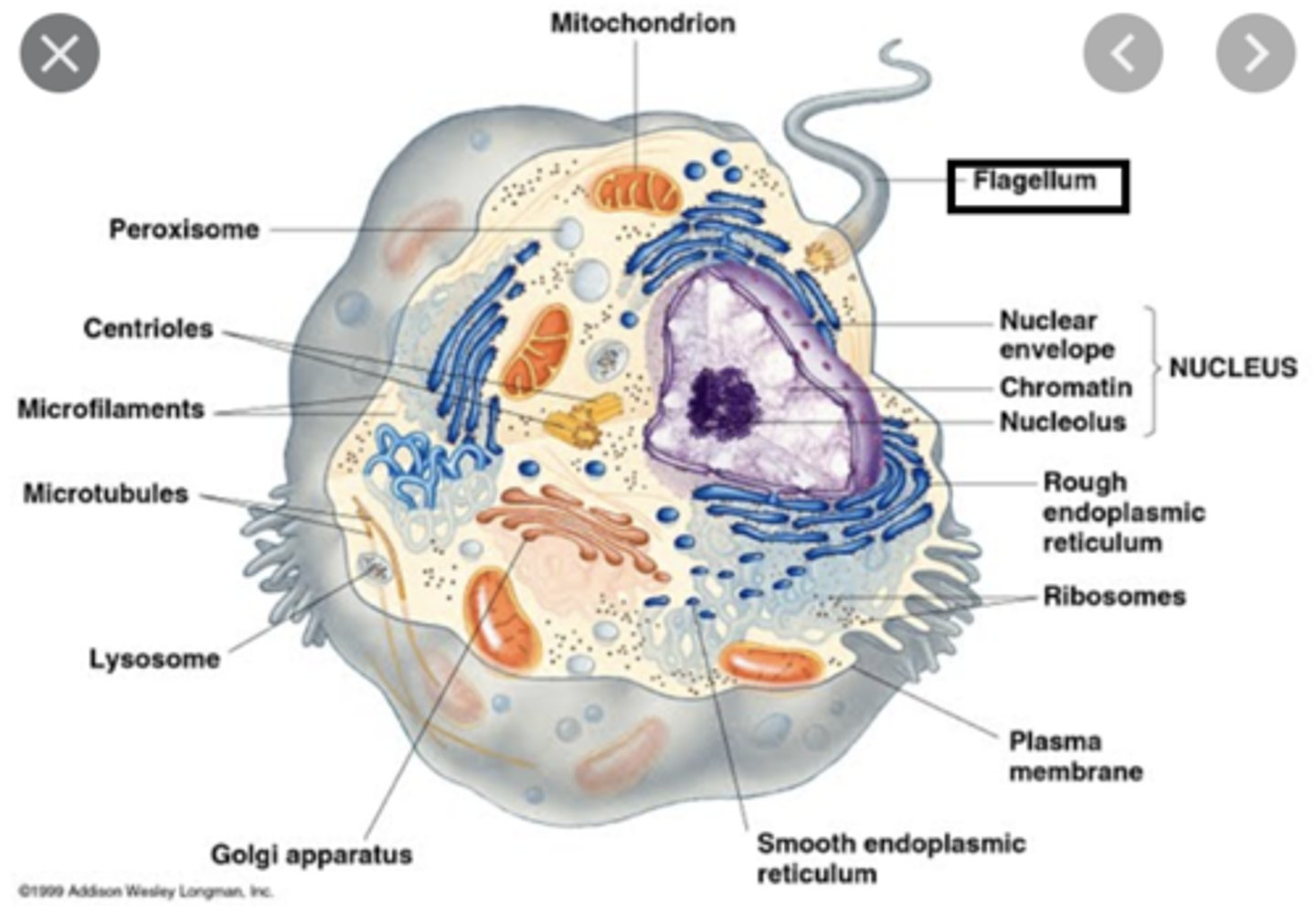
Flagellum
- long projections of the cell membrane containing 9 pairs of microtubules surrounding 1 pair
- allows flagellum to move sperm cells
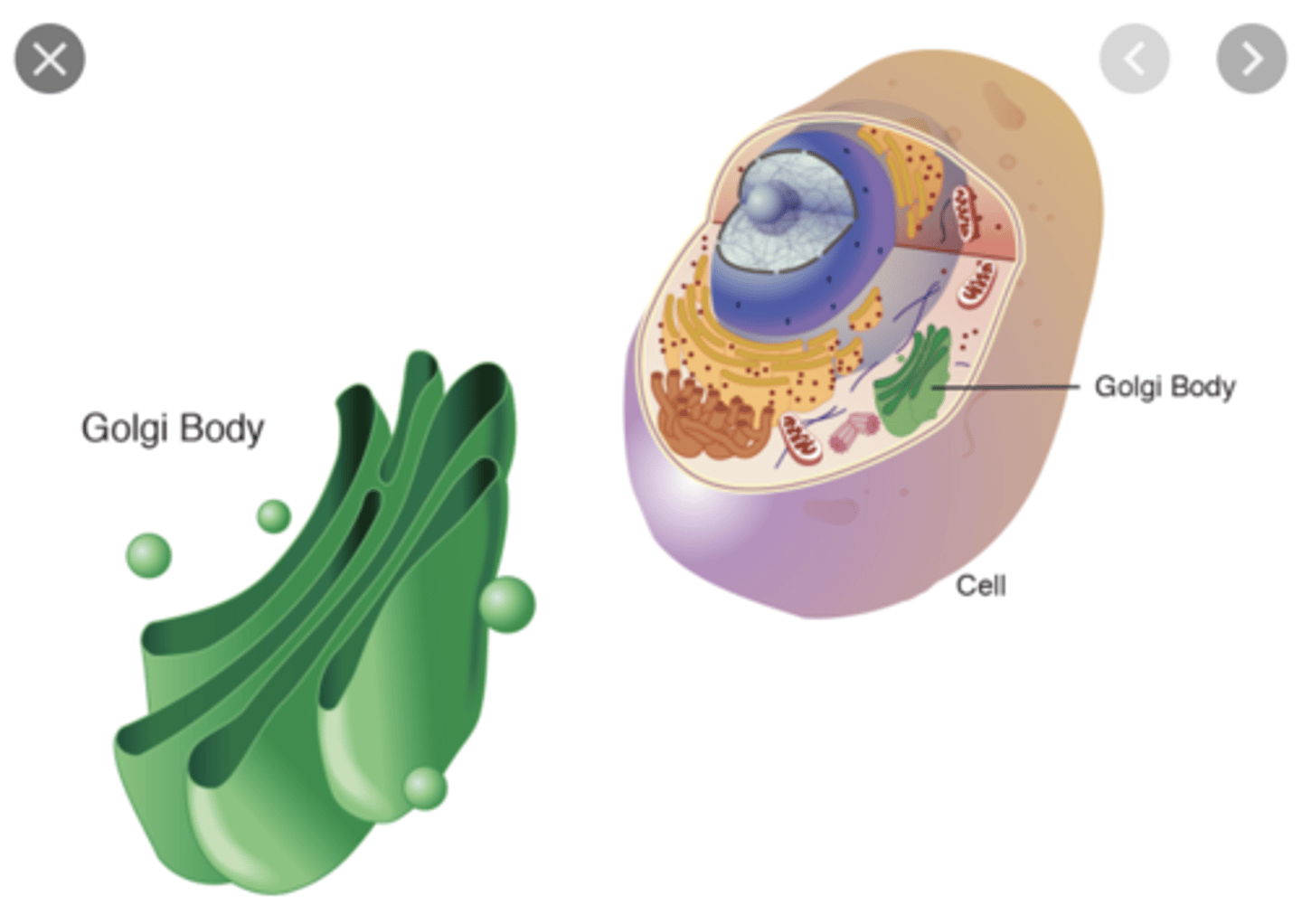
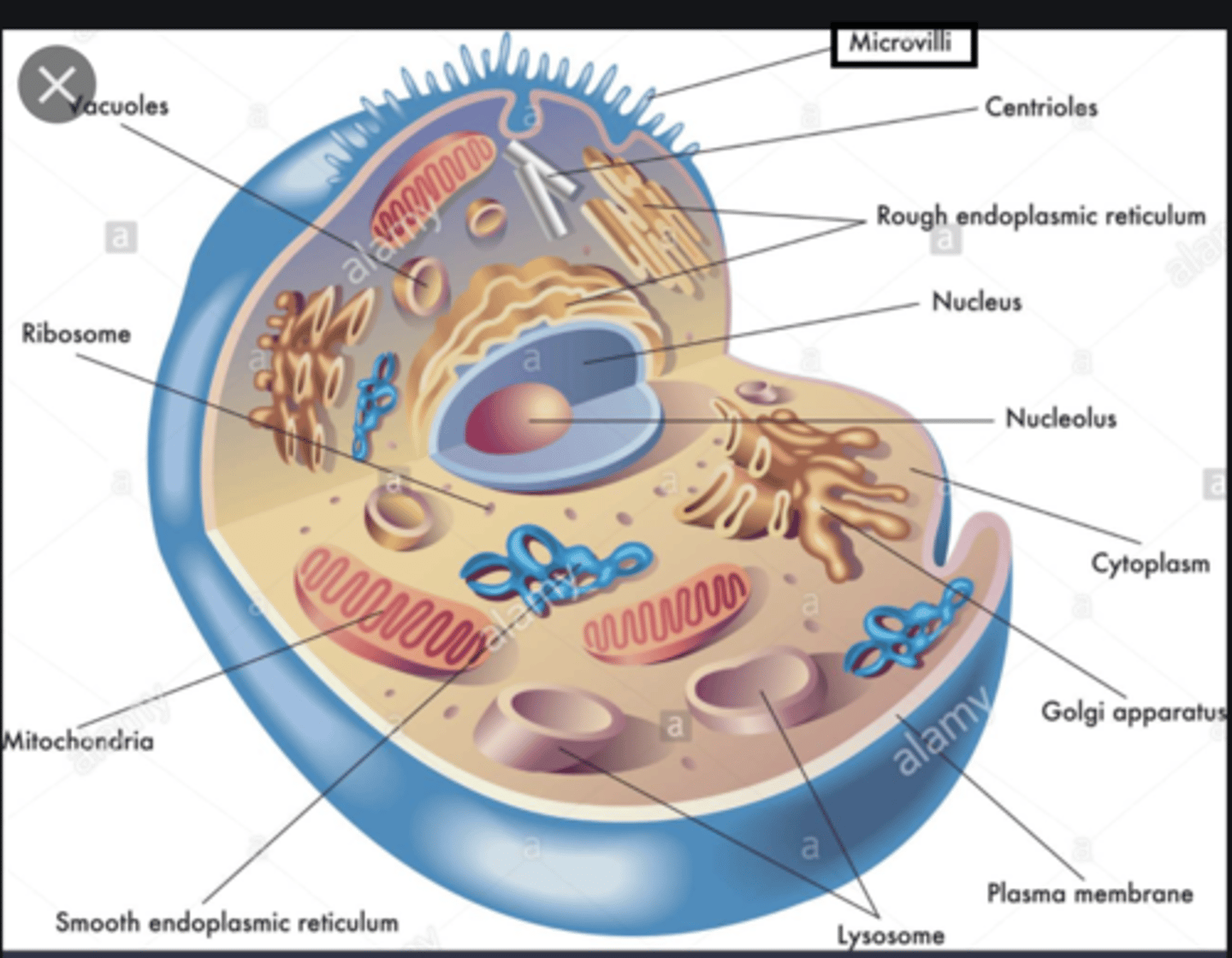
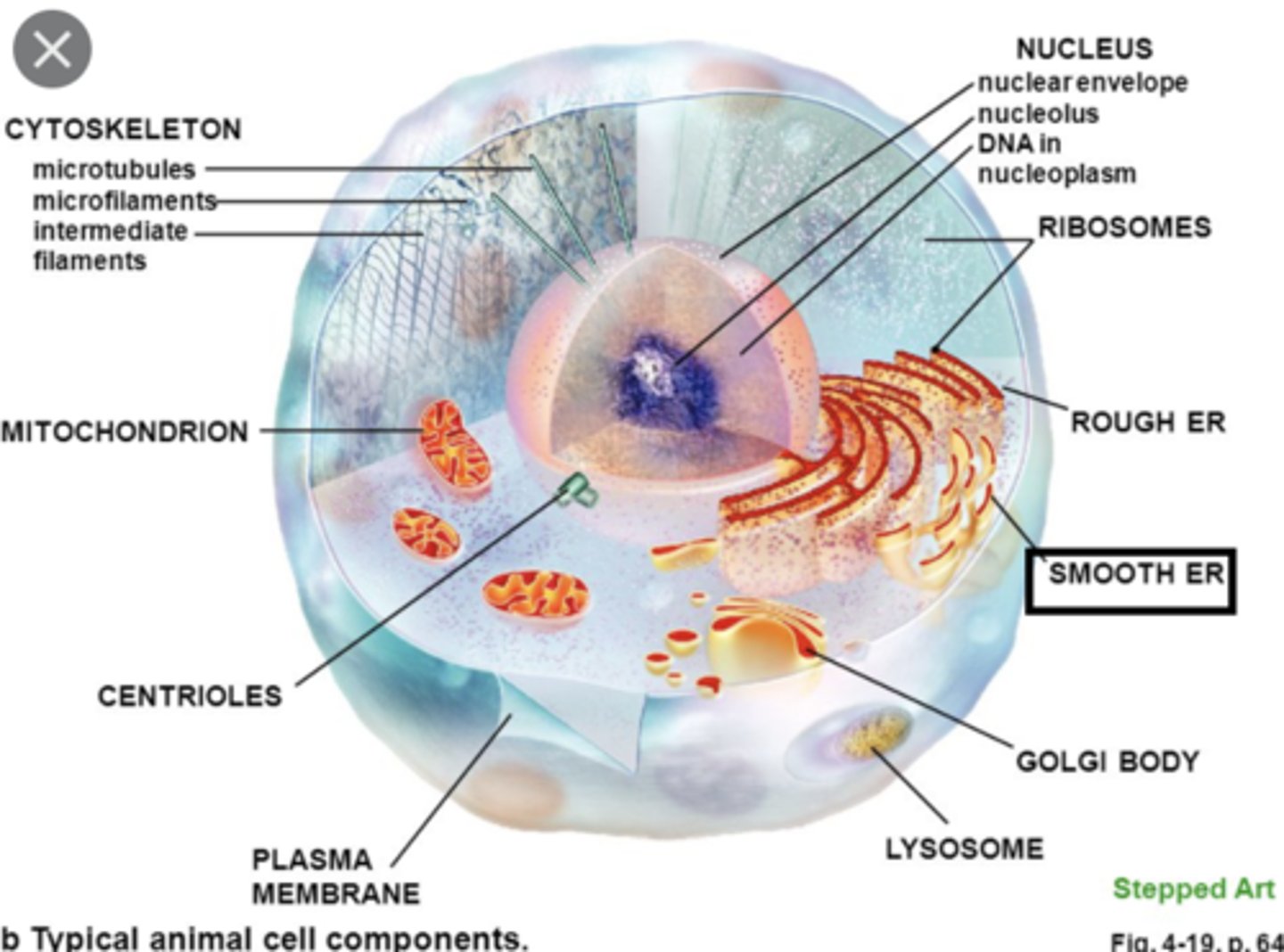
Golgi Body
- processes & packages items for the cell
- receives ER's transport vesicles at its cis face
- synthesizes glycoproteins
- gives rise to secretory vesicles & lysosomes in its trans face
Inclusions
- collection of substances in cytoplasm not contained in organelle
- glycogen, triglyceride, melanin, keratin, hemoglobin
Lysosomes
- specialized vesicles arising from golgi bodies
