HSCI Chapter 4
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Where is the epithelial tissue located?
Internal and external surfaces, the lining of hollow organs and cavities, and glands. They will always face towards an opening.
Epithelial Tissue Function
Protection through barriers and immune defense and absorption.
Key characteristics of epithelial tissue
Polarity with apical (top) and basal (bottom) surfaces, avascular but innervated, supported by connective tissue, cellularity, and regeneration.
Apical and Basal Surfaces
Closest to the outside of the cell and is mostly free but sometimes will contain cellular extensions and closest to the bottom/inside of the cell and is normally attached to connective tissues.
Avascular
Lack of blood vessels. Characteristic of epithelial tissue
Innervated
Abundance of nerves. Characteristic of epithelial tissue.
Cellularity
Large amounts of cells packed tightly together. Supported by tight junctions and desmosomes. Characteristic of epithelial tissue.
Simple epithelial tissue
Single layer of cells
Stratified epithelial tissue
2+ layers of cells
Squamous cells
Smooshed looking and fried egg shape
Cuboidal Cells
Cube shape
Columnar Cells
Cells that are taller than they are wide
Simple squamous epithelium structure, function, and locations
Structure: Single layer of flattened cells. Function: diffusion and secretion. Locations: Lungs (alveoli), capillaries, serous membranes.
Simple cuboidal epithelium structure
Single layer of cube like cells. Have a large spherical central nucleus.
Simple columnar epithelium structure, function, and location
Structure: Single layer of tall cells with round/oval nucleus that may have microvilli or cilia and goblet cells. Function: Absorption (Microvilli), propulsion (Cilia), and secretion (Goblet cells). Location: GI tract (microvilli), respiratory tract (bronchi, Cilia), and uterine tubes (cilia).
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium structure, function, and location
Structure: Single layer of tall cells with nuclei seen at different levels. Often looks stratified but is simple. May have cilia and goblet cells. Function: Propulsion and secretion. Location: Respiratory tract (Nasal cavity and trachea)
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium structure, function, and location
Structure: Several layers with dead apical squamous cells filled with keratin and cuboidal/columnar basal cells. Function: Protection (Waterproofs skin) Location: Skin
Non-Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium structure, function, and location
Structure: Several cell layers with squamous apical and cuboidal/columnar basal cells. Functions: Protection (Through layers) and Secretion (To keep tissues moist). Location: Esophagus, mouth, vagina.
Stratified cuboidal epithelium structure
Two cell layers thick with cuboidal shaped cells and nuclei.
Stratified columnar epithelium structure
Approx. 2 layers. Apical is columnar and basal is cuboidal.
Transitional epithelium structure, function, and location
Structure: Several cell layers with dome (empty) or squamous like (inflated) apical cells and cuboidal/columnar basal cells. Function: Stretch and storage Location: Urinary system
Glands
Synthesize and secrete products from secretory cells. Arise from epithelial tissue migrating deep into connective tissue.
Types of glands
Endocrine and exocrine
Endocrine Gland
Lacks ducts and secrets hormones into the bloodstream.
Exocrine Gland
Contain ducts and connect to the epithelium surface. 2 types: Unicellular and multicellular
Unicellular exocrine gland
Contains mucus/goblet cells that produce mucus. Located in the GI and respiratory tract. Stay in the epithelial tissue.
Multicellular exocrine glands
Contains ducts and secretory units. Surrounded by supportive connective tissue. Classified by mode of excretion. 3 types. Merocrine, apocrine, and holocrine.
Merocrine Gland
Multicellular exocrine gland. Packages molecules into vesicles and pushes them out through exocytosis. Found in salivary glands.
Apocrine glands
Multicellular exocrine gland. Pinches off apical portion of the secretory cells. Location in humans debated but probably found in mammary glands.
Holocrine Glands
Multicellular exocrine gland. Cells fill up with secretion continuously till they burst. These ruptured cells release secretions like oils to the surface. To combat constant destruction, it is constantly undergoing mitosis.
What is connective tissue composed of?
Fibers, ground substance, and cells
What is found in connective tissues extracellular matrix?
Fibers (Collagen, elastic, reticular) and ground substance (everywhere without a cell of fiber)
Collagen fiber function
Gives strength to tissues, thickest fiber
Elastic fiber function
Allow stretch and recoil of tissues
Reticular fiber function
Support cells through net like structures
Fibroblast
Synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen in connective tissues
Adipocyte
Also known as a fat cell. Makes up most of adipose tissue. Store energy as fats.
