Impact of Chemistry - Rutgers NB
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Matter
Tangible material that makes up everything in the universe
Atom
The smallest unit of matter that cannot be broken down (except in nuclear reactions)
Scientific Method
The general approach used for scientific experimentation worldwide
Steps of Scientific Method
1. Observation
2. Hypothesis
3. Experiments
4. Data Collection
5. Theory
Hypothesis
An initial best guess about your observation that can be tested by experiment

Theory
Detailed explanation of the experimental results. Cannot be proved
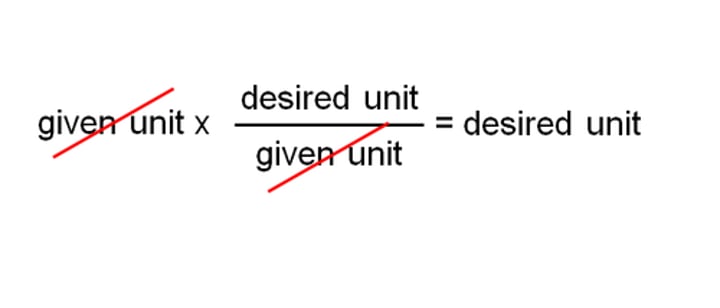
Dimensional Analysis
A method that uses conversion factors to convert from one unit to another
Atoms
3 Types of Particles : positive, negative and neutral
The number of pos. particles equal number of neg. particles
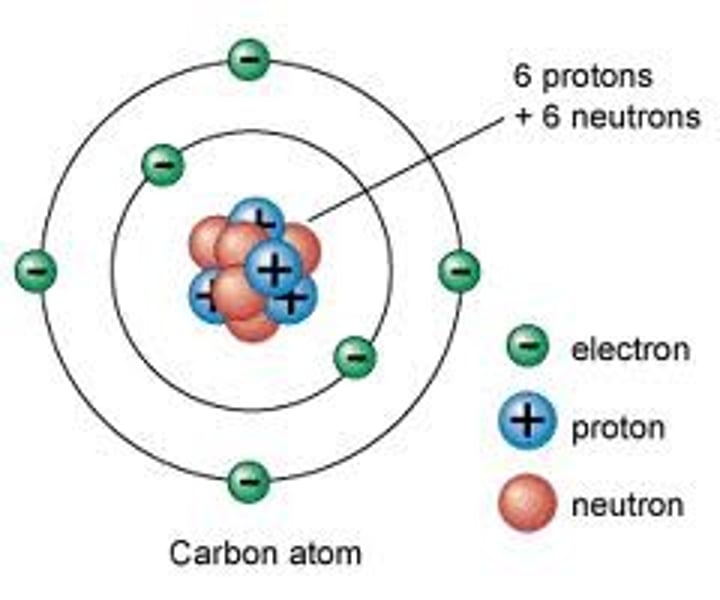
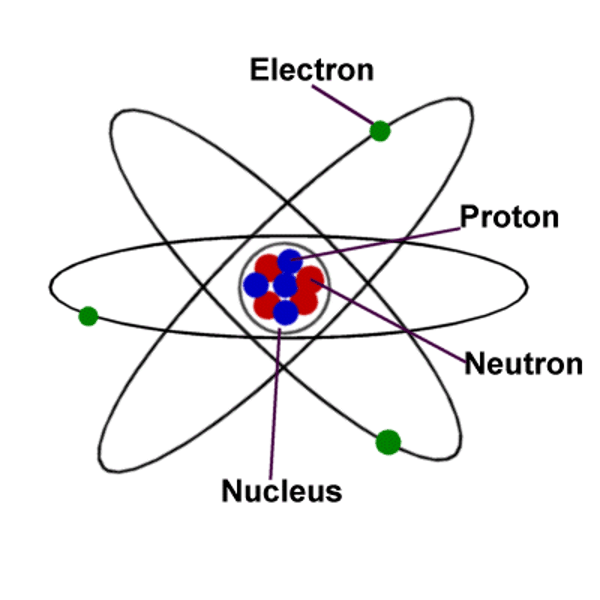
