Miller and Levine Biology: Chapter 9-Photosynthesis
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Photosynthesis
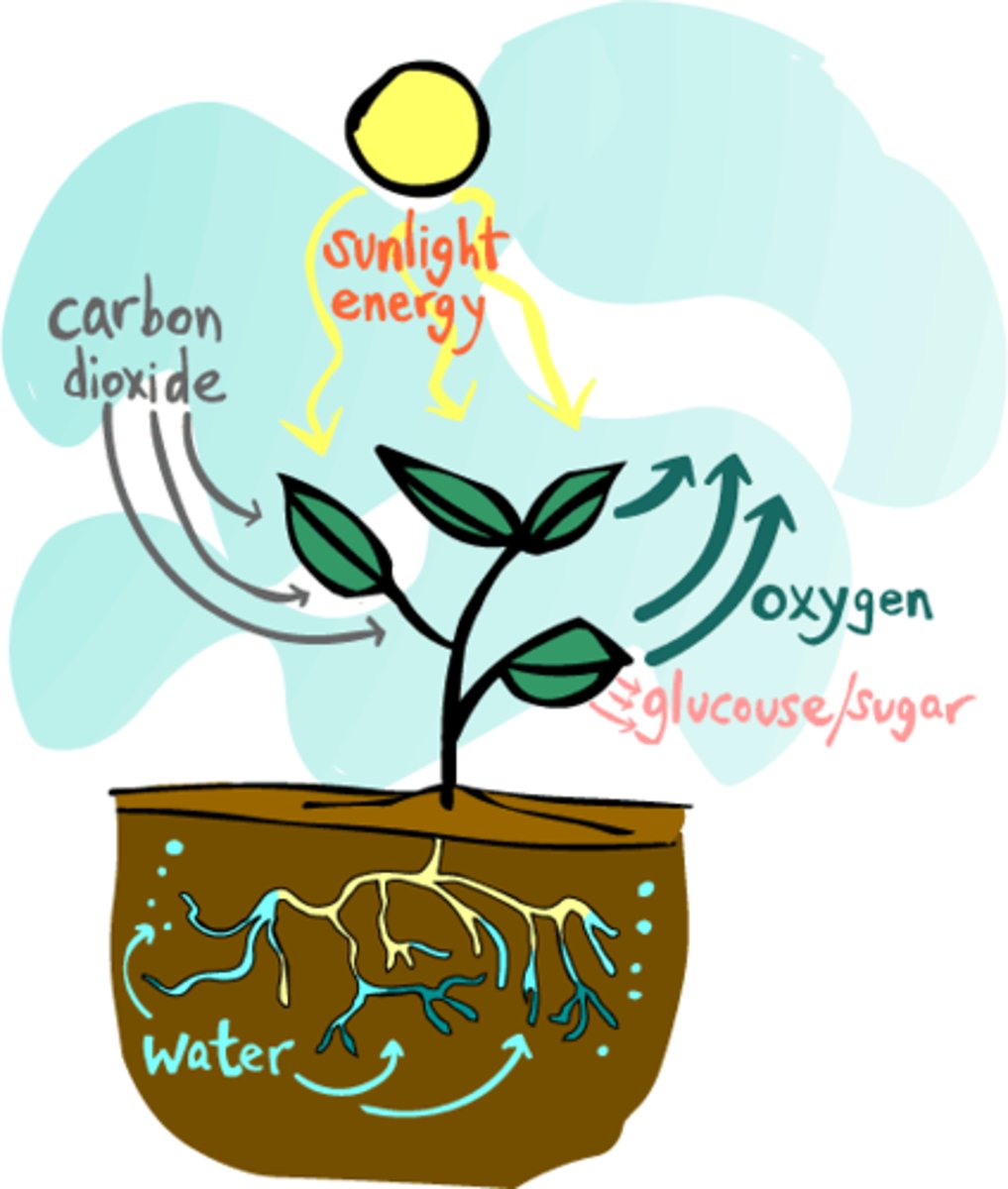
Conversion of light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in the bonds of carbohydrates(food)
pigment
A colored chemical compound that absorbs light

chlorophyll
A green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plants, algae, and some bacteria

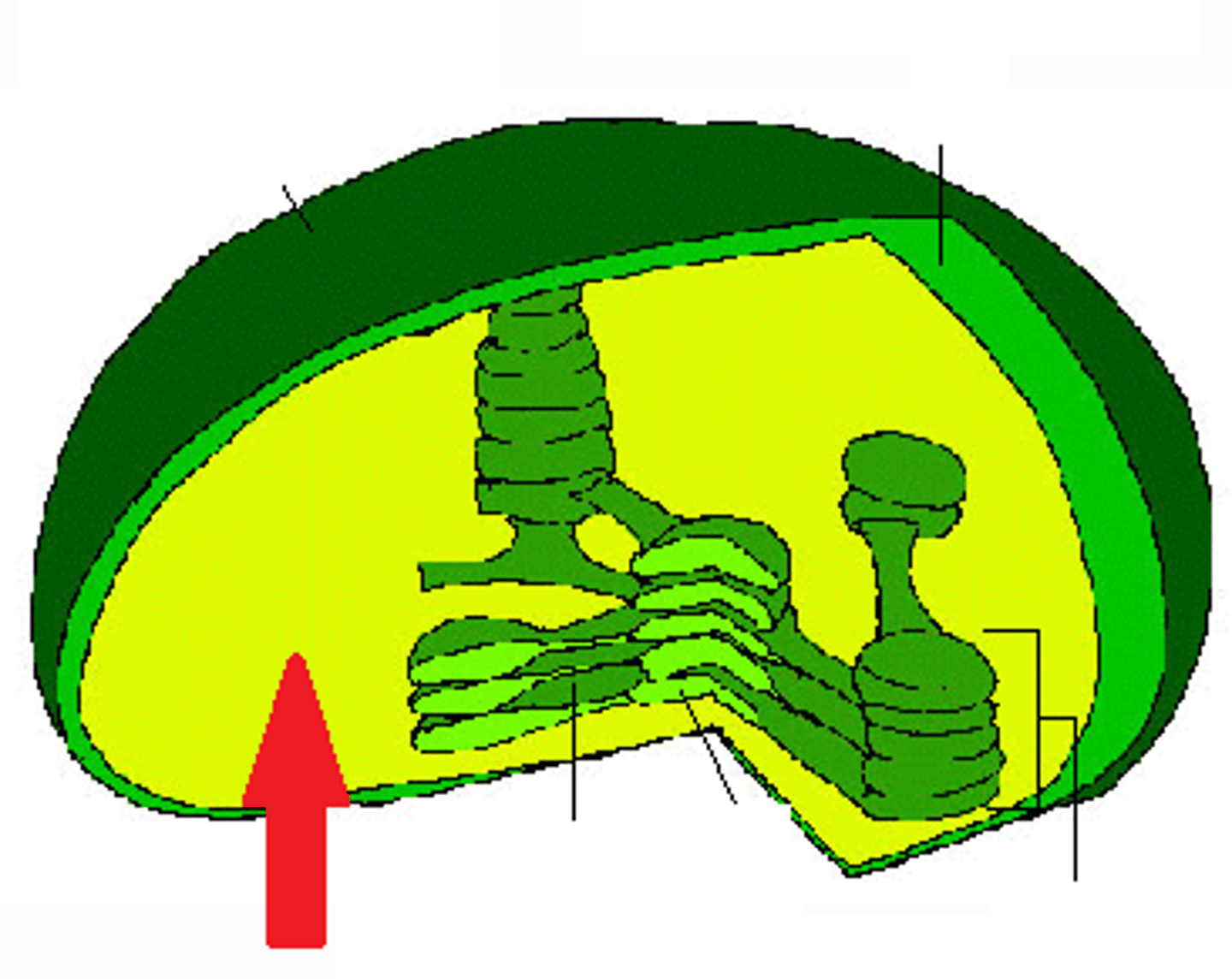
thylakoid
A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy into chemical energy.