- contain hydrolase that digests contents of endocytic vesicles
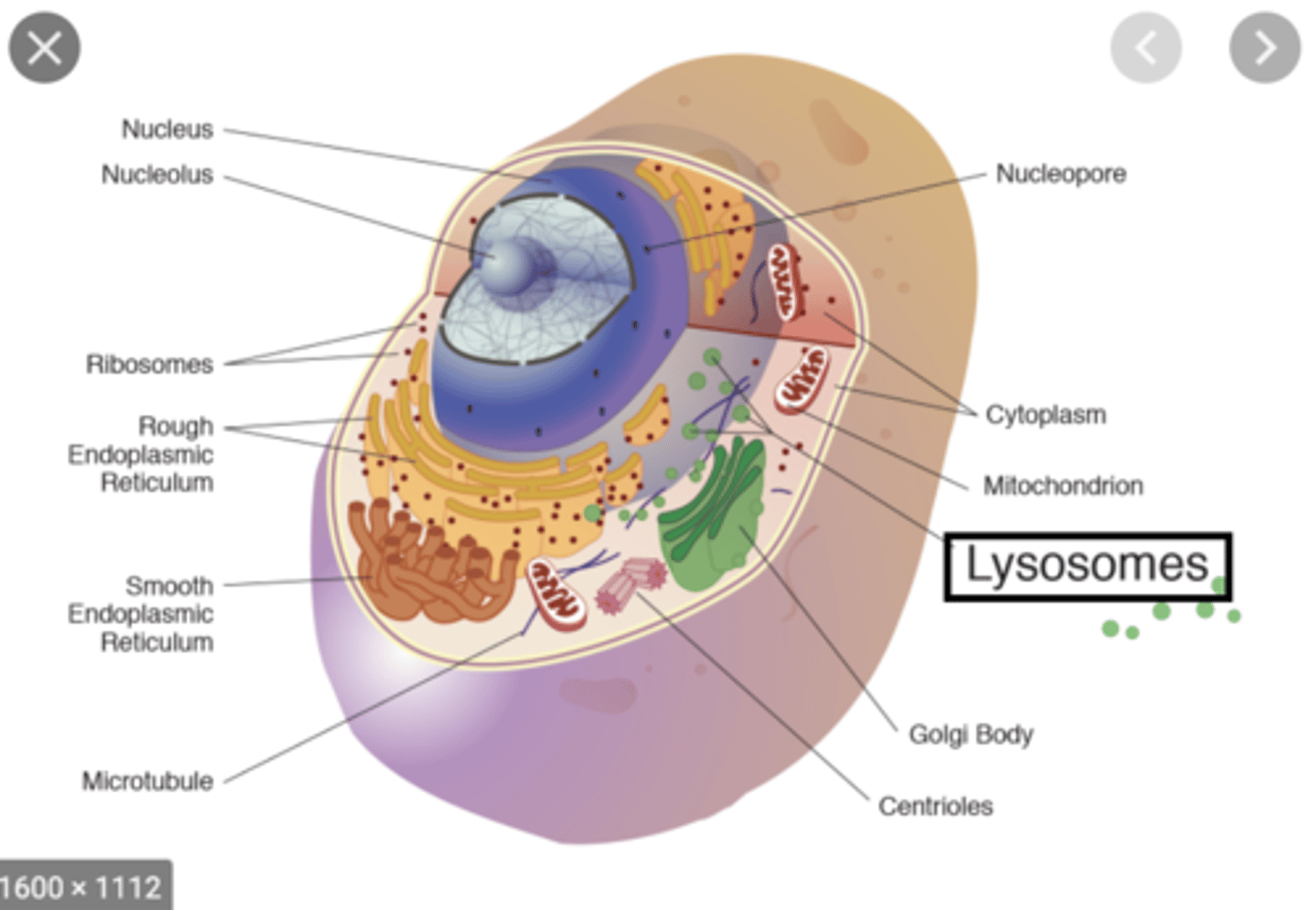
Microvilli
tiny extensions of the plasma membrane that increases cell's surface area for absorbing nutrients
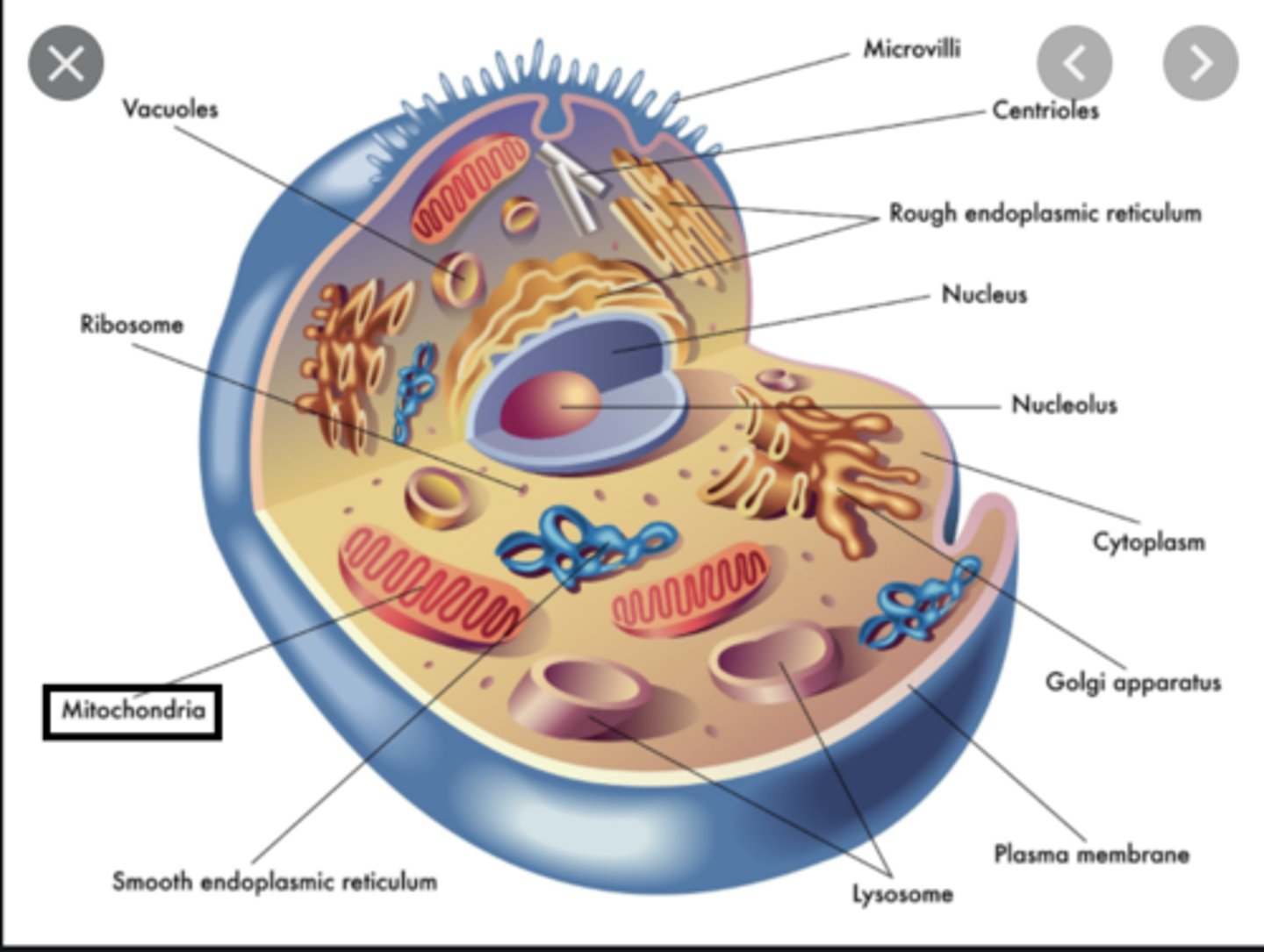
Mitochondria
- double-membrane organelles
- synthesizes cell's ATP
- has cristae
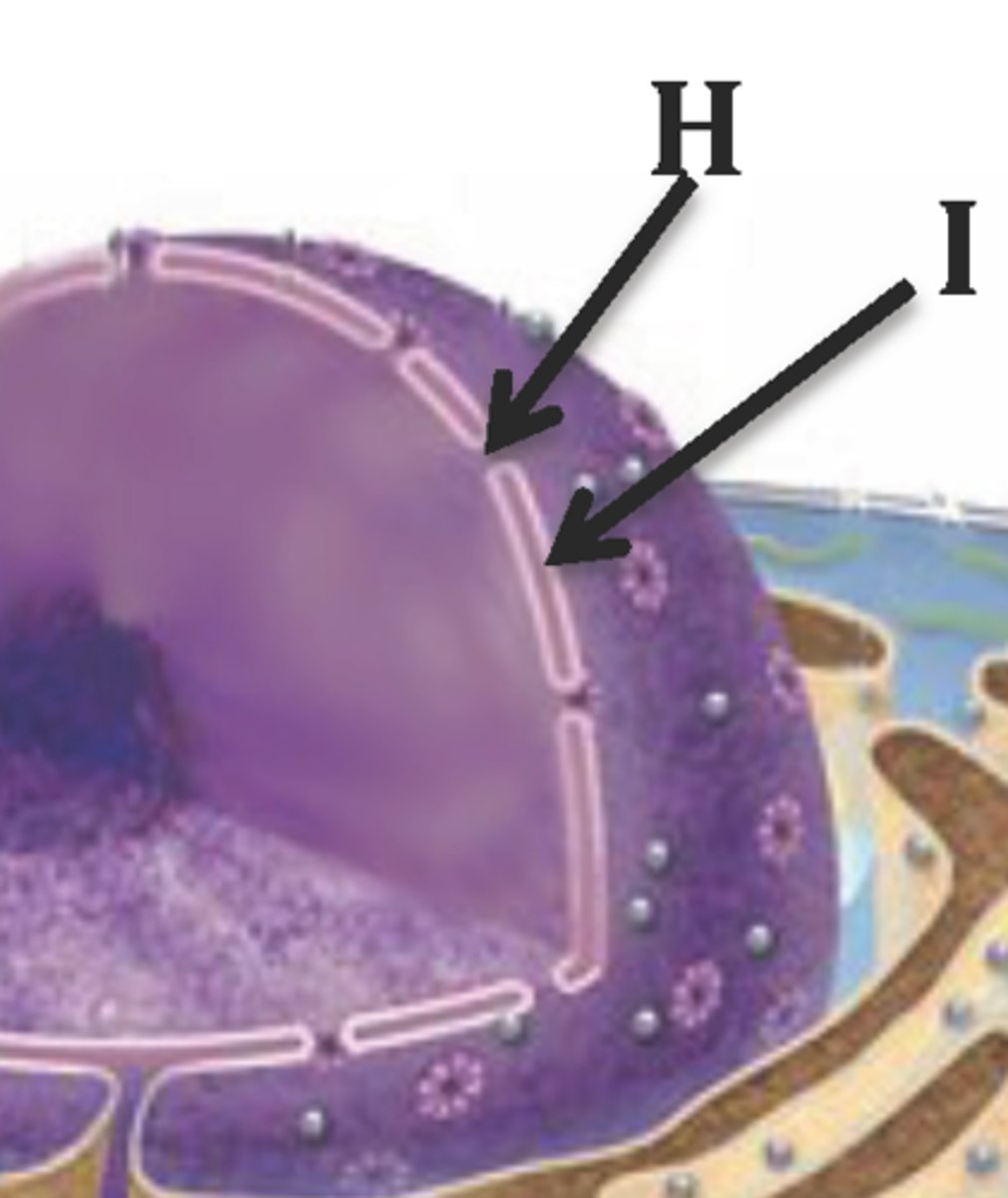
Nuclear Membrane
double membrane that encloses that nucleoplasm of the nucleus; continuous in ER
Picture: inner & outer
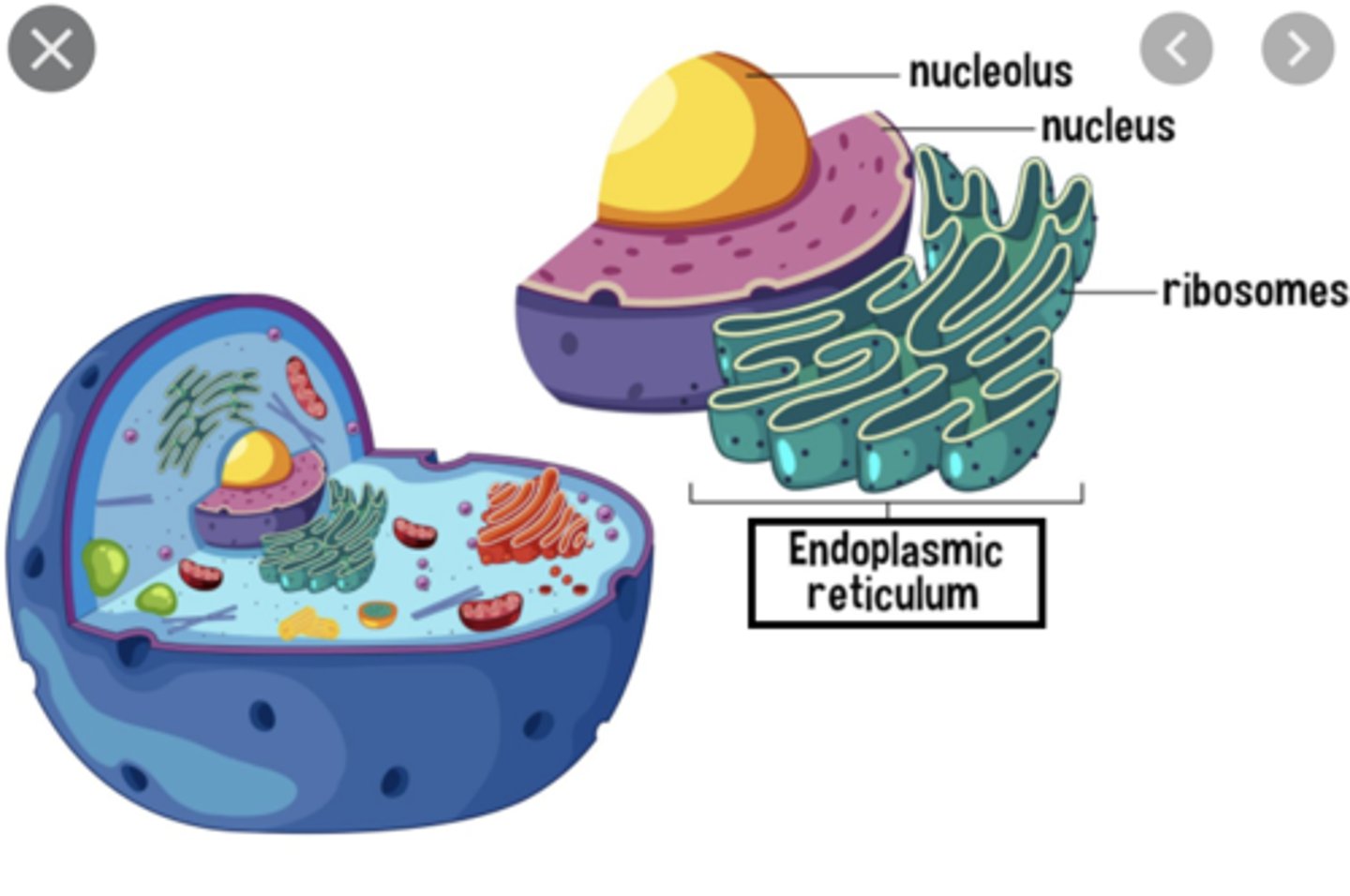
Nucleoli
dark-staining regions in nucleoplasm where ribosomal RNA molecules & proteins comes together to form large or small ribosomal subunits
Nucleoplasm
liquid material inside the nucleus
