differentiation quiz
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
zygote
this is how every baby starts out. a zygote is a single cell formed from fusion of the egg and sperm (which occurs during meiosis)
zygotes grow and develop through mitosis
blastocyst
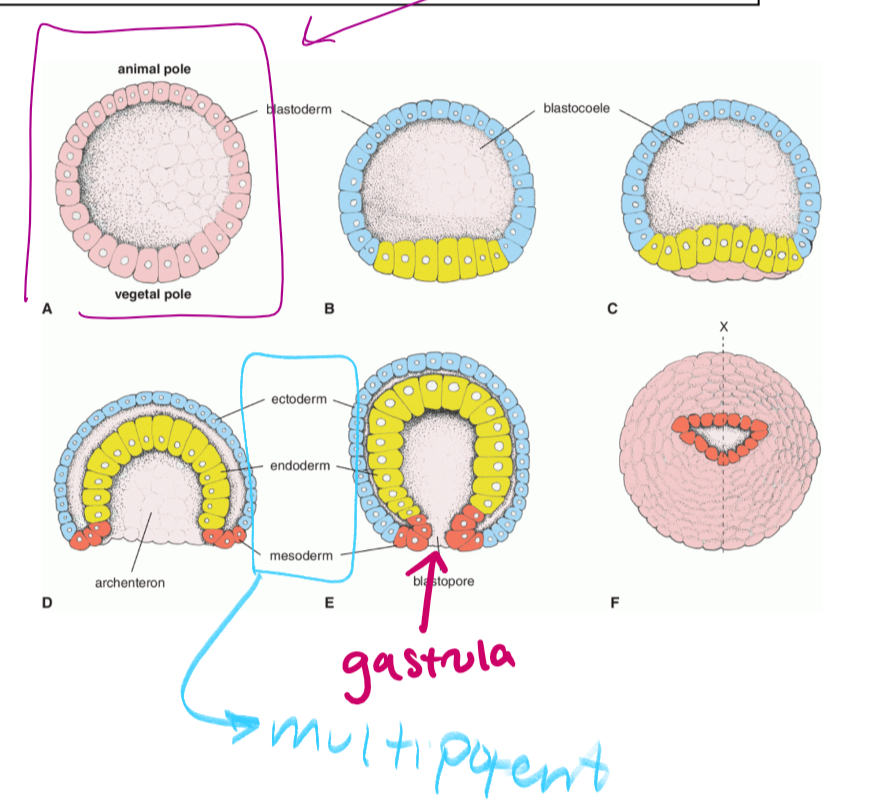
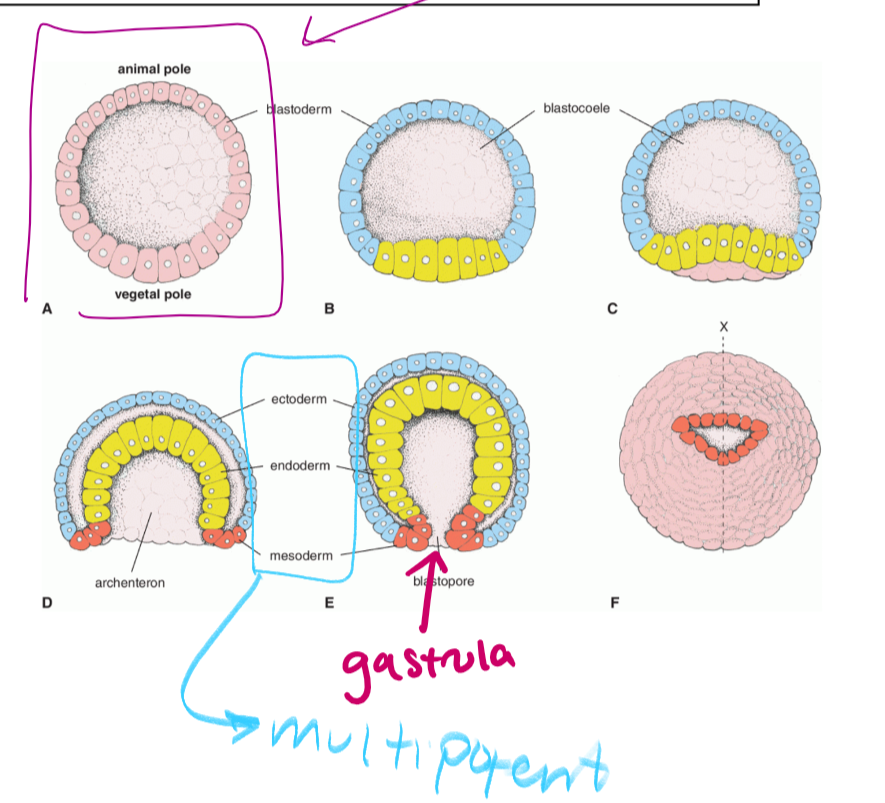