stroma
The fluid of the chloroplast surrounding the thylakoid membrane; involved in the synthesis of glucose from carbon dioxide and water.
NADPH
carrier molecule produced in the light dependent reactions that transfers high-energy electrons and hydrogen to the Calvin Cycle
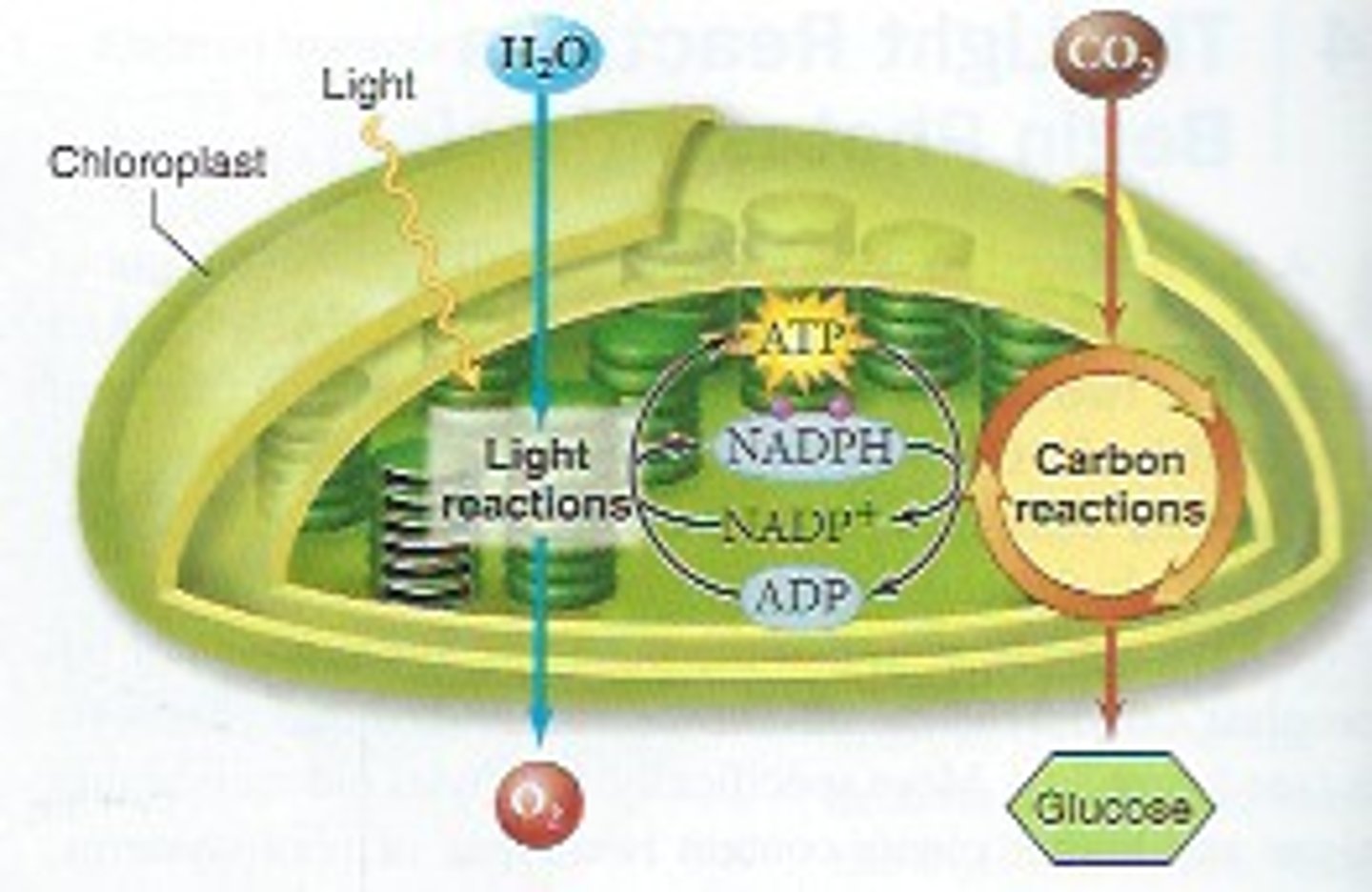
light-dependent reactions
reactions of photosynthesis that use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH
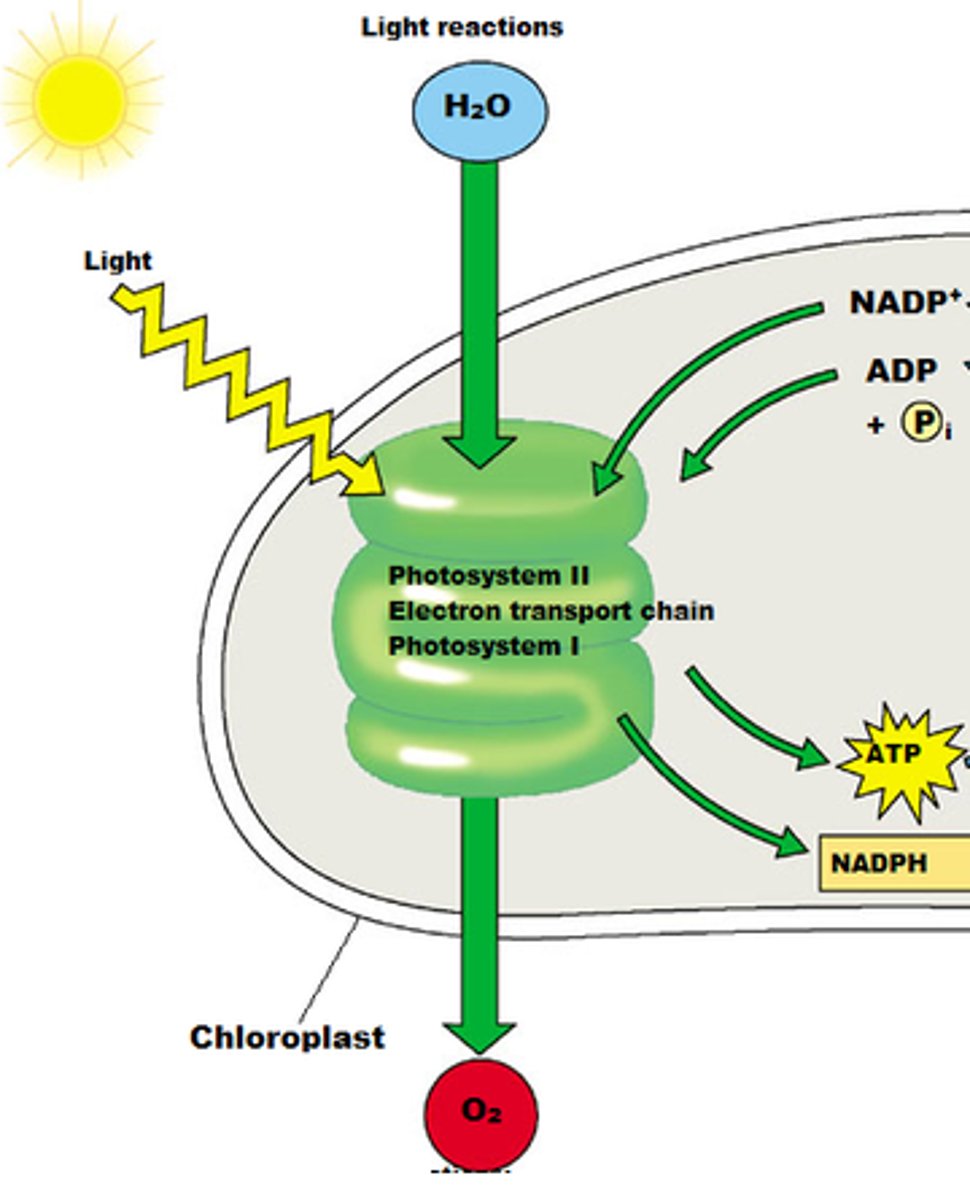
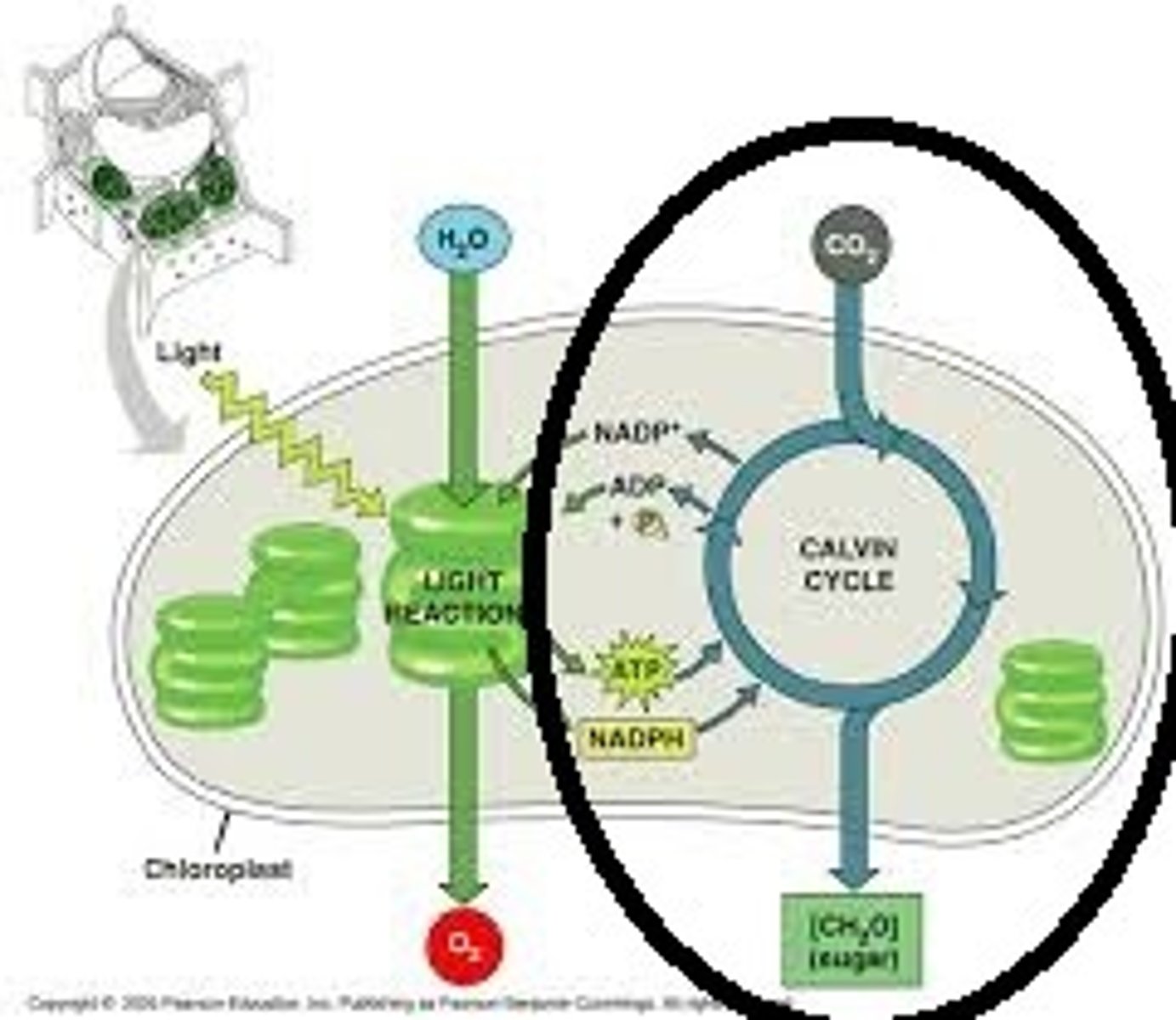
Calvin Cycle