What are the types of loose connective tissue?
Areolar, adipose, and reticular
What are the types of dense connective tissue?
Dense regular, irregular, and elastic
Areolar Connective Tissue structure, function, and location
Proper loose connective tissue. Structure: Gel-like matrix with elastic and collagen fibers along with fibroblasts and adipocytes. Functions: Support, cushion (like packing material), and bind. Locations: Papillary (superficial) layer of dermis, subcutaneous layer (protection), and surrounding organs, nerves, muscle cells, and blood vessels.
Adipose Connective Tissue structure, function, and location
Proper loose connective tissue. Structure: Adipocytes, fibroblasts, and highly vascularized. Majority adipocytes with lipid inclusions. Function: Fat storage, insulation in the subcutaneous, shock absorption and protection in the visceral serous membrane. Location: Visceral serous membrane and subcutaneous tissue.
Dense regular connective tissue structure, function, and locations
Proper dense connective tissue. Structure: Fibroblasts, primarily collagen fibers, and few elastic fibers. Packed with parallel fibers with few cells. Function: Attachment, resisting unidirectional stress. Locations: Tendons, ligaments, and aponeuroses
Dense irregular connective tissue structure, function, and locations
Proper dense connective tissue. Structure: Fibroblasts, primarily collagen fibers, and few elastic fibers. Fibers go off in all directions. Functions: Withstand multidirectional stress. Locations: Joint capsules (spaces between bones) and reticular (deep) layer of dermis.
Elastic connective tissue structure, function, and locations
Proper dense connective tissue. Structure: Primarily elastic fibers parallel to each other. Stain dark pink. Function: Stretch and recoil. Locations: Large arteries (aorta), trachea, and vocal cords.
Cartilage
Supporting connective tissue. Heavily packed with collagen and elastic fibers (hard to see). Avascular. Cells: Chondrocytes (primary cell) produce and maintain extracellular fluid. Housed in the lacunae. Looks like an eyeball. Chondrocytes (pupil), Lacunae (whites of eyes). Locations: Ear, fetal skeleton, meniscus, trachea, epiglottis, and tip of nose.