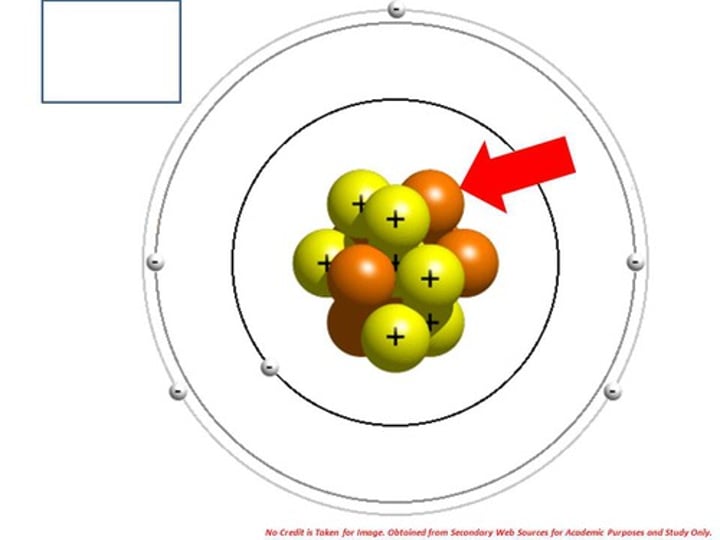
Atom Structure
- Dense positively charged nucleus (location of pos. protons and neutral neutrons)
- Cloud-like smear of negative charge around nucleus (location negatively charged electrons)
Atomic Number
Is equal to the number of protons an atom has

Periods
Horizontal rows in periodic table
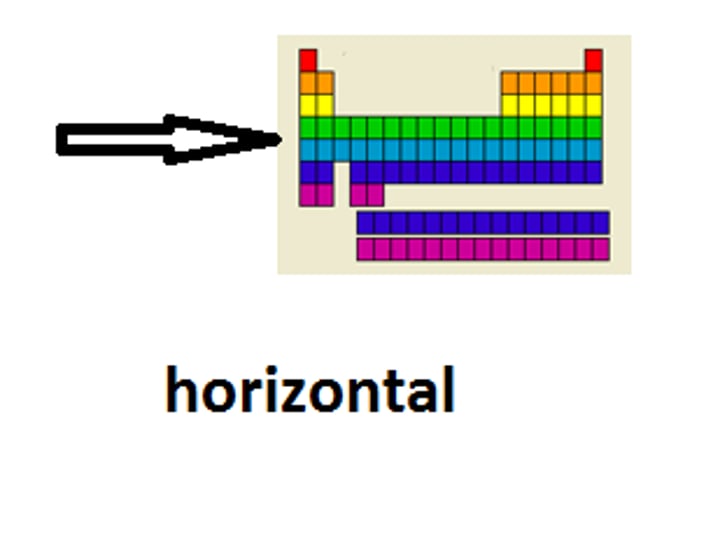
Groups/Families
Vertical columns in periodic table
Protons + Neutrons =
Mass number (superscript number)

Isotopes
Atoms that have the same number of electrons, the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons
Mass Number - Number of Protons =
Neutrons
Uses for Isotopic Percentages
Carbon Dating, Forensic Analysis, Identification of the Origin of a Sample of Matter
Number of Electrons =
Number of Protons
Ground State
Lowest energy level of a particular electron
Excited State
When an electron is energized, moves to a higher energy level
Radiant Energy
