chemistry unit 3 and 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:08 PM on 9/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
1
New cards
What is a haloalkane?
An alkane with at least one halogen atom in place of a hydrogen atom. eg. chloro, bromo...
2
New cards
What is an alcohol?
A hydroxyl group (OH) that is attached to saturated carbons. the parent chain ends with 'ol'
3
New cards
what are the 3 groups of alcohols
primary secondary and tertiary
4
New cards
what is hydroxyl?
"Hydroxyl" refers to -OH
5
New cards
what is carbonyl?
refers to C=O
6
New cards
what is carboxyl?
"Carboxyl" refers to COOH (double bonded to an oxygen atom)
7
New cards
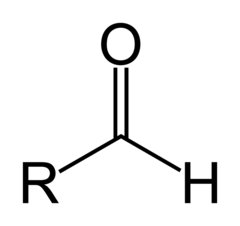
What is an aldehyde?
they contain oxygen at the end of a parent chain which is double bonded to a carbon. the carbon is always bonded to hydrogen. the name ends with 'al'
8
New cards
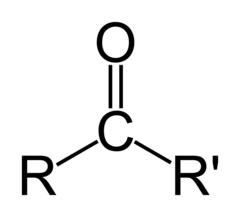
What are ketones?
they contain oxygen in the middle of a parent chain, double-bonded to carbon. the carbon is joined to 2 other carbons. the name ends with 'one'
9
New cards
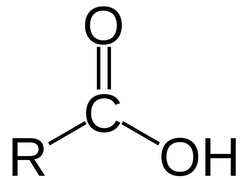
carboxylic acids
the chain containing the COOH becomes the main chain. the name ends with 'oic' eg. butanoic.
10
New cards
what is an Amide?
they are derived from carboxylic acids. they are classified as primary, secondary or tertiary.
11
New cards
What is chromotography?
a technique for the separation of a mixture by passing it in solution or suspension through a medium in which the components move at different rates.
12
New cards
what are the phases of chromatography?
Mobile and stationary
13
New cards
What is the mobile phase?
a liquid or gas that carries the sample through the column
14
New cards
what is the stationary phase?
a solid to which the sample molecules absorb as they move through the column
15
New cards
What is size exclusion chromatography?
relies on porous beads; larger molecules elute first because they are not trapped in small pores. the ability of molecules to pass through pores in the stationary phases.
16
New cards
What is mass spectrometry?
it determines the molecular mass of a compound, and the isotopic composition of an element. Molecular ions are separated by their mass through a magnetic field and collected by a detector.
17
New cards
what is Infrared Spectroscopy?
determines the bonds and functional groups that are present or absent in a compound
18
New cards
open system
allows matter and energy to be exchanged with the surroundings.
19
New cards
closed system
allows only energy to be exchanged with surroundings.
20
New cards
Law of Conservation of Mass
in a chemical reaction, matter is neither created nor destroyed
21
New cards
Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution
Shows the distribution of the molecular energies in a gas at a constant temperature. The area under the curve indicates the total number of particles present.
22
New cards
Reversibility
physical changes are usually reversible but only some chemical reactions are reversible
23
New cards
What is dynamic equilibrium?
Equilibrium in a closed system where the reactions occur at exactly the same rate in each direction
24
New cards
What are catalysts?
a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without participating in the reaction
25
New cards
Percentage yield
actual yield/theoretical yield x 100
26
New cards
Concentration
the amount of particles in a given volume
27
New cards
what effects equilibrium position?
temperature and concentration
28
New cards
How to change concentration
- add reactants/ products
- increase temp
- add inert gas
- increase temp
- add inert gas
29
New cards
What is Le Chatelier's principle?
if you change the conditions of a reversible reaction at equilibrium, the system will try to counteract that change
30
New cards
pH
measure of concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. tells us how acidic the solution is.
31
New cards
Equilibrium law
For the equilibrium aA+bB=cC+dD Kc=[C]^c[D]^d/[A]^a[B]^b
32
New cards
Exothermic
reactants have more energy
33
New cards
endothermic
products have more energy
34
New cards
monoprotic acid
an acid that can donate only one proton (hydrogen) to a base
35
New cards
polyprotic acid
an acid that can donate more than one proton per molecule
36
New cards
strong acids and bases
completely dissociate in water
37
New cards
redox reactions
When there is a transfer of one or more electrons from one reactant to another.
38
New cards
proton donor
a substance that can donate H+ (hydrogen ions)
39
New cards
strong acid vs weak acid
Strong-dissociates completely / more readily, releases more H+, weak acid does not, partly dissociates (same with strong and weak bases)
40
New cards
oxidation
when substances combine with oxygen
41
New cards
reduction
when substances give up oxygen
42
New cards
conservation of charge
The law that states that charges are neither created nor destroyed but only transferred from one material to another.
