Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1-4 Mcgraw Hill
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
Receptor
body structure that monitors changes in a controlled condition and sends input to a control center
Stimulus
a signal to which an organism responds
control center
processes the signal and sends instructions
Effector
an organ or cell that acts in response to a stimulus.
negative feedback
A primary mechanism of homeostasis, whereby a change in a physiological variable that is being monitored triggers a response that counteracts the initial fluctuation.
positive feedback
Feedback that tends to magnify a process or increase its output until a climatic event occurs.
An example of negative feedback
Controlling body temperature
An example of positive feedback
A mother breastfeeding
An example of homeostasis imbalance
Diabetes
What is an SSRI?
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor; an example of this is Serotonin, which is a neurotransmitter.
organic compounds
Compounds that contain carbon
inorganic compounds
Compounds that do not contain carbon
Examples of organic compounds
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
examples of inorganic compounds
water, salts, acids, bases
Properties of water
High heat capacity, high heat of vaporization, polar solvent, reactivity, cushion
Acid
A substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution (H+)
Base
A substance that decreases the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution (OH-)
As a liquid, how does water serve as a function in the body?
Transportation, lubrication, cushioning, and excretes wastses.
What kind of a solvent is water?
universal solvent - polar
What kind of substances dissolve in water?
polar molecules (glucose) and ions (Na+)
Hydrophobic
Water fearing
Hydrophilic
Water loving
Why do polar molecules dissolve in water better than others?
Because of the hydrogen bonds that form between those molecules and water molecules.
What is dissociation?
the process in which an ionic compound separates into ions as it dissolves
Electrolyte
An ionic compound whose aqueous solution conducts an electric current (salts, acids, bases).
polar
Molecule with partial charges. Mixes with water.
nonpolar
No partial charges. Do not mix with water.
proton donor
acid
proton acceptor
base
Acids scale
0-6
Bases scale
8-14
What kind of pH does pure water have?
7
Neutralization
When an acid and base mix to make a neutral substance
Buffer
compound that prevents sharp, sudden changes in pH
Triglycerides
an energy-rich compound made up of a single molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid.
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules are bonded together with the removal of a water molecule.
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
Lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (insoluble in water).
major classes of lipids
triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids
Saturated
Fats with the maximum number of hydrogens.
Unsaturated
Fat with less than the maximum number of hydrogens in one or more of its fatty acid chains
polyunsaturated
two or more double bonds
Lipogenesis
the metabolic formation of fat
Lipolysis
breakdown of fat
Phospholipids
a lipid consisting of a glycerol bound to two fatty acids and a phosphate group (modified triglycerides; important to cell membrane structure)
Steroids
lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings including and derived from cholesterol
Carbohydrates
hydrated carbon atoms; the starches and sugars present in foods
Monosaccharides
Single sugar molecules (galactose, fructose, ribose, deoxyribose). Can be five or six-carbon sugars
Disaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of two monosaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose).
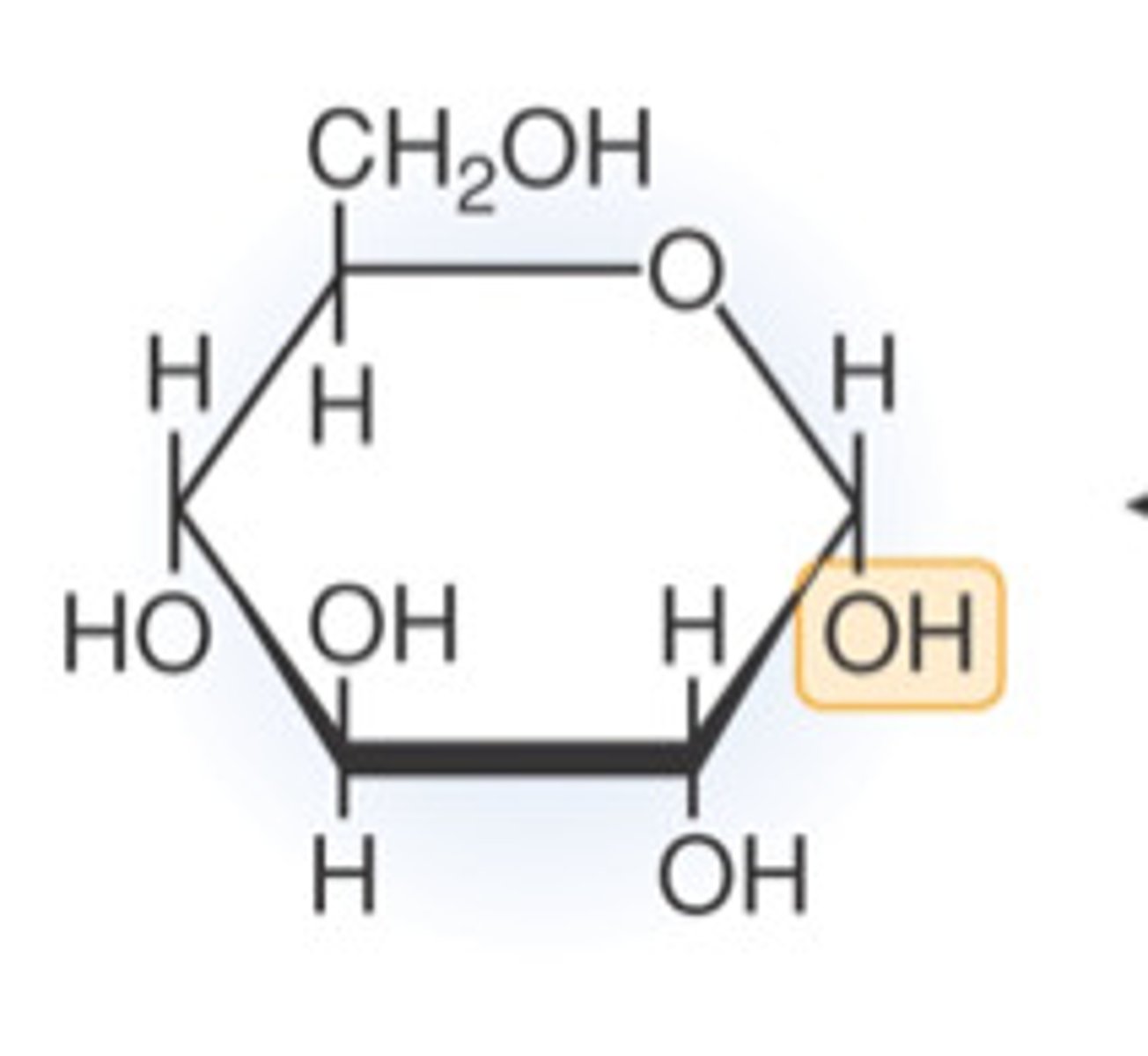
Glucose
A simple sugar that is an important and common source of energy.
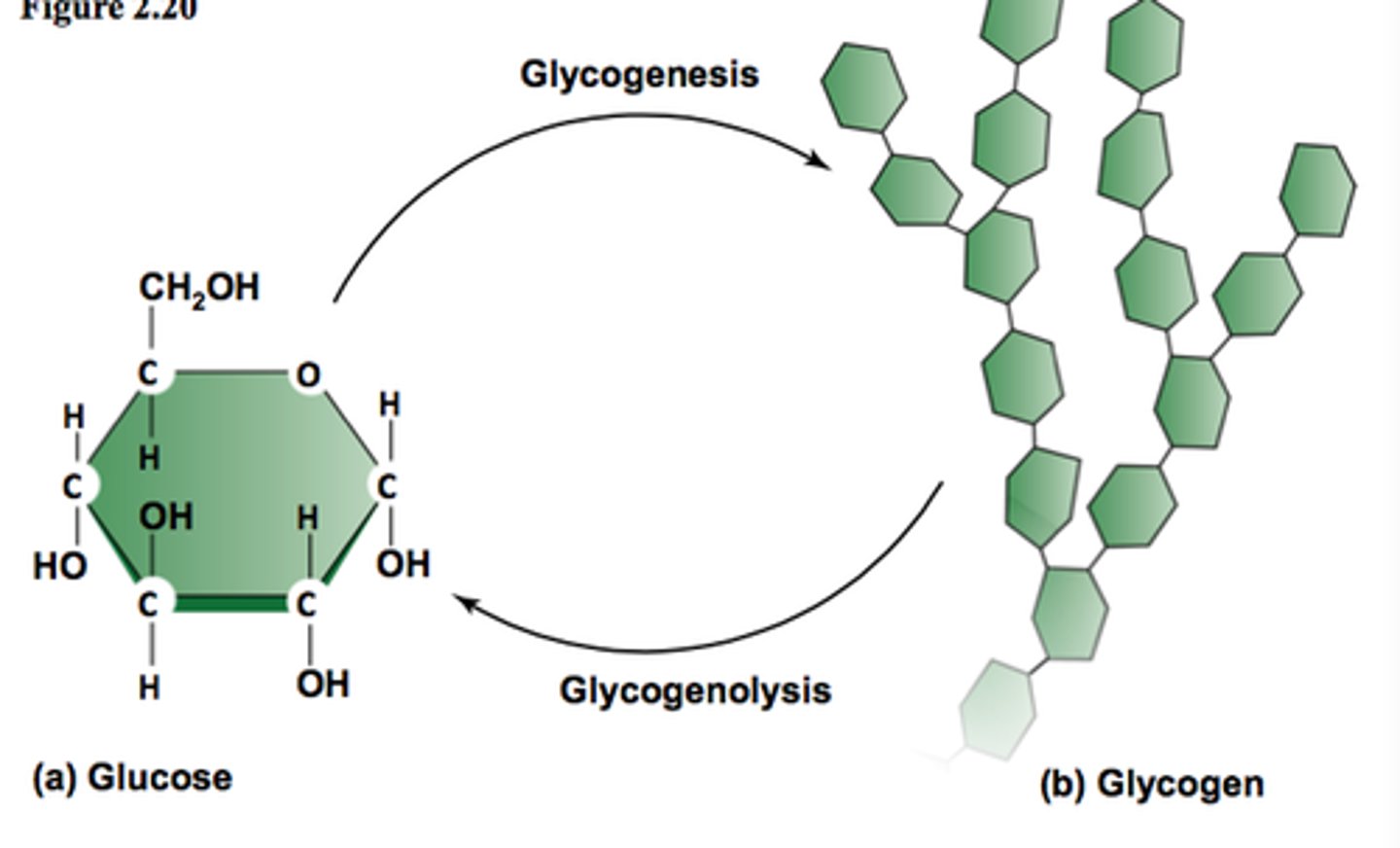
Glycogen
An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch.