Energy given off in the form of light when electrons relax and return to a lower energy level (Depends on the difference between energy levels)
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Different types of light on the scale
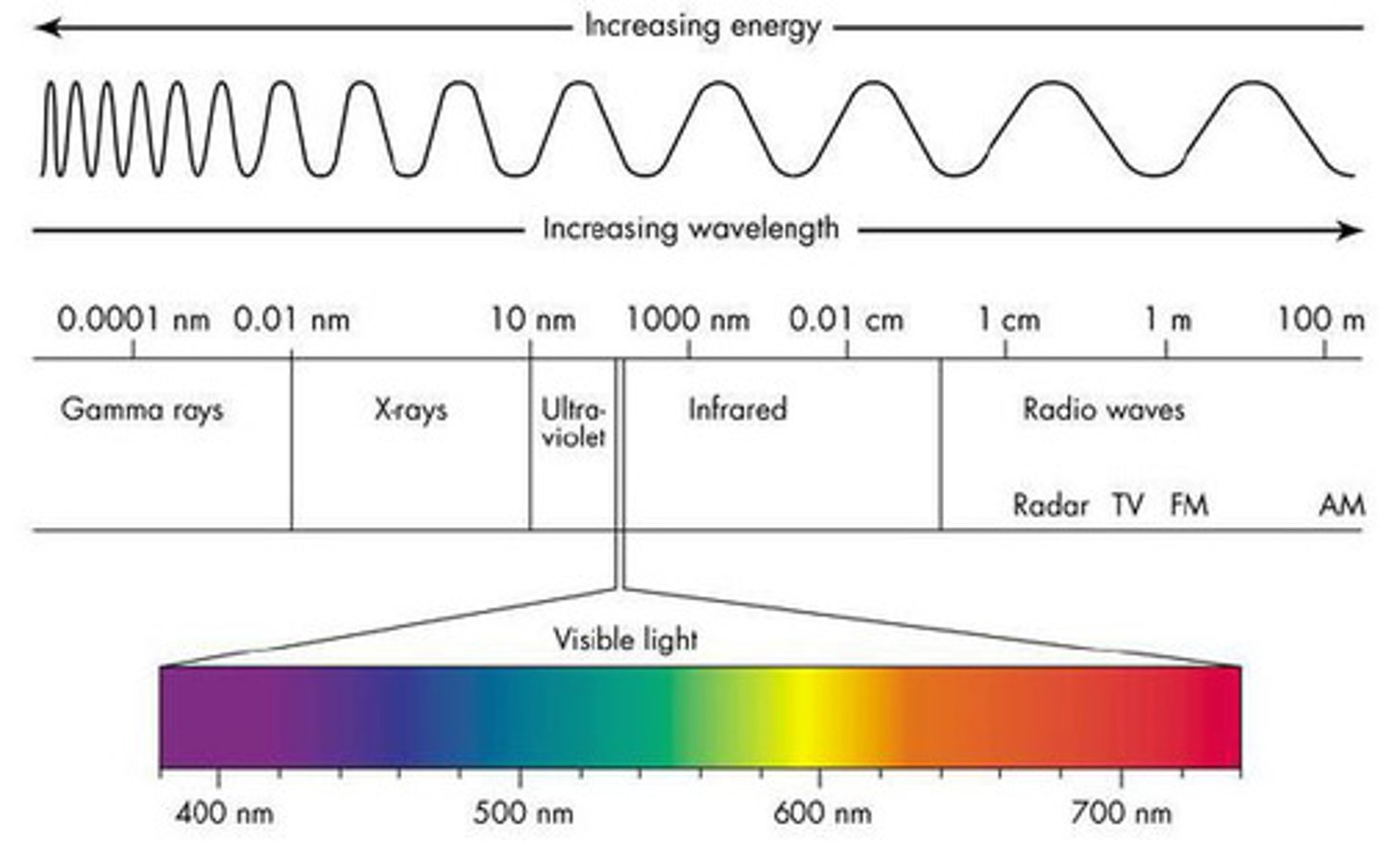
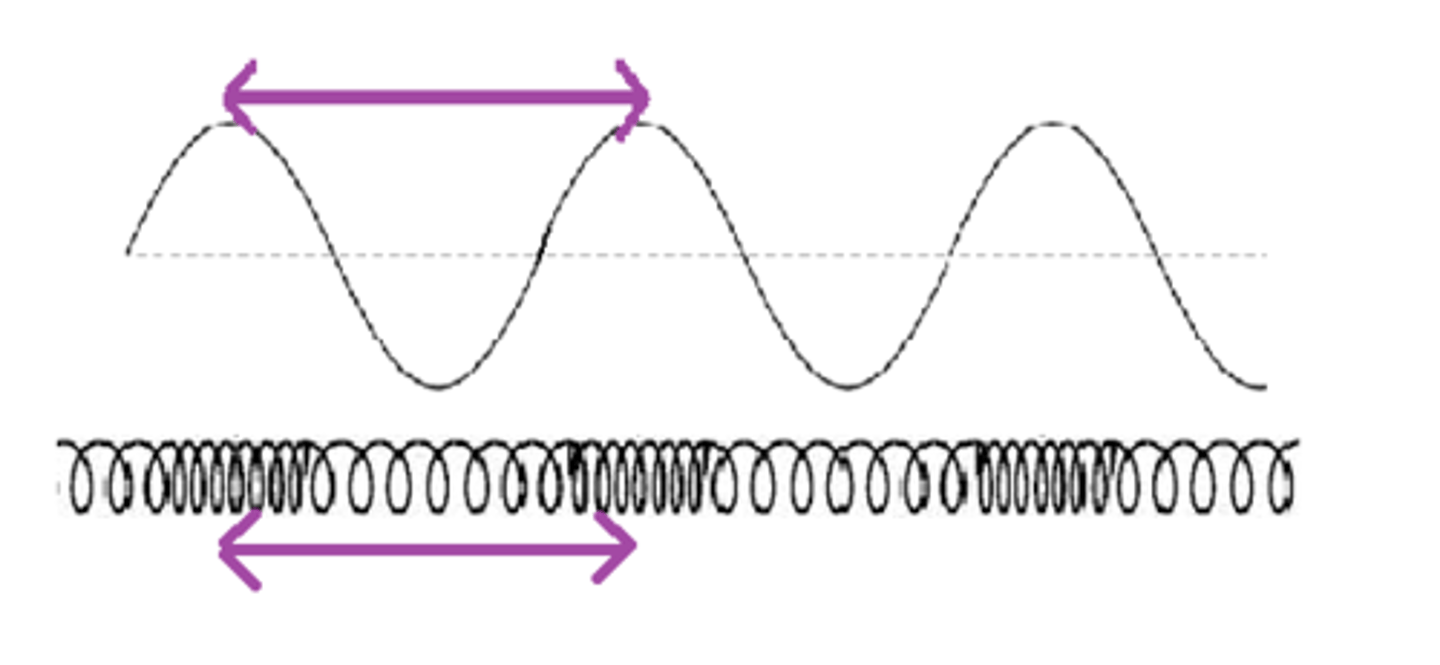
Wavelength
How light is classified; distance from one peak to the next of a wave; the shorter the more energetic
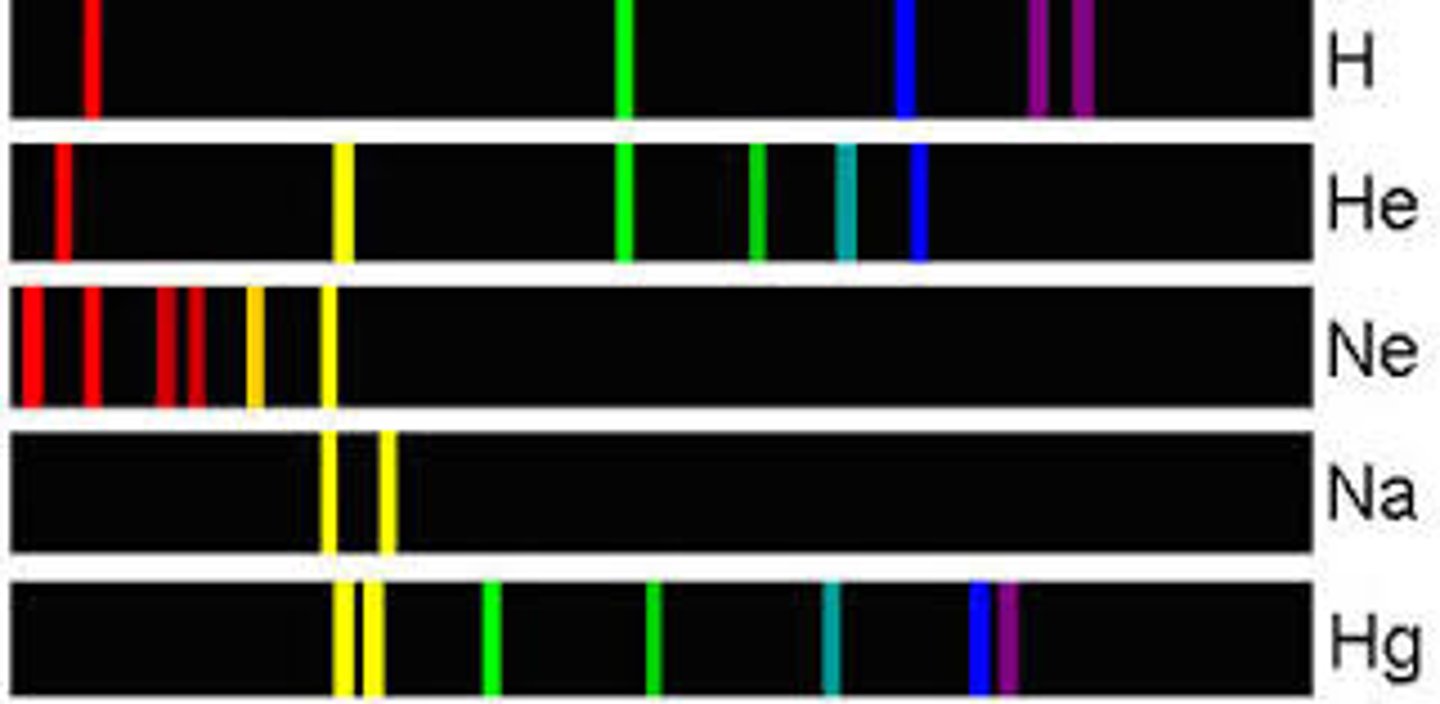
Line Spectrum
Pattern of lines of light that is characteristic of a given element; Specific wavelengths, given of by a specific element, of light that correspond to the spacing between energy levels of atoms
Periodic Table Parts
Metals, Nonmetals, Metalloids
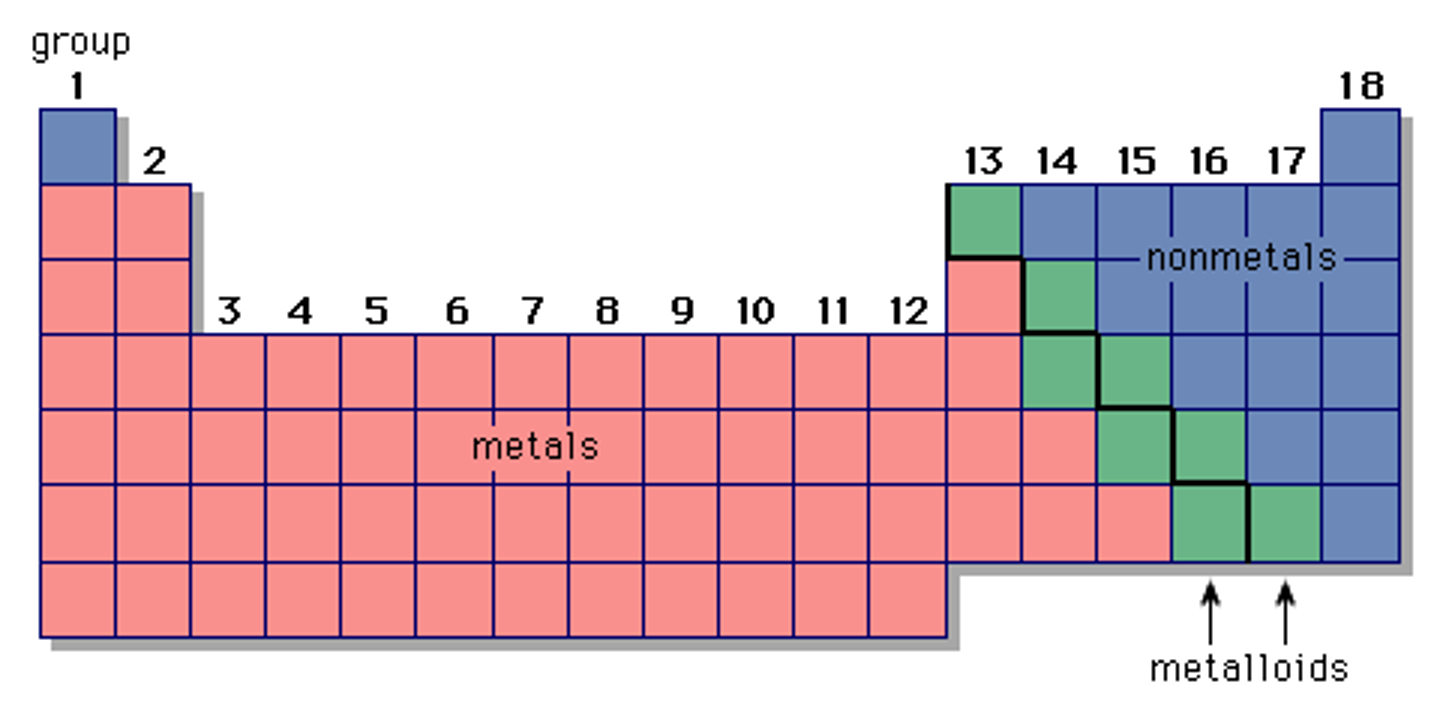
Metals
Mostly shiny solids; malleable, ductile, conduct electricity
Nonmetals
Mostly solids and gases; brittle, not malleable or ductile, do not conduct electricity
