Android
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
What is Android (3 answers)
A Linux based operating system
Mainly for touchscreen mobile devices
Plus more recently for other platforms
What are the other android platforms
What parts make up the Android Stack (6 answers)
Linux Kernel
HAL (Hardware Abstraction Layer)
Native Libraries
Android Runtime
Android Framework
Applications
What does the Linux Kernel do ?
DRIVERS (DISPLAY, KEYPAD, SHARED MEMORY)
POWER MANAGEMENT
What does HAL do ? (10 answers)
AUDIO
BLUETOOTH
CAMERA
DRM
EXTERNAL STORAGE
GRAPHICS
INPUT
MEDIA
SENSORS
TV
What do the Native Libraries do ? (9 answers)
AUDIO MANAGER
FREETYPE
LIBC
MEDIA FRAMEWORK
OPENGL/ES
SQLITE
SSL
SURFACE MANAGER
WEBKIT
What does android runtime do ? (3 answers)
CORE LIBRARIES
ART
DALVIK VM
What does the Android Framework do ? (3 answers)
CONTENT PROVIDERS
MANAGERS (ACTIVITY, LOCATION, PACKAGE, NOTIFICATION, RESOURCE, WINDOW)
VIEW SYSTEM
What does the Application Layer do ? (6 answers)
ALARM
BROWSER
CALCULATOR
CALENDAR
CAMERA
plus more
What are the ‘Standard’ Apps for Android Development ? (3 answers)
User Interface (UI) + managing data
XML for UI
Java (or Kotlin) for functionality
What are the ‘Non-Standard’ Apps ?
Start with standard, then link to C/C++
Increased performance or 3D graphics
Game engines (Unity)
Scripting (JavaScript, Python, Ruby, etc.)
What are the two ways to run your Application ?
Emulator
Your physical device
What are the main use cases of the emulator ?
Test your functionality, i.e. check that your app runs as expected
Test your layout on multiple devices with different shapes and sizes
What are the 4 main components of Android Apps
Activities
Services
Content providers
Broadcast receivers
What is an Android Activity ? (3 answers)