Glycogenesis
formation of glycogen from glucose
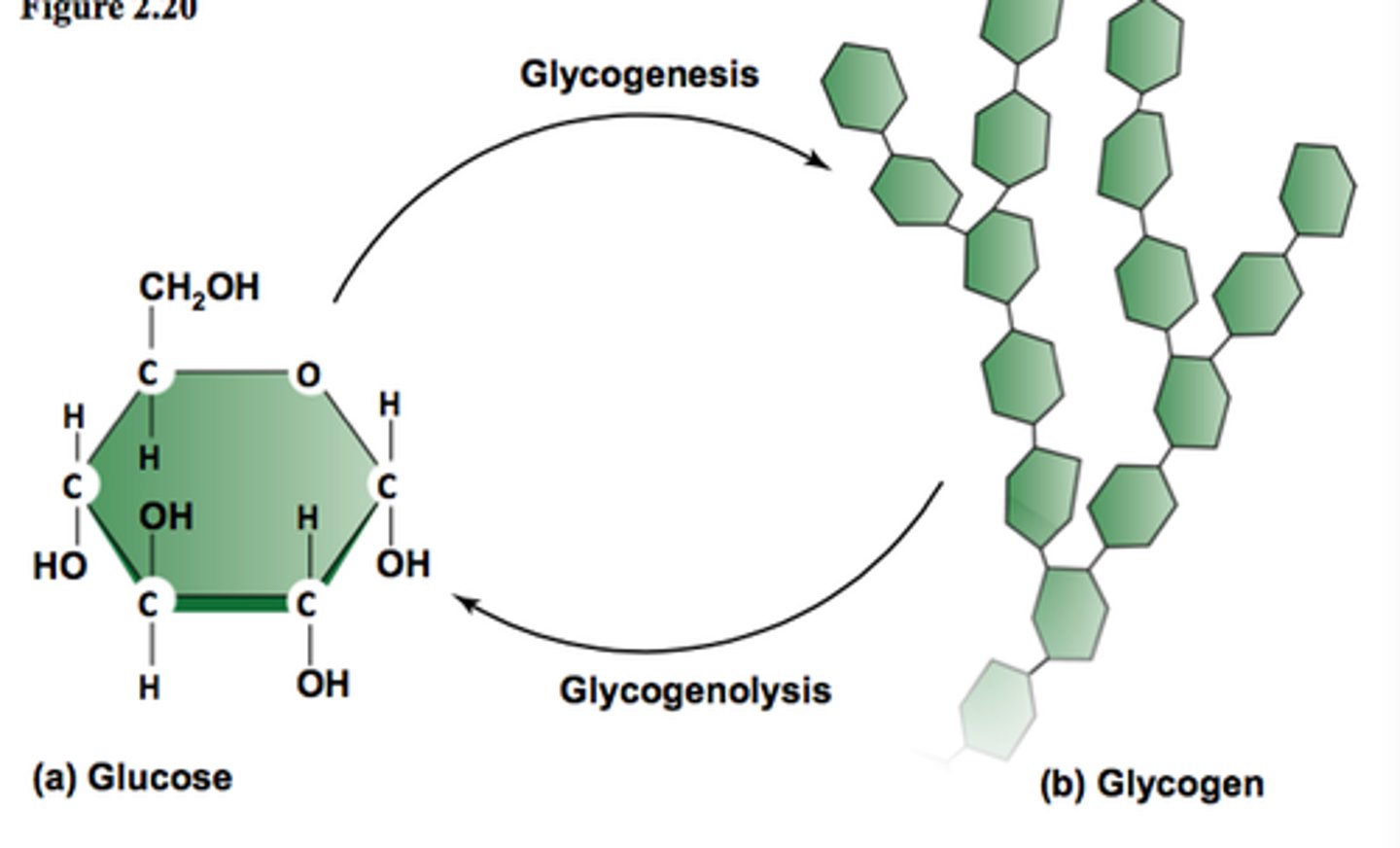
Glycogenolysis
breakdown of glycogen to glucose
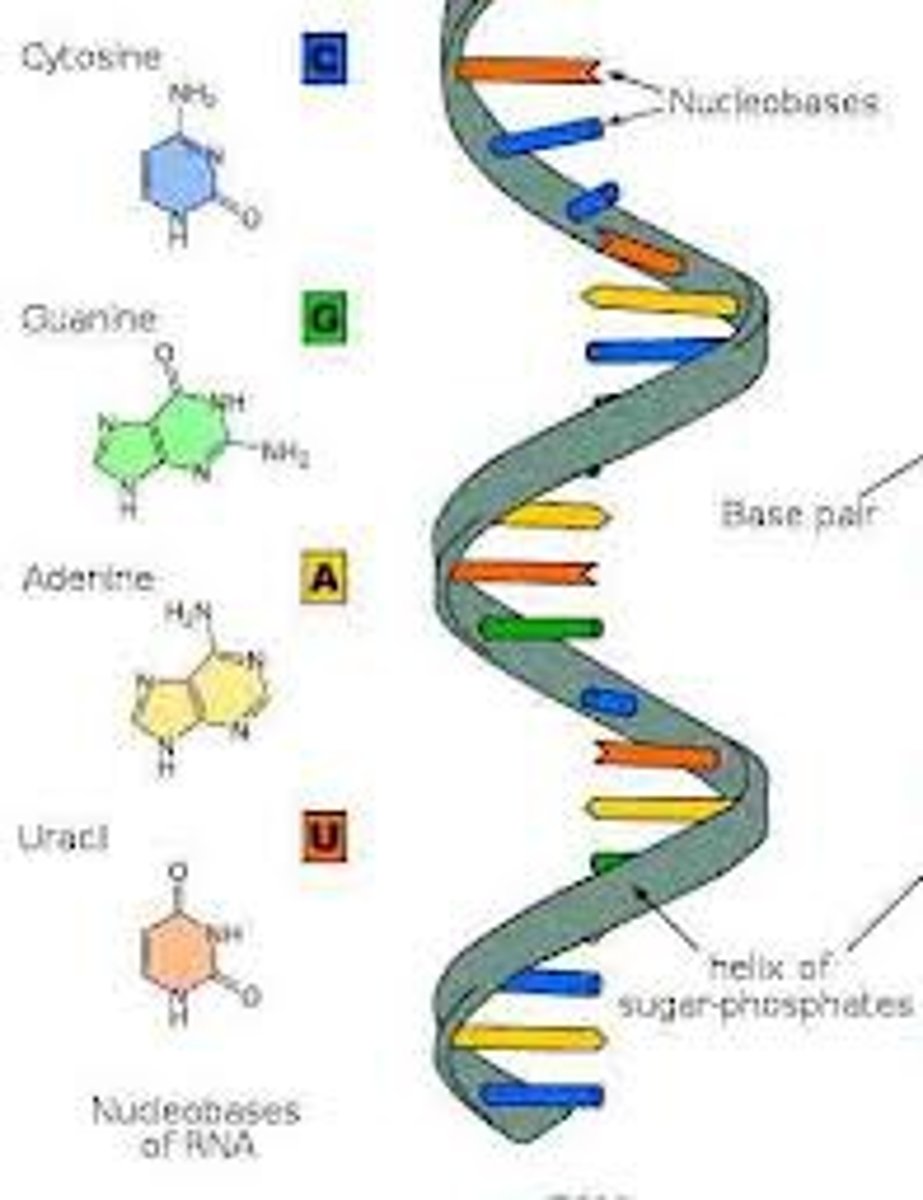
nucleic acids
biological molecules, such as DNA or RNA, composed of nucleotides that control cellular functions and heredity.