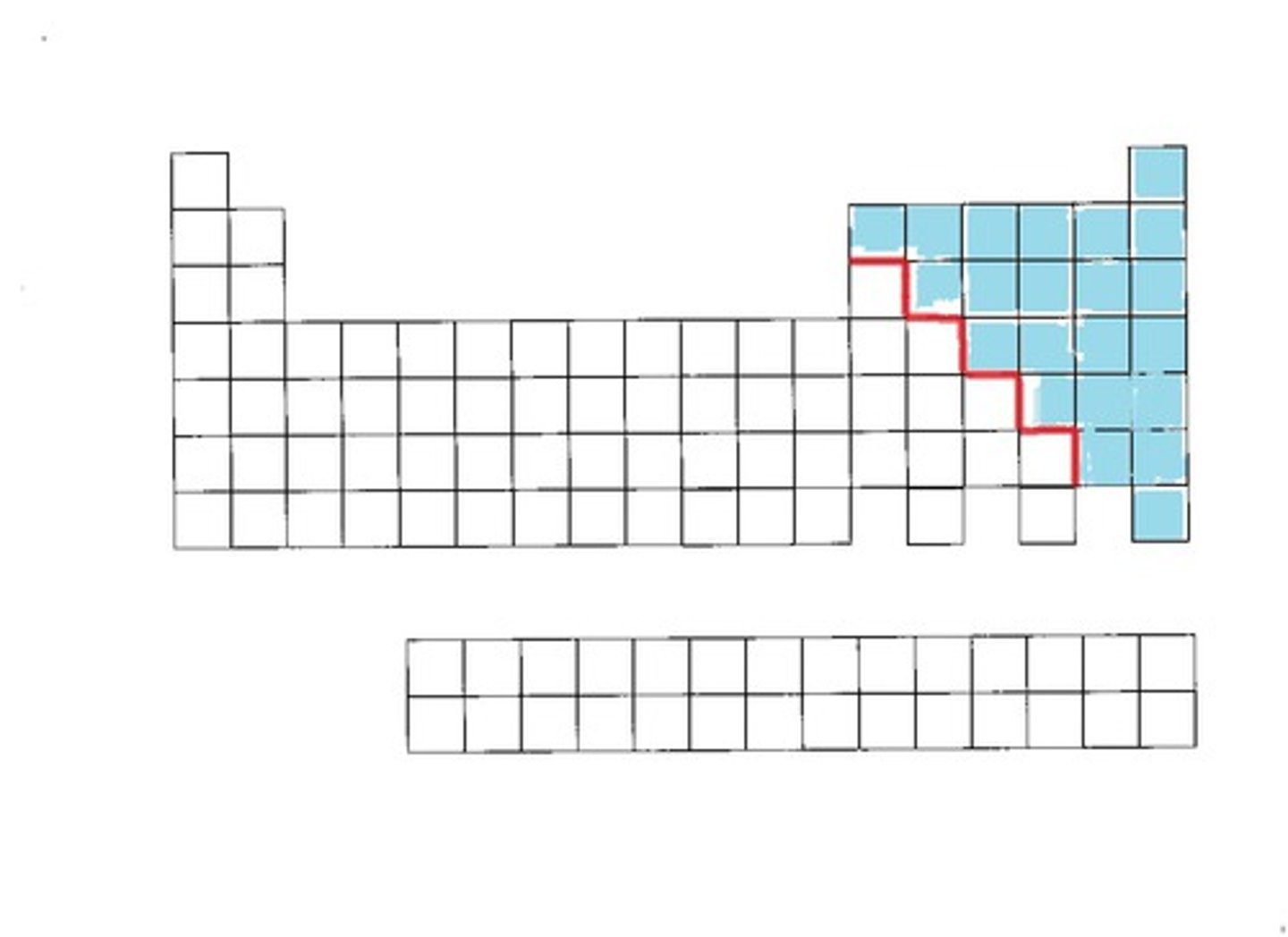
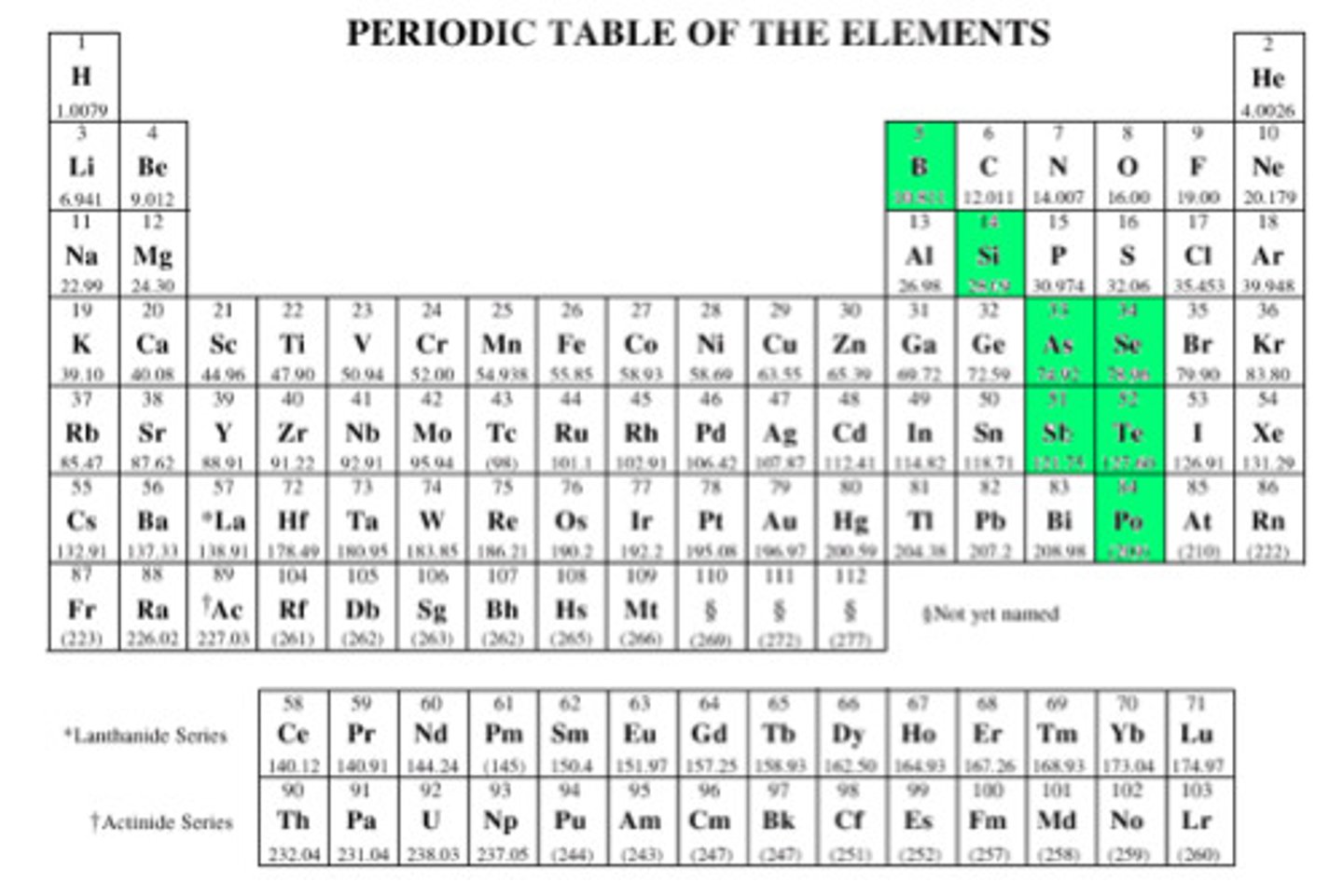
Metalloids
Found in semiconductors - these materials conduct electricity in certain conditions
Organic Substances
Carbon based
Inorganic
Not carbon based
Pure Substance
A specimen of matter that contains only a single element or compound
Mixture
Defined as one or more pure substances combined together
Heterogeneous Mixtures
Mixtures with boundaries we can see

Homogeneous Mixtures
Mixtures that are uniform in appearance

Pure Substance - Element
Contains atoms from only one element
Pure Substance - Compound
Contains atoms from more than one element
Law of Constant Composition
A given compound has a fixed and definite number of atoms of its constituent elements
Lone Pair
A pair of electrons in a Lewis Dot Structure, also called nonbonding pair
Ionic Bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
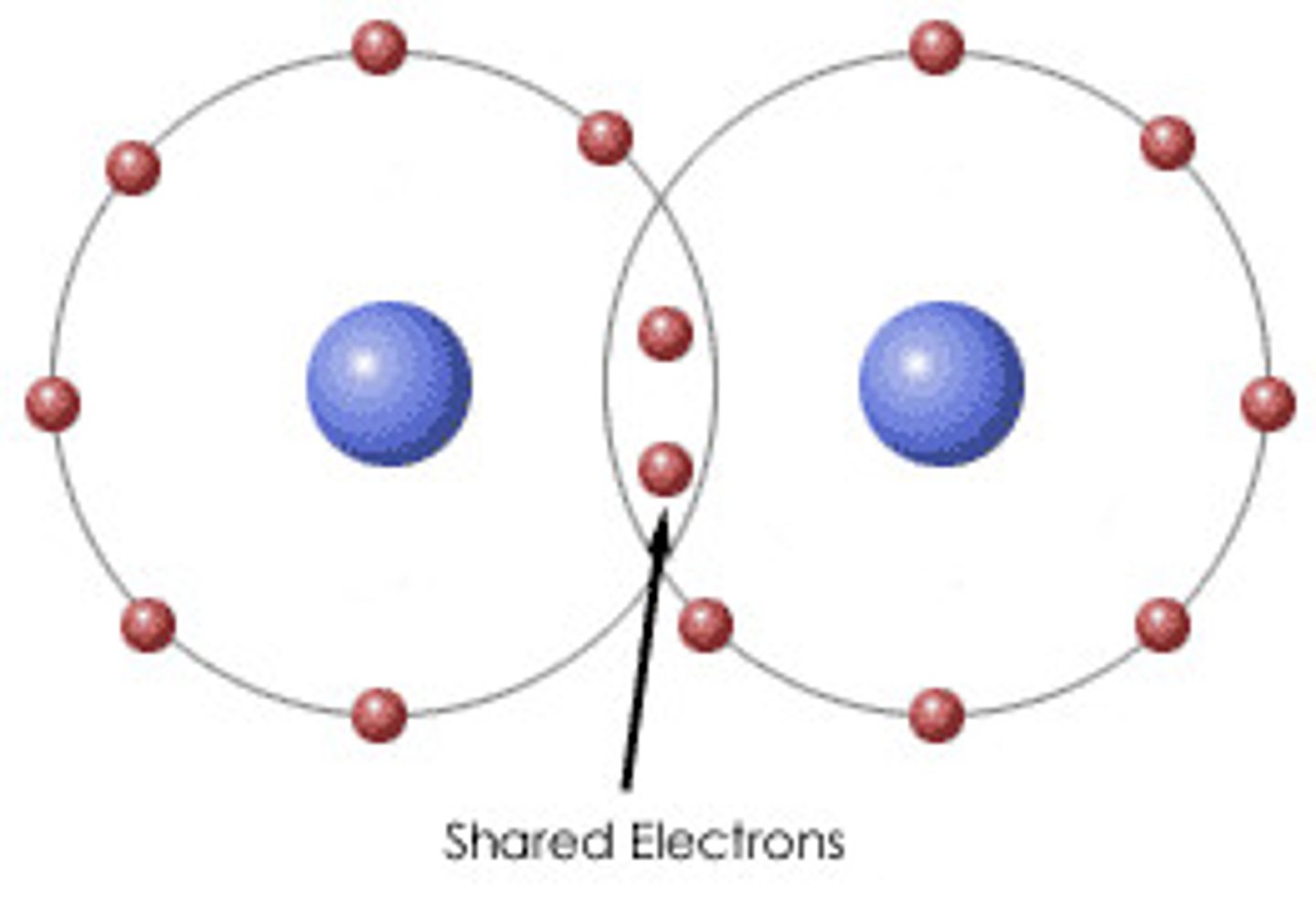
