ap world review terms (unit 5 continued)
1/47
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
did the napoleonic code grant equal rights?
nope, no equal rights for my women.


what did napoleon gain from establishing public schools?
schools were meant to indoctrinate children to obey napoleon without question

why was the napoleonic code good?
it guaranteed natural rights to ppl outside of france

what did napoleon do related to education?
he created a centralized school system (a network of public schools called lycées)

was napoleon a traitor to the french revolution? no - list
he liberated most of europe from absolute rule
the napoleonic code guaranteed natural free rights to ppl outside of france
the concordat with rome made peace between french gov and catholic church
he created a centralized school system (lycees)


was napoleon a traitor to the french revolution? yes - list
the napoleonic code did not grant equal rights to women
schools were meant to indoctrinate children to obey napoleon without question
he restricted freedom of press
he saw himself as the most important person in france


what was napoleon’s biggest mistake?
invasion of russia - many soldiers died from the cold
what is GDP short for?
gross domestic product
most philosophes saw slavery as a violation of natural law. what did montesquieu think?
slavery made brutes out of both master and slave
defended property rights (of slave owners too)
most philosophes saw slavery as a violation of natural law. what did diderot think?
slavery violated right to self-government
most philosophes saw slavery as a violation of natural law. what did voltaire think?
he believed that Africans were inferior.
you racist racist man smh

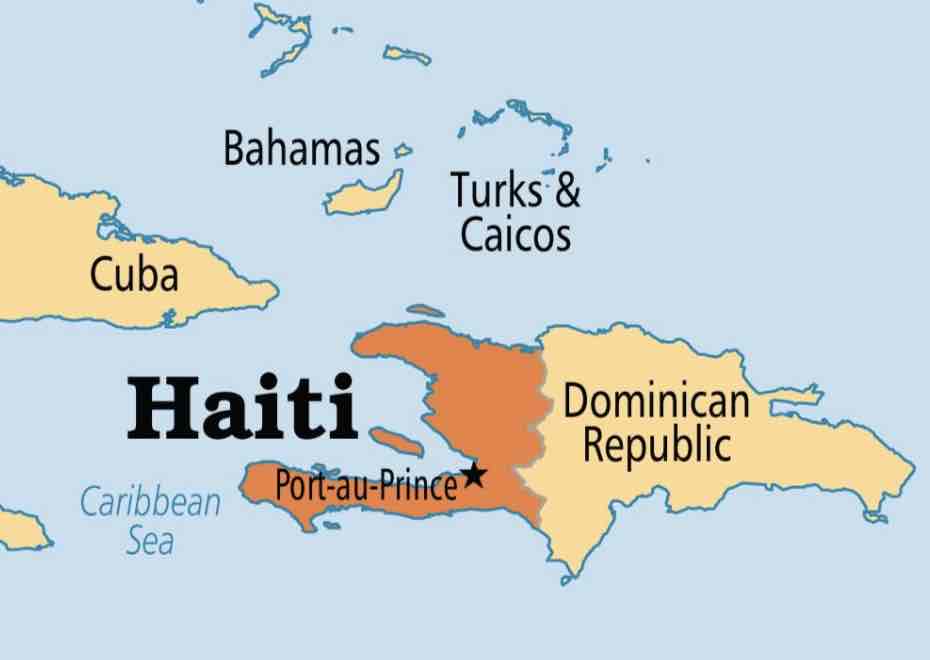
pre-revolutionary haiti
Profitable Sugar Plantations
white slave owners w/ large plantations (pop = 40k)
“free people of color” (pop = 30k)
black slave owners with smaller plantations
free people of mixed race (“mulattos”)
slaves (pop = 500k)
causes of the revolution
France
1791 - slavery abolished in france
1794 - slavery abolished in french colonies
Haiti
whites demand independence from france
free blacks demand equal rights, but not abolition of slavery
1791 - Haitian Civil War

