M2: BACTERIAL MORPHOLOGY, GROWTH REQUIREMENTS, THE CELL, BACTERIA STRUCTURE
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
ASK:
A - Attitude (heart)
S - Skill (hands)
K - Knowledge (head)
Anatomy of a Nurse
Bacteria
- A member of a large group of unicellular microorganisms that have cell walls but lack organelles
- Can cause disease
- Metabolically active single-celled prokaryotic bacteria divide by binary fission
Bacteria Morphology
Size, shape, and morphological arrangement of various bacteria can be easily viewed with a compound light microscope
Average coccus - is about 1um in diameter
Average bacillus - is about 1um wide x 3um long
Mycoplasma, the smallest microbe
Bacteria Size
Binary Fission
Bacteria Reproduce by?
Binary Fission
bacteria divide; one cell splits in half to become two daughter cells
Cocci - spherical
Bacilli - rod shape
Spirilla - spiral shape
Bacteria Basic Shapes
1. Diplococci
2. Streptococci
3. Staphylococci
4. Tetrad
5. Sarcina / Octad
6. Coccobacilli
7. Diplobacilli
8. Streptobacilli
9. Palisade
10. Vibrio
11. Spirochetes
12. Spirilla
Variety of Morphologic Arrangements
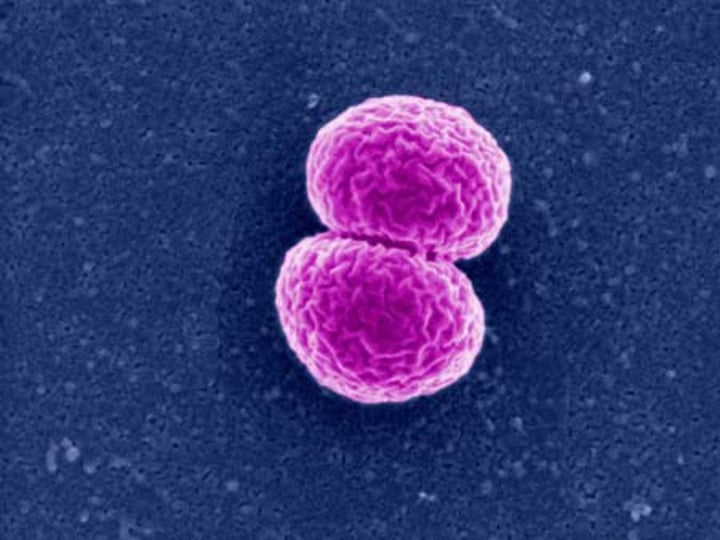
Diplococci
- singular: diplococcus
- cocci that divide and remain attached in pairs
- Examples: Streptococcus pneumonia, Moraxella catarrhalis, Enterococcus spp, Neisseria gonorrhea
Streptococci
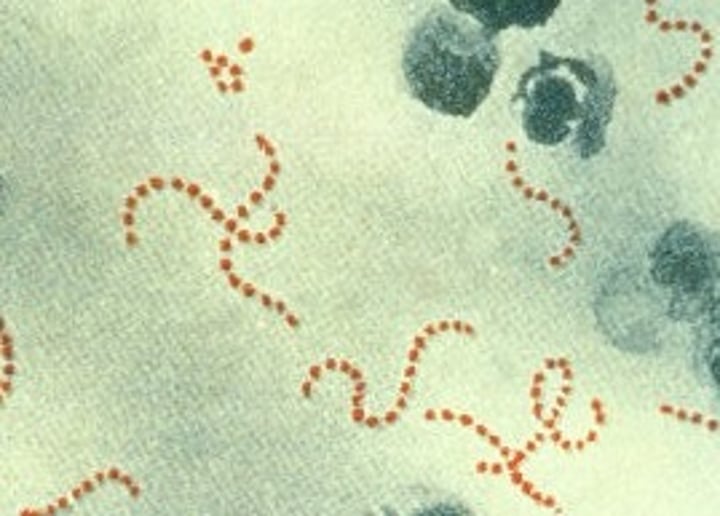
- singular: streptobacillus
- rods that remain attached in chains after cell division
- Examples: Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumonia, Streptococcus mutans
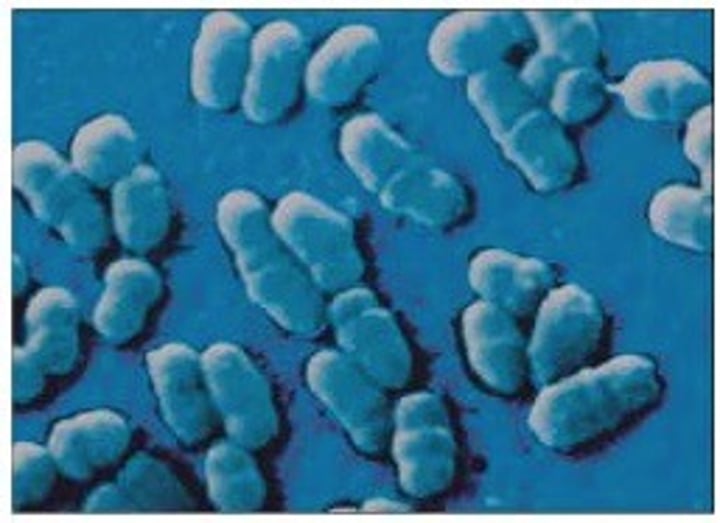
Staphylococci
- singular: staphylococcus
- cocci in a grape like cluster or broadsheet
- Examples: Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus capitis

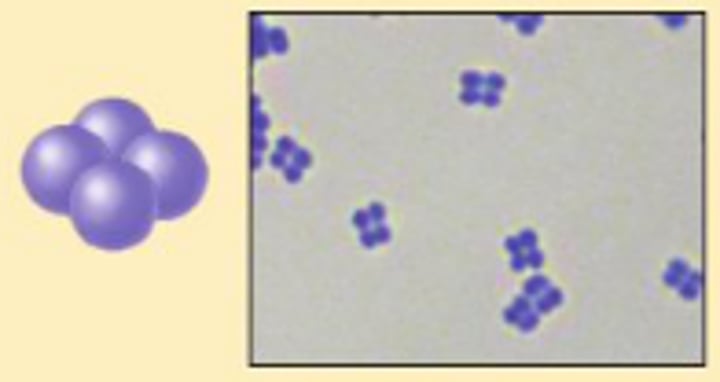
Tetrad
- a group of four cocci
- Examples: Aerococcus Pediococcus Tetragenococcus
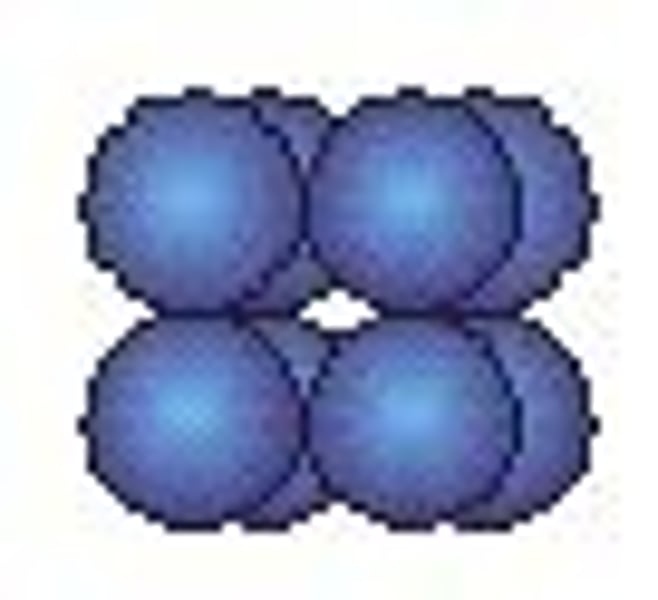
Sarcina / Octad
- plural: sarcinae
- a group of eight bacteria that remain in a packet after dividing
- Examples: Sarcina aurantiaca, Sarcina lutea, Sarcina ventriculi
Coccobacilli
- plural: coccobacilli
- a bacterium that is an oval rod
