Biology 121 Exam 2
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Genetics, etc
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Somatic Cells
Whole Body Cells
Germ Cells
Reproductive Cells (what gametes develop from)
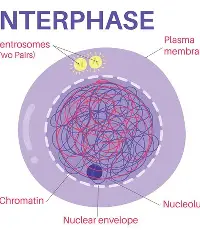
Interphase of Mitosis
Sister chromatids are created and wound around small proteins (histones)
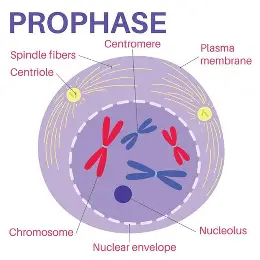
Prophase of Mitosis
Mitotic spindle is formed in prophase (connects to chromosomes and pull them towards different poles), nucleus starts breaking apart, chromosomes get shorter and thicker
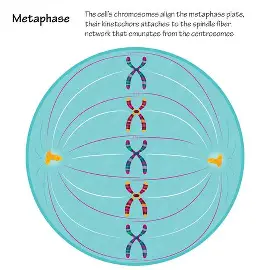
Metaphase of Mitosis
Chromosomes lined up in middle, nuclei are on different poles, mitotic spindle surround chromosomes
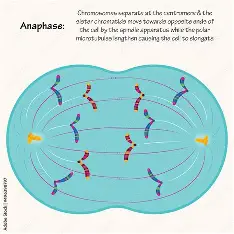
Anaphase of Mitosis
Sister chromatids pull apart from each other, move toward different poles
Telophase of Mitosis
New nuclear envelopes form, chromosomes are no longer connected to a spindle.
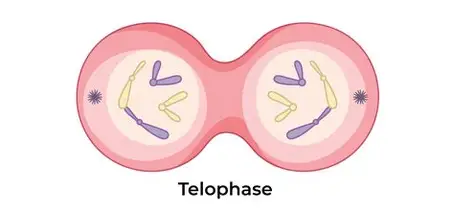
G1 of Interphase
Cell grows, acquires nutrients, synthesizes proteins.
S Phase of Interphase
DNA is Replicated (Daughter cells all have an identical set of chromosomes)
G2 of Interphase
Cell produces organelles and proteins needed for cell division.
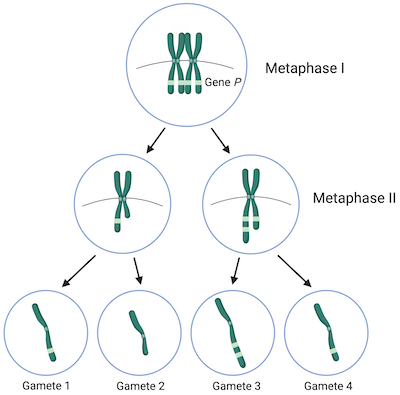
Independent Assortment
A genetic principle stating that alleles for different traits segregate independently during the formation of gametes.
Crossing Over
The process in which homologous chromosomes trade parts.
DNA is broken at the same spot on each homologue and reconnected in a crisscross pattern so that the homologues exchange part of their DNA (ABc and aBC are homologous chromosomes. When they cross over they become ABC and aBc).
Random Fertilization
The selection of each egg and sperm is completely random.
What happens to chromosomes before meiosis begins?