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
Prymidines
single-ring nitrogenous bases (thymine, cytosine, uracil)
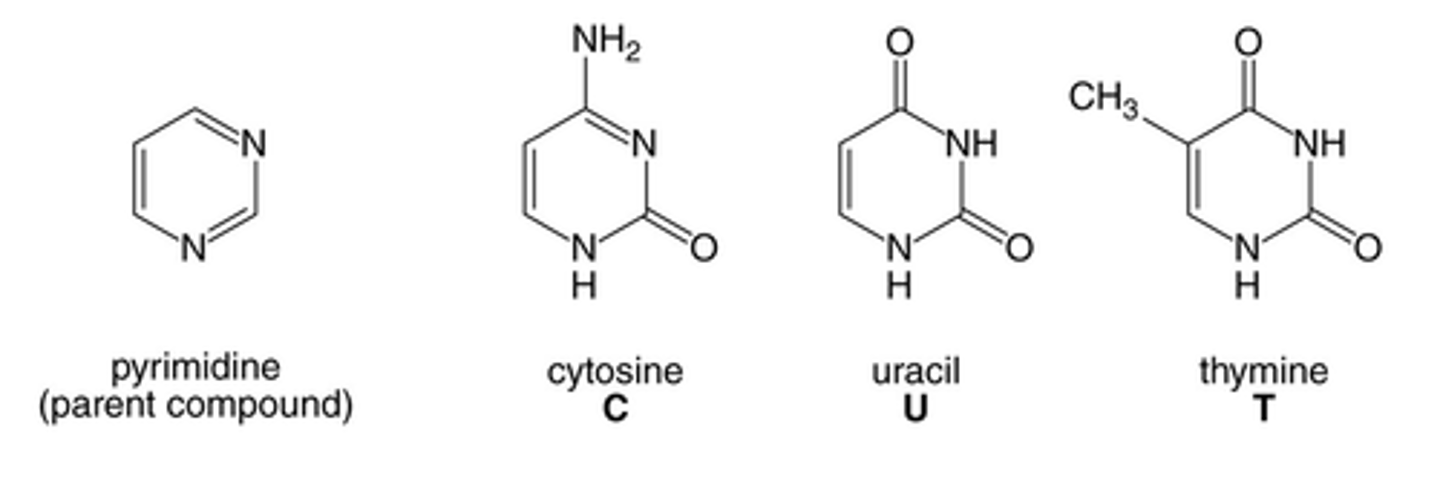
Purines
double ring nitrogenous bases (adenine and guanine)
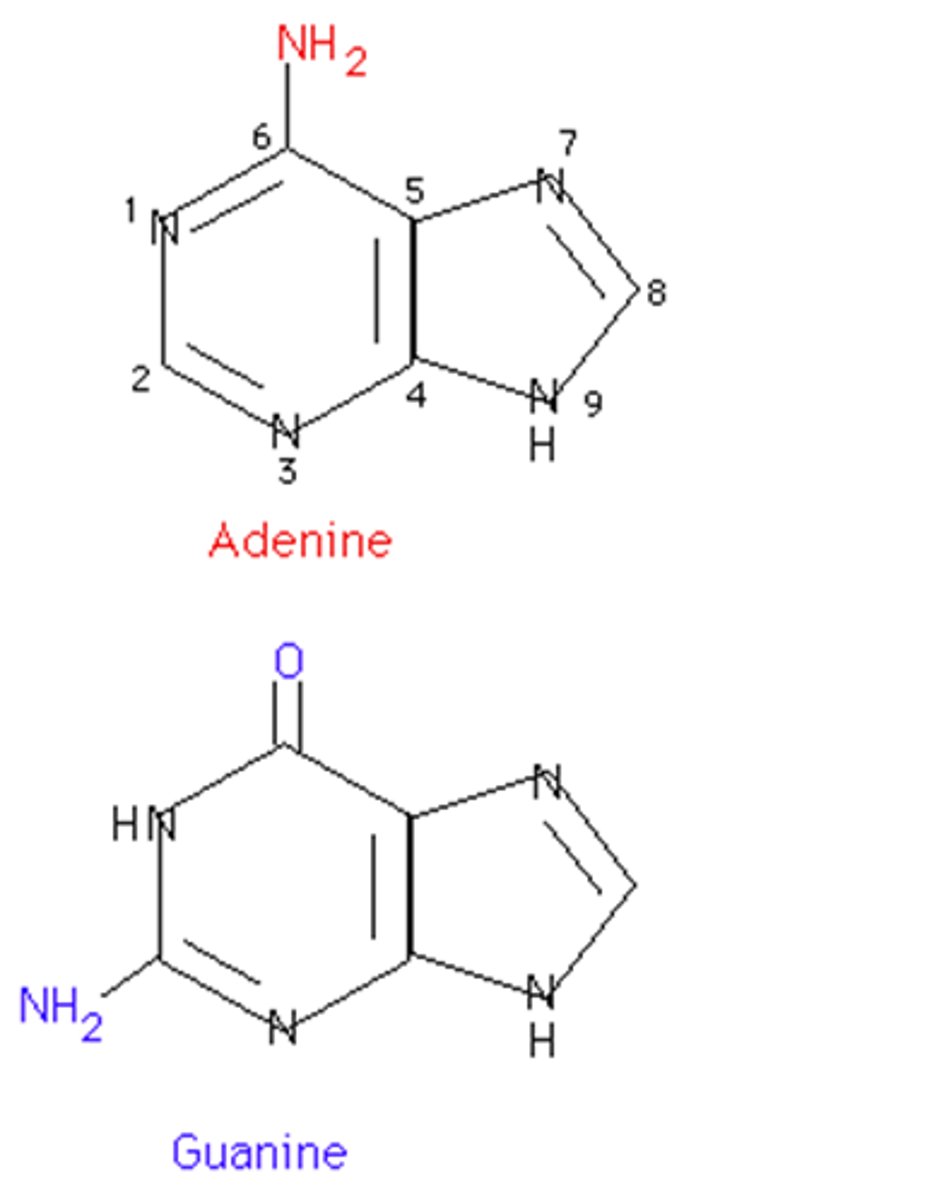
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
A double-stranded, helical nucleic acid molecule capable of replicating and determining the inherited structure of a cell's proteins.