- Examples: Chlamydia trachomatis, Haemophil
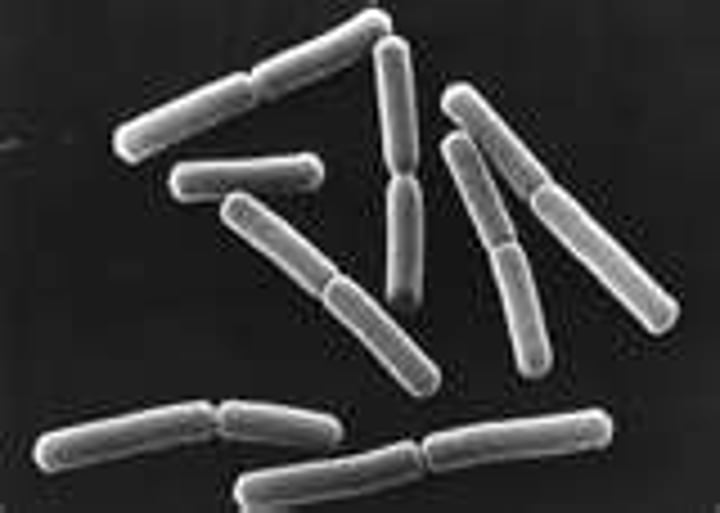
Diplobacilli
- singular: diplobacillus
- rods that divide and remain attached in pairs
- Examples: Coxiella burnetii, Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis, Moraxella bovis
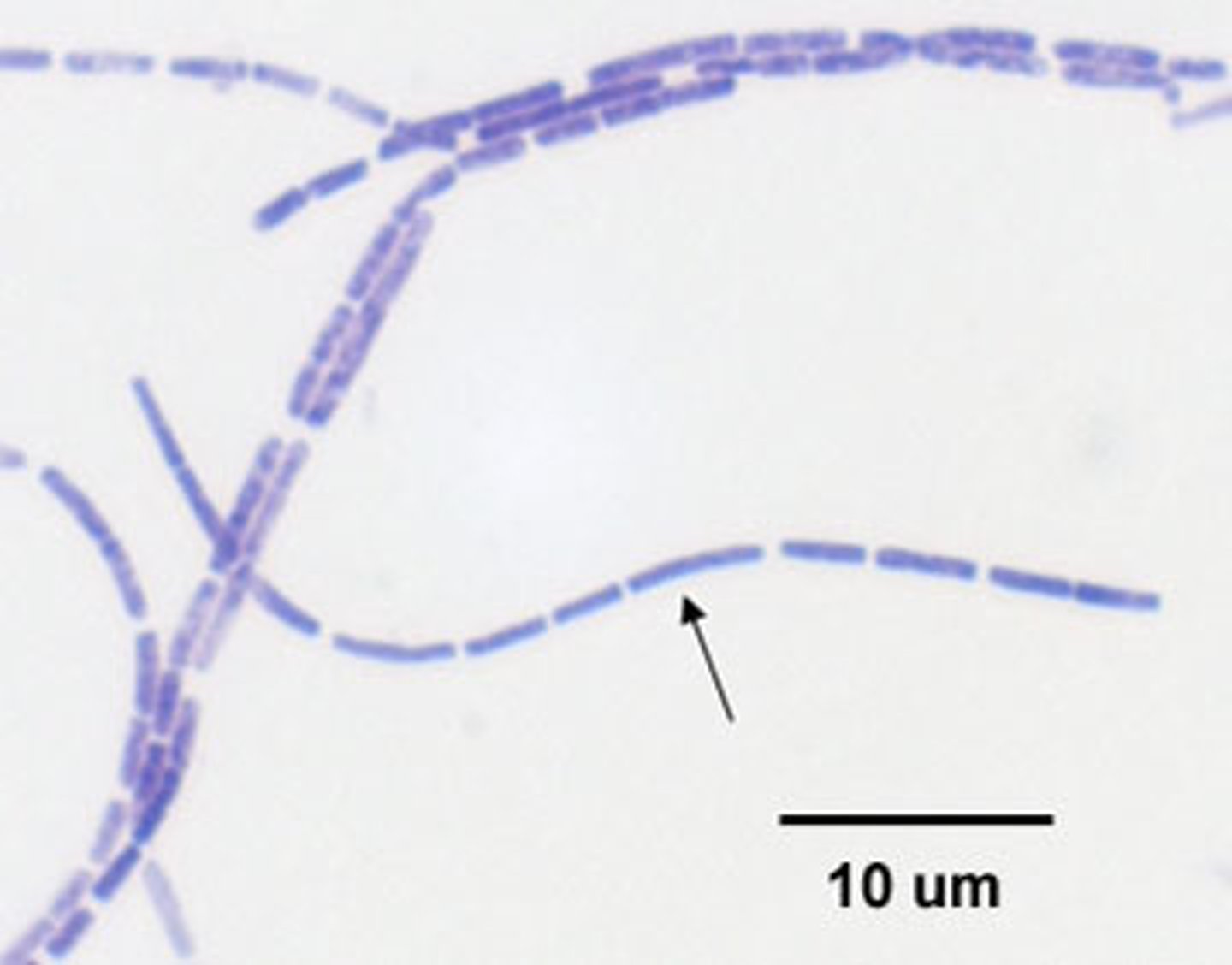
Streptobacilli
- singular: streptobacillus)
- rods that remain attached in chains after cell division
- Examples: Streptobacillus moniliformis, Streptobacillus levaditi, Streptobacillus felis, Streptobacillus hongkongensis
Palisade
- picket fence-like shape due to a bend at the site of division during cell division;
- bacilli stack up next to each other, side by side
- Examples: Corynebacterium diphtheria that causes diphtheria

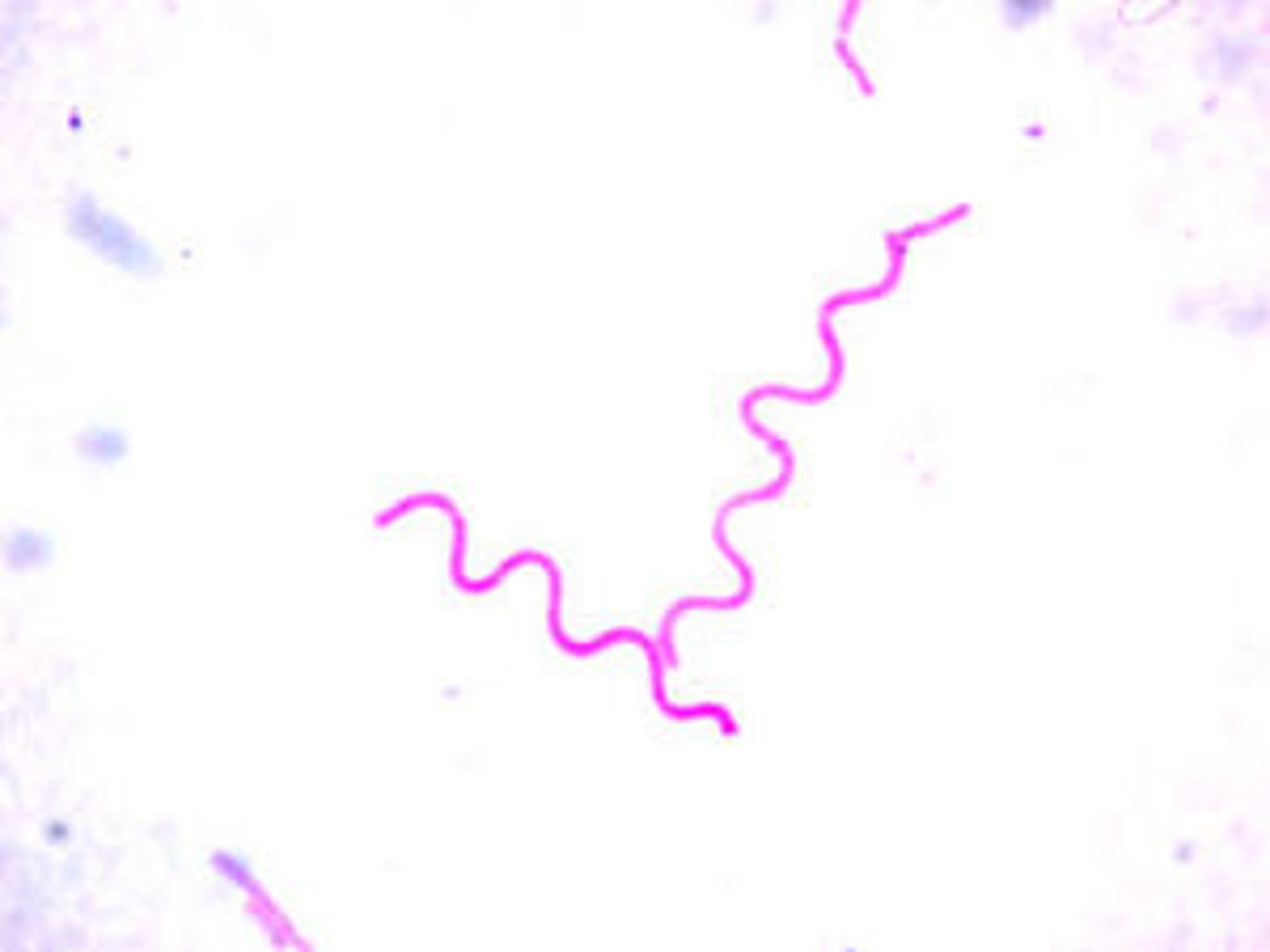
Vibrio
- these are the comma shaped bacteria that are slightly bent
- Examples: Vibrio mytili, Vibrio anguillarum, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Vibrio cholera
Spirochetes
- are spiral bacteria that have a helical shape
- flexible & have an axial filament which helps in motility