Toussaint L’Ouverture
born a slave and led the Haitian Revolution

The Haitian Revolution
Independence
led by Toussaint L’Ouverture
French kicked out by 1798
Napoleon
1802 - wanted to retake Haiti + restore slavery
L’Ouverture captured, dies in French prison
napoleon’s force surrenders
1804 - Haiti declares independence
which set of events is in the correct chronological order?
a. storming of the bastille, haitian evolution, death of toussaint l’ouverture
b. french revolution, napoleon’s invasion, haitian independence
c. napoleon’s invasion, abolition of slavery, haitian independence
d. reign of terror, haitian independence, napoleon’s invasion
b. french revolution, napoleon’s invasion, haitian independence
aftermath of haitian revolution
sugarcane fields became battlefields (loss of income)
most plantations were divided into small peasant plots (subsistence agriculture instead of cash crop agriculture)
rapid deforestation as peasants cleared more land for farming
U.S. refused to recognize Haitian independence (feared its own slave revolt)
Haiti paid France 150 mill francs in exchange for recognizing independence
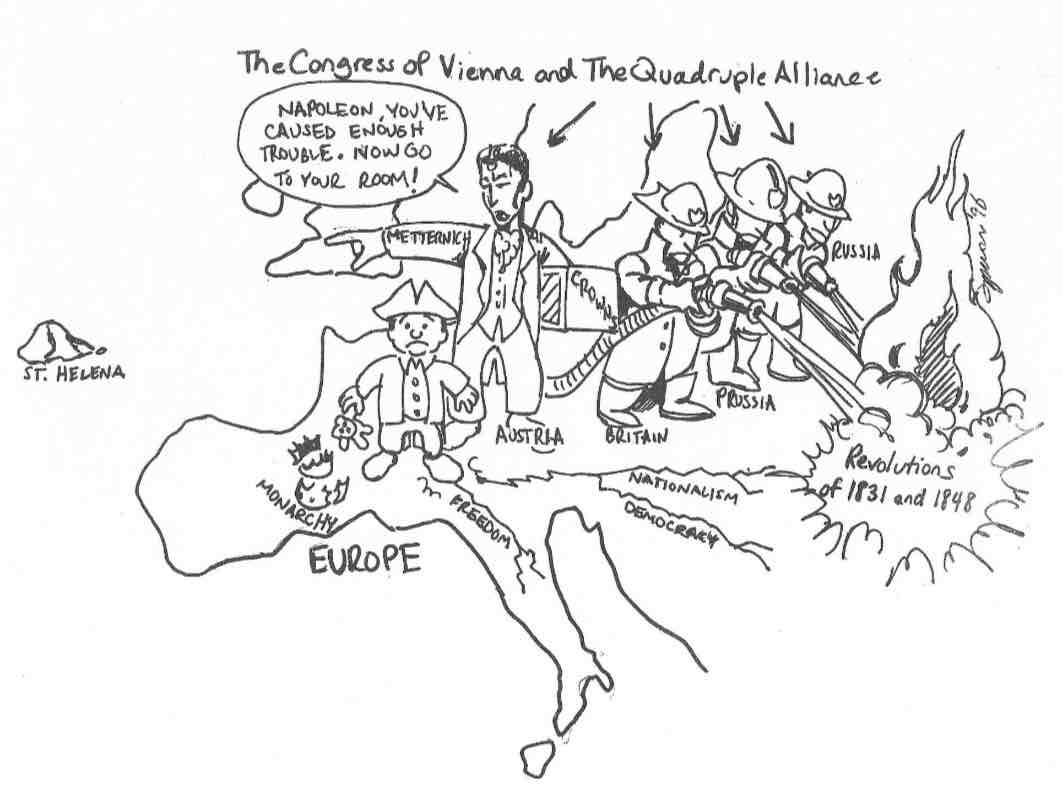
priorities of the congress of vienna
“restoration” - monarchs were returned to france, spain, and italy
“legitimacy” - new monarchs were from old royal families (Louis XVII was a bourbon)
“balance of power” - france was made weaker and its neighbors made stronger
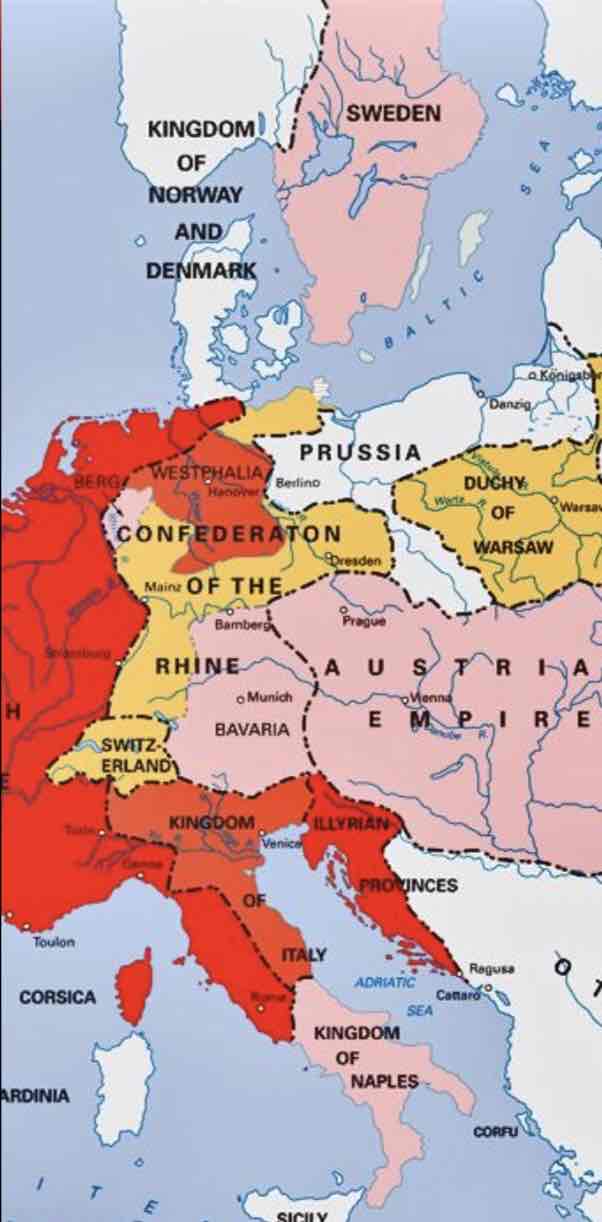
redrawing the map during the congress of vienna
prussia acquired french territory
austria gained italian provinces once controlled by france