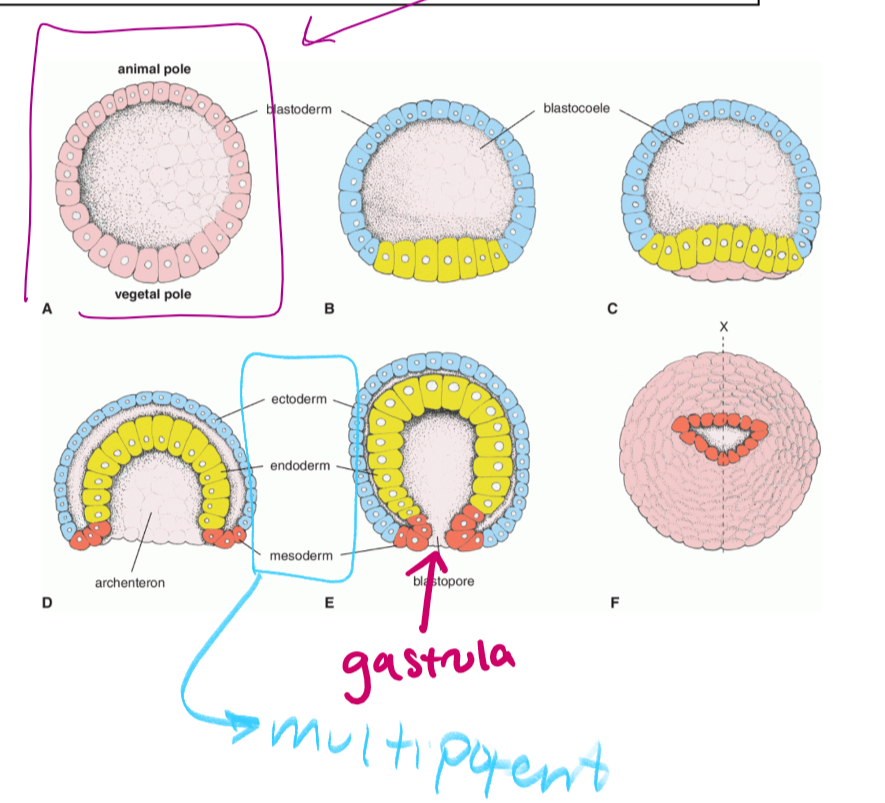
the hollow sphere that is formed when cells migrate outward so that the embryo can get amniotic fluid (circled in purple)
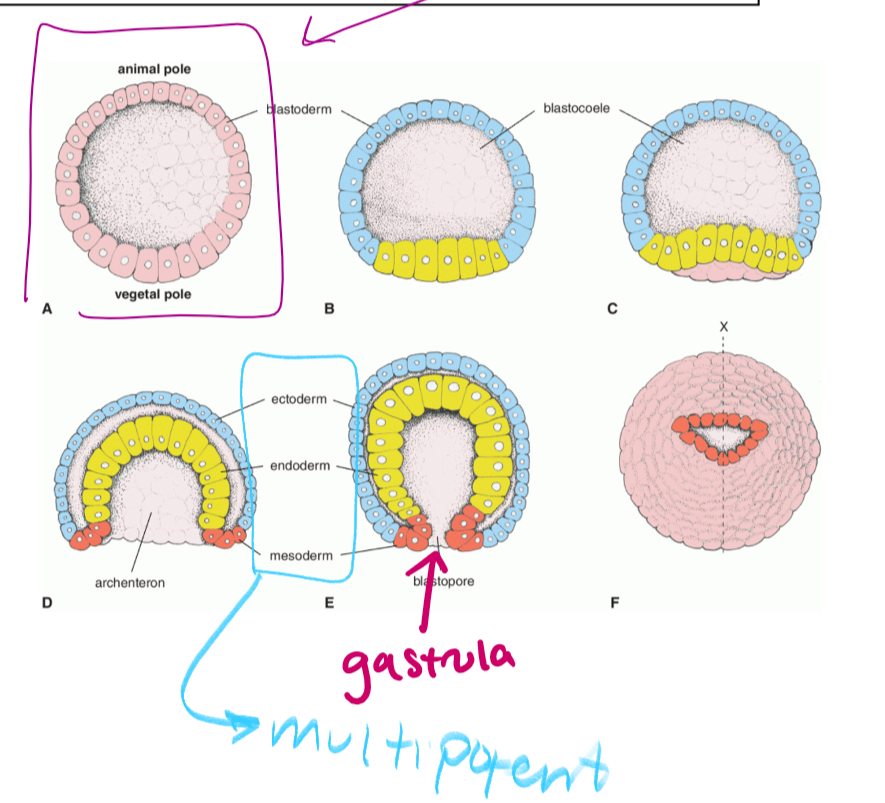
gastrulation
the cells in the blastocyst migrant inward to form a hollow tube called the gastrula (which is pluripotent)