- Examples: Leptospiraspecies (Leptospira interrogans), Treponema pallidum, Borrelia recurrentis
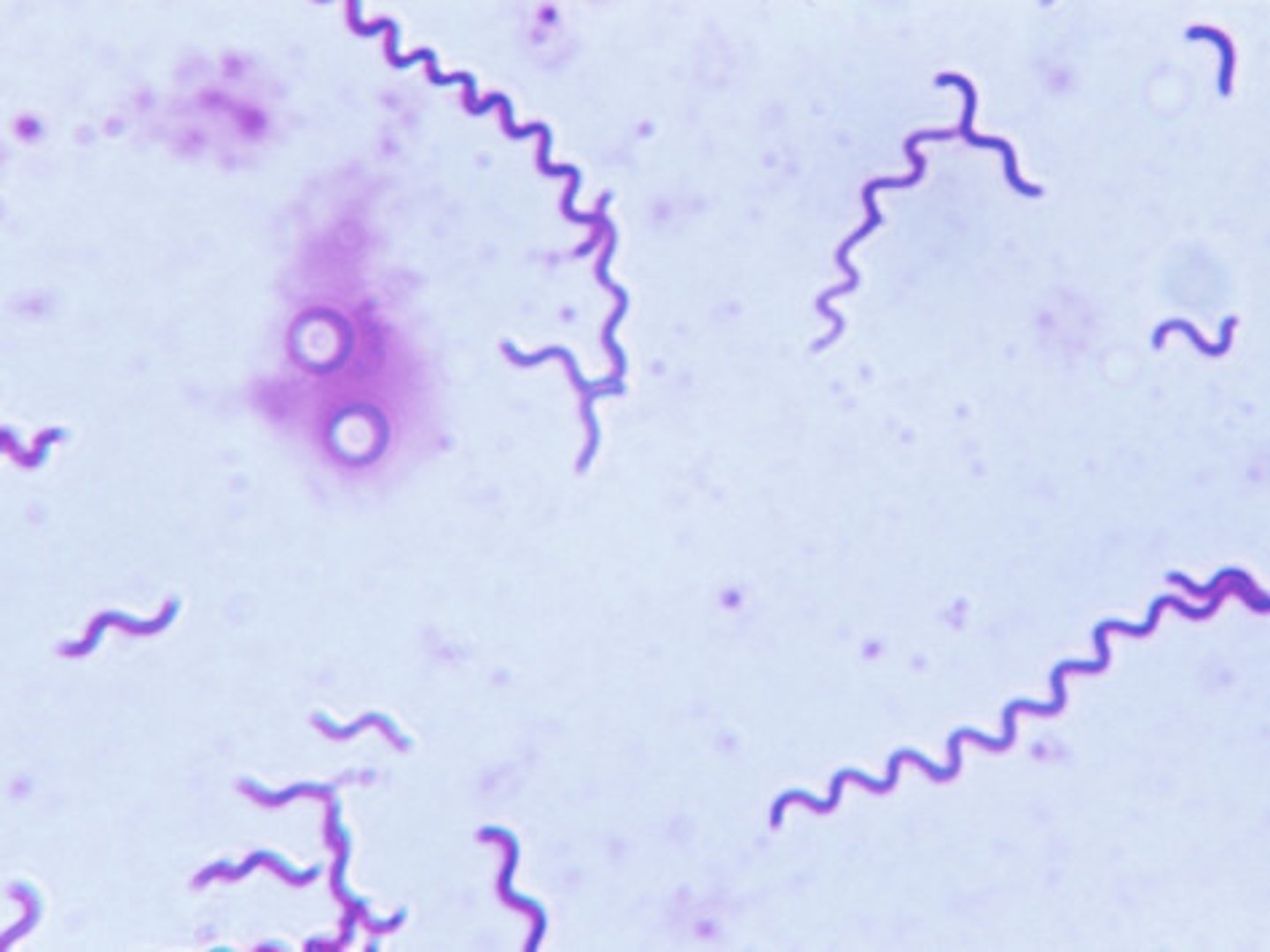
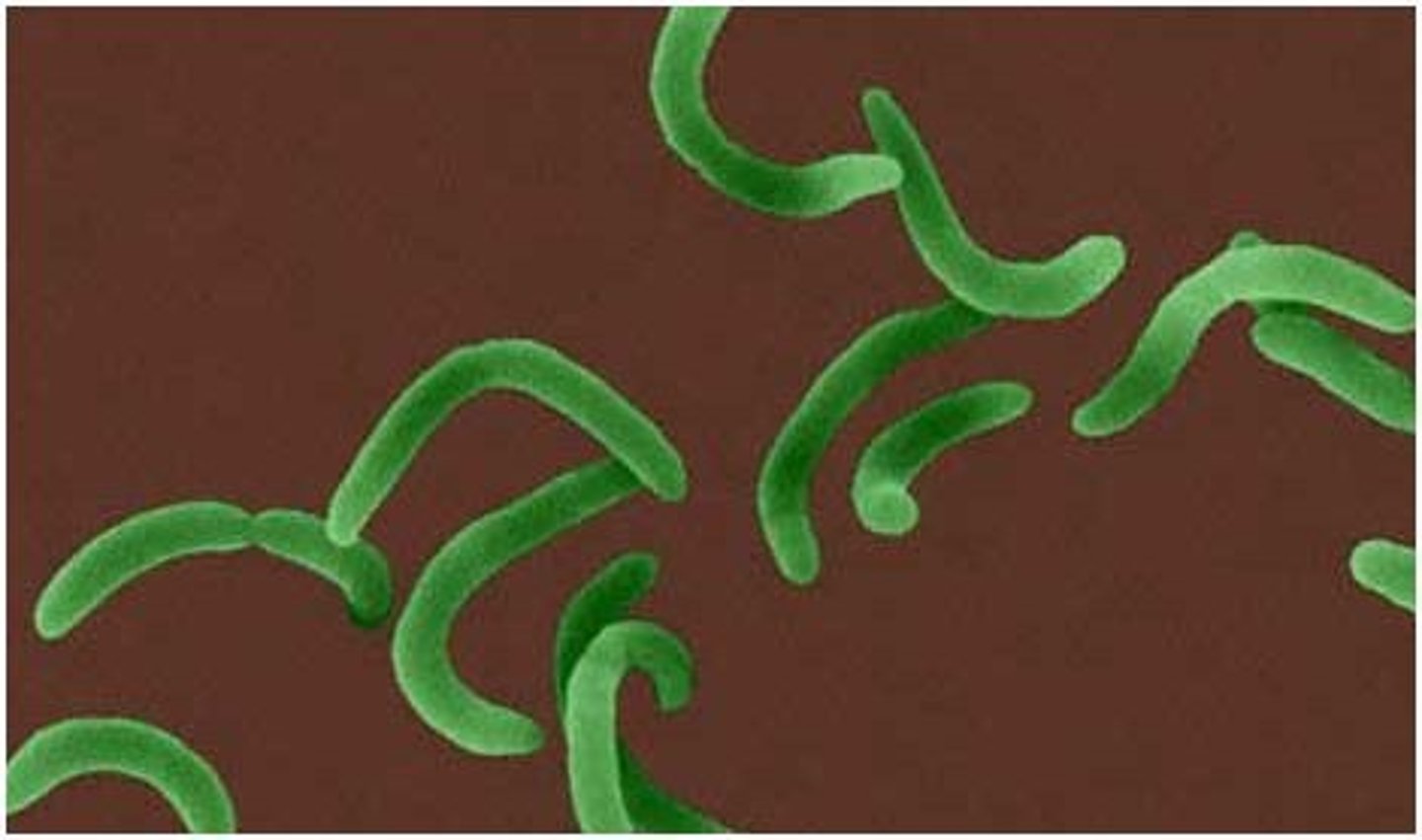
Spirilla
- helical shaped / corkscrew form
- have a similar structure with spirochete but more rigid
- like spirochetes, have a flagellum, but they lack the endo flagella
- Examples: Campylobacter jejuni, Helicobacter pylori, Spirillumwino gradskyi.
- Appendaged Bacteria
- Pleomorphic Bacteria
- Filamentous Bacteria
- Club-shaped Rod Bacteria
Other Shapes and Arrangements
Appendaged Bacteria
- bacteria that produce a distinct structure such as pillus or fimbriae. - those that produce these appendages are more virulent.
- Example: Neisseria gonorrheae, the agent of Gonorrhea.
Pleomorphic Bacteria
- this category includes bacteria that do not have a defined form.
- they can alter shape, but in pure culture, they appear to have a definite form
- Examples: Mycoplasma pneumoniae, M. genitalium.
Filamentous Bacteria
- this category includes bacteria that do not have a defined form.