(Or light independent reactions)
reactions of photosynthesis in which energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build high-energy compounds such as sugars from CO2 from the atomosphere
Sun
The ultimate source of energy for life
Autotrophs
Organisms capable of making their own food
Plants
Autotrophs that transform light energy into glucose that can be used for food or building blocks
Heterotrophs
Organisms that consume food for energy and building blocks
ATP
one of the principal chemical compounds that cells use to store energy form of energy used by cells to do work
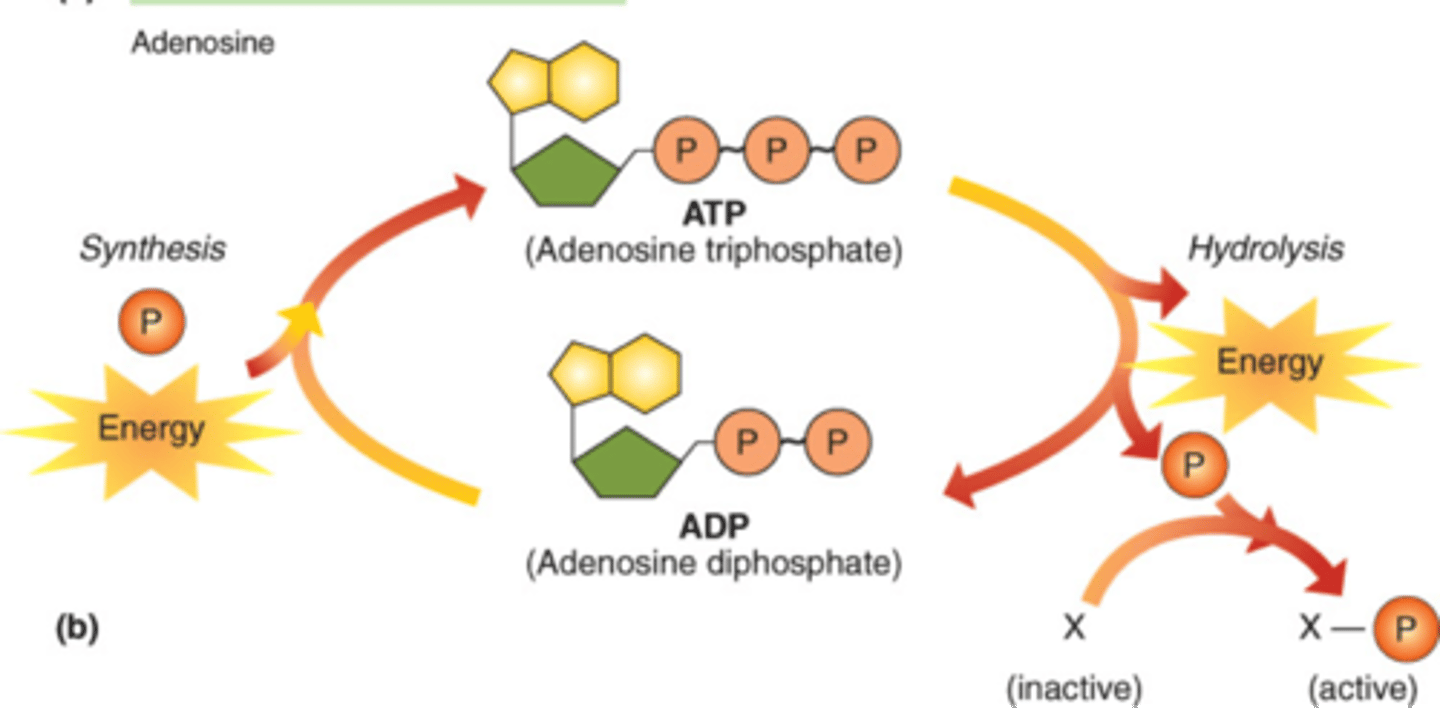
ADP
After ATP releases energy by transferring a phosphate to something else
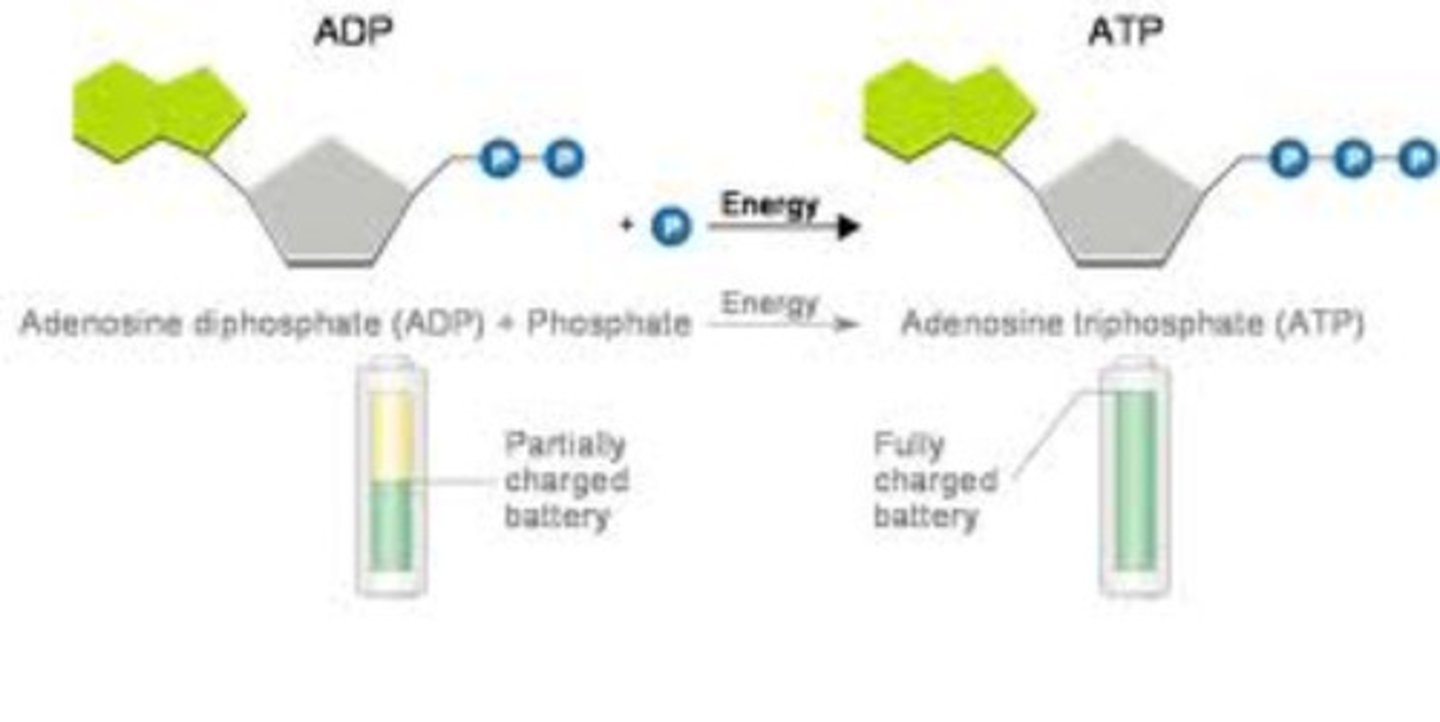
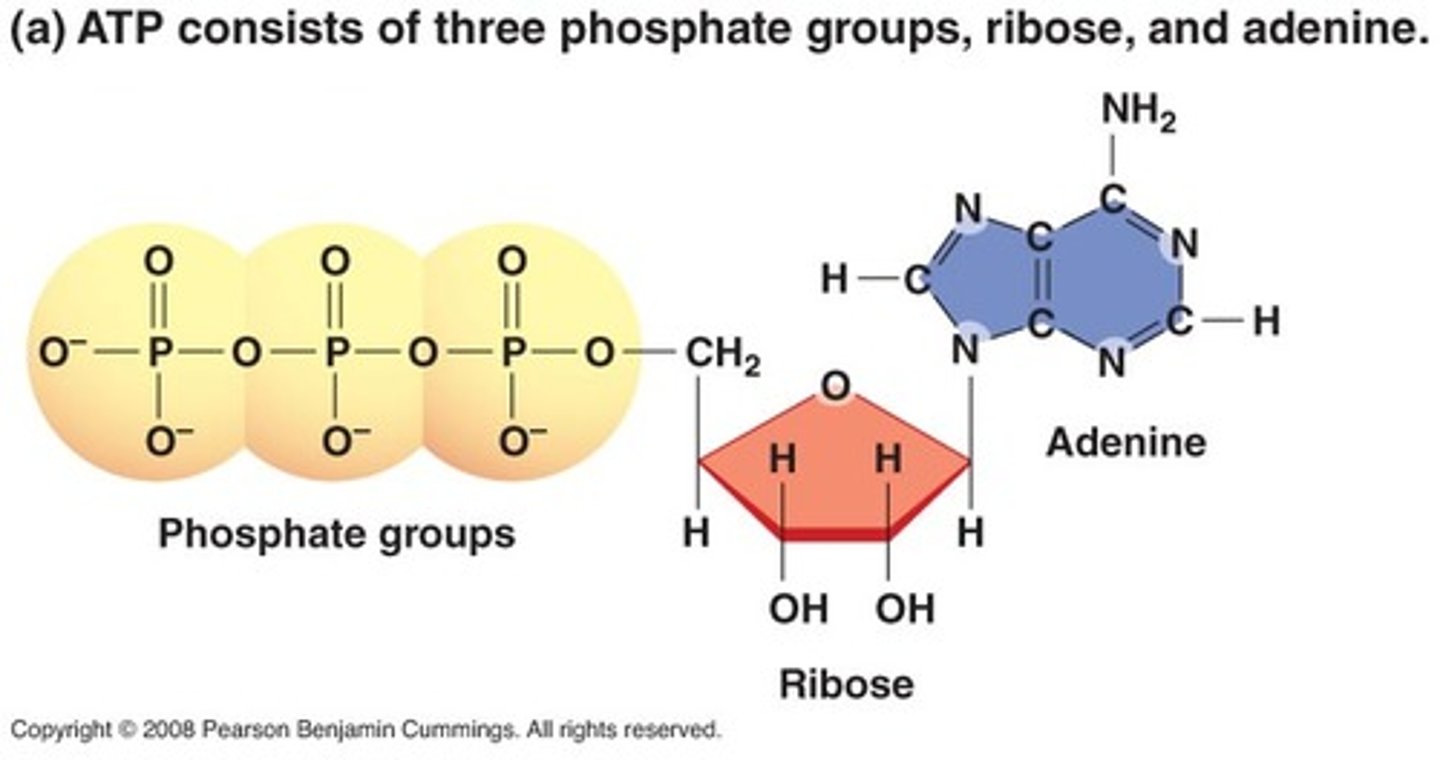
Structure of ATP
Adenine, Ribose, and 3 Phosphate groups
Food
The energy source used to turn ADP back into ATP
Chemical reaction of photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H20 (light)-> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Carbon dioxide + water (light) sugars + oxygen