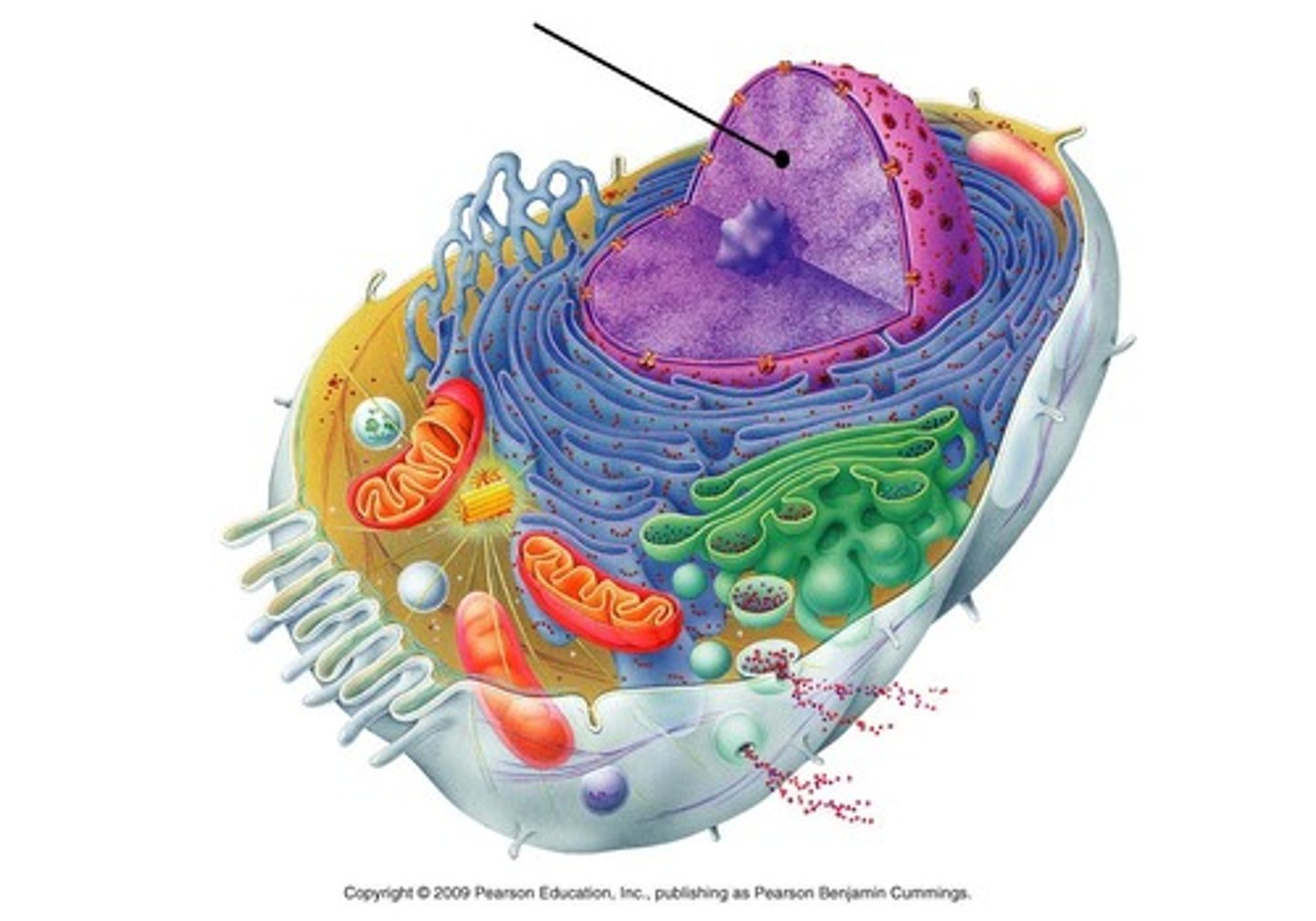
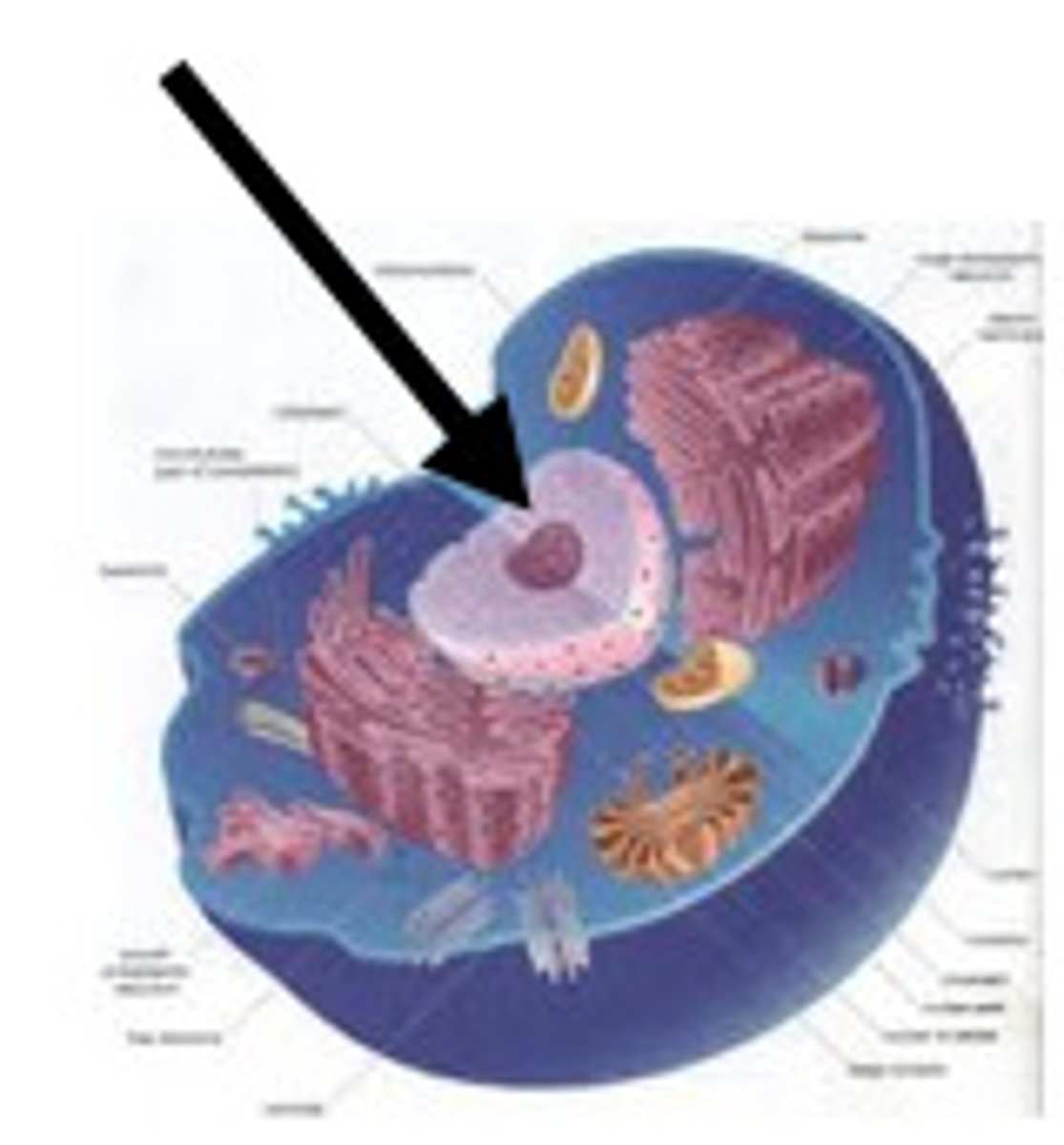
Nucleus
largest organelle; contains nucleoplasm and nucleoli
Organelles
structures within the cell that are specialized; includes nucleus and cytoplasmic organelles
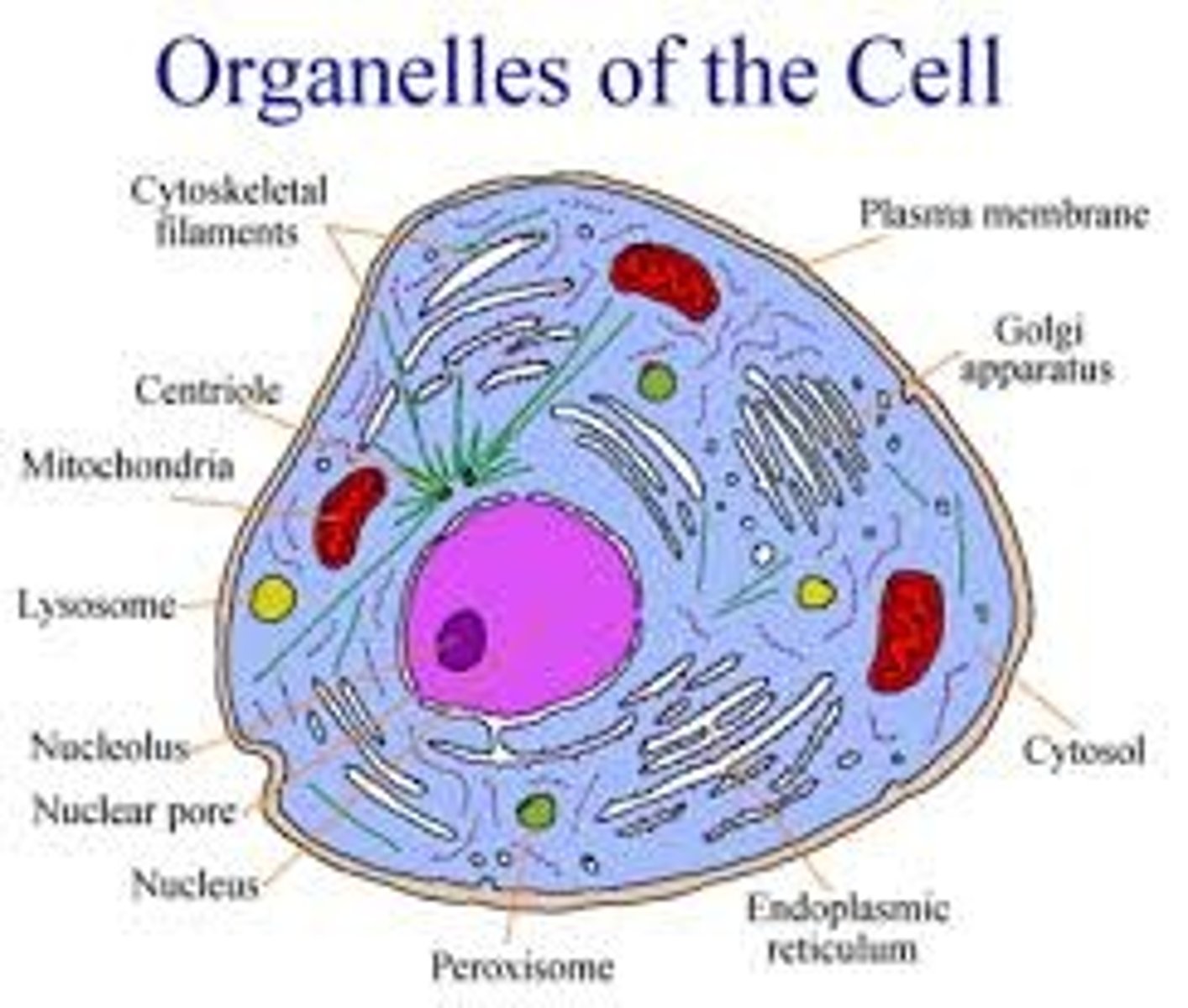
Peroxisomes
- small circle organelles that may bud off the ER or arise from others
- contain oxidase that bind to free radicals w/ H+ atoms to form hydrogen peroxide
- contain catalase that reduces hydrogen peroxide to form water and oxygen
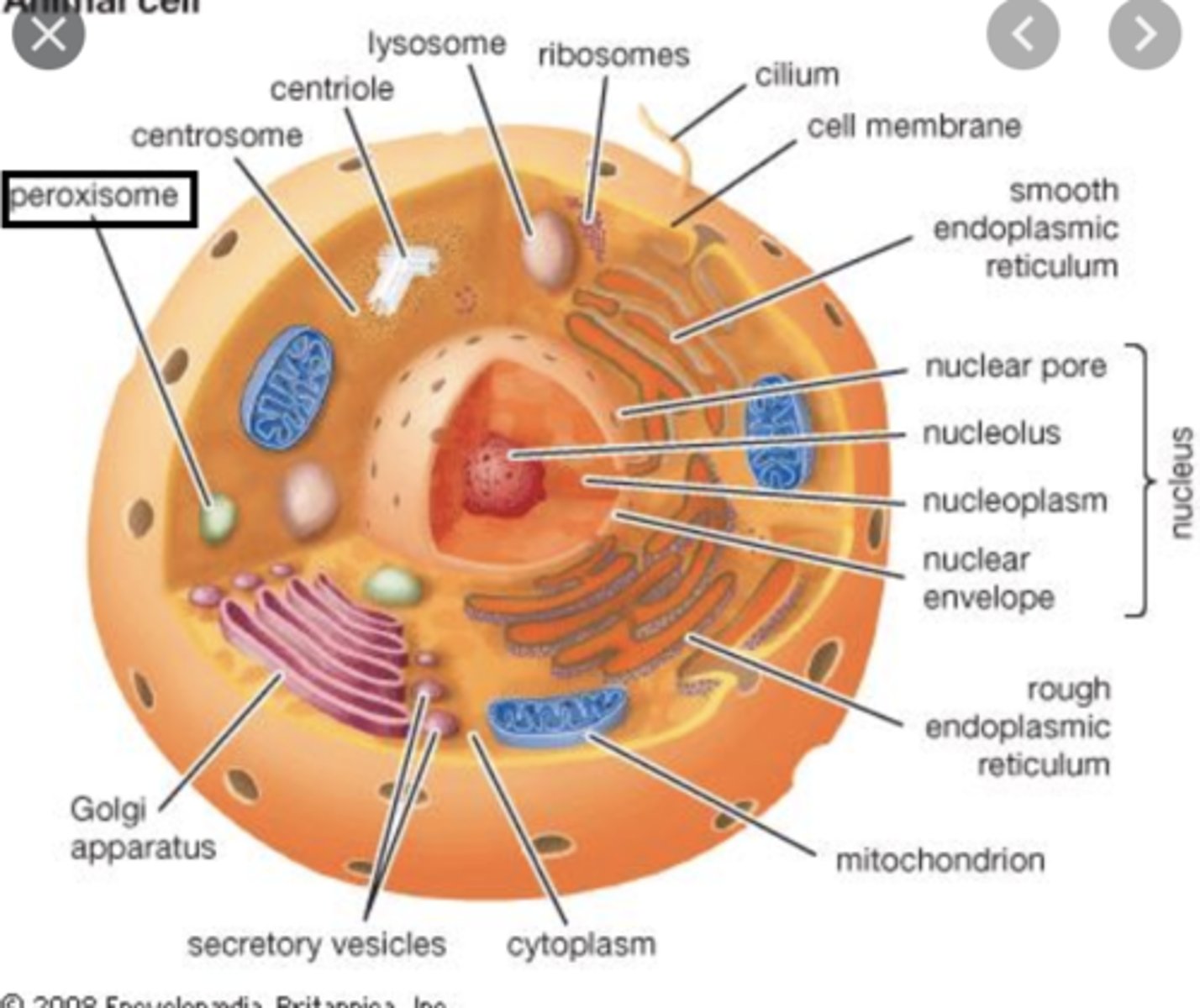
Ribosomes
- non-membranous organelles consisting of protein & rRNA
- sites where all protein synthesis occurs
