Schematic Diagrams and Circuits - (Physics 3)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Schematic diagram
A representation of a circuit that uses lines to represent wires and different symbols to represent components
Wire/Conductor
Wires that connect elements are conductors
Wires offer negligible resistance, they are represented by straight lines
Symbol for wires/conductors

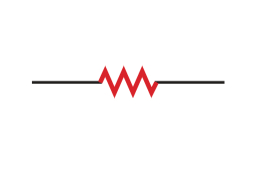
Resistor/Circuit load
Resistors are shown having multiple bends, illustrating resistance to the movement of charges
Symbol for resistors/circuit loads
Bulb/Lamp
The multiple bends of the filament indicate that the light behaves as a resistor
Symbol for bulb/lamp

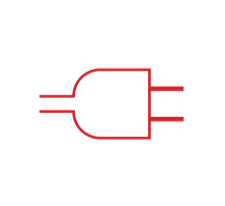
Plug
The emf between two prongs of a plug is symbolized by lines unequal length
Symbol for a plug
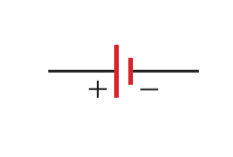
Battery
Differences in line length indicate a potential difference between positive and negative terminals of the battery
Symbol for a battery
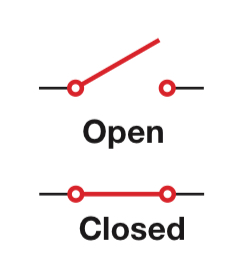
Switch
Circles used to indicate two places where contact is made with wires
Most switches work by breaking only one of the contacts, not both
Symbol for switches
Capacitor
Parallel lines used to symbolize two parallel plates of equal length
A curves line can indicate the usage of only direct current sources with polarity
Symbol for a capacitor
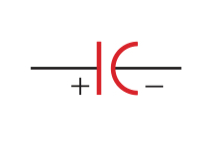
Electric current
What is formed when combining a bulb, battery, switch, and wire
Circuit diagram
A schematic diagram for a circuit
Load
Any element or group of elements in a circuit that dissipates energy
Closed circuit
A closed-loop path for electrons to follow
Open circuit
An incomplete path, no charge flow and no current
Short circuit
Without a load, the circuit contains little resistance to the movement of charges
Without potential difference,
There is no charge flow and no current
Emf
Electromotive force (energy per unit charge supplied by a source of electric current)
Electromotive force (emf)
Any device that increases the potential energy of charge circulating in a circuit
Terminal voltage
When charges move conventionally in a battery / the potential difference across the battery’s terminals
Small internal resistance can be represented with
An emf source and an internal resistance beside each other
(a battery symbol and resistor/circuit load symbol beside each other)