Lec 7: Vestibulocochlear Nerve Vestib Div
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Vestibular Nerve
Vestibulo-ocular
Vestibulospinal
Vestibular Circuitry
function parts of the cerebellum:
vestibulocerebellum
spinocerebellum
cerebrocerebellum
what is vestibulocerebellum
– Flocculonodular lobe
– Vestibular control of eye movement, posture, balance
what is spinocerebellum
– Vermis & Paravermis
– Receives postural sensory information from spinocerebellar tracts
– Sends outgoing signals to rubro, vesibulo and reticulospinal tracts
– Postural stability
what is cerebrocerebellum
– Cerebellar hemispheres
– Connects to Dentate nucleus
– Sends outgoing signals to motor cortex via thalamus
– Motor planning and control
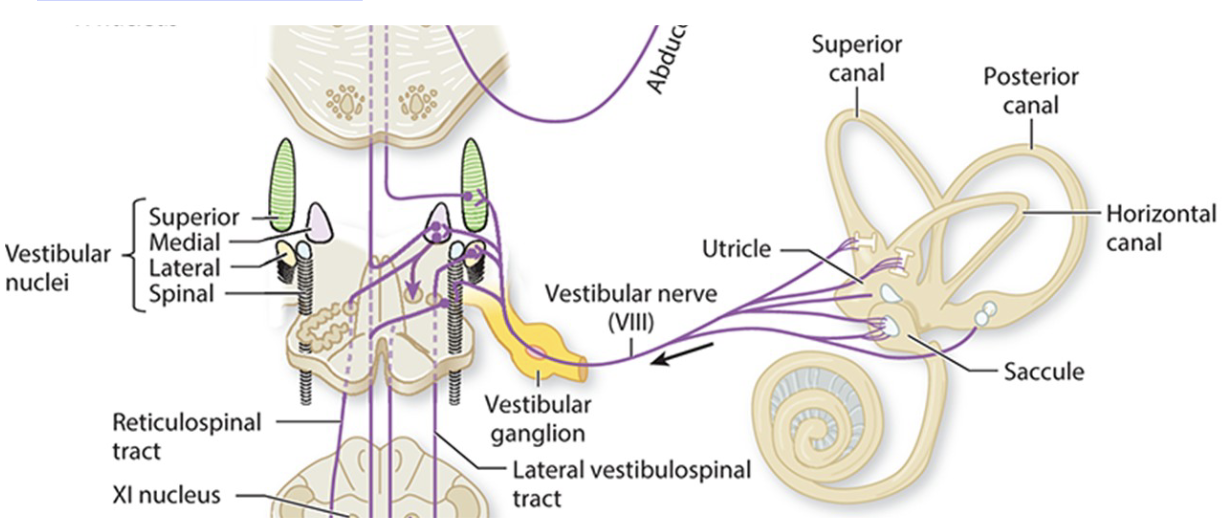
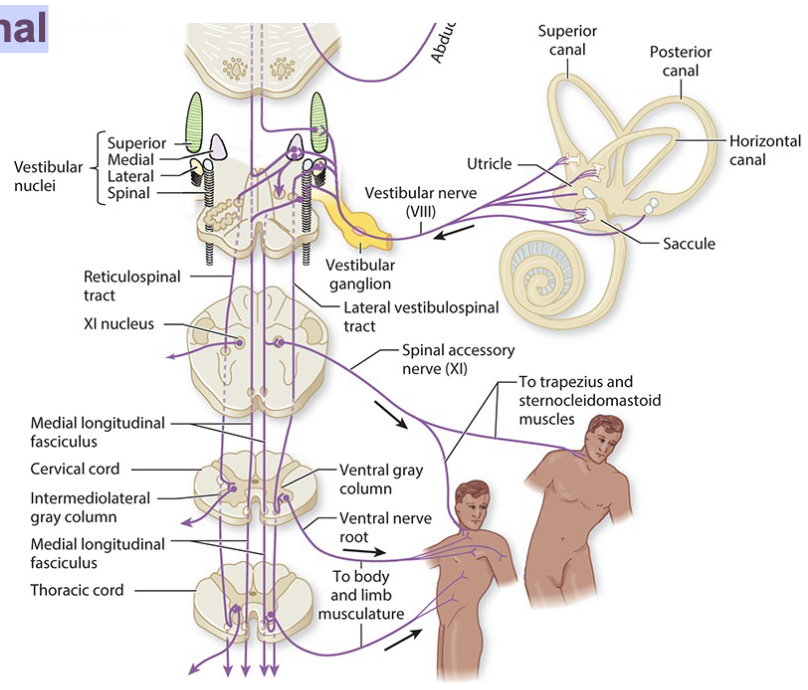
what is Vestibulospinal Tract (VST)
• Maintain balance in the body
• responsible for antigravity muscle tone (and neck movements) in response to the head being tilted in any direction
• Starts at the Lateral Vestibular Nucleus (LVN) in Pons/Medulla
• Descends the full length of spinal cord through the anterior column
• Communicates with every segment on the way down
• No Decussation – totally ipsilateral
lateral VST
Starts at the Medial Vestibular Nucleus (MVN) in Pons/Medulla
Axons descend Bilaterally through the medial portion of the anterior column
Stops at the thoracic spinal cord
Reflexive movements of the head and neck
Control neck flexors and extensors during falls
medial VST
Information relevant to maintaining balance:
• CN VIII – Semicircular canals and maculae of the inner ear
• CN II
• Ascending cutaneous and proprioceptive information from the spinal cord
• Cerebellum
• Vestibular Nerve
• Ends at 4 nuclei in the Dorsolateral Medulla and Pons
Equilibrium and Orientation