43
New cards
what is an anode in a galvanic cell
where oxidation occurs (negative charged)
44
New cards
what is a cathode in galvanic cell
where reduction occurs (positive charged)
45
New cards
which way do electrons flow in galvanic cell?
from anode to cathode
46
New cards
What is a fuel cell
a device that produces electricity combining hydrogen and oxygen without combustion
47
New cards
what is electrolysis?
the process where electric current is used to bring about a redox reaction when it doesn't occur spontaneously.
48
New cards
what is an electrolyte?
substance that conducts electricity when dissolved in water
49
New cards
What is brōnstead lowery
states that acids are any species that donates protons and bases are any species that accepts protons
50
New cards
end point
the point in a titration at which an indicator changes color
51
New cards
equivilance point
when chemicals have reacted according to the molar ratio
52
New cards
boiling / melting point of hydrocarbons
they have the lowest melting and boiling points because they only have hydrogen and carbon atoms joined by non polar bonds
branched alkanes have lower boiling points than straight chains
branched alkanes have lower boiling points than straight chains
53
New cards
Hydrocarbon solubility
they are not soluble in water because they are non polar
54
New cards
melting/boiling point of alcohols
is significantly higher than hydrocarbons, because of the hydrogen bonding. when there is more hydroxyl groups boiling point is higher
55
New cards
melting/ boiling points of aldehydes and ketones
the melting and boiling points are lower because there is no hydroxyl functional groups. they are more volatile than alcohols. the melting and boiling points are still higher than hydrocarbons.
56
New cards
Solubility of Ketones and Aldehydes
Small aldehydes and ketones are soluble in water
The longer the carbon chains, the less soluble they become
The longer the carbon chains, the less soluble they become
57
New cards
melting/ boiling point for carboxylic acids
they can hydrogen bond, and therefore they have higher melting and boiling points (higher than alcohol)
58
New cards
define substitution recation
when a substituent is replaced by another
59
New cards
Why is carbon susceptible to substitution reactions
because of its polarity (polar bonds)
60
New cards
Define esterification
The reaction of an alcohol with a carboxylic acid to produce an ester and water.
61
New cards
What is a condensation reaction?
A reaction in which two molecules combine to form a larger molecule, producing H2O as a by product
62
New cards
What is an amide synthesis reaction?
they are synthesised from carboxylic acids and amines
63
New cards
what is polymerisation
The chemical process during which hydrocarbon monomers are joined to make longer strings of molecules (polymers). addition of alkene monomers to form polymers
64
New cards
What is a homologous series?
A family of organic compounds that have the same functional group, similar chemical properties and the same general formula, but differ by 1 carbon atom
65
New cards
what is addition and elimination
addition occurs when atoms add across a double or triple bond in a hydrocarbon
66
New cards
what are the types of addition?
hydrogenation, halogenation, hydrohalogenation, hydration, polymerisation
67
New cards
what is hydrogenation
the addition of hydrogen to each carbon atom, converting alkenes to alkanes
68
New cards
What is halogenation?
the addition of a halogen to each carbon atom, converting alkenes to haloalkanes
69
New cards
What is hydrohalogenation?
The addition of HCl or HBr, converts alkenes to haloalkanes
70
New cards
What is Markovnikov's rule?
the carbon with the most H atoms gets the H
71
New cards
What is hydration?
addition of H2O, converts alkenes to alcohol
72
New cards
what is polymerisation
addition of alkene monomers to form polymers
73
New cards
What is the Haber-Bosch process?
an industrial process for producing ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen, using an iron catalyst at high temperature and pressure.
74
New cards
what is the contact process
an industrial process used to make Sulfur dioxide
75
New cards
Define biodegradation
the breakdown of a substance into micro-organisms
76
New cards
what are the 3 stages of the contact process
S + O2 = SO2
2SO2 + O2 = 2SO3
SO3 + H2O = H2SO4
2SO2 + O2 = 2SO3
SO3 + H2O = H2SO4
77
New cards
what is the difference between a reagent and a reactant
a reagent is used to detect something in a reaction (eg colour change) and a reactant is a molecule participating in the reaction.
78
New cards
What is a steroisomer?
compounds that have the same molecular formula and structural formula but a different arrangement of atoms in space
79
New cards
geometrical isomers
stereoisomers that have different arrangements of atoms around a rigid double bond. they can be cis or trans
80
New cards
Cis isomers vs trans isomers
Cis - Same Side of the double bond
Trans - Opposite of the double bond
Trans - Opposite of the double bond
81
New cards
Enantiomers
2 compounds that have the same atoms and bonding but a different arrangement of four substituents around a carbon atom
82
New cards
electrolysis
electrical energy is passed into a cell, using a power source, resulting int he reversal of spontaneous redox reactions
83
New cards
self ionisation of water
the reaction in which a water molecule loses a hydrogen ion to become a hydroxide ion and the hydrogen ion immediately reacts with another water molecule to form a hydronium
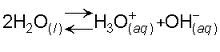
84
New cards
The Kw constant
is the constant for the self ionisation of water
Explore top notes
Explore top flashcards
Foundations of govt, British history, DOI, Articles of Confederation
Updated 881d ago