Covalent Bonding
sharing of electrons
Ion
Electrically charged atom
Cation
Positively charged ions
Anion
Negatively Charged ions
Covalent Bonds
Occur when electrons are shared between two atoms
Diatomic Molecule
A covalent bond between atoms of the same element
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
Bond between atoms of the same element; no lopsidedness in electron sharing
Polar Covalent Bonds
An unequal sharing of electrons in the bond
Bond Polarity (Most polar to least)
1. Ionic Bonds
2. Polar Covalent Bonds
3. Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
Metallic Bonds
Bonds within a pure chunk of metal; form a sea of negative charge - electrons move through the whole lattice of cations
Determining Electronegativity
Large: ionic bond
Moderate: polar covalent bond
Negligible: nonpolar covalent bond
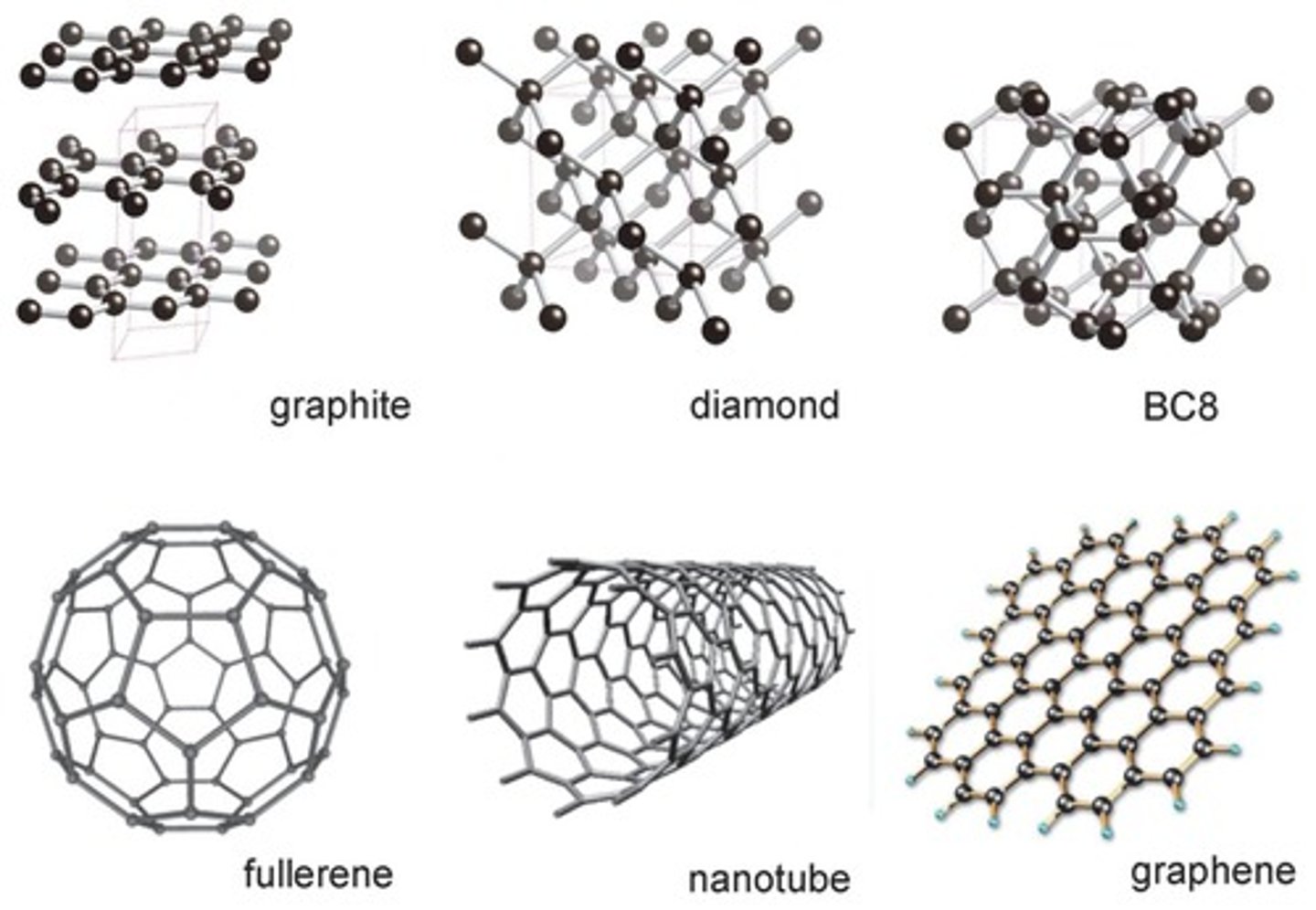
Allotropes
