3.2) Cell Surfaces & Junctions
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Cytoskeleton
These are networks of protein fibers that extend throughout the cell. These fibers provide structural support as well as movement.
From thickest to thinnest:
Microtubules
Intermediate filaments
Microfilaments
What are the three main kinds of fiber that make up the cytoskeleton?
Microtubules
This kind of fiber is straight and hollow tubes composed of proteins called tubulins.
In animal cells, these grow from the centrosome while plant cells have other means of synthesizing as they lack centrosomes.
Intermediate filaments
This fiber is found in cells of most animals, these reinforce cell shape and anchor some organelles.
For example, the outer layer of our skin is made of dead skin cells composed of this type of fiber.
Microfilaments
also called actin filaments
these help support the cell’s shape particularly in animal cells that lack cell walls.
these fibers are also involved in cell movements
True
True or False?
The plasma membrane is usually considered as the boundary of the cell, but most cells secrete materials outside the plasma membrane.
extracellular matrix (ECM)
animal cells produce this and it helps hold cells together and protects and supports the plasma membrane.
glycoproteins (proteins bonded with carbohydrates)
What is the main component of ECM?
integrins
The ECM may attach to the cell through other glycoproteins that bind to membrane proteins called _______?
As their name implies, they function in integration, i.e., transmit signals between the ECM and cytoskeleton; communicating changes occurring within and outside of the cell.
Tight junction
Anchoring junction
Gap junction
Neighboring animal cells often interact and communicate through specialized junctions between them. What are the three main types of cell junctions?
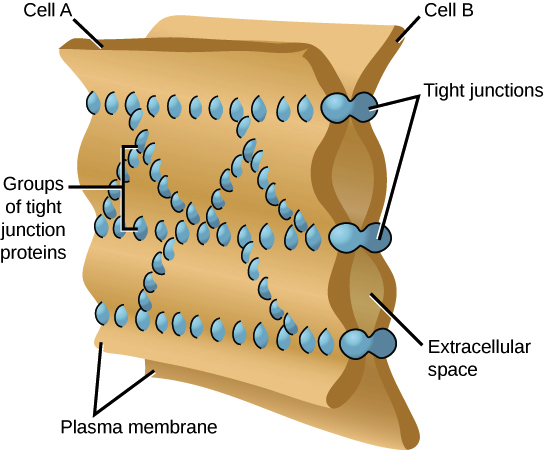
Tight junctions
This type of junction occurs when the plasma membrane of neighboring cells is knit tightly together by proteins.
They prevent leakage of fluid across a layer of cells.
For example, the food we ate and are within our digestive tract do not leak because of these cell junctions
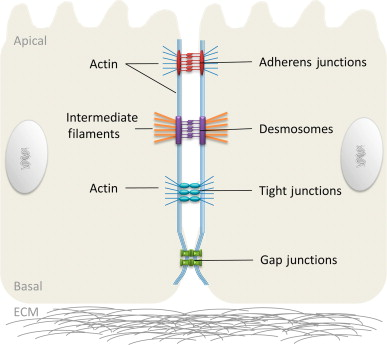
Anchoring junctions
This type of junction fasten cells into strong sheets.
These junctions are connected to the cytoplasm by intermediate filaments.
These junctions are common in tissues subjected often to stretching such as our skin and muscle
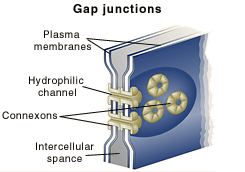
Gap junctions
also called communicating junctions, allow small molecules to flow through protein-lined pores between cells.
These junctions are common in babies in the womb since communication between the mother and the developing baby is necessary for the baby’s development.
pectin
Between adjacent cells is a sticky substance called _____, gluing cells together.
lignin
When the plant cell stops growing, it strengthens the wall. Some cells add a secondary wall next to the plasma membrane. For example, wood consists mainly of secondary walls strengthened by the rigid molecule, ______?
plasmodesmata
These are small channels that pass through the cell walls of plant cells, allowing water, nutrients, and chemical signals to move from one cell to another. These channels help plant cells communicate and share substances directly.
Found only in plant cells
Connect the cytoplasm of neighboring cells
Help in intercellular transport and communication
plasmodesmata
Although cell walls are thick, they do not isolate plant cells from each other. The ___________ allow water and other small molecules to freely move from cell to cell. These structures allow cells in plant tissues to share the water, nourishment, and chemical messages.
Hint: channels