- they can alter shape, but in pure culture, they appear to have a definite form
- Examples: Mycoplasma pneumoniae, M. genitalium.
Club-shaped Rod Bacteria
-these bacteria are thinner on one side than the other - Ex. Corynebacterium
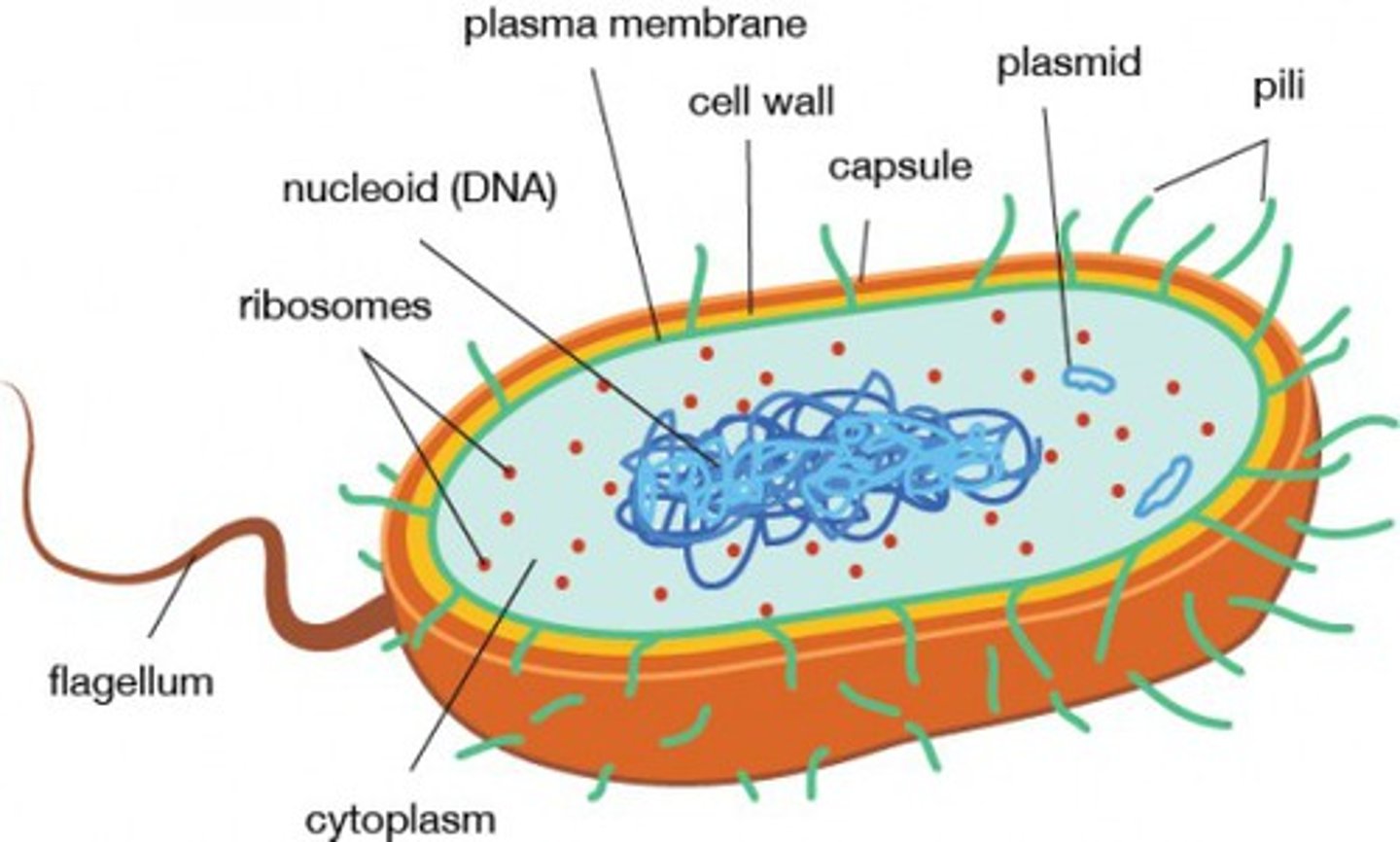
1. Glycocalyx
2. Cell wall
3. Outer Membrane
4. Cell Membrane
Bacteria Envelope Structures
Glycocalyx
- The external surface of a plasma membrane that is important for cell-to-cell communication
- has capsule and slime layer
Capsule
A sticky layer that surrounds the cell walls of some bacteria, protecting the cell surface and sometimes helping to glue the cell to surfaces.
Slime layer
a glycocalyx that is unorganized and loosely attached to the cell wall
Cell wall
- also known as Murein Sacculus
- outermost component of all bacteria is the cell wall (except Mycoplasma species, which are bounded by a cell membrane, not a cell wall)
- principal component is -
-PEPTIDOGLYCAN (aka murein)
- provide rigidity strength, and protection
- has murein
murein
bacteria exoskeleton that completely surrounds the cell
Gram +
Gram -
Two Types of Gram
Gram positive
- thick layer / multi-layered
- has Teichoic acid and Polysaccharides
Teichoic acid
- responsible for flexibility of cell wall of the microorganisms
- a polysaccharide found in grampositive cell walls
Polysaccharides
- carbohydrate consisting of many sugar units; glycogen, cellulose, and starch are examples
Gram negative
- thin layered / monolayer
- surrounded by an outer membrane
- has presence of a plasma membrane located outside of the peptidoglycan layers, known as the outer membrane
- has lipoprotein, periplasmic space, acid-fast
Lipoprotein
-- large molecules known as lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
- anchored into the outer membrane and project from the cell into the environment
Periplasmic space
The space between the plasma membrane and outer membrane of Gram negative cell wall
Acid-fast
- outer-layer is lipid-rich; myolic acids (hydrophobic)
- inner layer is peptidoglycan
Outer Membrane