as the cells form the gastrula, they will separate into three germ layers
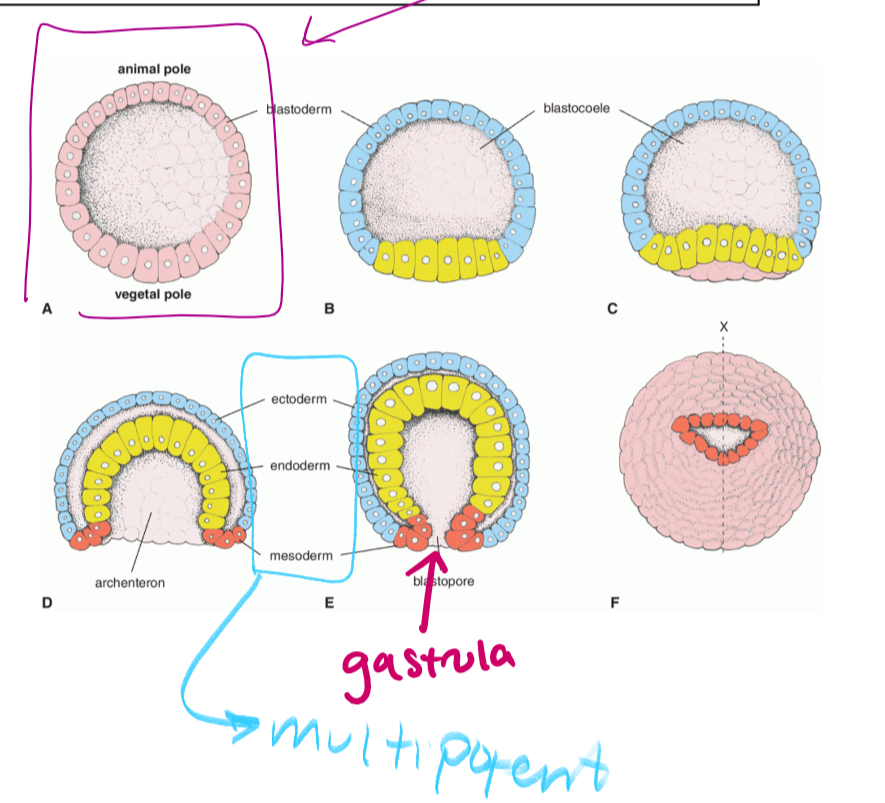
gastrula
what forms as a result of gastrulation. gastrula is pluripotent
germ layers
decide what the cell will differentiate into. for example, a cell that ends up in the ectoderm could become an epidermal cell.