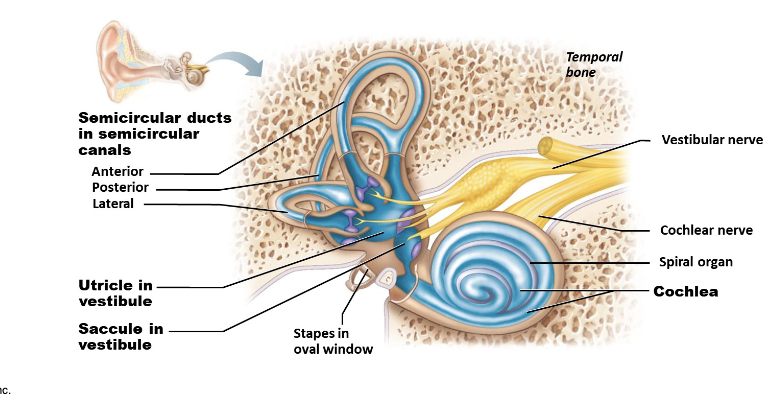
what is Vestibular apparatus?
– Equilibrium receptors in semicircular canals and vestibule
– Vestibular receptors monitor static equilibrium
– Semicircular canal receptors monitor dynamic equilibrium
Sensory receptors for static equilibrium
One in each saccule wall and one in each utricle wall
Monitor the position of head in space
– necessary for control of postureRespond to linear acceleration forces, but not rotation
Otolith membrane studded with otoliths (Calcium Carbonate Crystals)
Vestibular Receptors: Maculae
There are 2 Maculae in each ear:
utricle
saccule
Both respond to linear acceleration or tilt of the head in a forwards & backwards direction
– Tilting head changes the effect of gravity on the Otolith membranesMacula in utricle responds to Lateral Acceleration & lateral tilt of the head (side to side)
Macula in saccule responds to vertical acceleration
Hair cells synapse with vestibular nerve fibers
Maculae – Utricle & Saccule
• Anterior
• Posterior
• Horizontal (lateral)
Semicircular Canals
Sensory receptor for rotational acceleration
– One in each semicircular canal
– Major stimuli are rotational movementsCrista hair cells extend into gel-like mass called ampullary cupula
The Crista Ampullares (Crista)
Equilibrium information goes to reflex centers in brain stem
– Allows fast, reflexive responses to imbalance
Equilibrium Pathway to the Brain
Three modes of input for balance and orientation:
– Vestibular receptors (maculae ofutricle and saccule, and cristae of semicircular canals)
– Visual receptors
– Somatic receptors
what are the 3 semicircular canal planes
horizontal canals
anterior canals
posterior canals
what is horizontal canals?
Activated by:
– Cranial/Cervical Rotation
– Spinning on ice
what is anterior canals ?