two or more different molecular forms of the same element in the same physical state
crystalline solid
A solid that is made up of crystals in which particles are arranged in a regular, repeating pattern
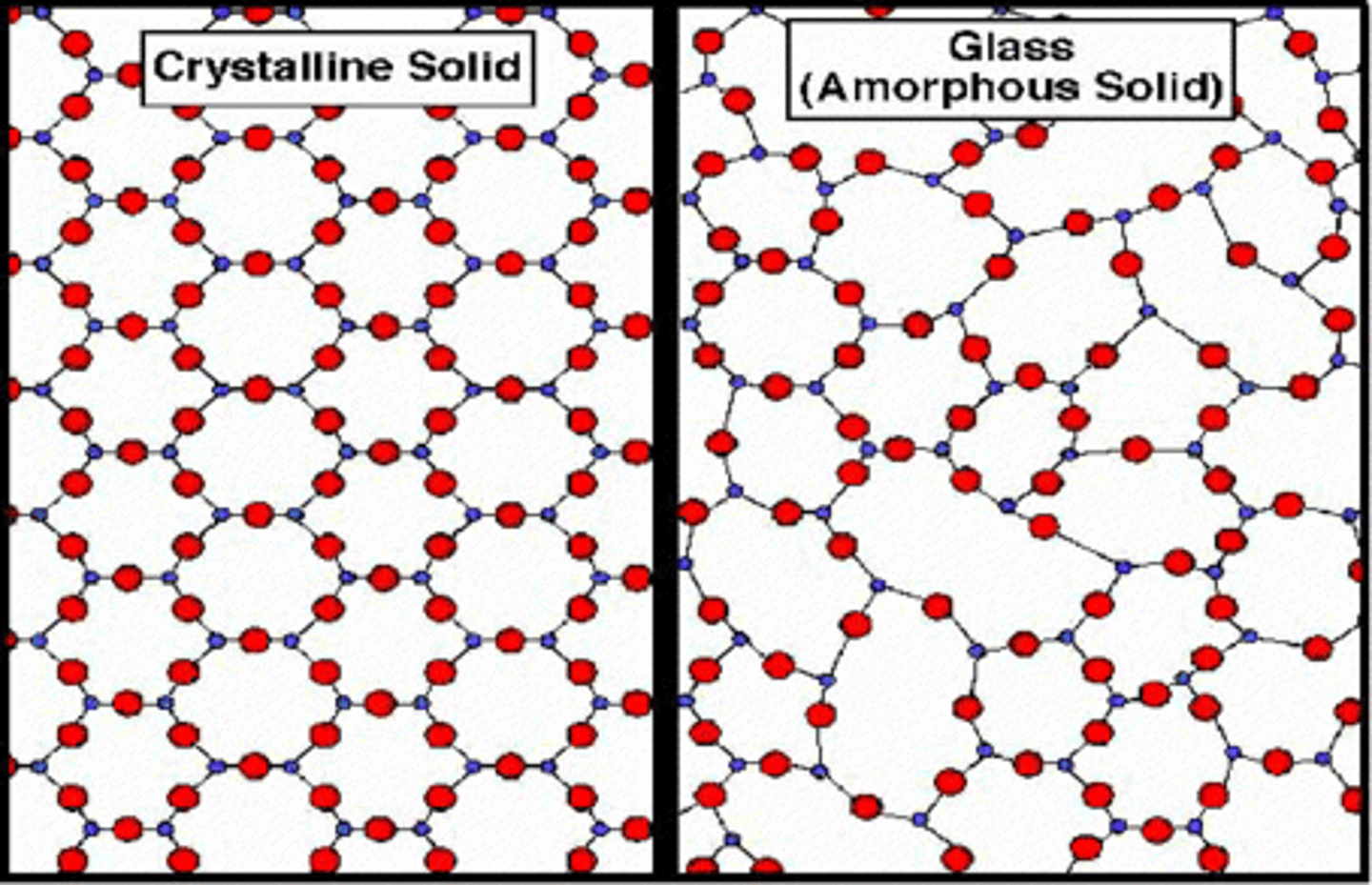
amorphous solid
A solid made up of particles that are not arranged in a regular pattern
Transparent solid
solids that allow the transmission of light through them.
The particles are arranged in a way that does not scatter or absorb light significantly
What country is the leading producer of rare earth metals
China
Cradle-to-Grave Recycling
collecting and reusing materials at the end of their life cycle, preventing them from going to waste or a landfill. The materials are typically downcycled into lower-value products or disposed of.
cradle to cradle recycling
materials are continually recycled into new products of equal or higher value without producing waste.
Layers of the atmosphere
exosphere, thermosphere, mesosphere, stratosphere, troposphere

