Ventricular system
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What are the three important components for controlling the brain extracellular fluid
Ventricular system, cerebrospinal fluid, and blood-brain barrier
What are the two fluid compartments of the brain and where are they located i
Interstitial fluid = in the brain
Cerebrospinal fluid = intraventricular and subarachnoid space
What regulates the homeostasis of the interstitial fluid and the cerebrospinal fluid compartments and the intracellular compartment of brain cells
Blood-brain barrier
Blood-CSF barrier
What forms the blood brain barrier and Blood-CSF barrier
Endothelial cells of capillaries (vascular)
Endothelial cells of choroid plexus
Cerebral ventricles; what are they, where is it located, what are they filled with, what produces/modifies what their filled with
Cerebral ventricle are a series of interconnected cavities
in the core of forebrain and brainstem
Filled with cerebrospinal fluid
produced and modified by choroid plexus
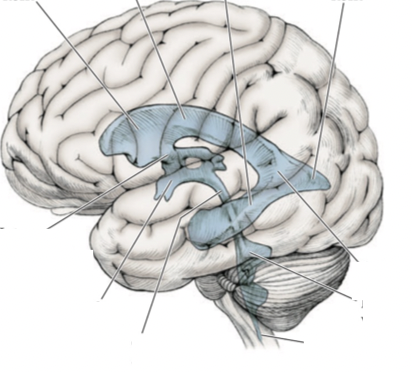
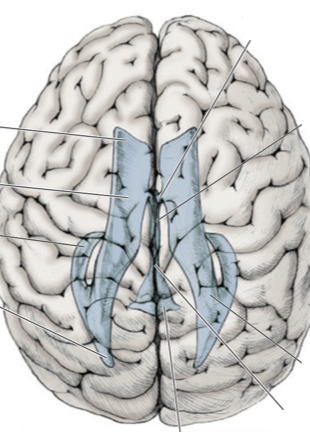
Label this diagram
What connects the two lateral ventricles
Inter-ventricular foramen of Monro
Where does the cerebral aqueduct lead to
The fourth ventricle
Choroid Plexus what is it and where does it get its blood supply from (3)
Network that secretes cerebrospinal fluid
Posterior; Anterior choroidal artery
anterior and posterior inferior cerebellar
What are the cellular make up of the choroid plexus and what do these cellular constituents form
Blood vessels and Pia = form the core of the choroid plexus and choroid epithelium
Choroid epithelium; what is it, what it forms
Specialized cells that secrete CSF to ventricles
Forms a blood-CSF barrier = prevent transport of materials from blood to CSF
How are choroid epithelial cells bound to one another
Tight junctions that separate ECF from CSF
Total CSF production per day
500mL/day
CSF forms in two sequential stages, explain them
Ultrafiltration of plasma occurs across the capillary wall to ECF below the membran of choroid epithelial cell
Choroid epithelial cells secrete fluid into the ventricle
CSF production occurs with a net transfer of what
Transfer of NaCl and NaHCO3 from plasma to CSF which drives water movement isosmotically
Name the two processes of how Na is secreted from the plasma to the CSF
Na-K pump in choroid plexus
Na-H and Na-HCO3 transporter
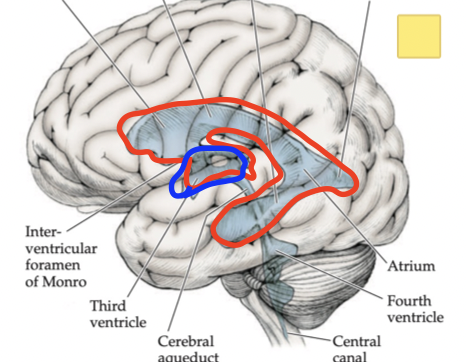
Cerebrospinal Fluid circulation
Lateral Ventricle
Interventricular foramina of Monro
Third ventricle
Cerebral aqueduct of sylvius
Fourth ventricle
Foramina of magendie and luschka
Subarachnoid space
Where is the CSF absorbed?
Venous sinuses through arachnoid granulation
What allows the absorption of CSF to the venous sinuses
Arachnoid granulations = one-way pressure sensitive valves that push CSF from Subarachnoid space to venous blood.
compare and contrast where csf and venous Blood can enter
CSF can cross into venous blood
Blood cant cross the CSF due to CSF having higher pressure than venous blood
The rate of CSF formation is NOT affected by what
CSF pressure
CSF formation remains constant no matter what the CSF pressure is
What happens when CSF pressure exceeds 70 mm H20
CSF absorption increases as CSF pressure go above 70 mm H20
Why does absorption increase when CSF pressure increased
Absorption increases as CSF pressure increases to prevent excess fluid building up in the brain.
Prevents dangerous brain conditions
What does an increase in volume od brain tissue, blood, or CSF cause
Causes an increase in Intracranial pressure could be caused by edema, tumor formation, cerebral abscess, or hematoma
Compare and contrast small and large volume changes in the brain tissue
Small volume changes can be compensated by reducing intracranial CSF and blood volume without causing much rise in ICP pressure
Large volumes however cant be compensated by reducing CSF leading to dangerous consequences
When large volume changes in the brain cant be compensated leading to increased ICP pressure, what does this lead to
Brain perfusion decreases leading to death or herniation
How is cerebral perfusion pressure determined
Cerebral perfusion pressure = Mean arterial pressure - intracranial pressure
What is the relationship of intracranial pressure and cerebral perfusion pressure
As ICP increases = CPP decreases meaning less blood is able to enter the brain
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
Procedure used to reduce ICP to normal levles
Needle inserted between fourth and fifth lumbar
Normal intracranial pressure in mm CSF or mm Hg
65 - 195 mm CSF
5-15 mm Hg
Papilledema
Optic disc swelling caused by blood build up in the optic disc by increased ICP
Decompressive hemicraniectomy
Surgical procedure that removes part of the skull to relieve brain swelling and increased ICP
Hydrocephalus
Caused by excess CSF in the intracranial cavity
What three conditions cause hydrocephalus
Excess CSF production
Obstruction of flow at any ventricles but ESPECIALLY the narrow joints or subarachnoid space
Decreased reabsorption via the arachnoid granulations
What are the narrow points obstruction can occur causing Hydrocephalus`
Interventricular foramina of Monro, the cerebral aqueduct, or the fourth ventricle
What are the two categories of Hydrocephalus
Communicating hydrocephalus = caused by impaired reabsoprtion of fluid in arachnoid granulations
Noncommunicating hydrocephalus = Caused by obstruction of flow within the ventricle system
Hydrocephalus treatment
Ventriculostomy = a surgical procedure where a catheter is inserted into the brain’s ventricular system to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and relieve increased intracranial pressure (ICP).
Ventriculoperitoneal shunt = shunt passes from the ventricle to the skull, uunder the skin and drains into the peritoneal cavity in the abdomen
Location of barrier sites in the CNS. In all these sites what are the physical barriers caused by
The brain endothelium forming the blood-brain barrier
The arachnoid epithelium forming middle layer of the meninges
The choroid plexus epithelium which secretes CSF
Each physical barrier is caused by tight junction
Astrocytic endfeet
Provide a continuous covering of the capillaries and facilitate transport between cells and blood
What molecules readily cross the Blood-Brain-Barrier
CO2, O2, ethanol, caffeine, nicotine, and opioids
Entry into the brain is achieved primarily in three ways; name them
Diffusion of lipid soluble substances
Facilitative and energy dependent receptor-mediated transport
Ion channels and exchangers