Gene Mutations
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Gene
Section of DNA; coding for a polypeptide
Polypeptide
Chain of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
Genome
All genetic material of an organism, including genes and non coding DNA
Protein
1 or more polypeptide chains folded
Histone
The protein DNA wraps around to form chromatin. Allows DNA to be more compactly packaged
Transcription
Process of copying DNA base sequence into mRNA
Translation
Process of using mRNA base sequence to produce a specific polypeptide chain
What is a mutation?
Change to the DNA bases/nucleotides
Chromosomal Mutations
These affect the whole chromosome/number of chromosomes within a cell
Point mutation
A type of chromosome mutation in which a single nucleotide in the DNA sequence is altered
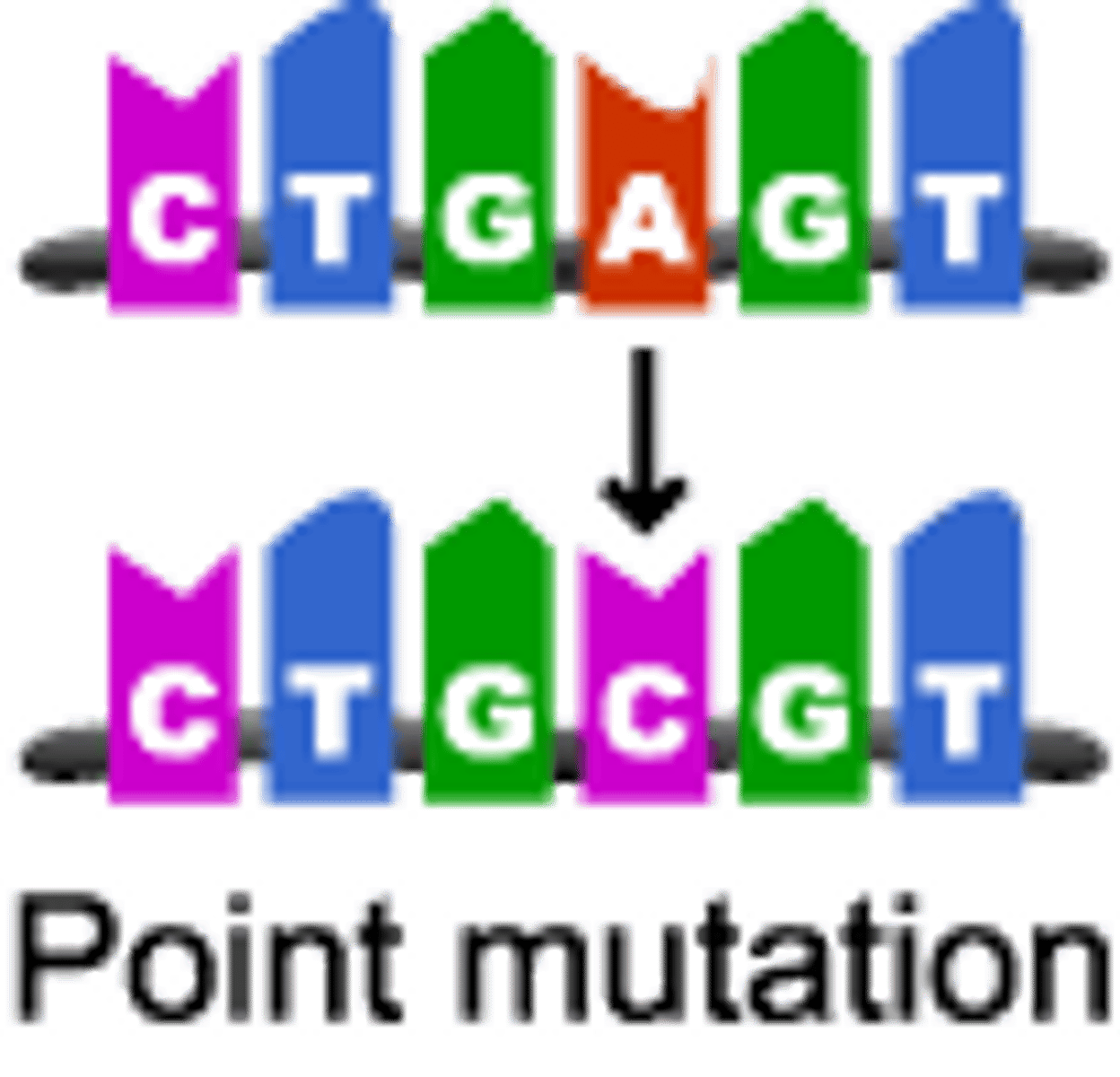
Gene Mutations
These are changes to the base sequence of genes in DNA
Types of Gene Mutation
- Substitution
- Insertion
- Deletion
Substitution:
One or more bases are swapped for others, like A to G

3 types of Substitution Mutation:
- Mis-sense
- Nonsense
- Silent
1) Mis-sense
A substitution causes a different amino acid to be coded for
This change to the primary structure may change the tertiary structure and overall 3D shape of the protein
If this happens, then the functionality of the protein is likely to change.