An Activity is a component that has a UI and some functionality:
The UI is defined in XML
Functionality is defined in Java
What are the 4 main files of the Android File Structure ?
app
manifests
java
java (generated)
res
Gradle Scripts
What are the 4 parts of the res file ?
drawable
layout
mipmap
values
What is in the drawable file
Bitmap files (.png, .9.png, .jpg, .gif) or XML files that are compiled into drawable resource files.
What is in the layout file
XML files defining the architecture for the UI. Both for Activities and components within Activities.
What is in the mipmap file
Drawable files for different launcher icon densities. Only used for launcher icons.
What is in the values file
XML files that contain simple values, such as strings, integers, and colors.
Where is the activity_main.xml file located ?
In the layout file
What is XML and what does it stand for ?
XML = eXtensible Markup Language
Kind of like HTML
BUT XML does not DO anything.
XML is just information wrapped in tags.
Also, unlike HTML, XML does not have pre-defined tags
But Android pre-defines tags for us…
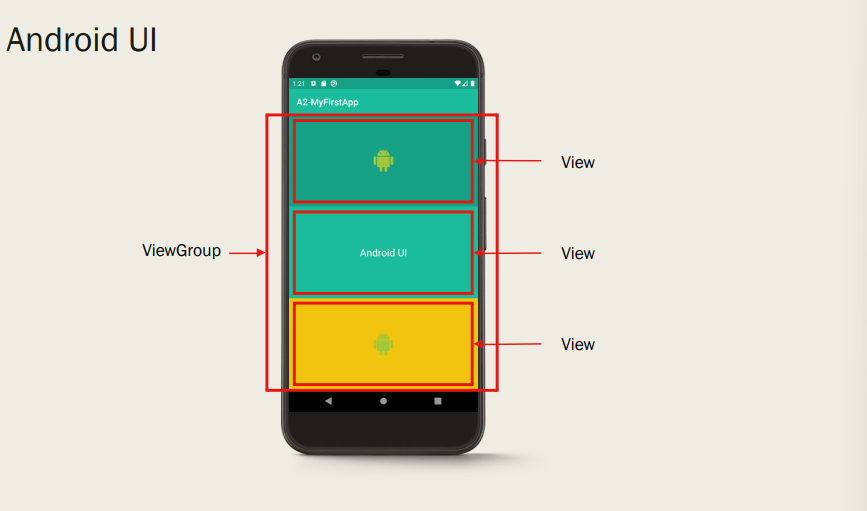
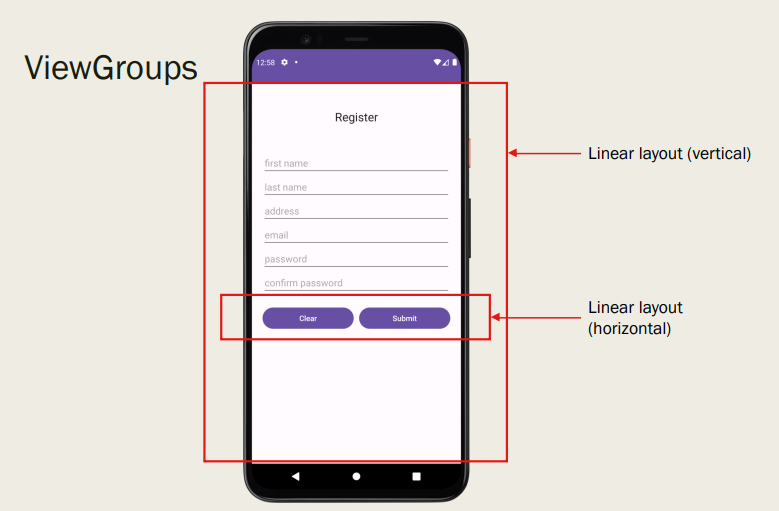
What are the two main components of the Android UI ?
Views – actual widgets that you can see and/or interact with
ViewGroups – describe the layout
What are the main ViewGroups layouts ? (6.5 answers)
LinearLayout
RelativeLayout
ConstraintLayout
WebView
ListView
GridView
+ more
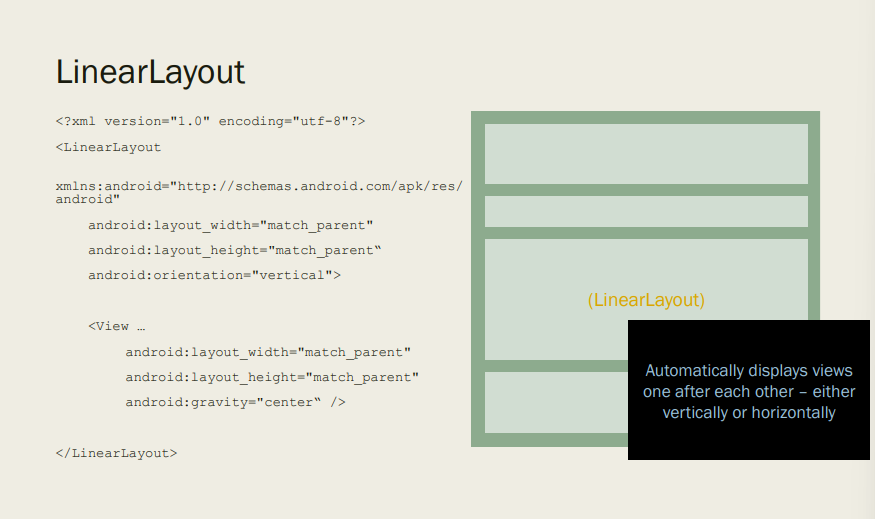
How does LinearLayout work ?
Automatically displays views one after each other – either vertically or horizontally.
How does RelativeLayout work ?
Specify position relative to other views. I.e. below view1, above view2, etc.

How does ConstraintLayout work ?