Types of muscle tissues and the body movement they’re responsible for
Skeletal: Locomotion (run, walk). Cardiac: Blood propulsion through circulation. Smooth: Propel substances through internal passageways (ex. digestive tract)
Nervous Tissue
Regulates and controls body functions. Made up of neurons and supportive glia (neuro) cells.
Membrane definition and the 3 types
Thin sheets of 2+ tissues with the epithelial layer resting on the connective tissue. Types: Serous and mucous membranes, and cutaneous.
Serous membranes structure, function, and locations
Structure: Folded tissue (outer parietal, inner visceral) and serous cavity with serous fluid. Functions: Reduce friction from organ movement. Locations: Surrounds lungs (pleurae), heart (pericardium), and abdominal (peritoneum).
Mucous membrane structure, function, and location
Structure: In the epithelium will always contain goblet cells and in the connective tissue is areolar. Function: Absorption, protection, and secretion. Locations: Lines the passage to any opening. Respiratory tract, mouth, and nasal cavity.
Cutaneous membrane structure, function, and location
Structure: Epidermis and dermis (papillary and reticular). Function: Protection and prevention of water loss. Location: Skin
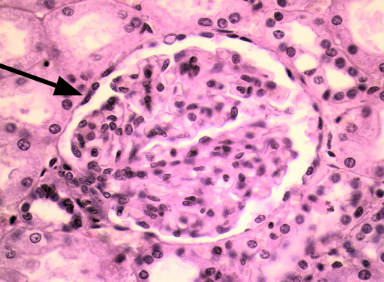
Identify
simple squamous epithelium
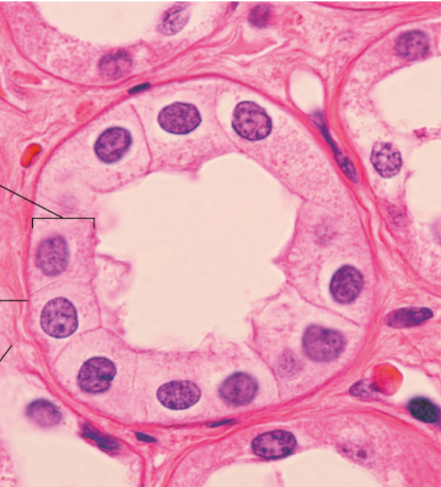
Identify
Simple cuboidal epithelium
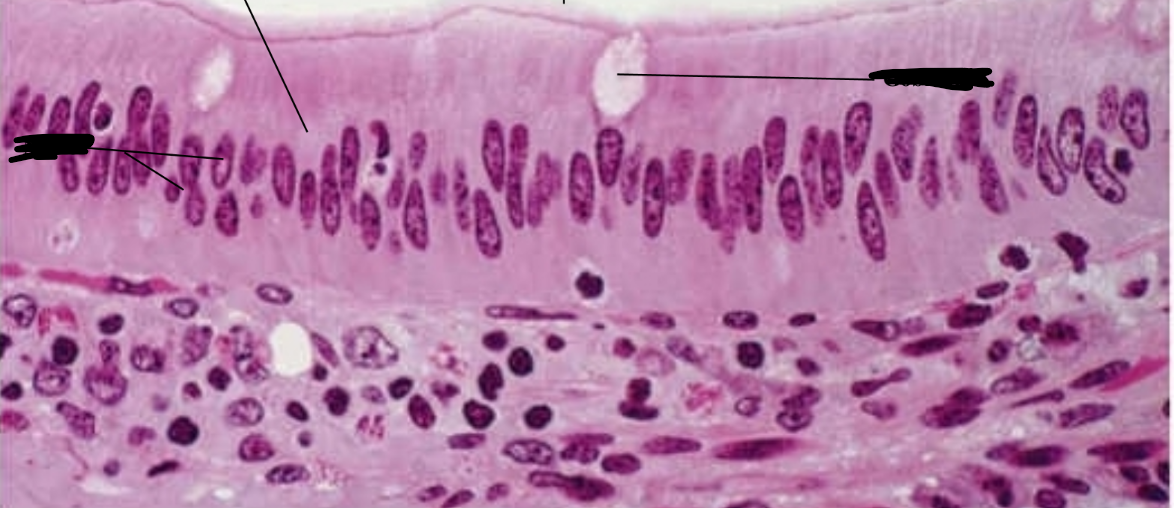
Identify
Simple columnar epithelium
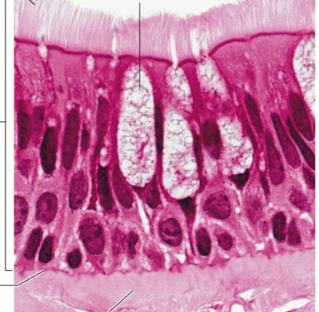
Identify
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
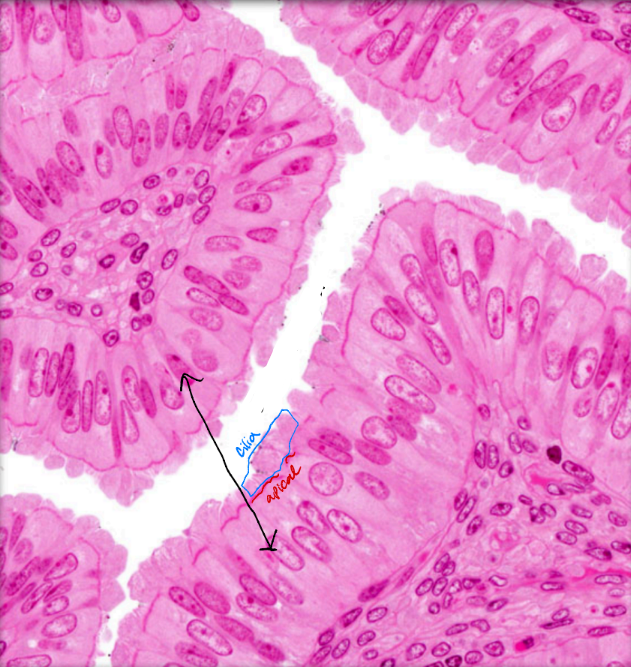
Identify
Simple columnar epithelium
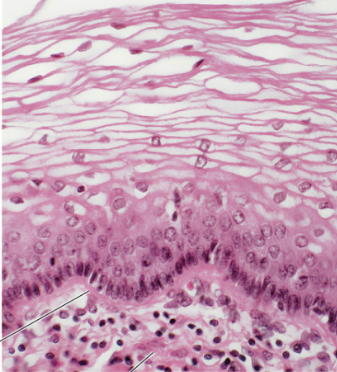
Identify
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
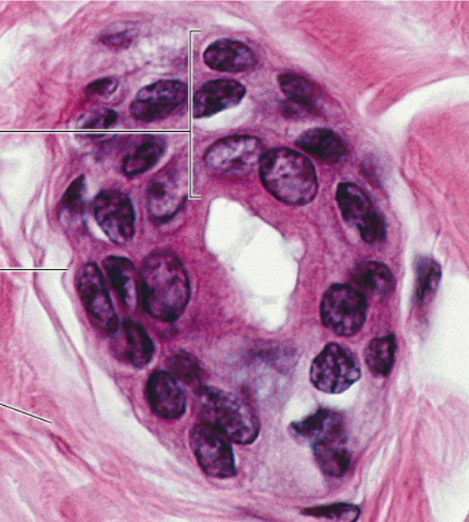
Identify
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
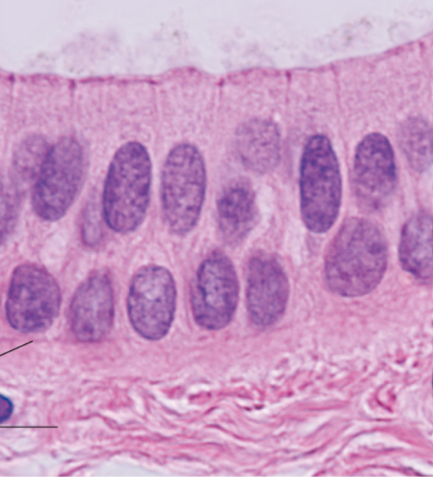
Identify
Stratified columnar epithelium