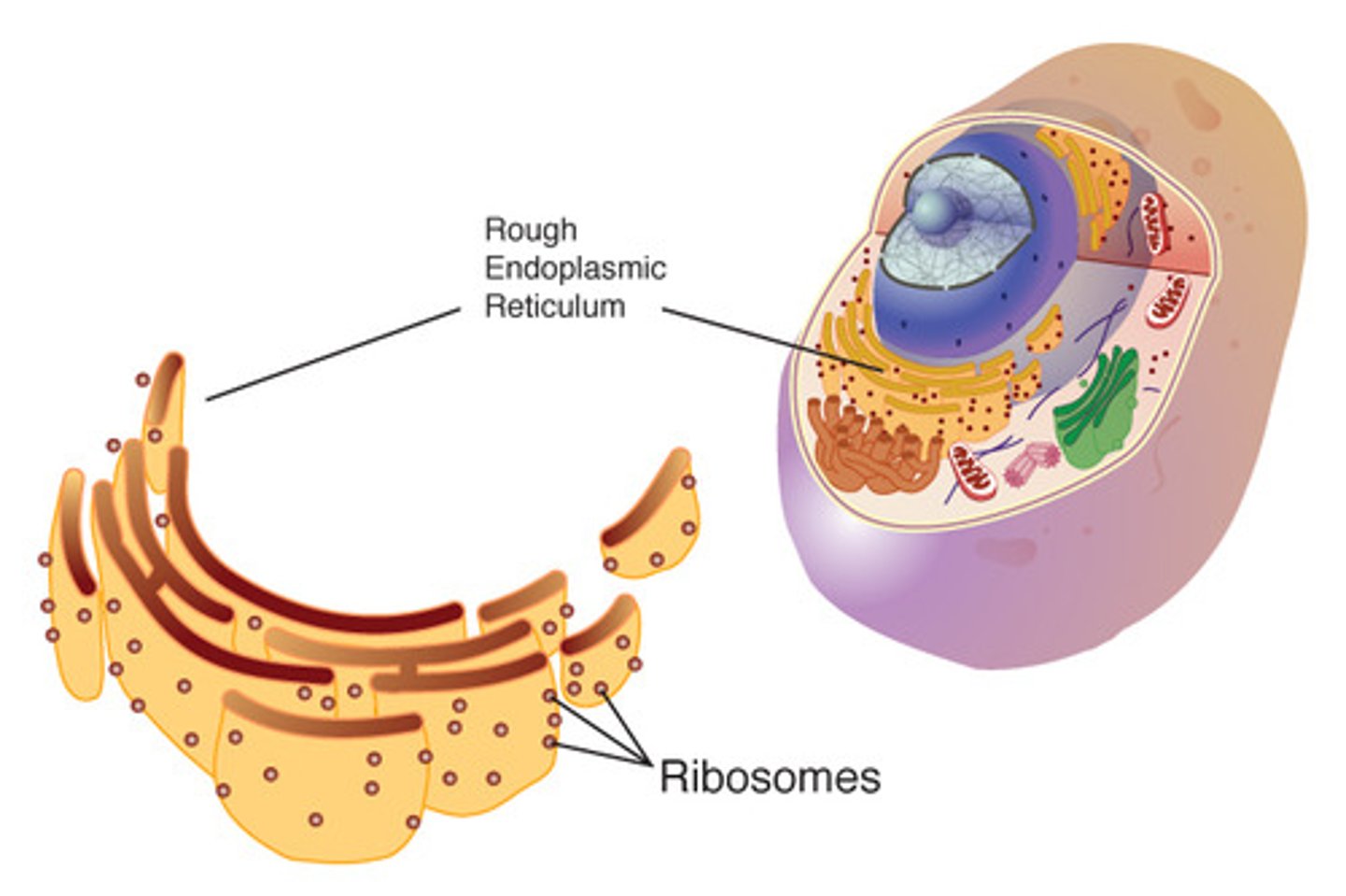
Endoplasmic Reticulum
double-membrane channel system that serves as a intracellular "highway" for transporting materials
Rough ER
has ribosomes and is a site for protein synthesis and modification
Smooth ER
- lacks ribosomes and is the site of lipid synthesis and hydrolysis of alcohol & drugs
- stores Ca2+ ions in muscle cells
Vesicles
small membrane sacs that specialize in moving products into, out of, and within a cell
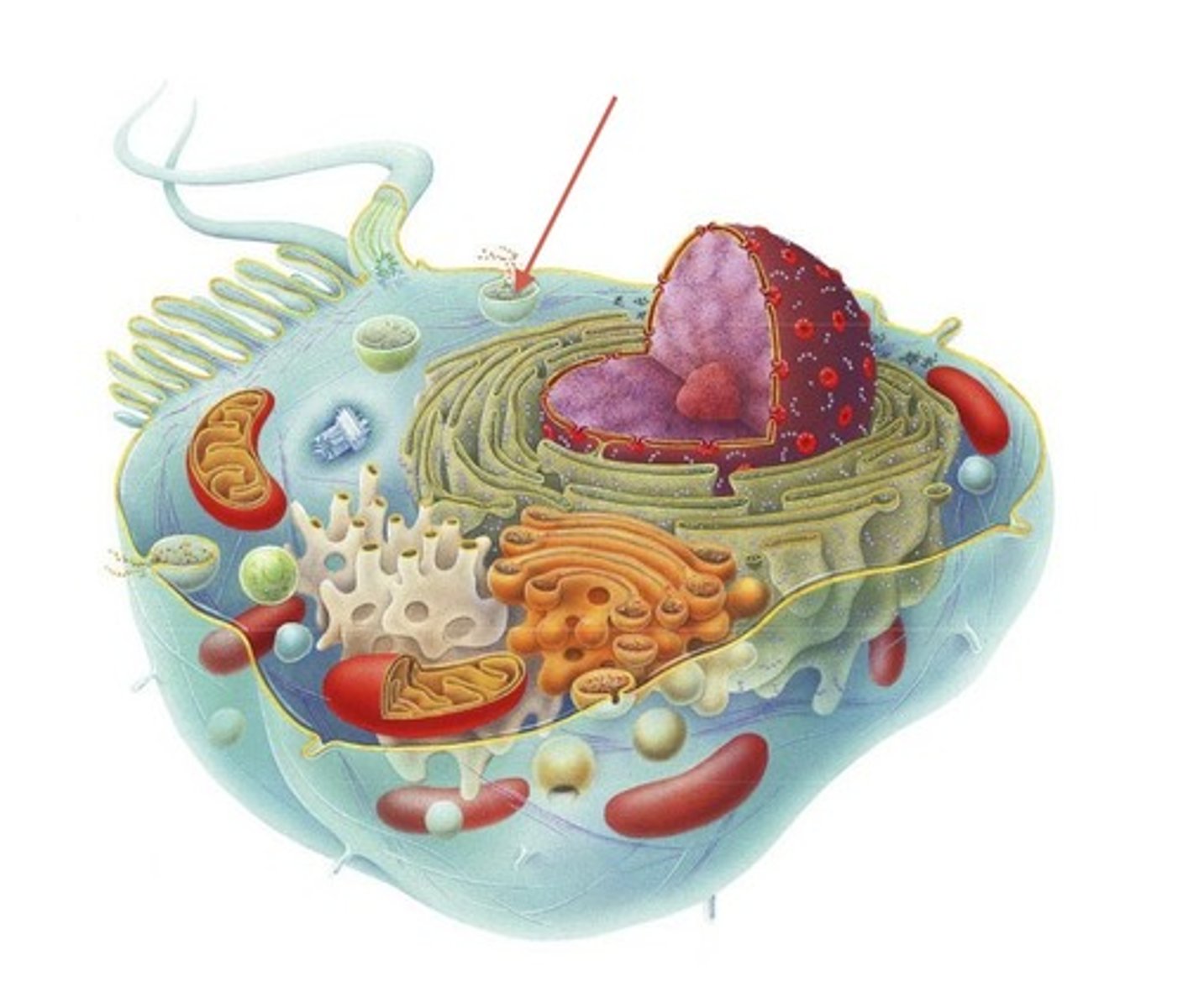
Transport Vesicles
formed from ER
Secretory Vesicles
formed form golgi complex
Endocytic Vesicles
formed from cell membrane
Autosome
any linear chromosome not classified as a sex chromosome
Chromatid