- Gram (-) bacteria's outer membrane
- made of LPS (LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE)
- Has Lipid A and O polysaccharide
Cell Membrane
- other name cytoplasmic membrane
- located beneath the cell wall
- encloses the cytoplasm of cell
- cell sac or plasma membrane
- selective permeable
- property of a plasma membrane to allow certain molecules and ions to move through the membrane while restricting others
Antibiotic
Destroy the peptidoglycan or inhibit the synthesis of forming cell wall
Anti-fungal
Destroy the cell membrane
1. Flagella
2. Pili or Fimbriae
3. Axial filaments
Projecting Structures
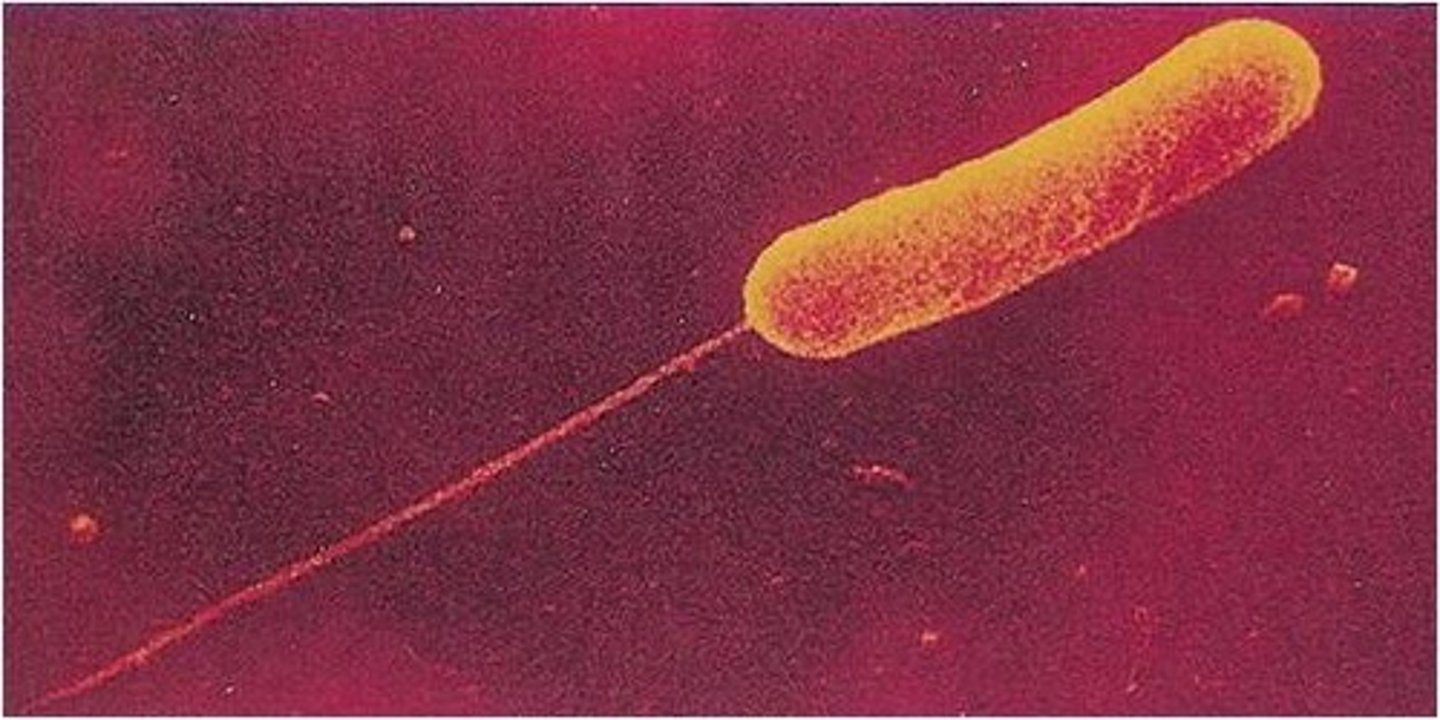
Flagella
whiplike tails found in one-celled organisms to aid in movement
Taxis
- movement of a bacterium toward or away from a particular stimulus
Polar
- Molecule with partial charges. Mixes with water.
- at one or both ends of the cell
monotrichous
a single flagellum
lophotrichous
a tuft of flagella coming from one pole
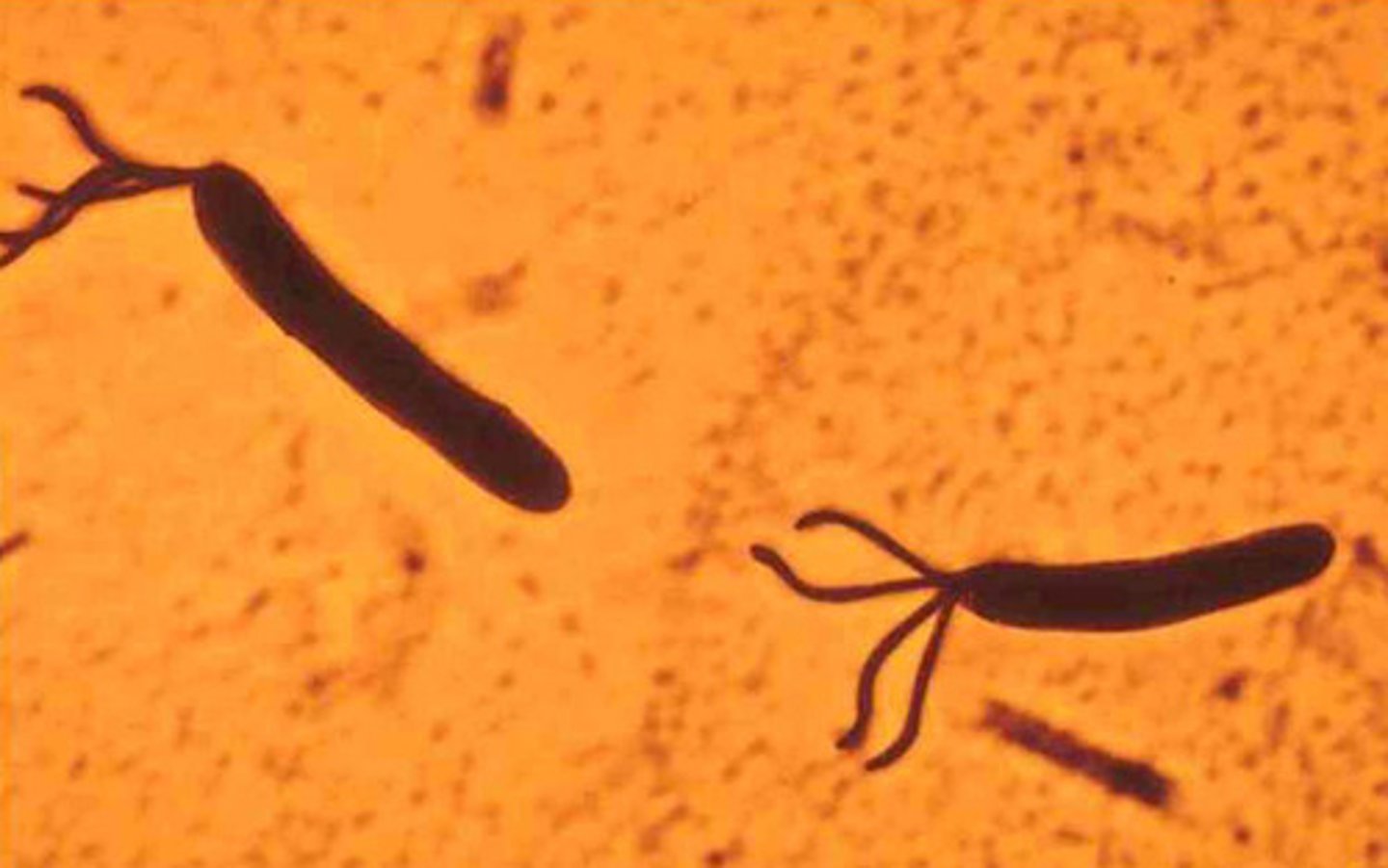
amphitrichous
flagella at both poles of the cell
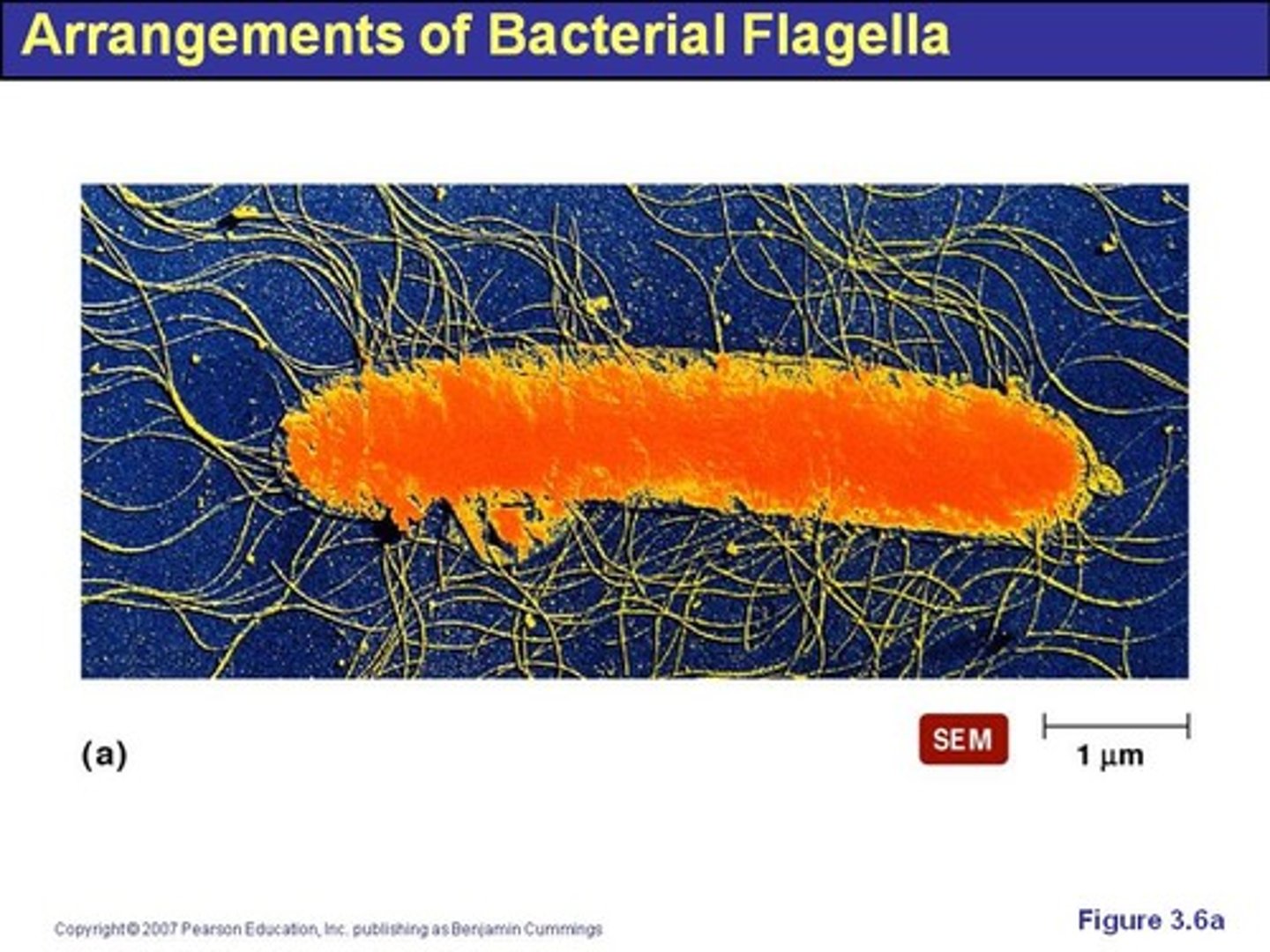
Peritrichous
having flagella distributed over the entire cell
Atrichous
bacteria that lack flagella

Pili or Fimbriae
function is adherence to cell surface
Fimbria
plural: fimbriae
an appendage on a bacterial cell used for attachment
Pilus
plural: pili
an appendage on bacterial cell; for Conjugation & gliding motility
Conjugation
transfer of genetic material from one cell to another involving cell-to-cell contact
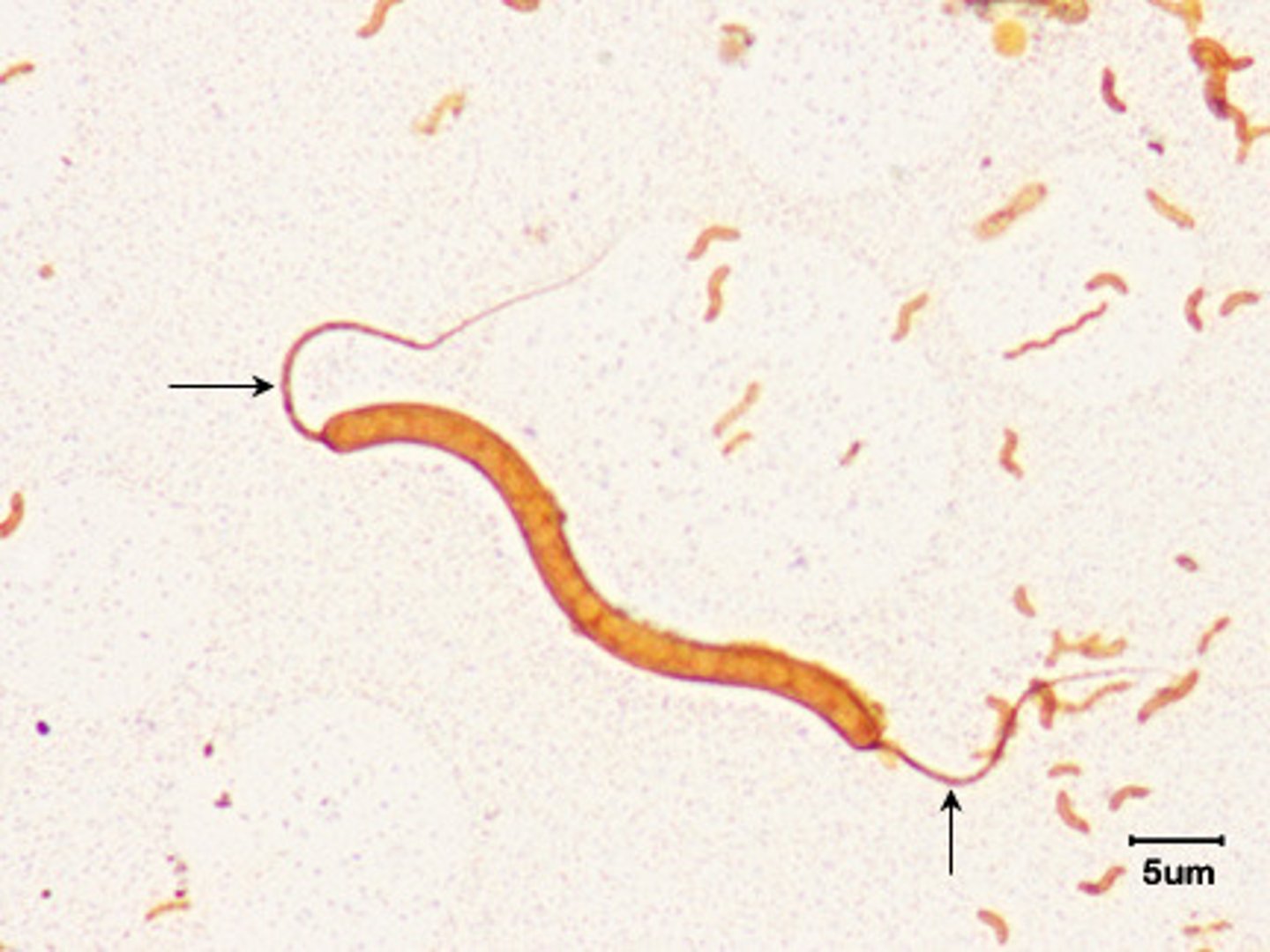
Axial filaments
structure for motility found in spirochetes; also called endoflagellum
other name bundle of fibrils
function is motility
Cytoplasm (Cytoplasmic Membrane)
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
In a prokaryotic cell, everything is inside the plasma membrane
Nucleoiod
Mesosomes
Ribosomes
Granules
Endospores
Internal Structures of the Cytoplasm
Nucleoid
Region in a bacterial cell containing CHROMOSOMES
single circular, double-stranded DNA