Reactants of Photosynthesis
Carbon Dioxide + water
Products of Photosynthesis
Sugars (primarily glucose) + oxygen
Pigments
Light absorbing molecules that gather the sun's energy; found in plants
Chlorophyll
Principal pigments in plants
green
Pigments reflect electromagnetic wavelenght of this color
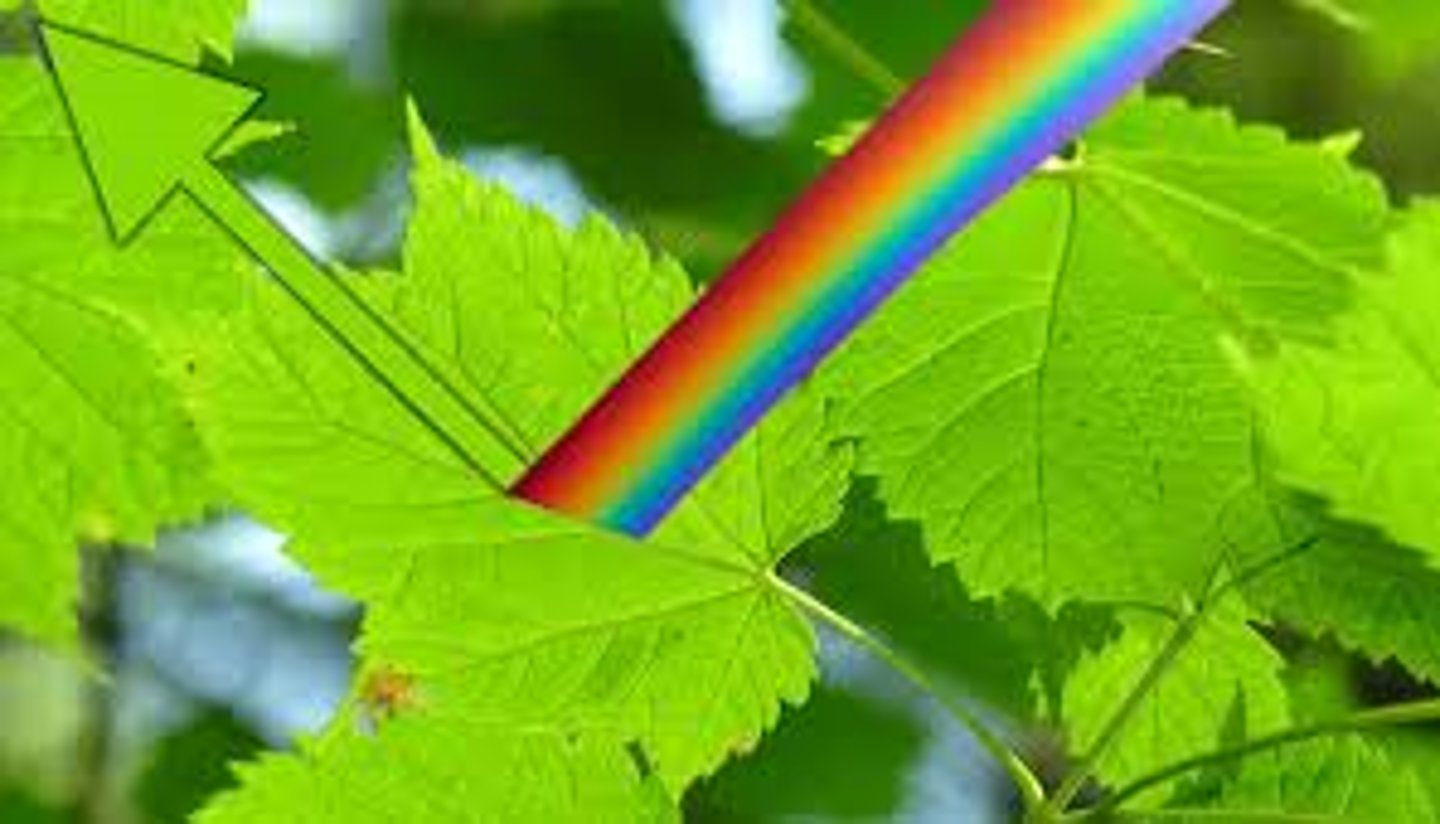

Blue-violet and Red
Colors of visible light chlorophyll absorbs well
2 main stages of photosynthesis
1) Light Dependent Reactions
2) Light Independent Reactions or Calvin Cycle