endoderm
the origin of the alimentary canal (mouth to anus)
forms digestive/respiratory system
ectoderm
becomes the epidermis and nervous system
mesoderm
forms everything else
embryonic stem cells
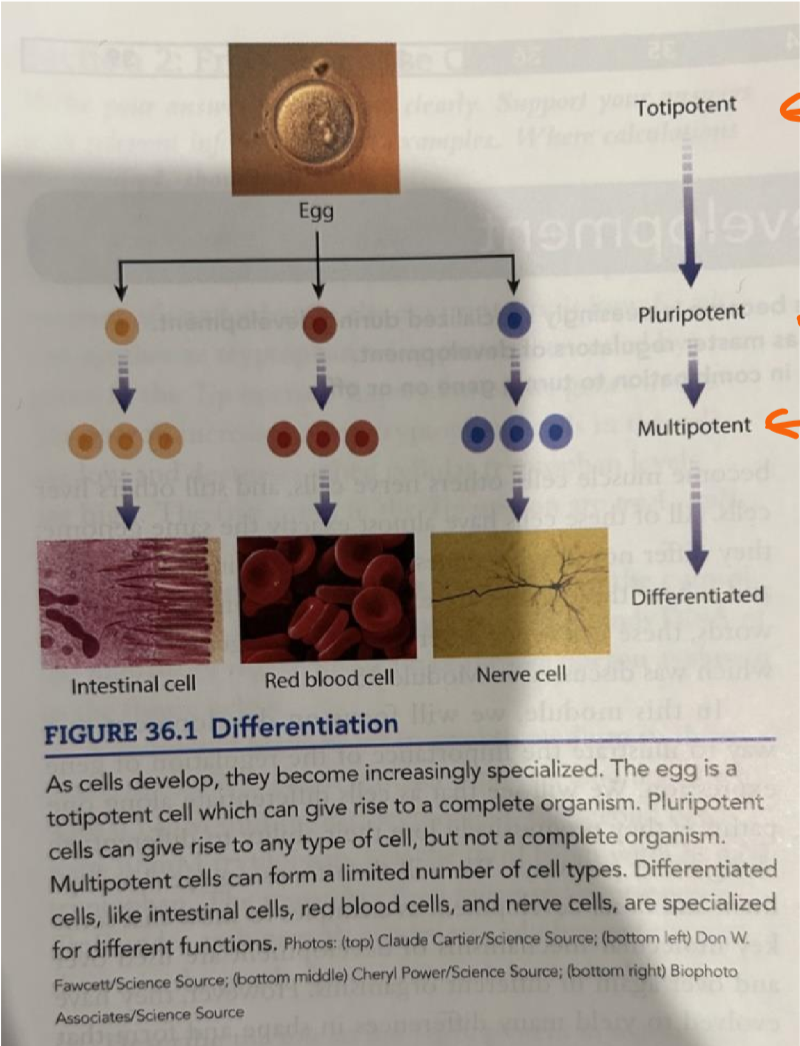
totipotent and can therefore be induced to differentiate into any other cell
embryonic stem cells are only found in early embryonic tissue
the criticism about using them is that you have to destroy an embryo. adult stem cells, when turned into embryonic stem cells, turn cancerous.