Chromosomes
What does a nucleoid contain?
Mesosomes
an extension of the cell membrane that folds into the cytoplasm and increases surface area.
Serve in DNA replication and guide distribution of duplicated bacterial chromosomes into the two daughter cells during cell division
bacterial binary fission
process bacteria use to carry out cell division
(a) DNA Cycle that includes DNA replication and chromosome segregation
(b) Division Cycle that leads to cytokinesis and cell separation
Two segments of bacterial cell cycle
DNA CYCLE
includes DNA replication and chromosome segregation
DIVISION CYCLE
leads to cytokinesis and cell separation
Ribosomes
tiny spherical organelles that make proteins by joining amino together
function: protein synthesis
70S Proteins
all prokaryotes have 70S (where "S" = Svedberg units) ribosomes
composed of TWO SUB-UNITS:
50S
30S
Svedberg unit
offers a measure of particle size based on its rate of travel in a tube subjected on high G-force
Inclusion Bodies
Also referred to as "GRANULES"
a granule or viral particle in cytoplasm
or nucleus of some infected cells
Important in the identification of infectious viruses.
storage vessels of GLYCOGEN as a reserve for carbohydrates and energy
Main Function of Inclusion Bodies
Endosperes
resting structure formed inside SOME bacteria.
Allows bacterium to produce a dormant and highly resistant cell to preserve the cell's genetic material in times of extreme stress.
dipiclonic acid (DPA)
protects endospore genome from UV light.
plays roles in endospore heat resistance
Sporulation
aka "sporogenesis"
process of spore and endospore formulation
Vegetative State
normally-growing cell that forms the endospore
Germination
the process of beginning to grow from a spore to an endospore
(a) Endotoxins
(b) Exotoxins
Types of Toxins
Endotoxins
released only when bacteria die and their cell walls break down
activates host complement and coagulation cascades
causes septic shock
non-disease specific symptoms: fever, pain, shock, fatigue, discomfort
Exotoxins
produced and secreted