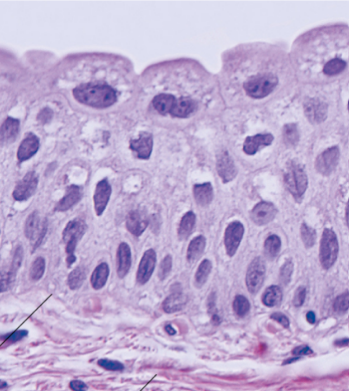
Identify
Transitional epithelium
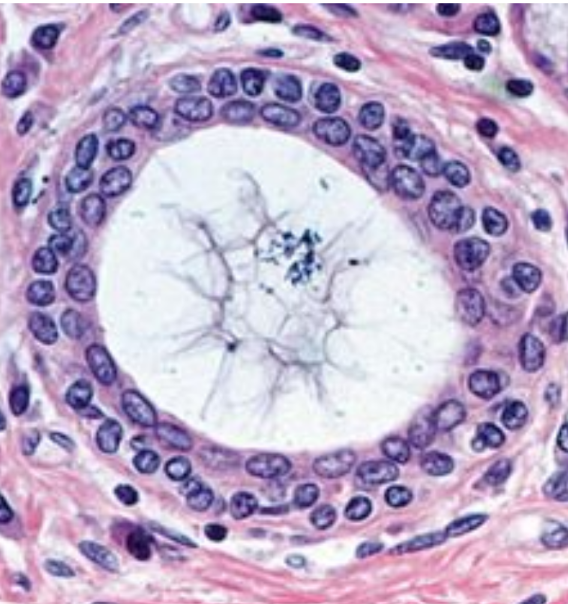
Identify
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
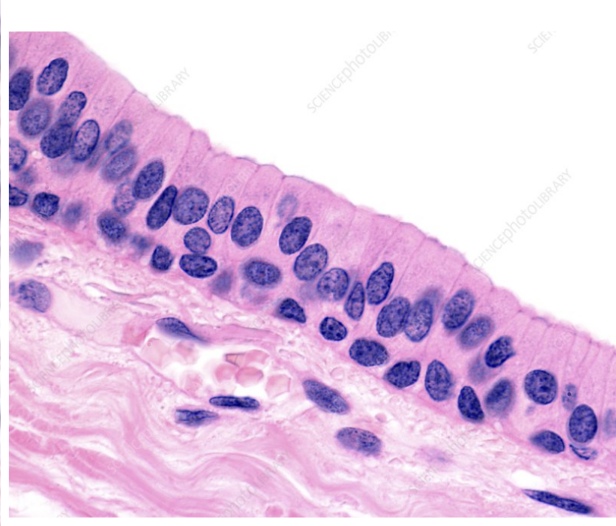
Identify
Stratified columnar epithelium
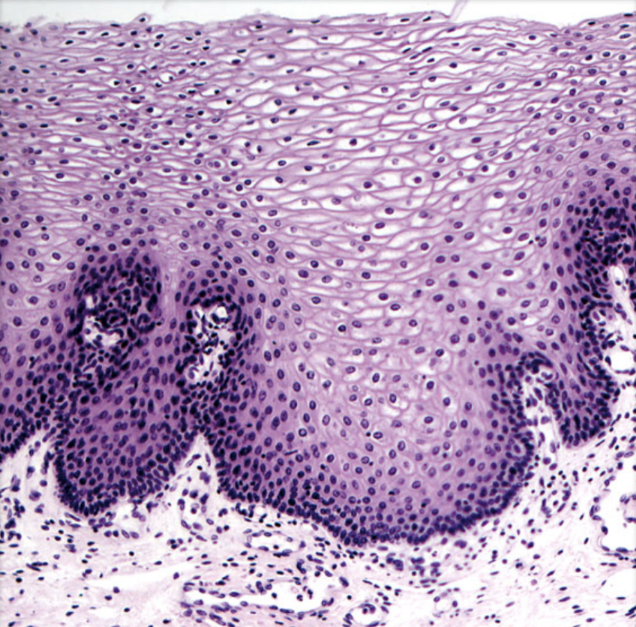
Identify
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
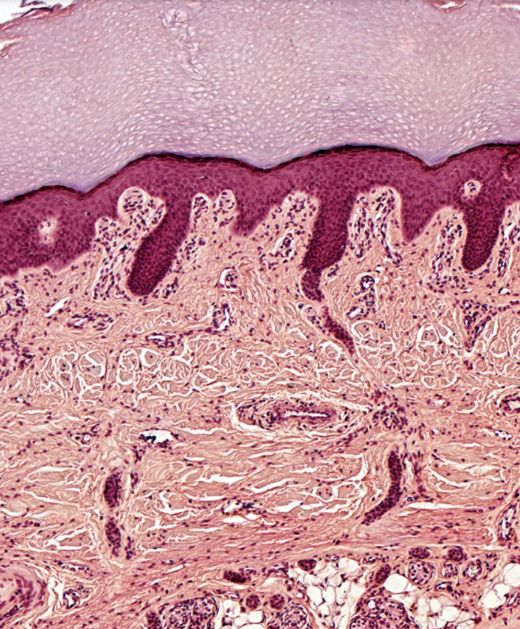
Identify
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
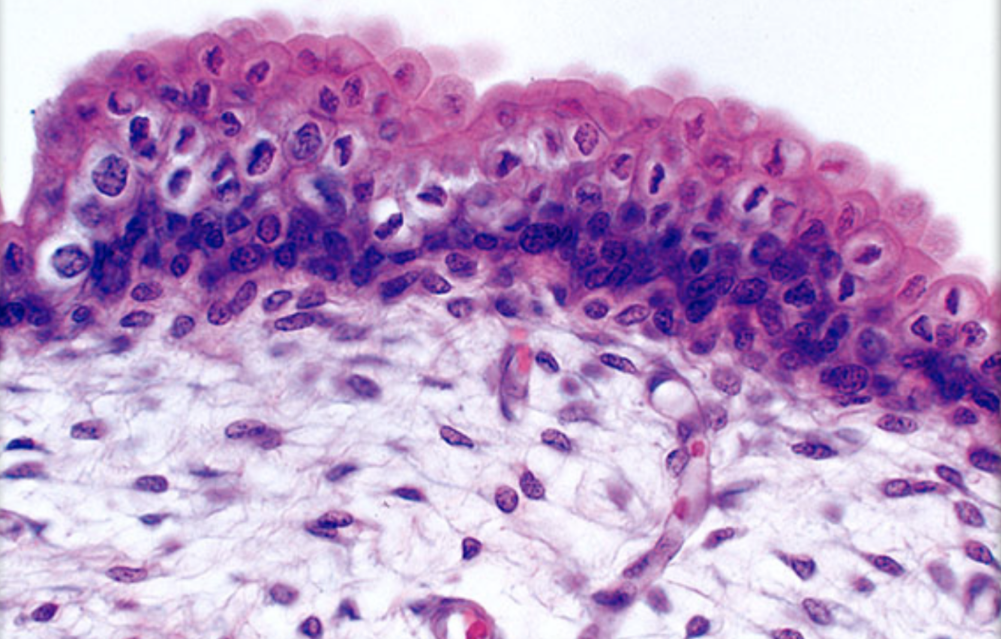
Identify
Transitional epithelium
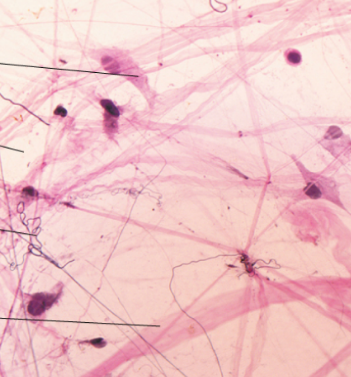
Identify
Areolar connective tissue
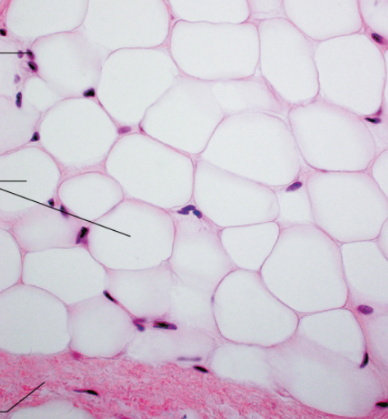
Identify
Adipose connective tissue
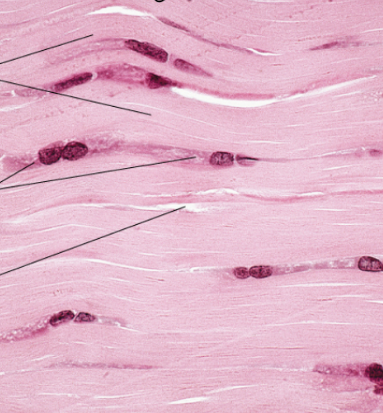
Identify
Dense regular connective tissue
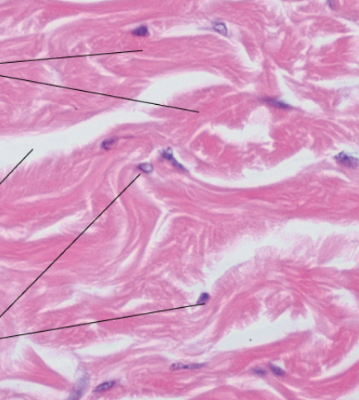
Identify
Dense irregular connective tissue
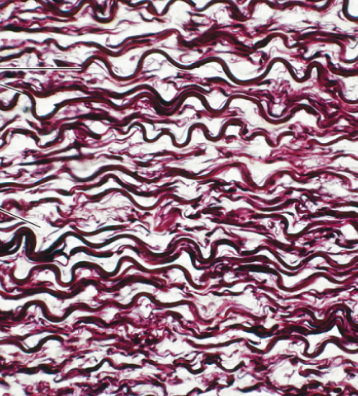
Identify
Elastic connective tissue
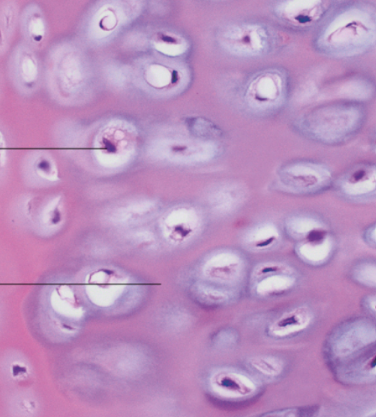
Identify
Cartilage
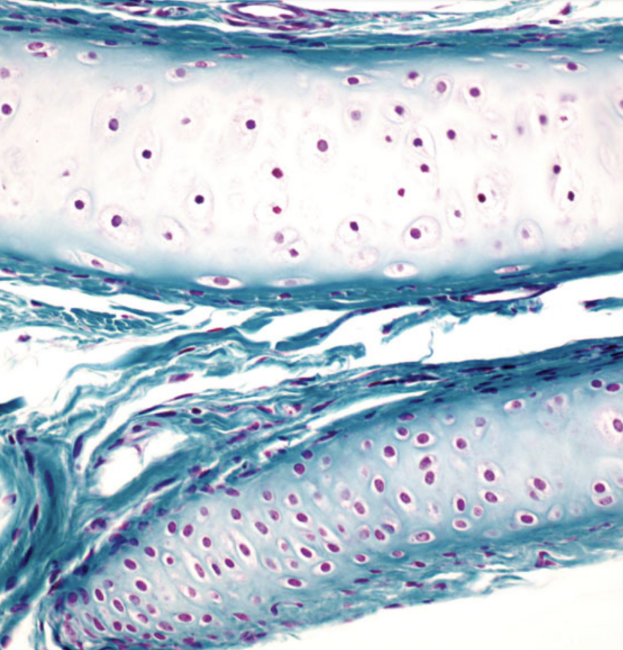
Identify
Cartilage