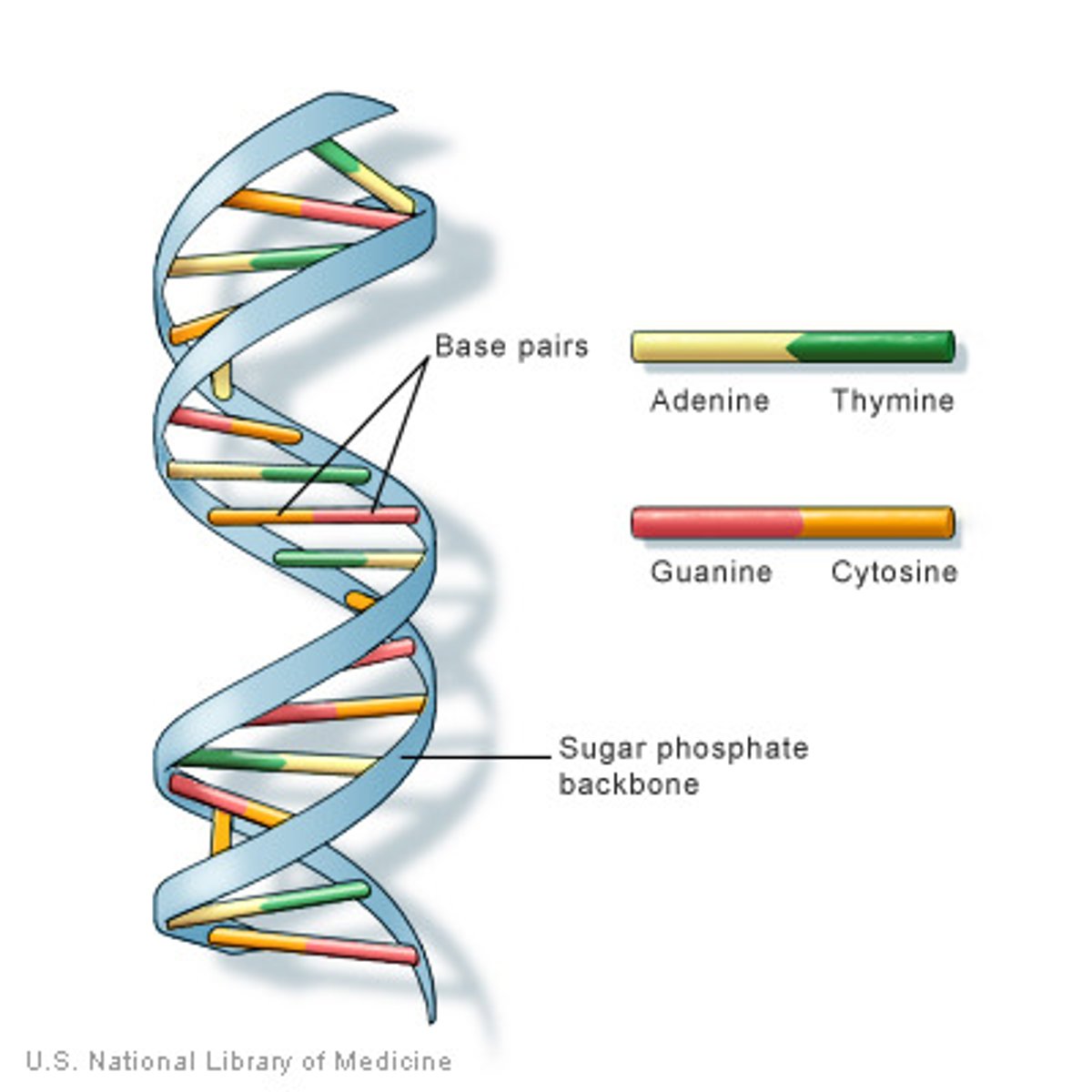
Nitrogenous bases in DNA
adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine
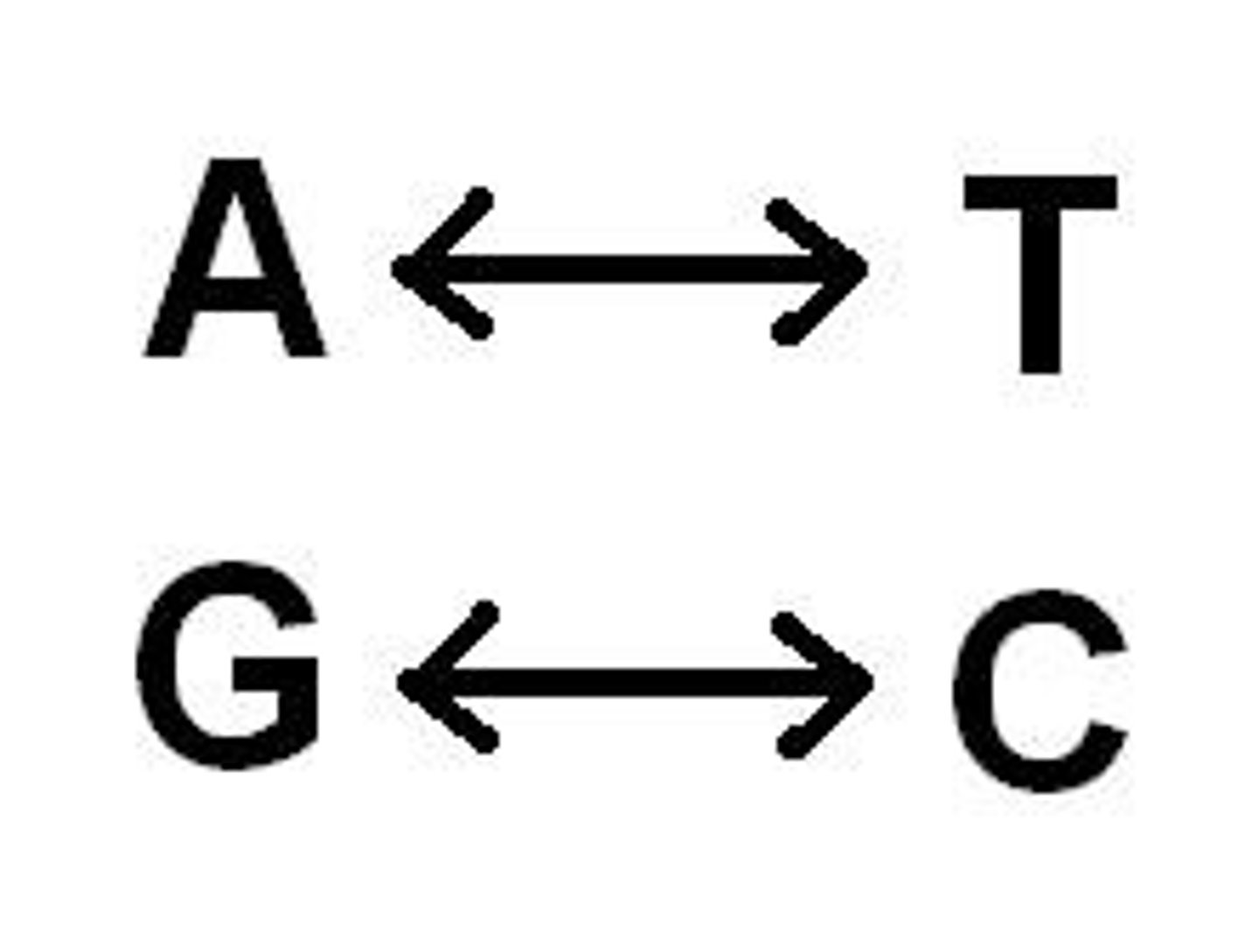
Nitrogenous bases in RNA
adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil
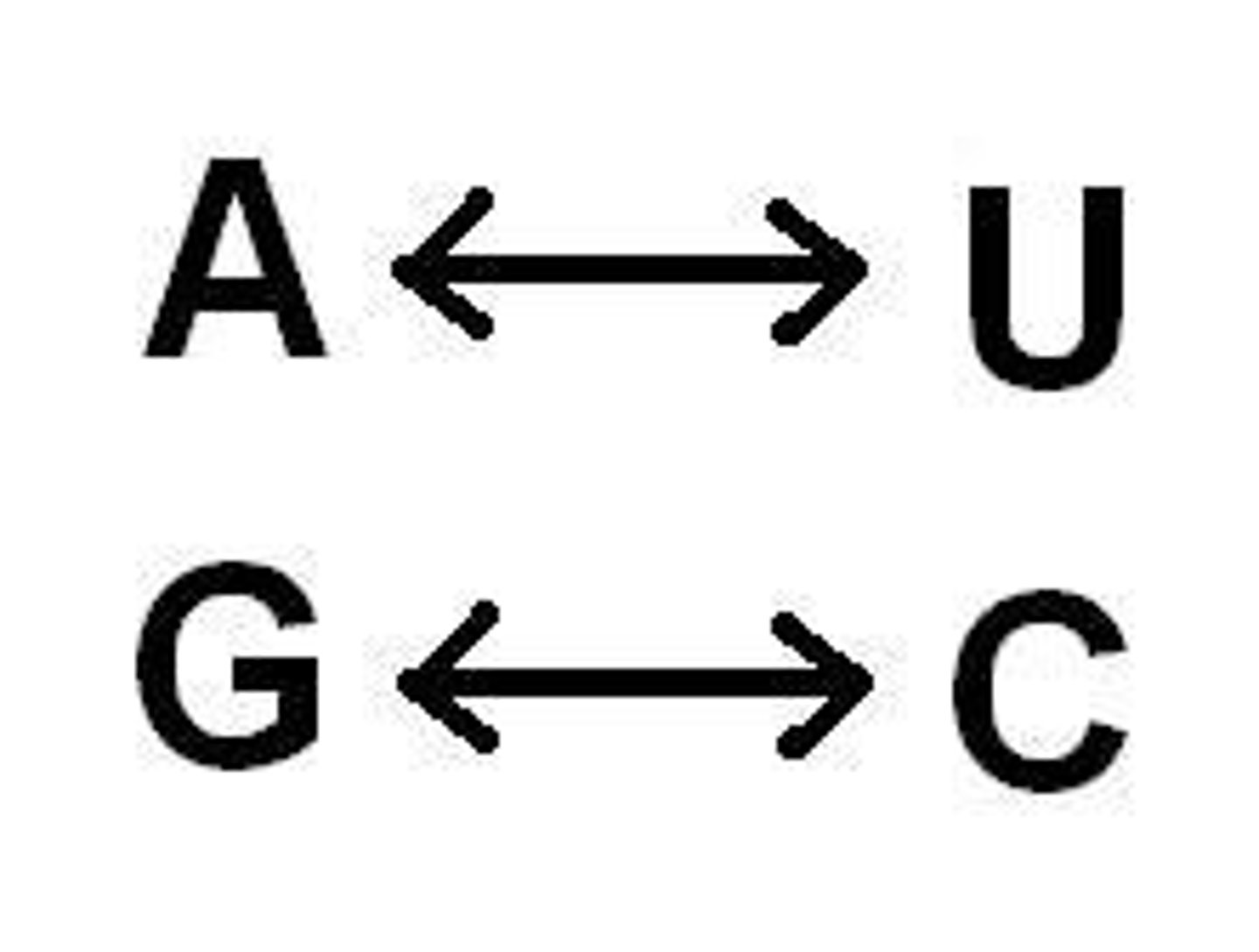
ribonucleic acid (RNA)
single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose, located within the cell nucleus and cytoplasm.