Similar to relative layout but “more flexible and easier to use”

What are the main Views (8.5 answers)
TextView (label that shows text)
EditText (field for users to enter text)
ImageView (displays an image)
Button
Checkbox
RadioButton
FloatingActionButton
ProgressBar
+ more
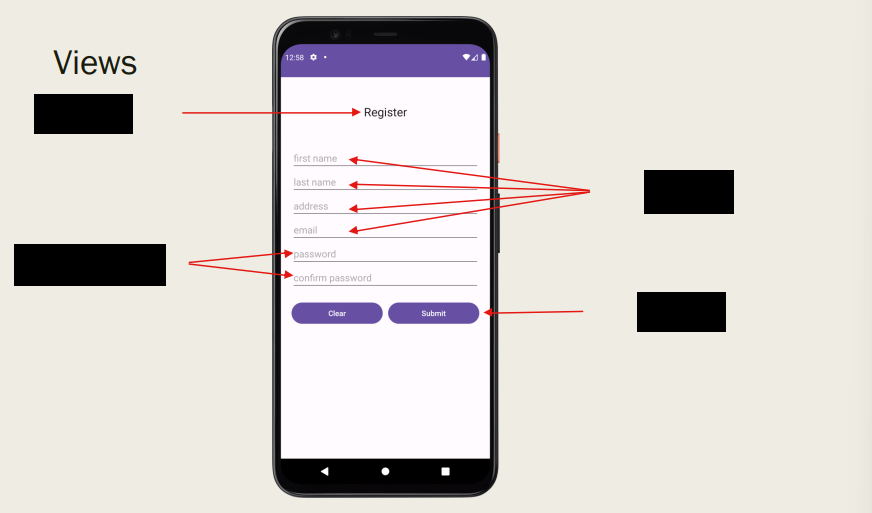
Fill in these Views
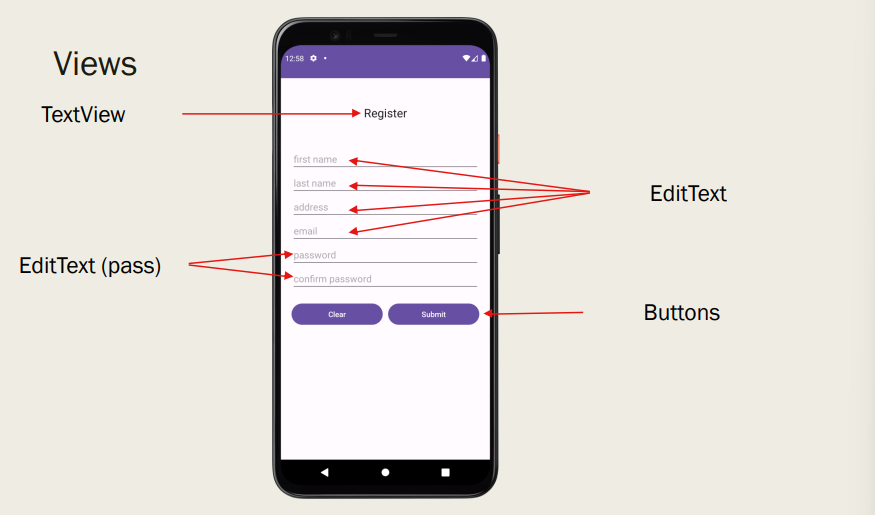
Determine ViewGroups
What is a Responsive Layout ? (3 answers)
Mobile devices come in all sorts of shapes and sizes – Mobile phones (large and small) – Tablets (large and small) – And more recently, foldable devices like the Samsung Galaxy Zip Fold
A single layout needs to look good on all of these devices
A responsive layout is a layout that grows, shrinks, and rearranges itself to different screen sizes and orientations.
What are the two main ways to design a Responsive Layout ?
Create a Flexible Layout
Use Alternative Layouts
What should you do to create a Flexible Layout ? (4 answers)
ConstraintLayout
LinearLayout with weights
ListViews and ScrollViews
Avoiding hard-coded sizes

What should you do to create Alternative Layouts ? (4 answers)
Orientation qualifiers
Smallest width qualifiers
Available width qualifiers
Fragments
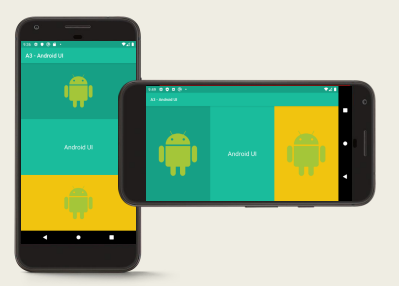
What are the two main ways to avoid using hard-coded sizes ?
wrap_content(tells the view to set its size to whatever is necessary to fit the content within that view.)match_parent(makes the view expand to as much as possible within the parent view.)
What are the 3 units of measurement used for adding specific sizes i.e. for margins, padding, text, etc.
Pixels (px)
Density independent pixels (dp)
Scalable pixels (sp)
What are pixels and when should you use them?
DO NOT USE PIXELS. Not only do Android devices come in different screen sizes but their screens also have different resolutions (pixels).
What are Density independent pixels and when should you use them?