Activated by:
– Neck flexion
– Front flip
what is posterior canals
Activated by:
– Neck extension
– Back flip
The three semicircular canals ararranged in
orthogonal planes
– at right angles to each other – like the corner of a box
Each semicircular canal is paired with a
complementary canal in the opposite labyrinth
– each pair responds to specific angular motion
The medial and inferior vestibular nuclei are located close to one another in the rostral medulla
The smaller lateral and superior nuclei lie within the pons
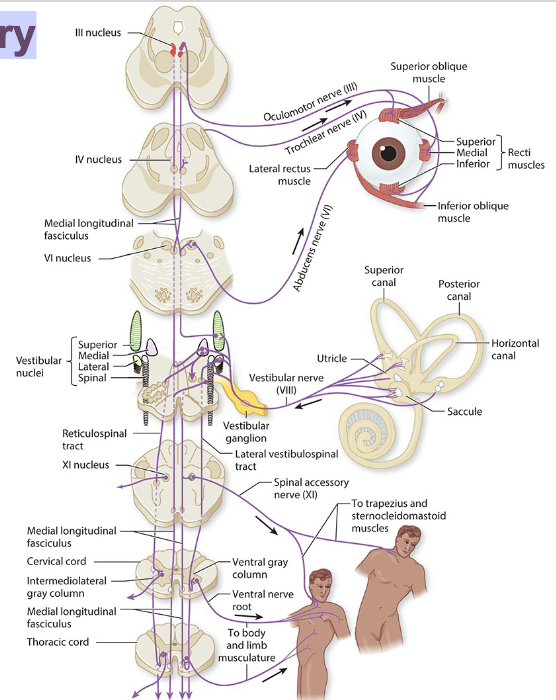
Vestibular nuclei and pathways
The four vestibular nuclei give rise to both ascending and descending tracts, sending projections to the:
– Cerebellum
– Brainstem nuclei
• especially the extraocular nuclei
– Cerebral Cortex
– Spinal cord
Information from the Semicircular canals goes to the __
Medial Vestibular Nucleus
– The medial nucleus activates the Medial Vestibulospinal Tract
• Reflexive movements of the head and neck
Information from the Utricle and Saccule goes to the
Lateral Vestibular Nucleus
The Lateral nucleus activates the__
• Activates extensors in limb and trunk muscles
Lateral Vestibulospinal Tract
Lateral Nuclei to the:
– Spinal Cord
• Lat. Vestibulospinal Tract
Medial Nuclei to the:
– Spinal Cord
• Medial Vestibulospinal Tract
• AKA Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus (MLF)
– Descending part
Other Destinations for Vestibular Nuclei signals:
– Ipsilateral Cerebellum
• Via Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle
– Bilateral CN 3,4&6 Nuclei
• Via MLF, Ascending part
– Contralateral cerebral cortex
Maintain head, trunk, and eye alignment during movements
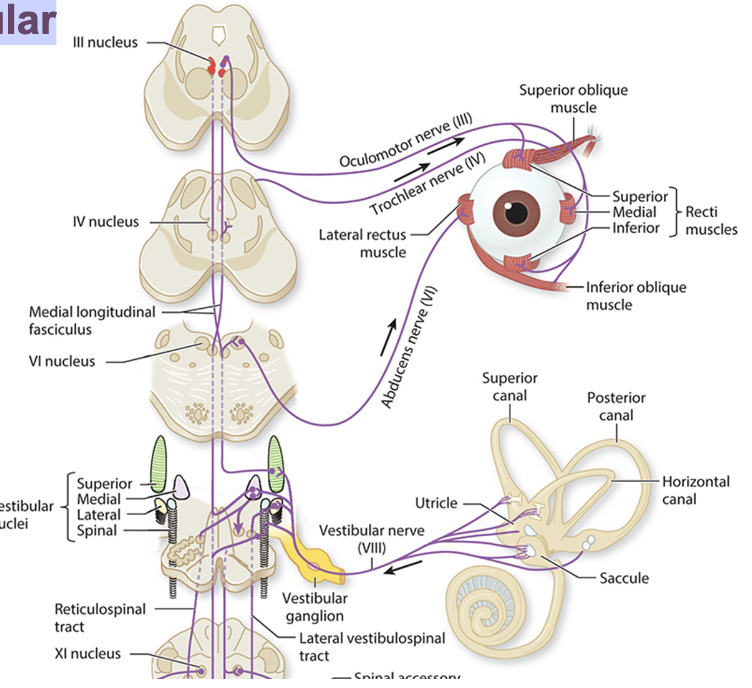
1. Vestibulo-ocular Reflex
2. Vestibulospinal Reflex
3. Vestibulocollic reflex
Movement in any direction excites the vestibular neurons on the side to which the head turns
– inhibiting contralateral neuronsCentral projections excite the ipsilateral vestibular nuclei
Vestibular nuclei excite the ipsilateral abducens nucleus and contralateral oculomotor nucleus
Controls and coordinates binocular gaze opposite in direction to the head movement
Vestibulo-ocular Reflex
For example, with bilateral stimulation of the posterior canals:
resulting eye movement is oblique and downward, as it excites the inferior recti and superior obliques
– and inhibits the superior recti and inferior oblique
Vestibulo-ocular Reflex example
what is Vestibulospinal Reflex
• regulates full-body balance and postural responses
• Excite limb Extensors, Antigravity muscles
• Via Lateral Vestibulospinal Tract
what is Vestibulocollic Reflex
coordinates vestibular activity, with input from proprioceptors in the neck to precisely coordinate and align head position during postural adjustments
Via Medial Vestibulospinal Tract