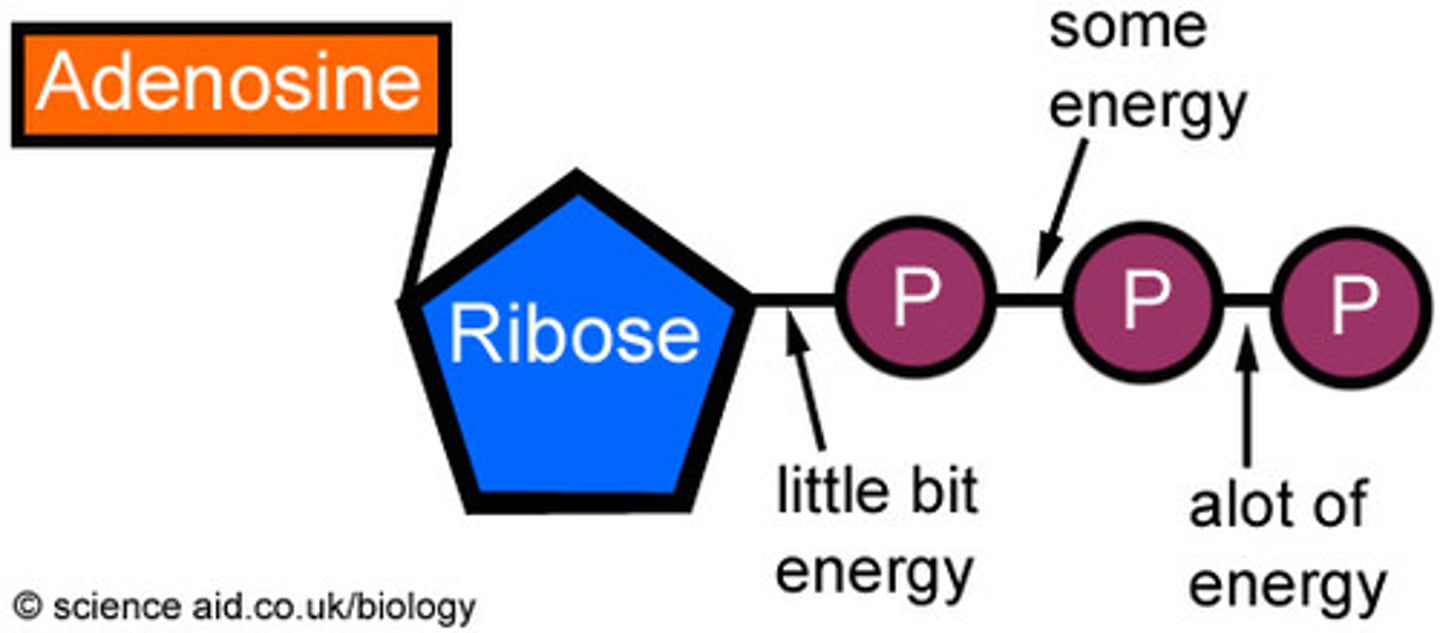
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
compound used by cells to store and release energy (composed of the nitrogenous base adenosine and a ribose sugar)
Proteins
polymers composed of one or more linear stands of amino acid monomers.
amino acids
building blocks of proteins
peptide bond
The chemical bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid
primary structure of protein
linear sequence of amino acids

secondary structure of a protein
protein structure is formed by folding and twisting of amino acid chain, resulting in an alpha helix or beta pleated sheet