2) Non-sense
One base is substituted with another and this causes a STOP codon to be created. This will produce a shorter polypeptide that is likely to fold differently. If this happens, then the functionality of the protein is likely to change.
3) Silent
A substitution occurs that has NO effect on the amino acid coded for due to the degenerate nature of the code
Insertion:
One or more bases are added into the sequence of the gene
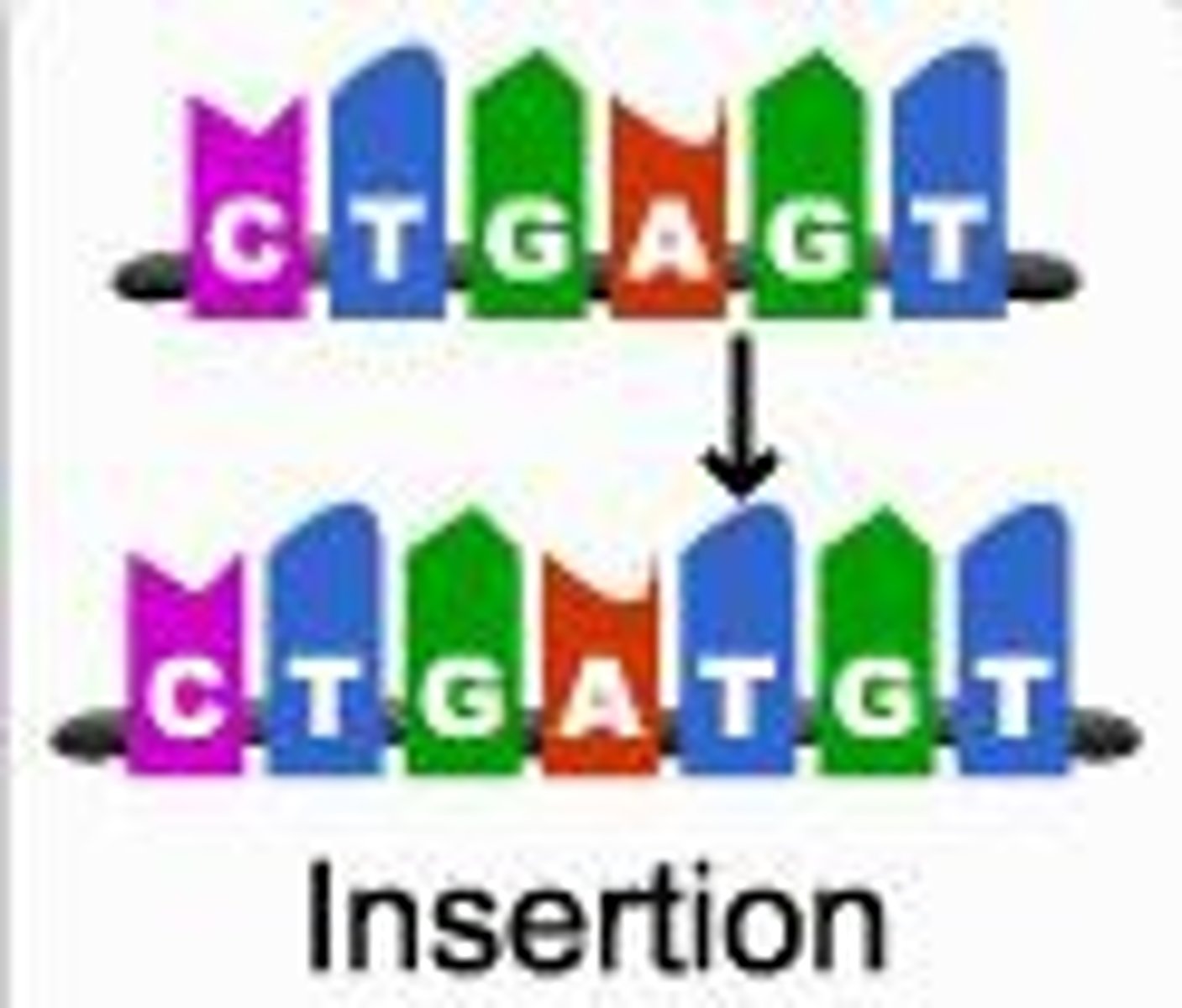
Deletion:
One or more bases are removed from the sequence of the gene

Insertions & deletions cause:
a frameshift
- Every codon after the mutation is affected
- The protein will have a different sequence of amino acids
- And a different tertiary structure
If one or more bases are removed or added to the DNA base sequence of a gene, then...
...a frameshift mutation will occur. The reading frame will now line up different triplets after the point of mutation.
Whole Chromosome Mutation Example
Down Syndrome
Deletions in Chromosomal Mutations
A section of chromosome breaks off and is lost within the cell
Duplications in Chromosomal Mutations
Sections of chromosomes (or entire chromosomes) are duplicated
Translocations in Chromosomal Mutations
A section of one chromosome breaks off and joins another non-homologous chromosome
Inversions in Chromosomal Mutations
A section of one chromosome breaks off, is reversed, and joins back to the chromosome