the netherlands acquired belgium
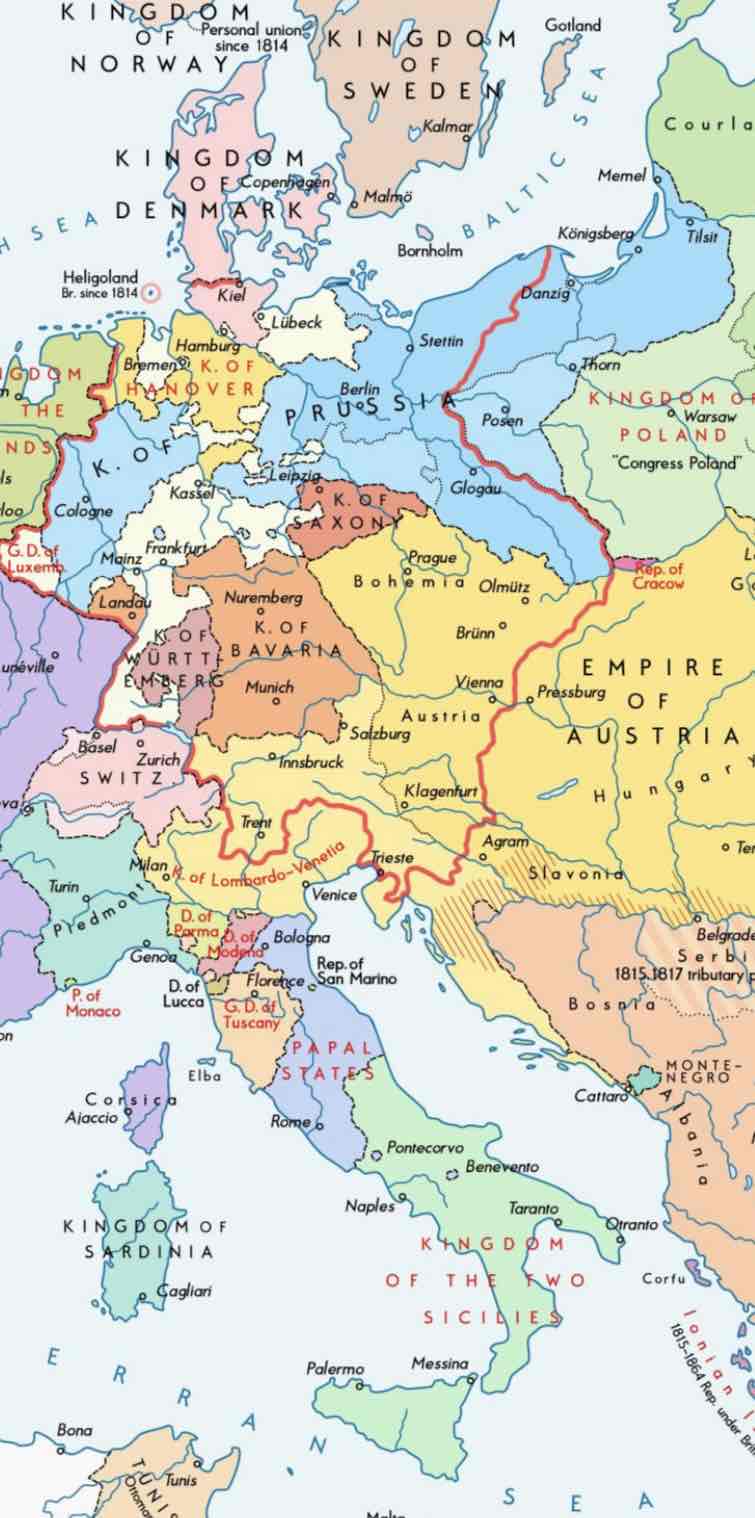
quadruple alliance (concert of europe)
Britain, Russia, Prussia, and Austria united to crush revolutions
Actions
rulers were encouraged to resist any change
books and newspapers were censored
liberal reformers were arrested
reactionary and conservative
why was the quadruple alliance formed?
the nations feared a revolution of their own as prussia, russia, britain, and austria all had monarchies
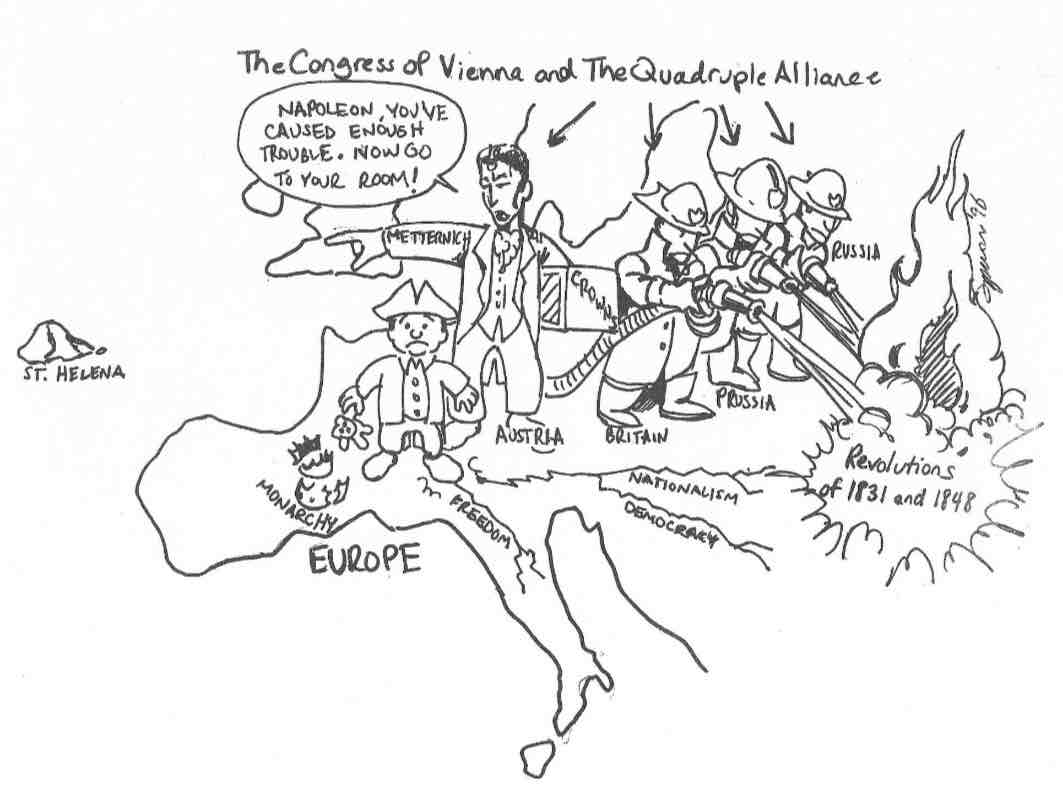
why are the members of the quadruple alliance drawn as firemen?
a. they are trying to defeat napoleon
b. they are trying to protect the people of Eastern Europe
c. they are trying to contain the flames of revolution
d. they are trying to end the congress of vienna
c. they are trying to contain the flames of revolution