Exosphere
The outer layer of the thermosphere, extending outward into space.

Thermosphere
The outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere.
Mesoshpere
the strong, lower part of the mantle between the asthosphere and the outer core.
Stratosphere
The second-lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere.
Troposphere
The lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere
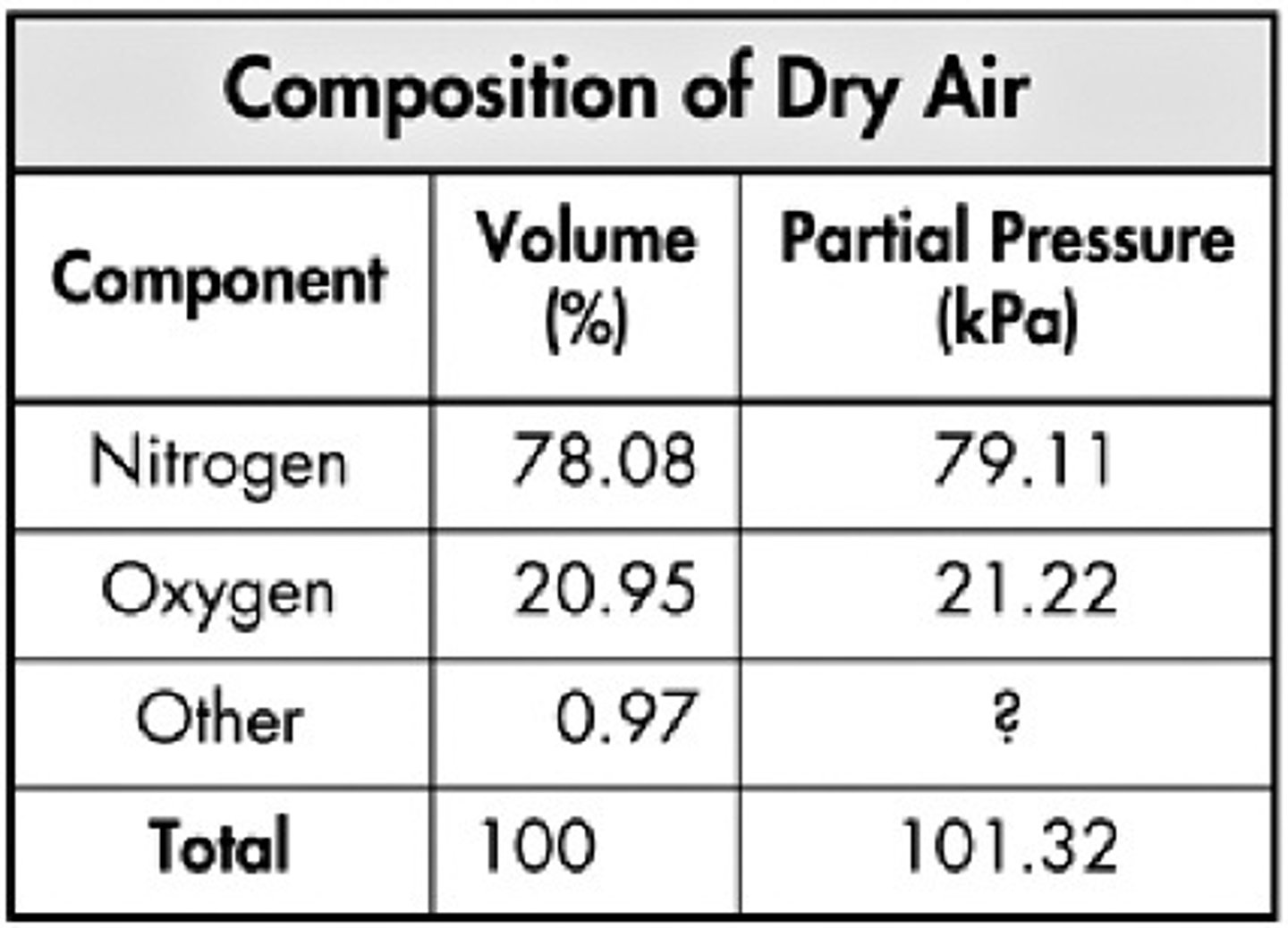
Gases that make up air
nitrogen (biggest part- 78%), oxygen (21%), others: water vapor, argon, carbon dioxide, other things
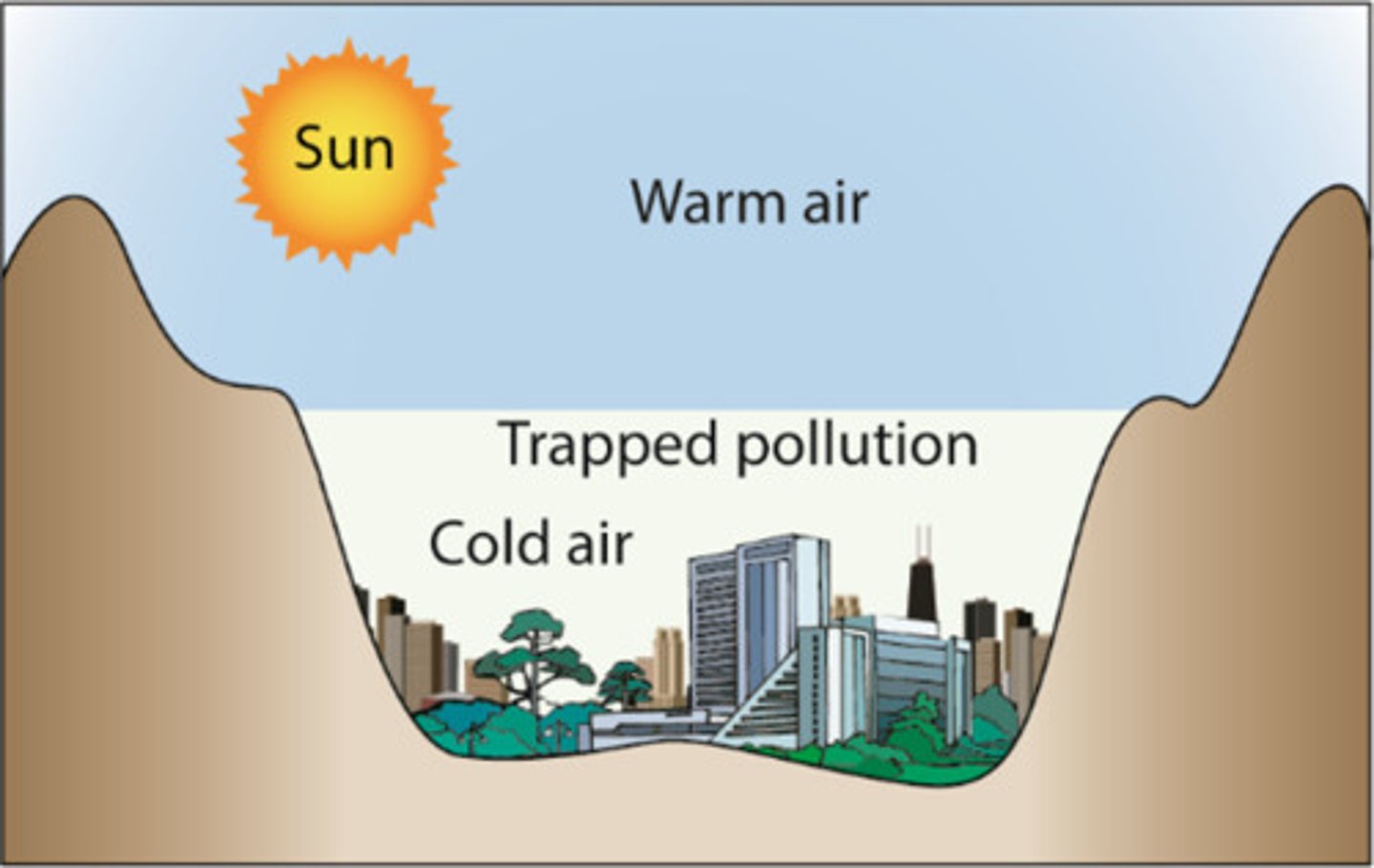
air inversion
When cooler air is trapped under warmer air. Pollutants can accumulate here
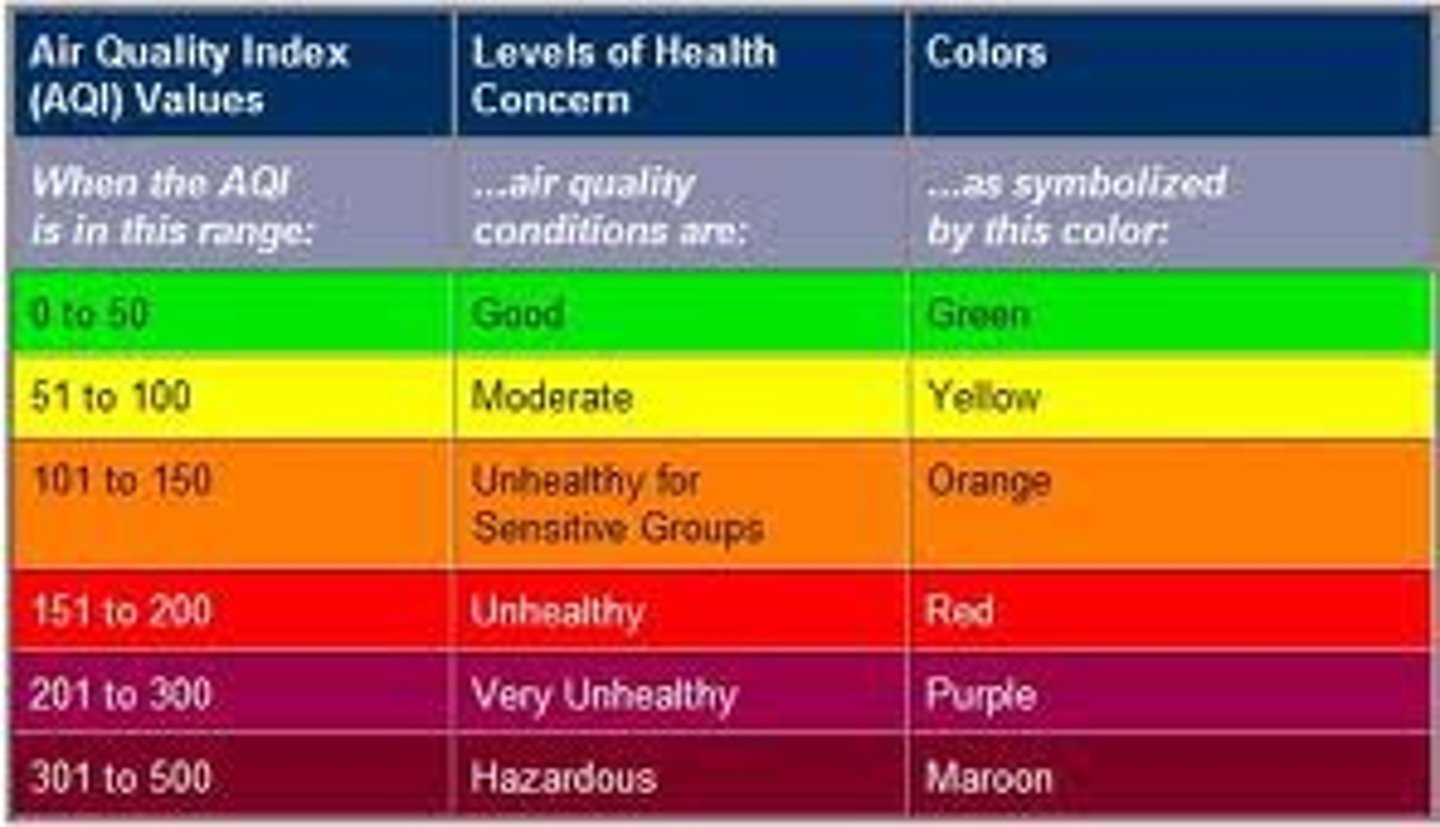
Air Quality Index
a scale that ranks levels of ozone and other air pollutants
chemical reaction
the rearrangement of atoms when reactants are transformed into products.