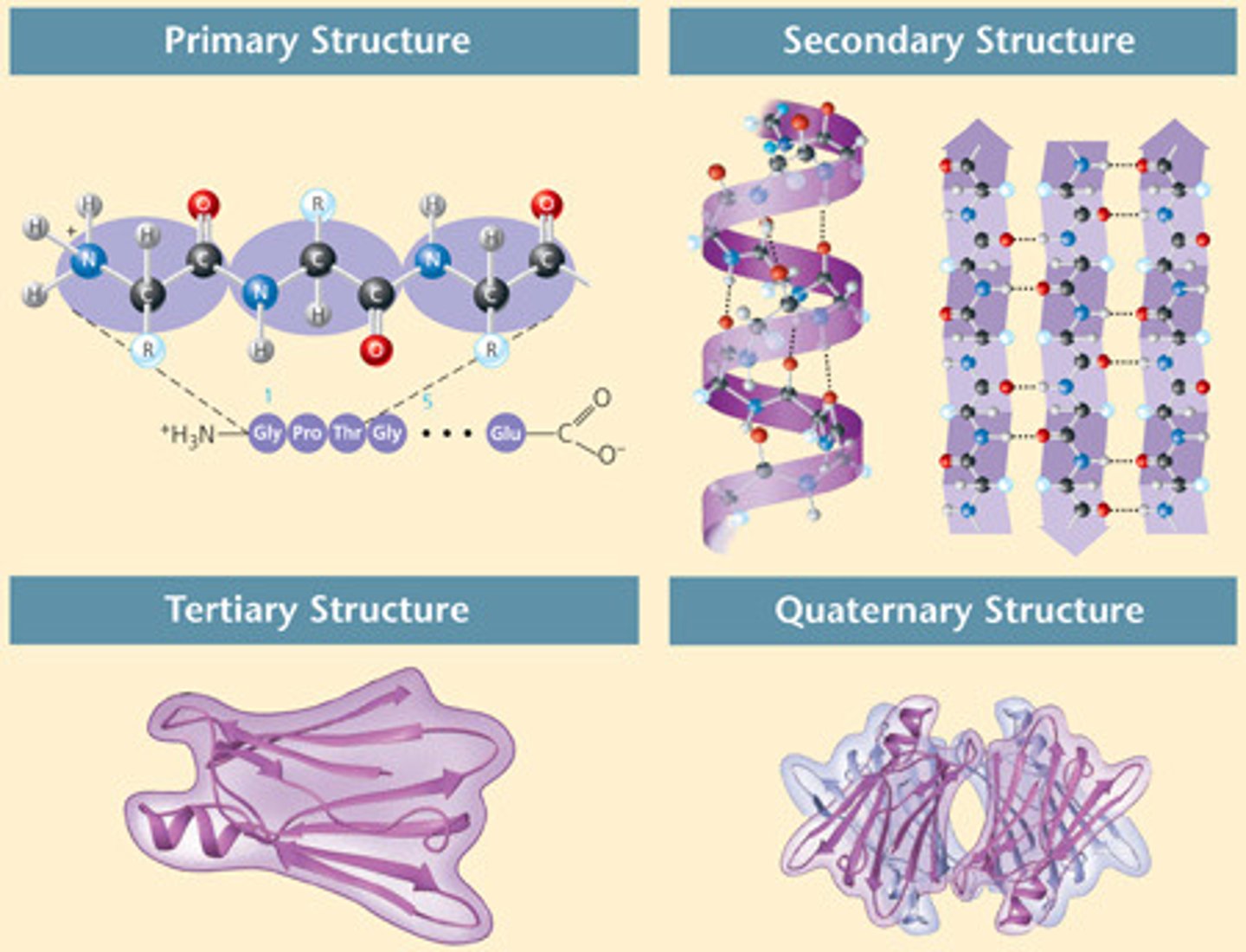
tertiary structure of protein
3D shape of protein with repeated secondary structures to form globular or fibrous protein
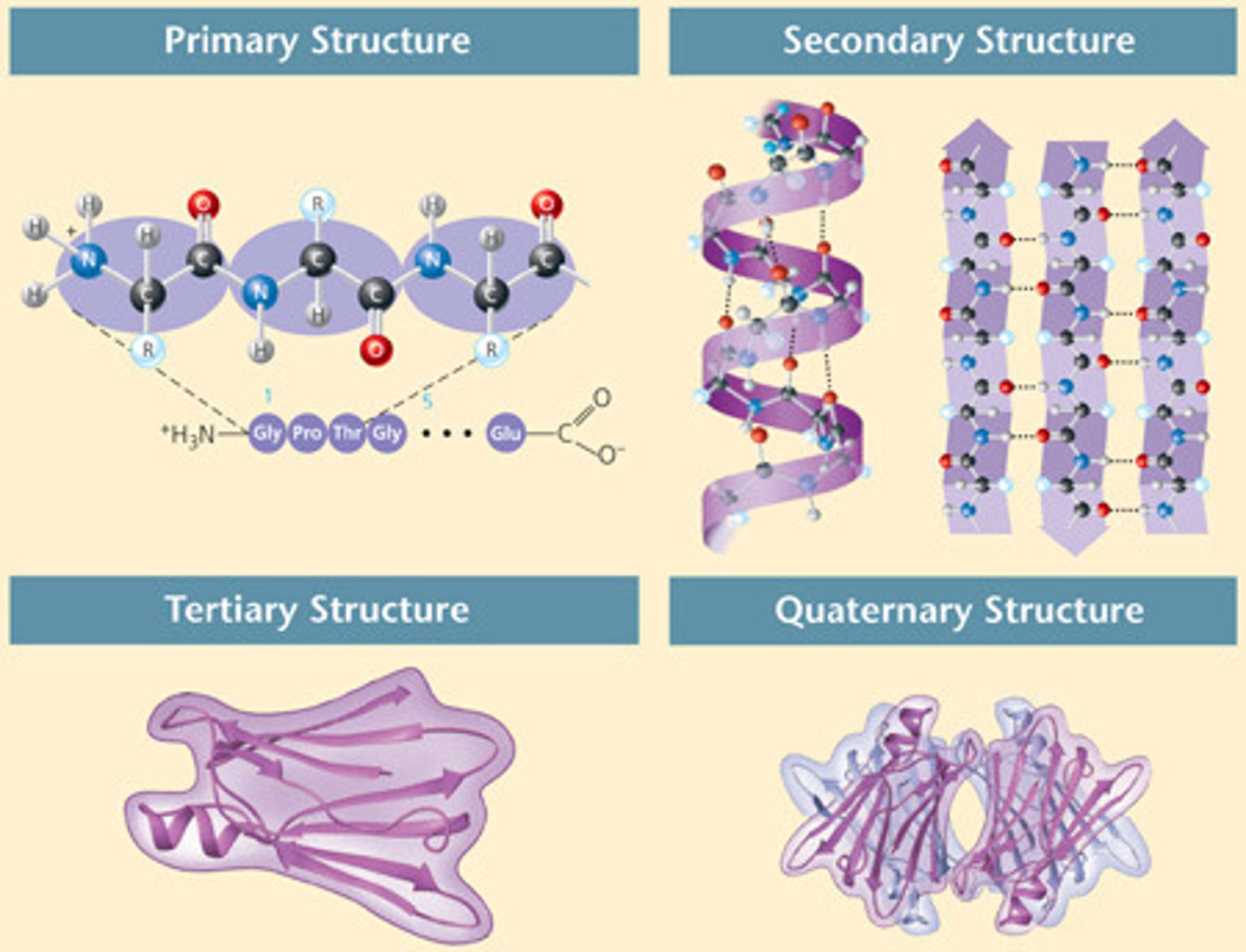
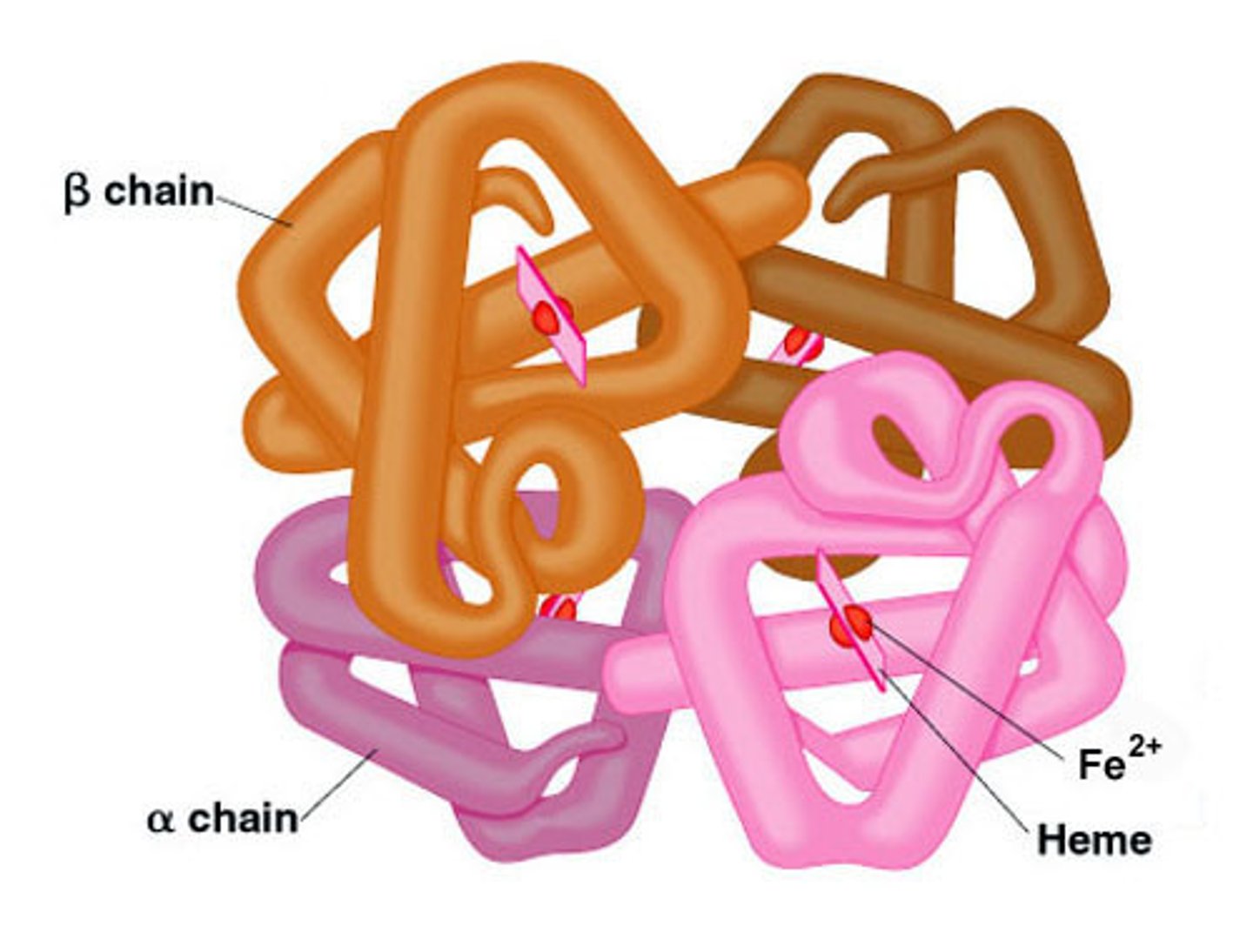
quaternary structure of a protein
a molecule composed of two or more separate proteins
protein denaturation
when proteins are subject to heat, acid or other conditions that disturb their stability; protein uncoils, loses its shape, and loses its function
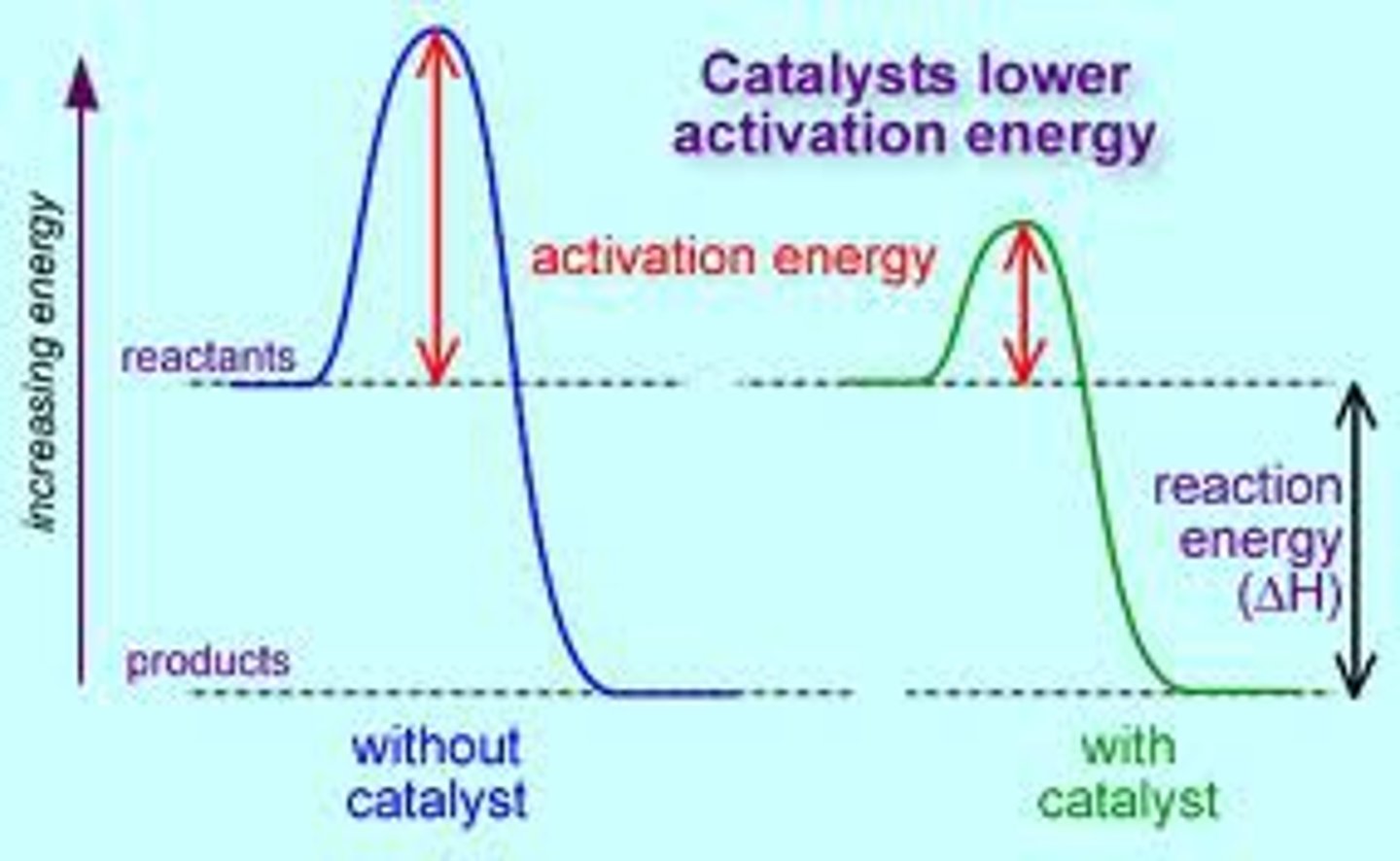
Catalysts
Chemical agents that selectively speed up chemical reactions without being consumed by the reaction.