Reactant of light dependent cycle
water, NADP+ and ADP
Product of light dependent cycle
Oxygen, NADPH and ATP
Reactants of Calvin Cycle
carbon dioxide, NADPH and ATP
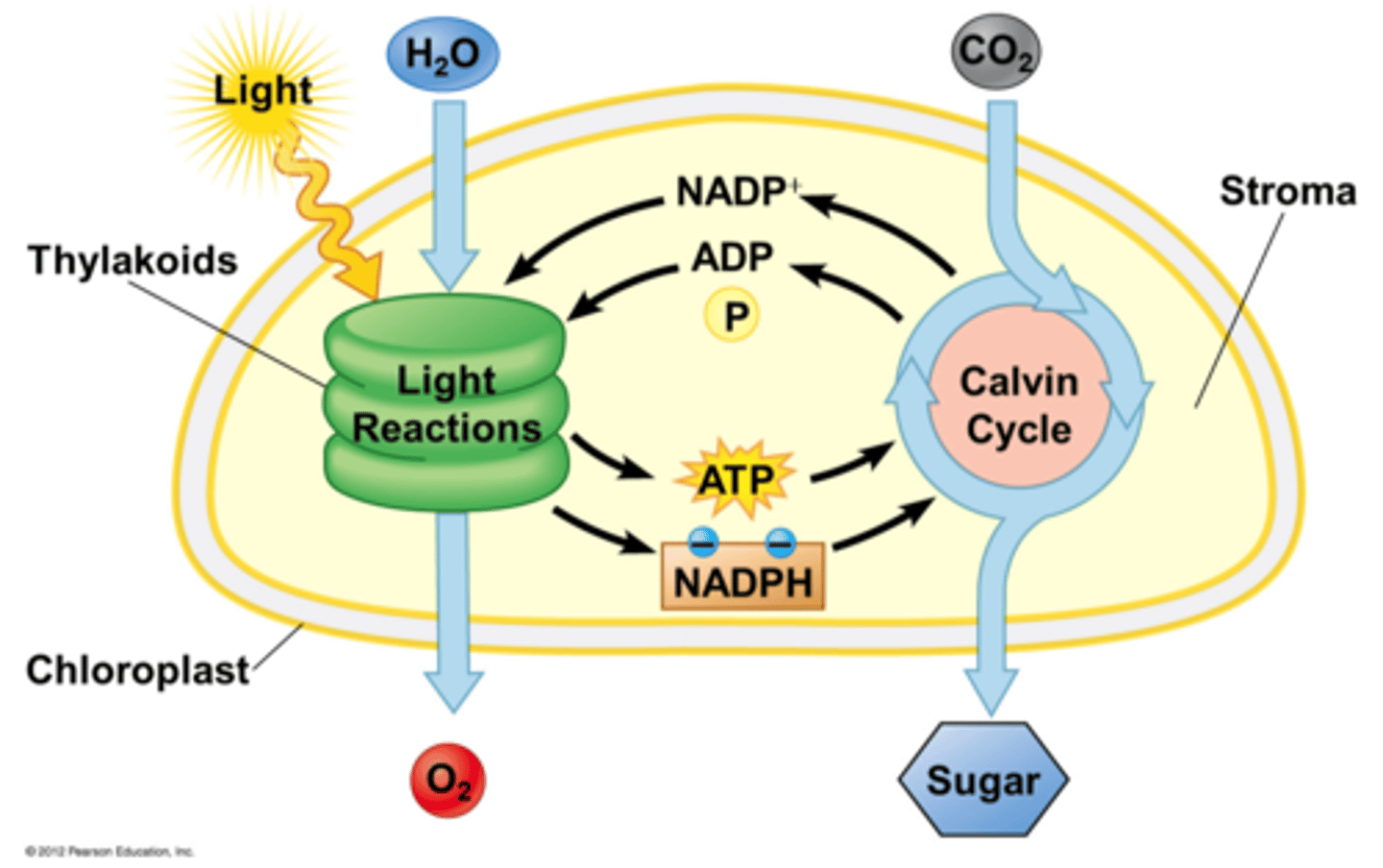
Products of Calvin Cycle
Glucose, NADP+ and ADP
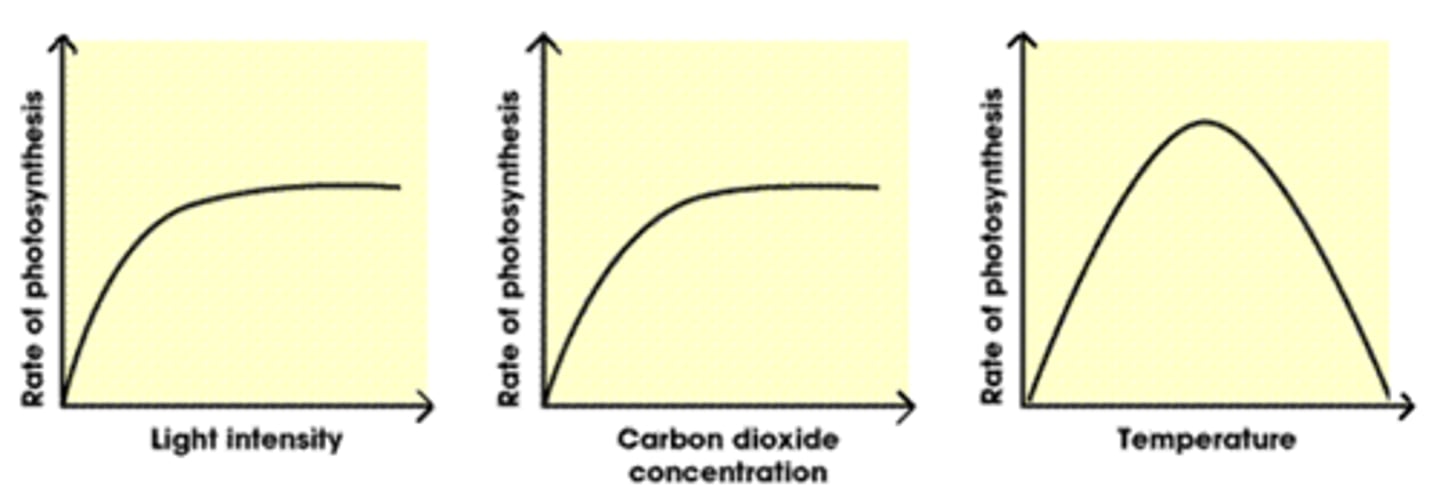
Factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis
The amount of light, carbon dioxide, water and temperature
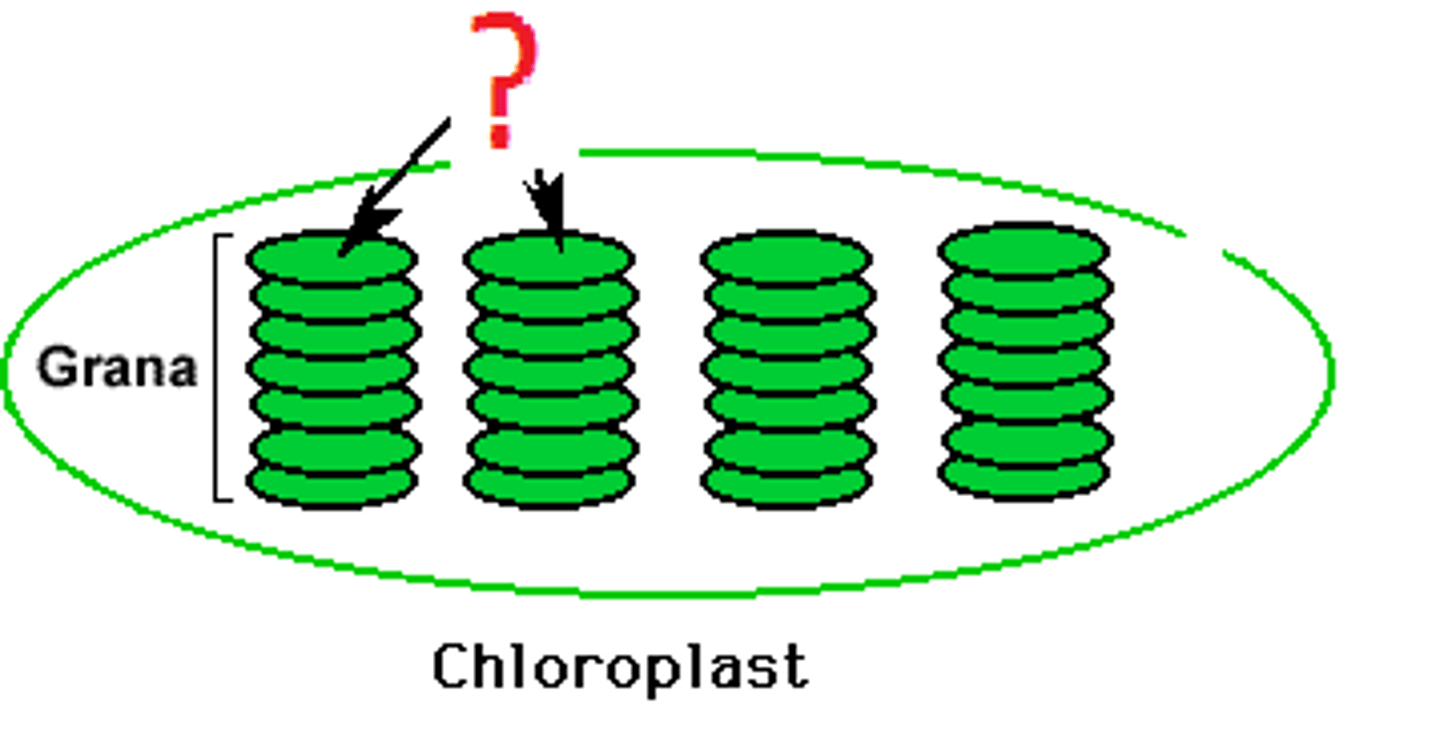
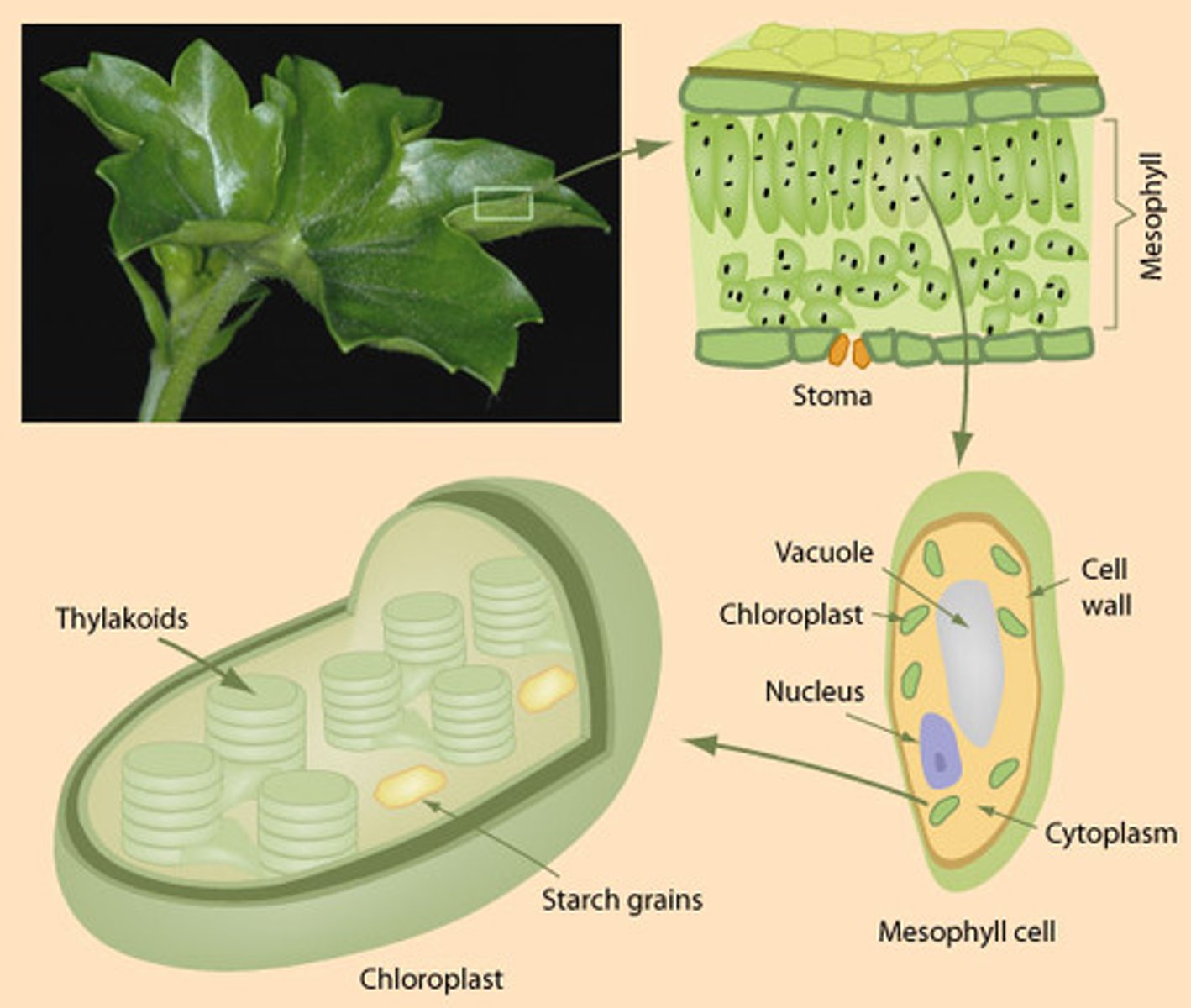
Chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
grana (granum)
stacks of thylakoids
electron carriers
molecules that can carry high energy electrons through the electron transport chain
Photosystem
cluster of chlorophyll and proteins found in thylakoids
photosystem II (PS II)
1st of two light harvesting units in thylakoid membrane that passes excited electrons to reaction-center chlorophyll makes ATP
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
series of electron carrier proteins that shuttle high-energy electrons during ATP-generating reactions
photosystem I
One of two light-harvesting units of a chloroplast's thylakoid membrane; it uses the P700 reaction-center chlorophyll. makes NADPH
ATP synthase
Large protein that uses energy from H+ ions to bind ADP and a phosphate group together to produce ATP
CAM plants
A plant that uses crassulacean acid metabolism, an adaptation for photosynthesis in arid conditions. In this process, carbon dioxide entering open stomata during the night is converted to organic acids, which release CO2 for the Calvin cycle during the day, when stomata are closed.