can result in severe disease-specific symptoms
ex: cholera, botulinum, diphtheria, tetanus toxin
(a) Enterotoxins
(b) Neurotoxins
(c) Cytotoxins
three main categories of extoxins
1. Carbon
2. Nitrogen, Sulfur, Phosphorous
3. Inorganic Ions
4. Growth Factors
Bacterial Growth Reuirements
Carbon
an essential element in building every macromolecule
Nitrogen
used in protein/amino acid synthesis and nucleic polymerization
Phosphorus
essential in nucleic acid synthesis and form of phospholipids
Sulfur
present in certain amino acids such as cysteine and methionine.
Inorganic Ions
small amounts of inorganic ions are required by all bacteria
Ex: Sulfur, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, and calcium
Growth Factors
some bacteria cannot synthesize cell constituents
organisms can display wide variety of factor requirements
(a) Amino Acids
(b) Nucleotide Bases
(c) Enymatic Cofactors or "vitamins"
Typical Growth Factor Molecules
Vitamins
referred to as enzymatic cofactors
1. Moisure/Water
2. Oxygen
3. Temperature
4. pH
5. Osmotic Condition
Physical Requirements of Bacyeria
Moisture (water)
medium in which bacteria acquire nutrients
Oxygen
Include the following:
obligates aerobes - AEROPHILIC
obligate anaerobes
microaerophiles
facultative anaerobes
aerobes
Bacteria that require oxygen to grow
anaerobes
Bacteria that grow in the absence of oxygen and are destroyed by oxygen
Microaerophiles
require oxygen concentration lower than air
Aerobes that require Oxygen levels from 2-10% and have a limited ability to detoxify Hydrogen Peroxide and Superoxide Radicals
Facultative Anaerobes
can live with or without oxygen
Temperature
include the following:
mesophiles
pyschrotrophs
psychrophiles
hyperthermophiles
mesophiles
moderate temperature loving microbes
Psychrotrophs
microbes that have a maximum temperature for growth above 20 degrees C and are widespread in NATURAL environments and in foods.
causes food spoilage
Psychrophiles
have a maximum temperature for growth at 20 degrees C or below and are restricted to permanently COLD habitats.