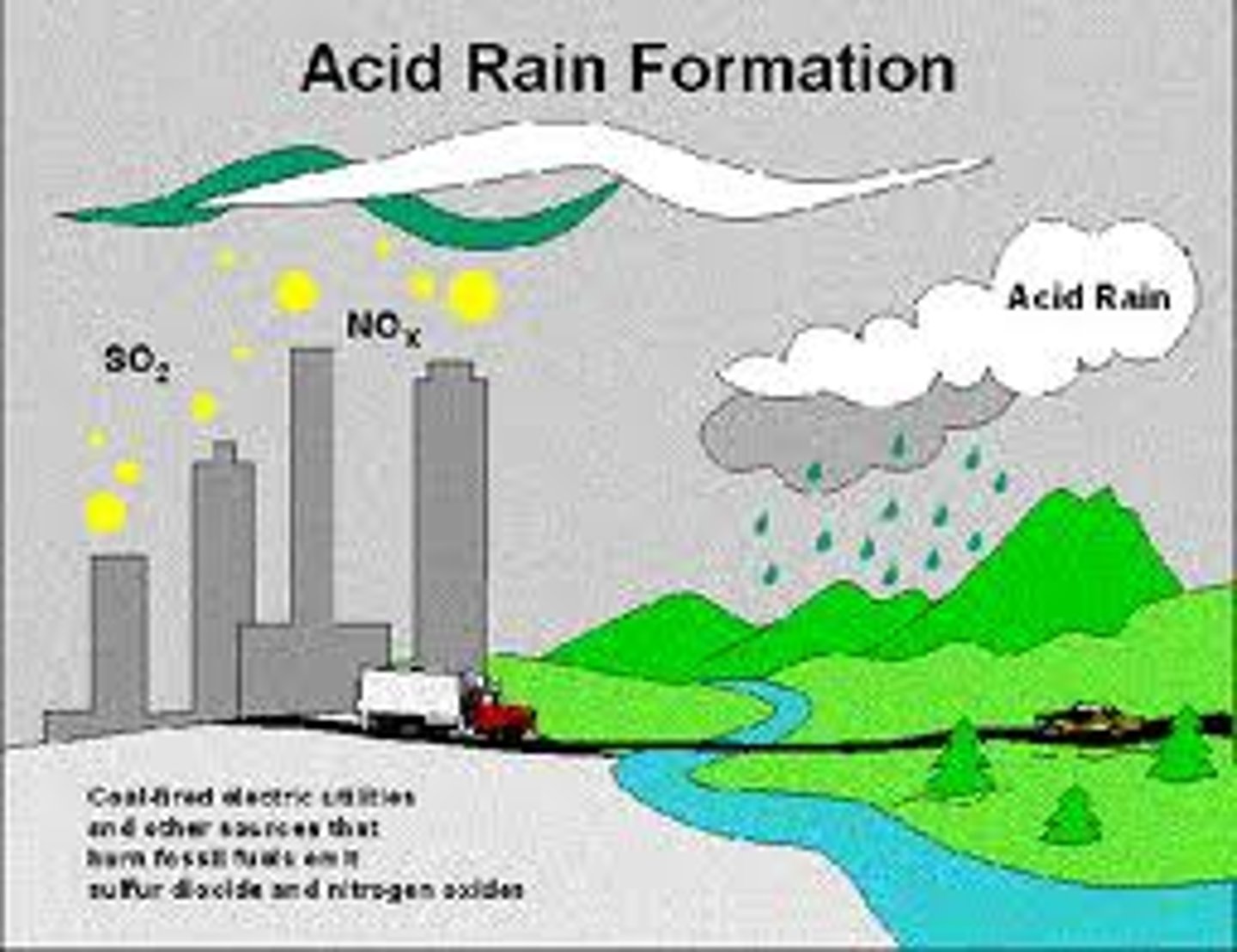
How does acid rain form?
air pollutants combine with water vapor to create acids, which mix with rainwater and fall to the ground, causing environmental harm.
Catalytic converters
Used in a car to convert toxins such as CO, NO, NO2 and hydrocarbons to harmless gases, like nitrogen and carbon dioxide.
common sources of indoor air pollution
- tobacco smoke
- Rados gass
- mold and mildew
green chemistry
the design of products and processes that reduce hazardous substances.
Sustainability
The ability to keep in existence or maintain. A sustainable ecosystem is one that can be maintained
explain the relationship between the speed of light, wavelength and frequency
the speed of light is equal to the product of the wavelength and frequency.
If the wavelength (λ) increases, the frequency (f) decreases, and vice versa.
The product of wavelength and frequency is always equal to the speed of light, which remains constant.
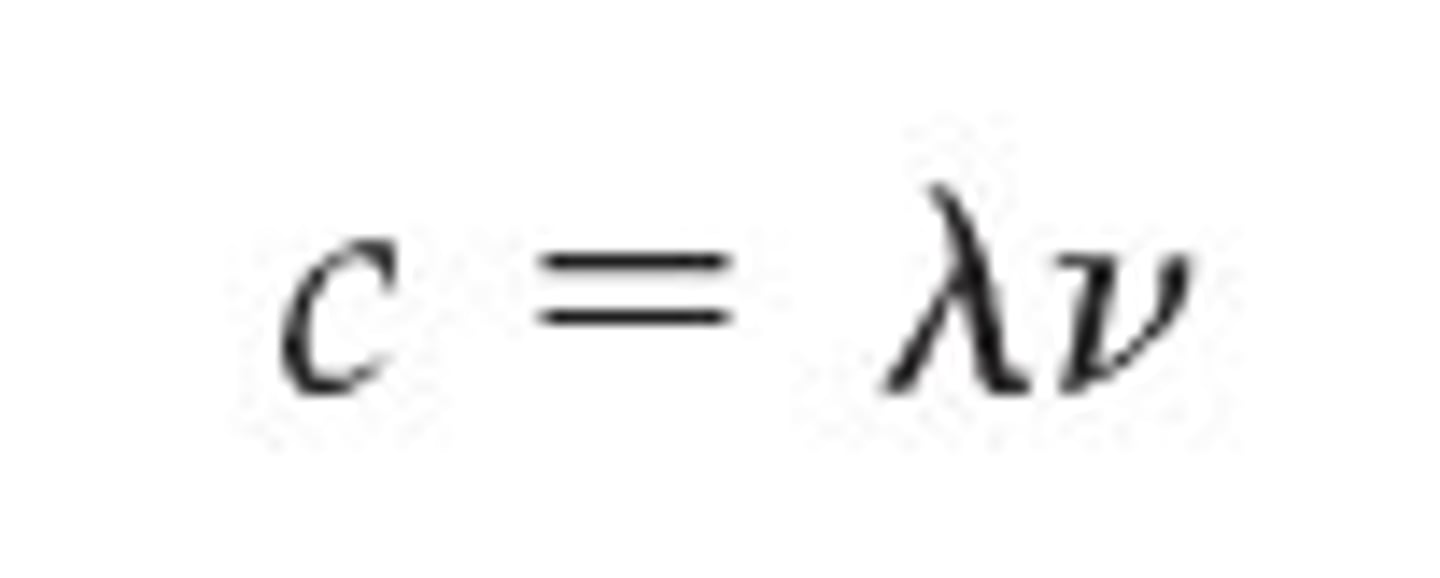
relationship between the energy of electromagnetic radiation andits frequency or wavelength
-The energy of electromagnetic radiation, like light, is directly related to its frequency.
-The higher the frequency, the higher the energy.
-Wavelength is the opposite: shorter wavelengths have higher frequencies and more energy, while longer wavelengths have lower frequencies and less energy.
UVB radiation
290 to 320 nanometers. It has shorter, burning wavelengths that are stronger and more damaging than UVA rays. It causes burning of the skin as well as tanning, skin aging, and cancer.
most is absorbed in the ozone
UVA radiation
320 to 400 nanometers that penetrate deeper into the skin
Reaches Earth's surface in thegreatest quantity and penetratesfarthest into the skin
UVC radiation
200 to 280 nm
most dangerous type of UV radiation
ozone hole
A thinning of stratospheric ozone that occurs over the poles during the spring