adult stem cells
are not totipotent
specialized/differentiated cells
specialized cells that come from more “general cells”. differentiated cells include blood cells, nerve cells, etc. and have NO POTENCY so they cannot further specialize
differentiation
the process of cells becoming more and more specialized
totipotent
found in early embryonic tissue/zygotes, can divide into anything and can give rise to a complete organism
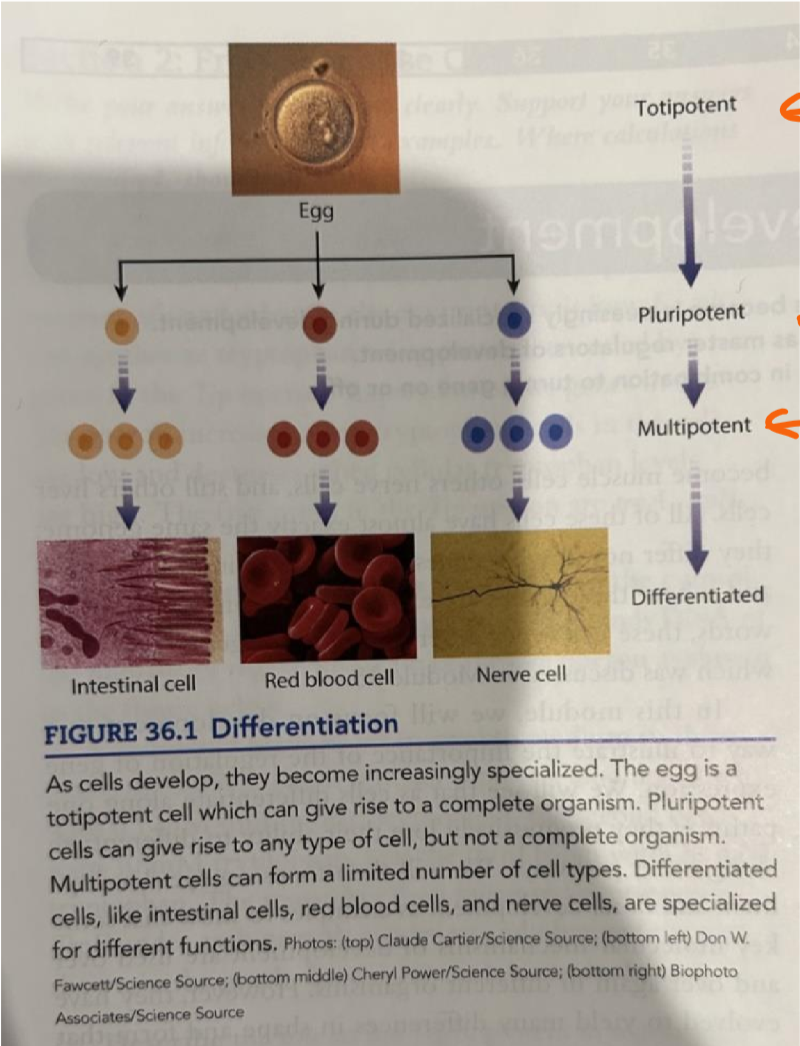
pluripotent
can give rise to any time of cell, but not a complete organism, found in blastocyst
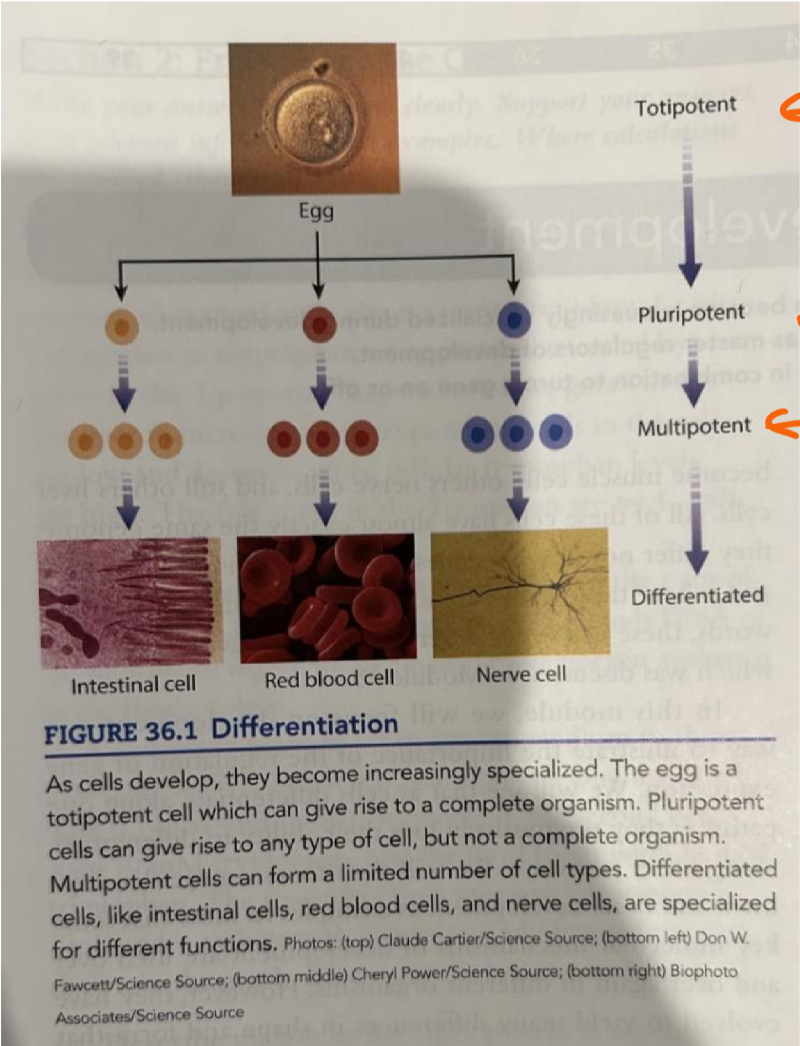
multipotent
form a limited number of cell types, found in adult stem cells in endo/ecto/mesoderm
development
how cells come from different less specific cells over time (idrk)
how do babies grow from a single cell
babies start out as a zygote which is a single cell. the zygote grows through mitosis. the zygote becomes an embryo (what a baby is called during the first 8 weeks in fetus) which has totipotent stem cells. these stem cells can divide into ANYTHING so the cells differentiate and over time babies are formed
how do embryos from different species show how species have changed over time
ok i lowkey called in chat for this one but if you look at embryos you can see slight similarities that point to them all having a common ancestor, and as they develop, the differences that become apparent show how they have adapted to different circumstances