Louis Napoleon
nephew of napoleon bonaparte
first president of france (1848-1852)
emperor napoleon III (1852-1871)

Revolutions of 1830-1831
France (July Revolution)
Louis XVIII (brother of Louis XVI) protected many of the rights of the 1789 Revolution
1824 - his brother, Charles X, tried to return to absolute rule
1830 - Paris Revolt - workers and students force Charles to England
Louis Philippe (“Citizen King” - the son of a liberal noble) named new ruler of France
other revolts in belgium, poland, and italy
paris revolt
workers and students force Charles X to England b/c he tried to return absolute rule in France
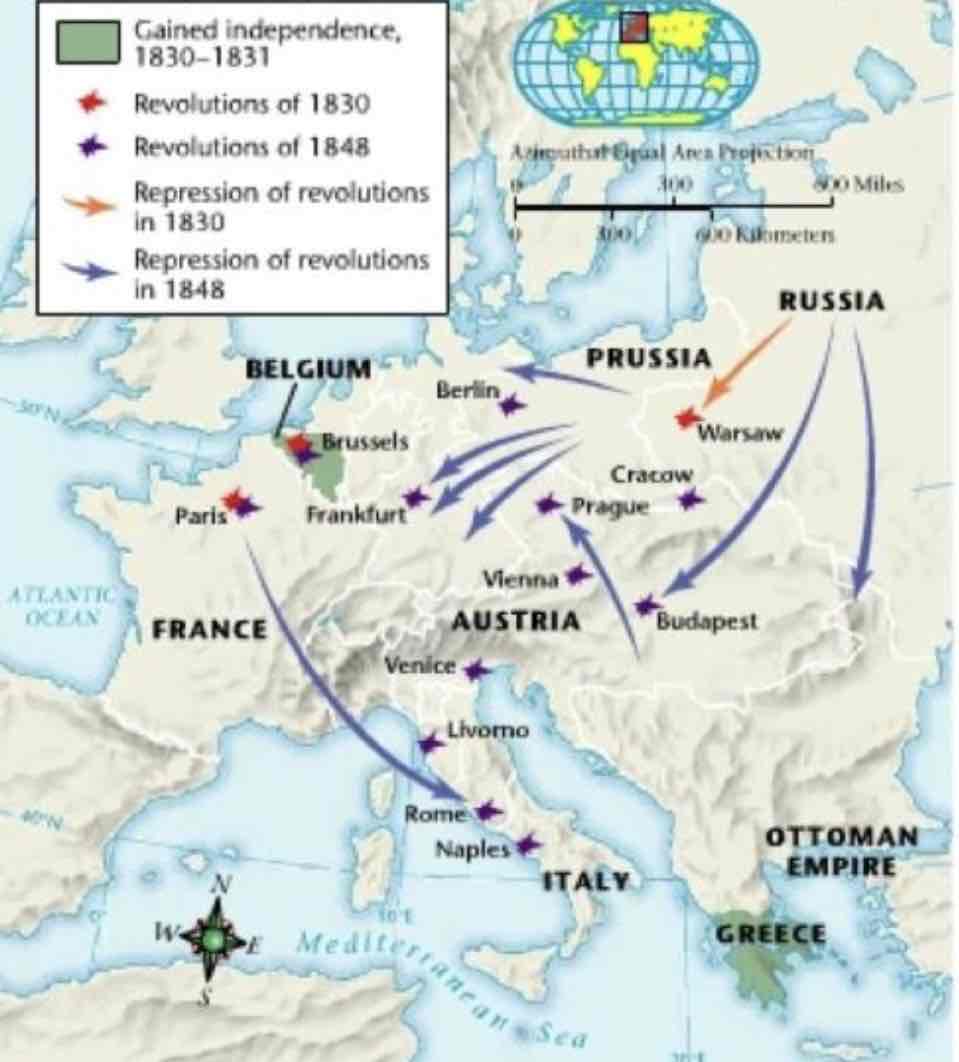
Revolutions of 1848
France
February Revolt : workers force louis philippe from power
“june days” : 3 days of fighting kill or injure 10,000
second republic established
Louis Napoleon elected president (1852 - named Napoleon III)
other revolts in austria, germany, and italy
most fail to gain mass support, but ideas would find success 50-60 years later