Sister chromatids are formed and DNA replicates (interphase)
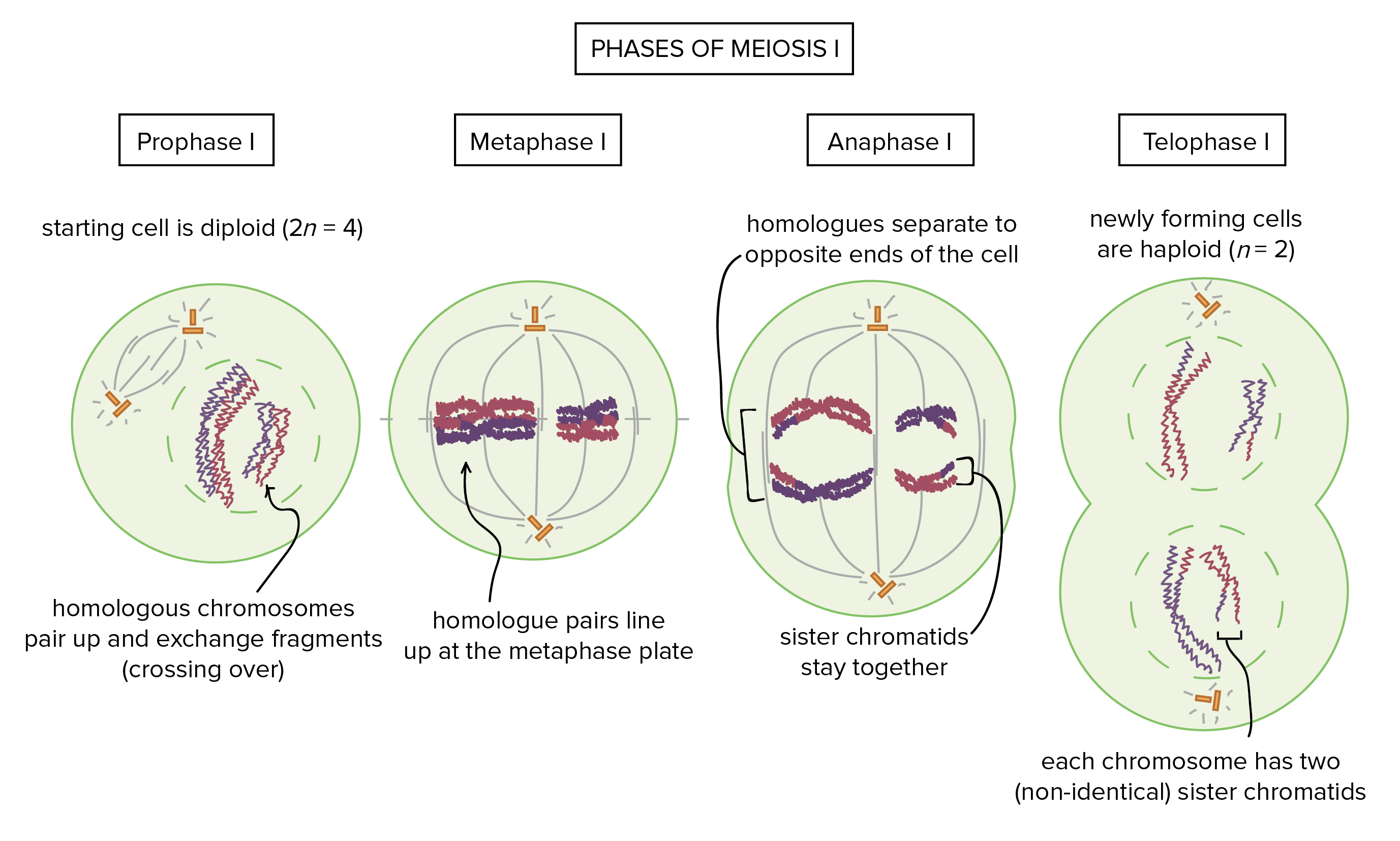
Prophase I of Meiosis
Chromosomes begin to condense and homologous chromosomes pair up along with the sister chromatids
Metaphase I of Meiosis
Homologous pairs are lined up in the middle, mitotic spindles are connected to sister chromatids.
Anaphase I of Meiosis
Homologues are pulled apart and move to opposite ends of the cell. Sister chromatids remain attached to one another and won’t come apart.
Telophase I of Meiosis
Homologous Chromosomes are fully separated in different cells, sister chromatids are still together. The nuclear membrane doesn’t reform and the chromosomes don’t decondense in every case because the cells will go through Meiosis II.
