Invertebrates I Bio 1108
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Invertabrates
Animals without a backbone
Comprise over 95% of animal species
Changing environmental conditions, enhanced locomotion and predator-prey relationships fueled evolution through natural selection
Adaptation and counter adaptation led to the diversity of contemporary invertebrate animals
Parazoa
Includes Phylum Porifera
Loosely organized and lack tissues
Multicellular with several types of cells
8,000 species, mostly marine
No apparent symmetry
Adults sessile, larvae free-swimming
Sponges
These organisms are part of the Phylum Porifera
Simplest animals
All are aquatic
No true tissues
Asymmetrical
Adults are sessile abut larvae have motility
Filter feeders
Reproduce sexually (hermaphroditic) and asexually through budding
Choanocytes
defining feature of sponges that facilitate filter feeding by drawing water through the sponge’s body where food particles are trapped and ingested
Phylum Cnidaria
This phylum consists of sea anemones, corals, and jellies
Have radial symmetry
Mostly marine
Diploblastic
Mesoglea connects layers
cnidocytes
specialized cells containing a stinging organelle called a nematocyst used for prey capture and defense
nematocysts
a specialized cell in the tentacles of a jellyfish or other coelenterate, containing a barbed or venomous coiled thread that can be projected in self-defense or to capture prey
Polyp and Medusa
Two forms of Cnidarians
Cnidarian Functional Anatomy and Reproduction
Asexually reproduce via budding
Sexually reproduce by releasing gametes into the water
Primitive nervous system - nerve net
Gastrovascular cavity: one opening for both mouth and anus
Carnivorous
Platyhelminthes
Phylum that is an acoelomate
Lophotochozoans and Ecdysozoans (sometimes Platyhelminthes)
Phylums that are protostomes and coelomates
Echinoderms and chordates
Phylums that are deuterostomes and coelomates
cephalization
concentration of nerve tissue in the head (anterior) of the animal
cephalization
this enhances an organism’s ability to sense its environment, find food, and evade predators
lophophore
a crown of ciliated tentacles that are used to filter feed and in gas exchange; includes Bryozoans, Brachiopods, Rotifers

trochophore
a free-swimming, ciliated larval stage; includes Mollusks, Annelids, Platyheminthes (flatworms)
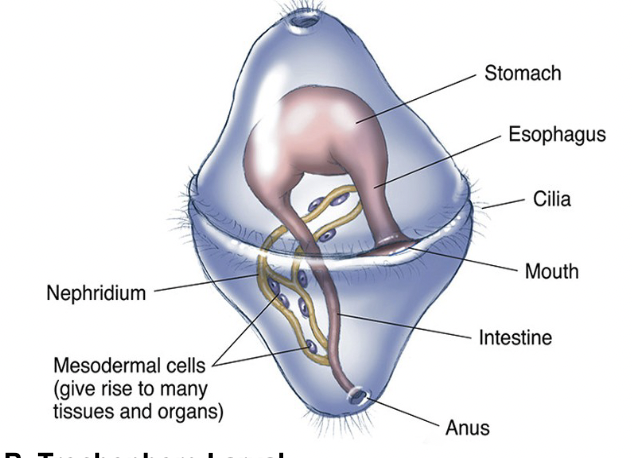
Platyhelminthes
This phylum consists of flatworms, lacks a specialized respiratory or circulatory system (respire by diffusion); among the first animals with an active predatory lifestyle, bilaterally symmetrical with head; have a gastrovascular, can be free-living or parasitic
flame cells
specialized excretory cells, found in simple invertebrates like flatworms, rotifers, and nemerteans, that function like a kidney, removing waste materials and maintaining osmotic balance
Classes of Flatworms
Class Turbellaria - planarian
Class Monogenean - monogeneans
Class Trematoda - flukes
Class Cestoda - tapeworms
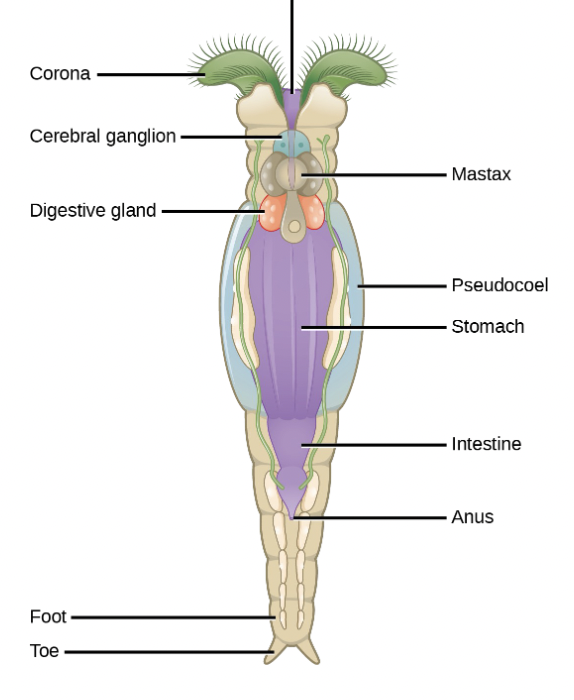
Rotifera
This phylum in known as “wheel-bearer”, microscopic and mostly aquatic and get their name from the corona
corona
pair of ciliated feeding structures that appear to rotate when viewed under the light microscope
Bdelloid Rotifer
This organism is a pseudocoelomate divided into head, trunk, and foot
Covered by a culitcle and contains skeletal and visceral muscles
Free-swimming or planktonic; uses sticky material on foot for adhesion
Filter feeders and consume algae and microscopic organisms
Dioecious with sexual dimorphism; some species exhibit
Also can reproduce through parthenogenesis
Capable of extended dormancy to survive harsh conditions
haplodiploidy
a sex-determination system where males develop from unfertilized, haploid eggs, and females develop from fertilized, diploid eggs