1 of 2 identical linear DNA molecules held together at a centromere
Chromatin
Linear DNA plus protein (histones) that coil to make a visible chromosome
Linear DNA Molecule
double helix nucleic acid that comprises each non-replicated chromosome in the nucleus and each chromatid in a replicated nuclear chromosome
Circular DNA Molecule
double helix nucleic acid found within a mitochondrion
Diploid Number
condition which a nucleus has 2 sources of each type of linear chromosome: mother (maternal) or father (paternal) chromosomes
Diploid Number for Humans
46 or 23 chromosomes for each parent
Gene
Segment of DNA containing info for sequencing amino acids in a specific protein
Genome
complete set of genes in an organism; it is all genes found on all 46 chromosomes
Haploid Number
- number of different types of linear chromosomes in a cell's nucleus
- identified by length, centromere location, &/or banding pattern
- number for human is 23
Homologous Chromosomes
- linear chromosomes that contain info responsible for same genetic traits
- humans have 23 pairs in each diploid nucleus
Kinetochore
- region on a chromatid where a spindle fiber attaches
- consists of DNA and proteins
Maternal Chromosome
any linear chromosome donated to the offspring by the mother
Nucleosome
Cluster of 8 globular, histone proteins around which a segment of linear DNA coils
Paternal Chromosome
any linear chromosome donated to the offspring by the father