Meiosis II
DNA is not copied between telophase I and prophase II. It’s basically mitosis for haploid cells. Cells are haploid with a diploid amount of DNA— One chromosome from each homologous pair, but two sister chromatids. Sister Chromatids will separate during this phase.
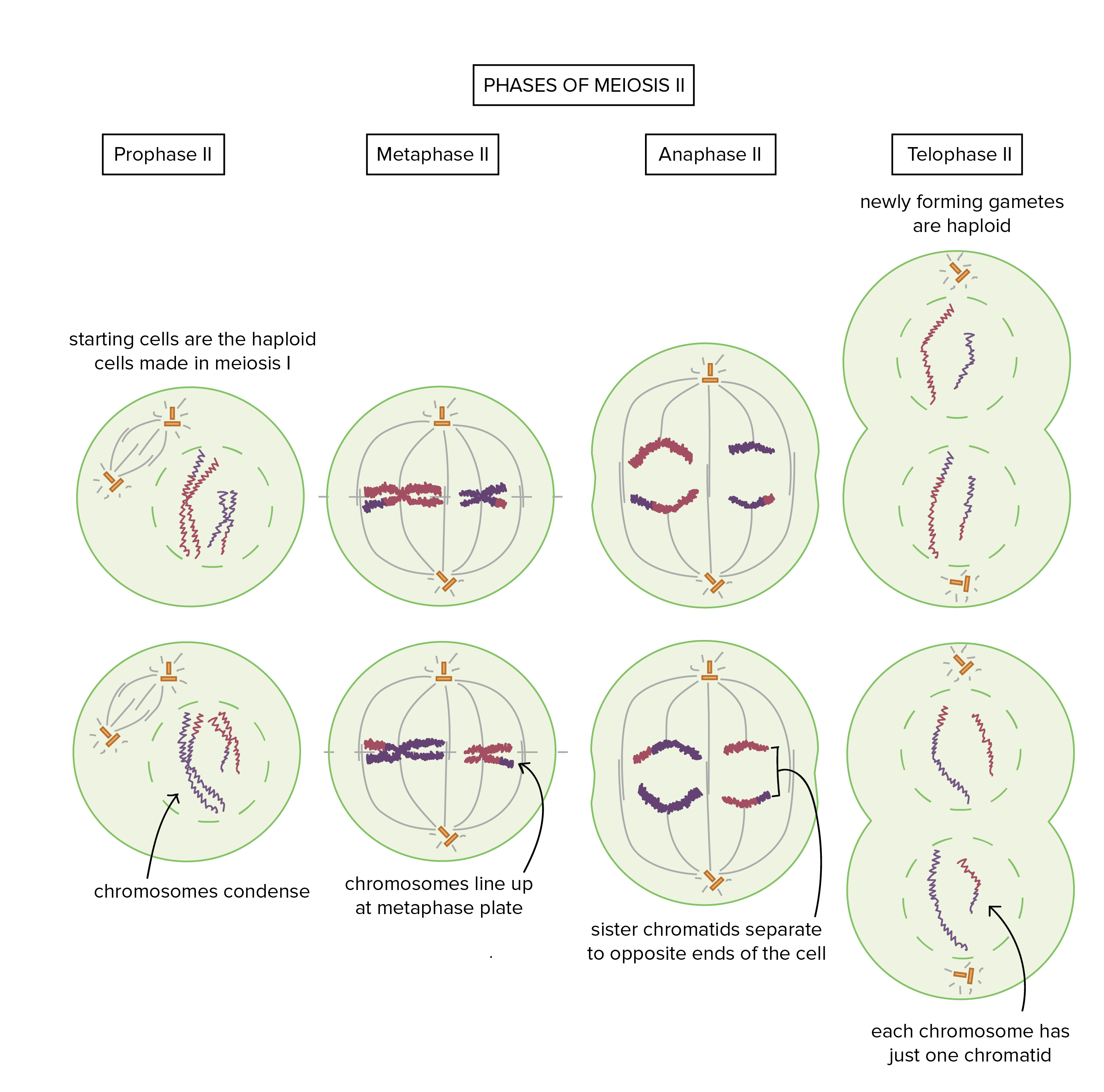
Prophase II
Starting cells are haploid cells made in meiosis I, chromosomes condense and, if the nuclear envelope was developed, it breaks down. Centrosomes move apart, spindle forms between them, spindle microtubules begin to capture chromosomes.
