Human Lungs
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
We exchange gas in…
alveoli
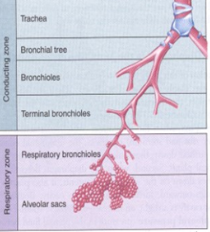
Human Respiratory System: Conduction Zone
Only moves air
1.) Trachea
2.)Brinchial Tree
3.)Bronchioles
4.)Terminal Bronchioles
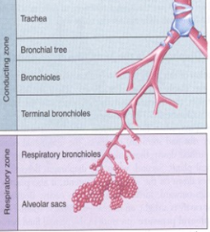
Human Respiratory System: Respiratory Zone
1.) Respiratory Bronchioles (begin gas exchange because of alveoli)
2.) Alveolar Sacs (alveoli)
Thoracic Cavity Structures (3)
-Visceral Pleural Membrane
-Pleural Cavity
-Parietal Pleural Membrane
THoracic Cavity
hold/separates lungs
Parietal Pleural Membrane
outside
Visceral Pleural Membrane
holds lung intimately and sirus
Alveolus Cells Type I
gas exchange
Alveolus Cells Type II
surgactin production
Talking about a closed space, if I apply a pressure that expands that space, what will happen to the pressure in that pleural sac?
go down
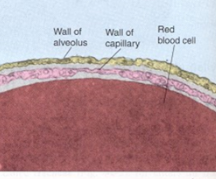
Respiratory membrane pathway for gas exchange
-Lung Surface: epithelial type I cell → epithelial basement membrane
-Interstitium
-Blood Vessel: endothelial basement membrane → endothelial cell
Ventilation Pressures (4)
-Atmospheric
-Intrapleural : pressure in plural space
-Transpulmonary Pressure: pressure difference from pleural sac and alveoli
-Intraaveolar Pressure: pressure in alveolar pocket
Mechanics of Inspiration (7)
1.) Diaphragm, chest wall muscles contract (active)
2.)Volume of thoracic cavity increases
3.)Intrapleural pressure decreases
4.) Tranpulmonary pressure increases (un-out)
5.) Lung inflates
6.) Intraalveolar pressure drops below atmospheric pressure
7.) Air enters lungs
Lung Properties: Elasticity
Able to return to shape after being distorted (inflated)
Lung Properties: Distensubility
Ability to stretch
Lung Properties: Compliance
volume change occurred in lung compared to pressure difference that cause that to occur
Closed System Lung Inflation:
-Intrapleural Pressure_______
Decreases
Change in transpulmonary pressure (increases) inflates the lung NOT the _______
alveolar pressure (decreases)
Increase in intraaveolar pressure =
air out
(drop,drop,drop, inc = air out) and vice versa
Describe
-Normal=left
-Abnormally high (overly complaint): easy to inflate, hard to deflate
- like emphysema
-Abnormally low in compliance: easy to deflate and hard to inflate
- elasticity changes when older (less compliance)
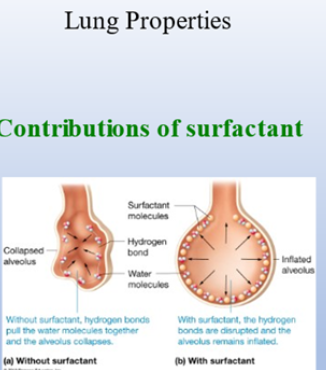
If I take alveoulus and line it with water, as I decrease the volume, what is happening with the water molecules?
surface tension is going to go up
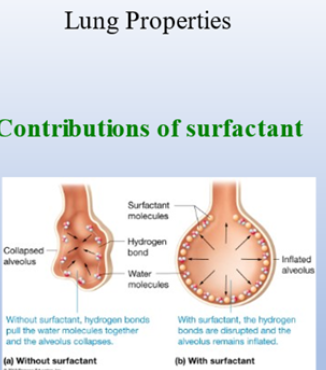
If surface tension goes up, how hard is it going to be to inflate alveoulus again?
Hard
Surfactan: mixes with water surface to help reduce surface tension => lung easier to inflate