Replicated Nuclear Chromosome
a linear chromosome derived from 1 parent consisting of 2 double-helix DNA molecules (chromatids) joined by a centromere
Replicated Mitochondrial Chromosome
a circular chromosome within a mitochondrion and consisting of 2 circular, double helix DNA molecules prior to binary fission
Sex Chromosome
- Linear chromosome responsible for determining the sex of the individual
- designated "X" & "Y" in humans
- female = XX
- male = XY
Somatic Cells
any cell not considered a sex cell; sometimes a called a general "body" cell
Spindle Fibers
microtubules (tubulin polymers) that aid in the separation of sister chromatids during mitosis
If an organism's 1N number = 12, how many chromatids are presents in one of its 2N cells during metaphase?
48
How many linear, double-helix DNA molecules are present in one of YOUR 2N cells during prophase?
92
How many kinetochores are present in one of YOUR 2N cells during metaphase of mitosis?
92
How many replicated autosomes are present in one of your 2N body cells during G2 phase?
44
How many centromeres are present in one of YOUR 2N body cells during G1?
0
How many centromeres are present in one of YOUR 2N body cells during G2?
46
How many centromeres are present in one of YOUR 2N body cells during Prophase?
46
Why must cells replicate their DNA prior to entering mitosis?
There would be no loss of DNA when splitting.