Metaphase II
Chromosomes line up individually along the metaphase place.
Anaphase II
Sister chromatids separate and are pulled towards opposite pole of the cell.
Telophase II & Cytokinesis
Nuclear membranes form around each set of chromosomes, chromosomes decondense. Cytokinesis splits chromosome sets into new cells.
Final product: four haploid cells in which each chromosome has just one chromosome. (GAMETES)
How is Mitosis and Meiosis Different?
Mitosis produces daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell.
Meiosis produces gametes that are genetically unique.
Phenotypic Plasticity
When a single genotype produces multiple phenotypes under different environmental conditions.
How many Homologous pairs —> How many Total Chromatids
A diploid cell has 2 complete sets of chromosomes. So a germ cell containing X amount of chromosomes would have X/2 homologous pairs. Each of the chromosomes consists of 2 sister chromatids after DNA replication, so the X/2 pairs of chromosomes contain X*2 chromatids total at the beginning of Meiosis I
Chromosomal Deletion
The deletion of parts of chromosomes.
Law of Segregation
Only one of the two alleles present in an organism is distributed to each gamete that it makes, and the allocation of the gene copies is random.
What fuels evolution?
Variation
Epistasis
Where a gene at one locus alters the phenotypic expression of another gene. Multiple genes affect one trait (hair color, etc)
Polygene Inheritance
Multiple gene inheritance and the environment’s influence.
How are maternal lines traced in females?
Mitochondrial DNA
T.H. Morgan
Exponentially increased knowledge of genetics through the fruit fly experiment.
Rules for Crossing Over
Recombination Frequency is NEVER OVER 50% UNLESS THE ALLELES ARE ON DIFFERENT GENES (Analogous chromosomes put together by the chiasmata can recombine but the sister chromatids on the outside never cross over)
The closer together genes are, the less likely that are to recombine.
Map Unit
1% recombination frequency (centermorgans)
X-0 Sex
Many insects don’t have a Y-chromosome, males have X-0 Chromosomes.
ZW Sex
Birds and Butterflies have the opposite dynamic of mammals— males have the homogametic sex chromosomes (ZZ) while females are heterogametic (ZW).
Haploid Sex
Male Bees don’t have fathers, as they are from unfertilized eggs and are therefore haploid.
Female Bees are from fertilized eggs which are diploid.
Barr Body
Early in development— embryo is ~16 cells big— every cell is an identical daughter cell until on of the two X’s in a female cell shrivels up and is moved to right outside of the nucleus.
The same specific X chromosome does not shrivel in every cell, so females can present different genetics throughout their body.
Shriveled X’s — the Barr Body— appears as a smudge.
Nondisjuntion
When pairs of homologous chromosomes do not separare normally during meiosis I.
One gamete gets two of the same type of chromosome and another gamete receives no copy.
Two ways this could occur: in Meiosis I with homologous chromosomes or Meiosis II with Sister Chromatids.
Occurs in Meiosis I: all 4 resulting haploids are affected (½ are n+1, ½ are n-1)
Occurs in Meiosis II: only 2 of 4 resulting haploids are affected (¼ is n+1, ¼ is n-1, ½ are n)
Aneuploidy
Results from the fertilization of gametes in which nondisjunction occurred.
most aneuploids die by miscarriage
Monosomy (one of a chromosome in a fertilized diploid gamete), some trisomy (3 of a chromosome in a fertilized diploid gamete) survive like with Klinefelter Syndrome, Turner Syndrome.
XXX can survive while I-I-I can’t survive.
When does sex cell development occur in male vs females?
Males are constantly creating sperm through meiosis in the testes while females start developing eggs through meiosis until the beginning of meiosis I during fetus development and then stops until puberty.