Enzymes
Catalysts for chemical reactions in living things
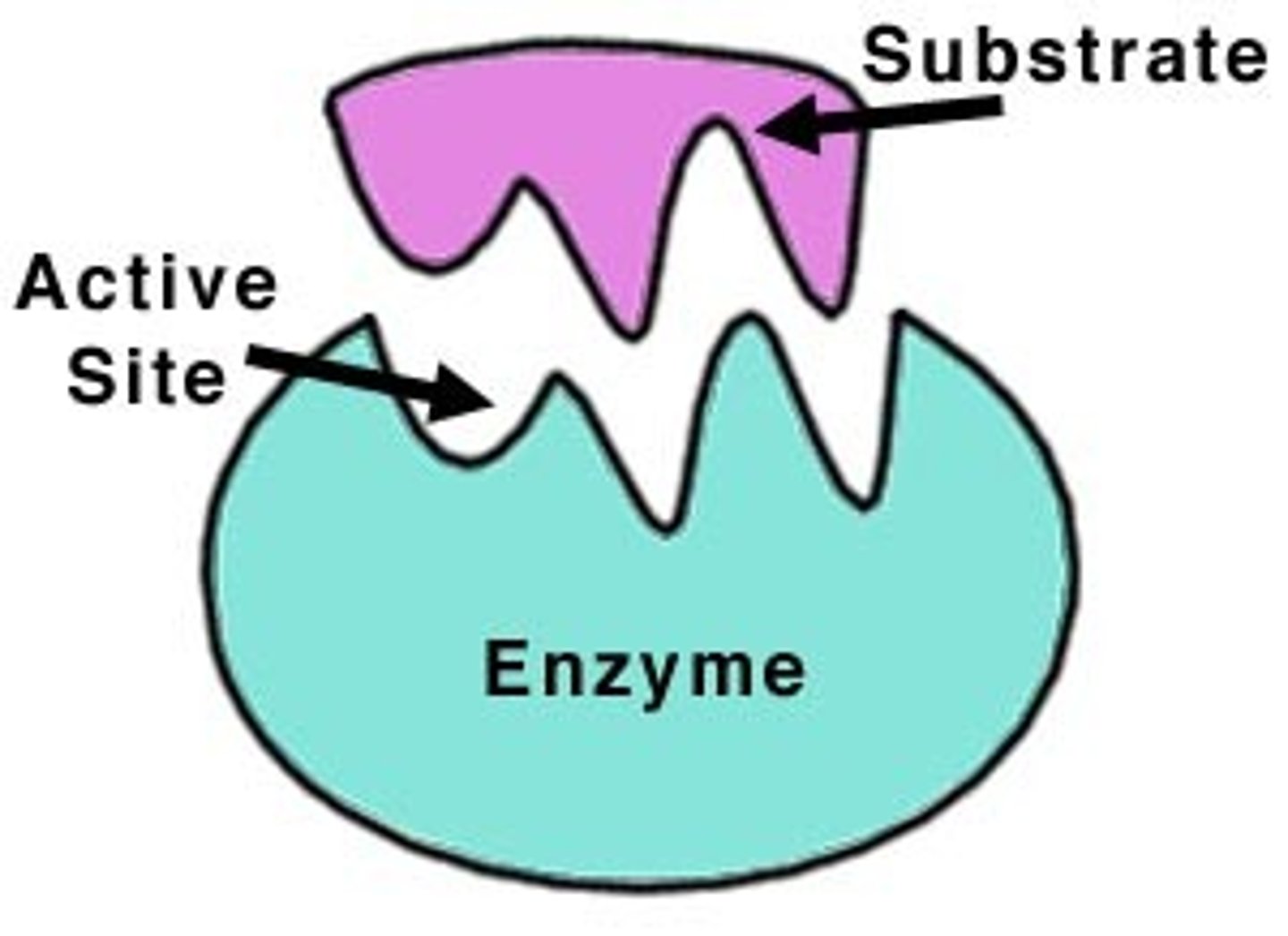
active site
The part of an enzyme or antibody where the chemical reaction occurs.
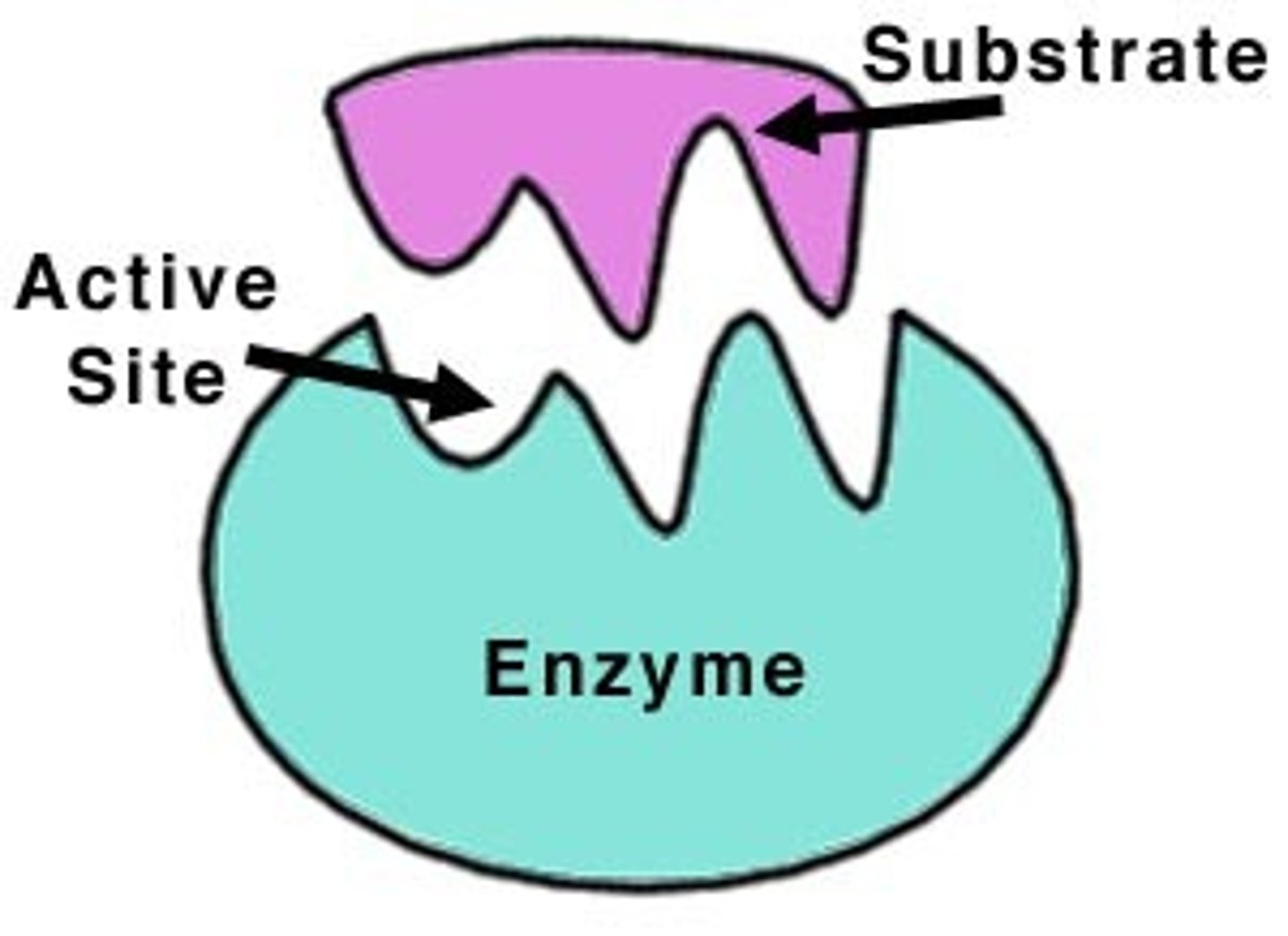
Substrate
A specific reactant acted upon by an enzyme
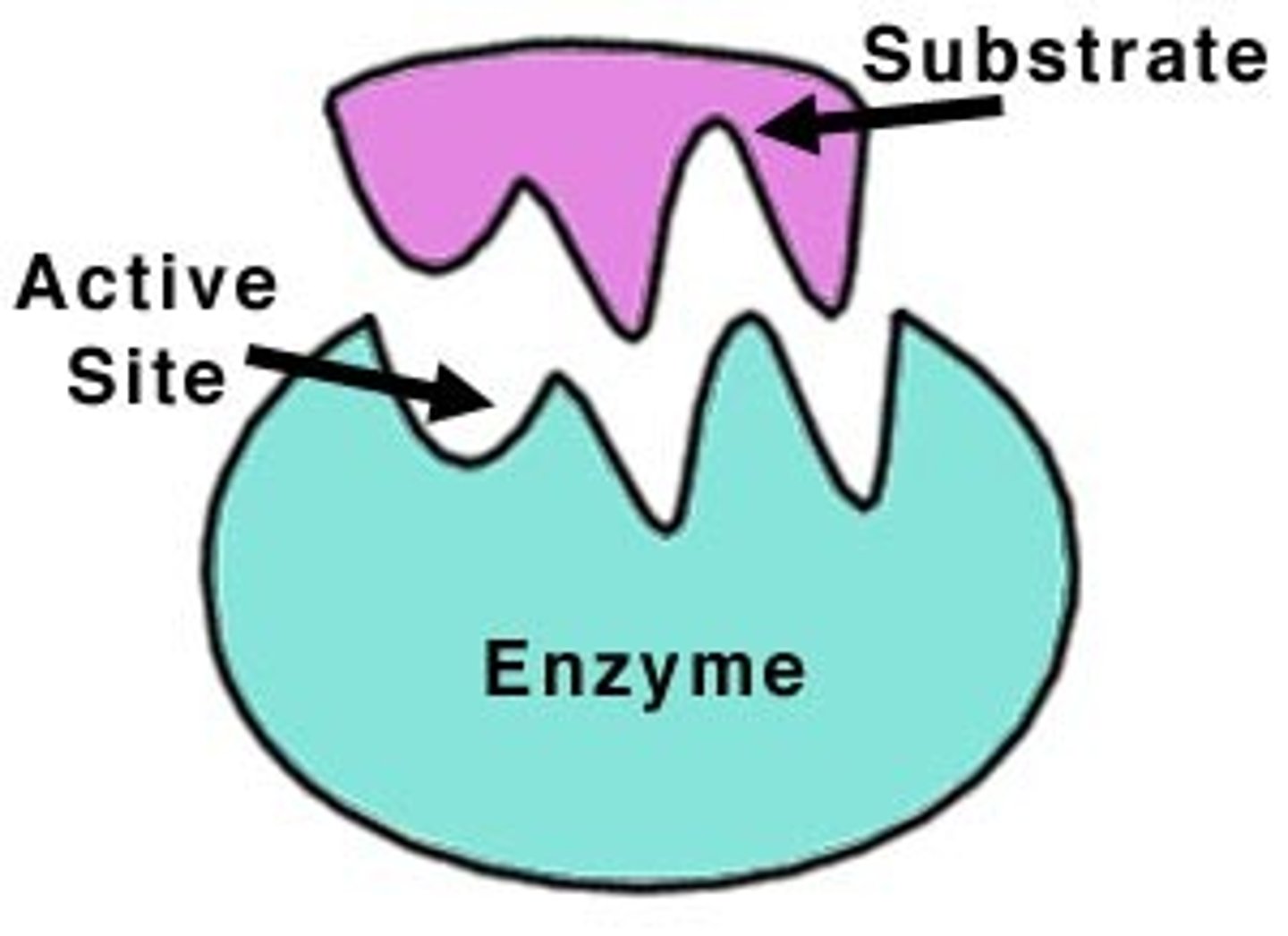
enzyme-substrate complex
A temporary complex formed when an enzyme binds to its substrate molecule(s).
decomposition reaction
a reaction in which a single compound breaks down to form two or more simpler substances
synthesis reaction
a reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a new compound
Saturation
the state or process that occurs when no more of something can be absorbed, combined with, or added within enzyme reactions.
Effects of temperature on enzymes
if temp is too low enzymes slow down, if temp is too high causes denaturation but a high tolerable temp causes enzymes to work faster (optimum temperature)
Effects of pH on enzymes
Different enzymes have different optimum pHs, at extreme pHs, enzymes become denatured
Inhibitors of enzymes
substances that bind to enzymes to stop enzyme activity, turning it off.
competitive inhibitor
resembles the substrate and binds to the active site of the enzyme
noncompetitive inhibitor
A substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by binding to a location remote from the active site, changing its conformation so that it no longer binds to the substrate.