They are virtual pixels that are roughly equal to one pixel on a medium-density screen. Android translates this value to the appropriate number of real pixels for each other density.
What are Scalable pixels and when should you use them?
Used for text sizes. Same size as dp, by default, but it resizes based on the user's preferred text size.
What are Alternative Layout Qualifiers ?
You can provide screen-specific layouts by creating additional res/layout/ directories
What is an Orientation Qualifier and How do you create one ?
Where in the Android project structure is your activity_main.xml layout stored?
res/layout/activity_main.xml
You can create a second layout qualifier for landscape
res/layout-land/activity_main.xml
Android will load the first activity_main.xml when in portrait orientation and the second when in landscape.

What is an Smallest Width Qualifier and How do you create one ?
The smallest width qualifier specifies the smallest of the screen's two sides, regardless of the device's current orientation, so it's a simple way to specify the overall screen size available for your layout.

What are some of the common smallest width values ?
320dp: a typical phone screen (320x480)
480dp: a large phone screen ~5" (480x800)
600dp: a 7” tablet (600x1024)
720dp: a 10” tablet (720x1280)
For example: res/layout-sw600dp/activity_main.xml
What are Drawables ?
A drawable resource is a general concept for a graphic that can be drawn to the screen.
What are the most common Drawable Files
Bitmap file
State list
Shape drawable
What are the 3 Bitmap image formats and where should they be saved ?
png (preferred)
jpg (acceptable)
gif (discouraged)
Should be saved in the
res/drawable/folder
How is a drawable called ?
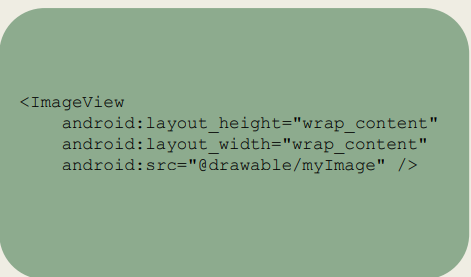
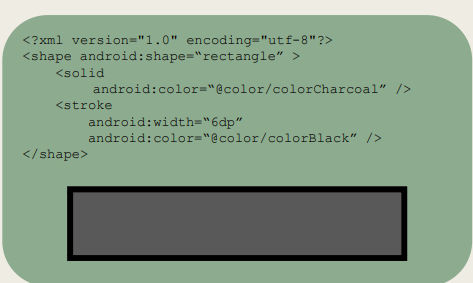
What data is stored within the Shape Files and where should it be saved ?
A generic shape defined in XML.
Rectangle, oval, line, or ring
Can specify:
Size
Corners
Padding
Solid (colour)
Stroke (colour)
Gradient (colour)
Should be saved in the res/drawable/ folder
How is a shape created ?
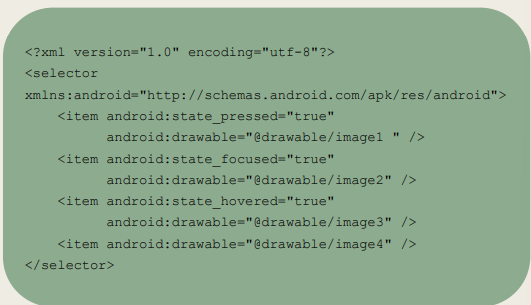
What are Statelist Files used for and where should they be saved?
Represent different states of an object
state_pressed
state_focused
state_hovered
state_selected
state_checked
+ others
Should be saved in the res/drawable/ folder
How is a Statelist file created
What is the purpose of the Mipmap folder ? (3 answers)
The Mipmap folder should be used exclusively to store your app launcher icons.
You can create a new launcher icon in Android Studio by using the Image Asset Studio.
This will automatically generate appropriately sized launcher icons and store them in the Mipmap folder for you.
What is the purpose of the Values folder ?
The Values folder contains simple values. Files in the values directory describe multiple resources, i.e. a list of strings.
What is the difference between the Values folder and the rest of the res folders ?
The other “res” subdirectories (drawables, layouts, mipmap) define a single resource based on the XML filename whereas files in the values directory describe multiple resources.
What are the 4 most commonly used files in the Values directory
string
color
dimension
theme
What is a theme in the context of android studio ?
Your theme describes the overall look of your application.
The color of your Action bar and Status bar
The default button color
The style for ‘day’ and ‘night’
What are resource qualifiers ?
They are used to make an application more responsive similar to orientation qualifiers. Basically just extra folders in your application.