classes of Latin America (highest to lowest)
Peninsulares
Creoles
Mestizos
Native Americans
African Slaves
Peninsulares
colonists who were born in Spain
served in top government positions
fun fact! when a peninsular couple were expecting a baby, they would often travel back to spain before the baby was born
creoles
colonists born in latin america
privileged class
remained below peninsulares
even wealthiest creoles were still
mestizos
colonists with native american and spanish parents
one of the lowest classes
many latin american nations had majority mestizo populations
native americans
native american slavery illegal, but still worked in intense manual labor
many were forced to convert to christianity
african slaves
slaves were property of their masters
unlike in the US, slaves in Latin America could buy their freedom
true or false: the spanish had a special name for every combination of racial mixing. if true, what was it called?
true, the casta system
causes of the latin american revoltions
internal
class conflict
european-educated leaders
external
american revolution
french revolution
napoleon’s invasions of portugal (1807) and spain (1808)
true or false. mestizos were the most likely group to lead revolutions against spain
false
name 3 areas that had latin american revolutions
mexico, south america, and brazil
who initiated the mexican revolution?
Miguel Hidalgo and Jose Morelos
mexican revolution
initiated by two priests, Miguel Hidalgo (creole) and Jose Morelos (mestizo)
creoles eventually worked with lower classes b/c they feared a “revolution from below”
independence in 1821
revolution in south america
led by creoles (Simon Bolivar and Jose de San Martin)
Bolivar frees Columbia, Venezuela, Ecuador, and Peru
San Martin liberates Argentina, Chile, Ecuador, and Peru
what was bolivar’s nickname?
El Libertador
true or false. the revolution in brazil was started by the ruler of the country.
true
revolution in brazil
portuguese royal family flees to brazil following napoleon’s invasion
king returns to portugal, but son Pedro stays
1822 - pedro declares himself emperor
pedro creates constitution, freedom, elections
“Revolution from above”
in which nation did creoles fear a “revolution from below”
mexico
in which area was there a “revolution from above”?
brazil
true or false. the class conflict created by spanish rule disappeared after independence.
false

failed revolutions
Continued Class Conflict
Peninsulares removed, but creoles become new conservatives
Constitutions restricted vote to propertied class
Liberals were from lower classes and mostly powerless
The Church
owned land, controlled education and charity
redistribution of church land failed
church was too conservative and powerful
Gran Colombia (1819-1830)
Venezuela, Colombia, and Ecuador united under one gov
Simon Bolivar dreamed of uniting all the nations of South America
rivalries among the revolutionary leaders broke up the union
true or false. simon bolivar tried to create the united states of south america.
true

why did gran colombia fail?
rivalries between revolutionary leaders