why do researchers focus on embryonic stem cells
because they can potentially: clone, repair tissue, regenerate neurons, etc. and they are totipotent whereas adult stem cells are not
embryo vs fetus
for the first 8 weeks a baby is an embryo
then it becomes a fetus
what type of cells make up an embryo?
stem cells, specifically totipotent stem cells which are only found in early embryonic tissue
totipotent stem cells can differentiate into any other cell type
embryo starts as a ball of cells, but in order for amniotic fluid (nutrient rich fluid) to diffuse into the embryo it must change form
the cells migrate outward, forming a hollow sphere called blastocyst
different types of cells function by…
reading different chapters of the DNA. all of an organism’s information is carried in the DNA and all cells have the complete genome (all the DNA)
how does embryonic development begin

most developmental processes depend on…
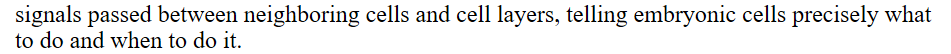
potency
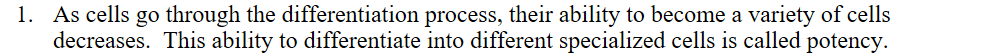
how do mitosis and apoptosis relate to embryonic and fetal development?
apoptosis—getting rid of bad cells or unneeded ones, helps sculpt tissue and organs
mitosis—zygotes grow through mitosis