allosteric site
A site on an enzyme other than the active site, to which a specific substance binds, thereby changing the shape and activity of the enzyme.
metabolic pathway
A series of chemical reactions that either builds a complex molecule or breaks down a complex molecule into simpler compounds.
multienzyme complex
a group of enzymes, each of which catalyzes one reaction, that are physically joined to each other
Multienzyme complex advantages
-Less likely substance will diffuse away into different biochemical pathway
-Single complex can be regulated rather than individual enzymes
cells
The basic unit of structure and function in all living things; considered the functional units of the body
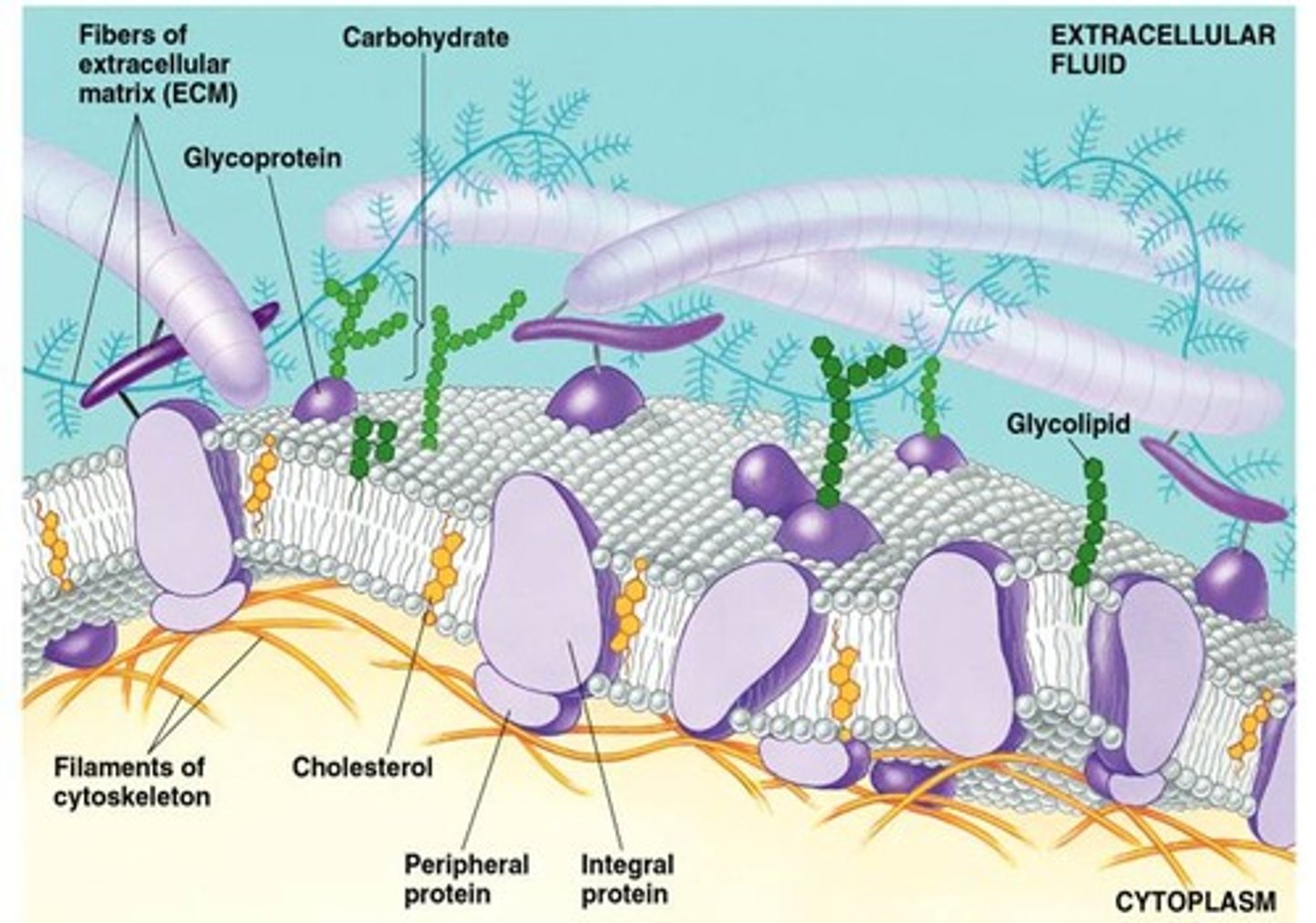
plasma membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
interstitial fluid
fluid between cells
phospholipid bilayer
Plasma membrane layers composed of phospholipid molecules arranged with polar heads facing the outside and nonpolar tails facing the inside.
Cholesterol
A lipid that forms an essential component of animal cell membranes and acts as a precursor molecule for the synthesis of other biologically important steroids.
Glycolipids
Membrane carbohydrates that are covalently bonded to lipids.
integral proteins
spans the entire membrane
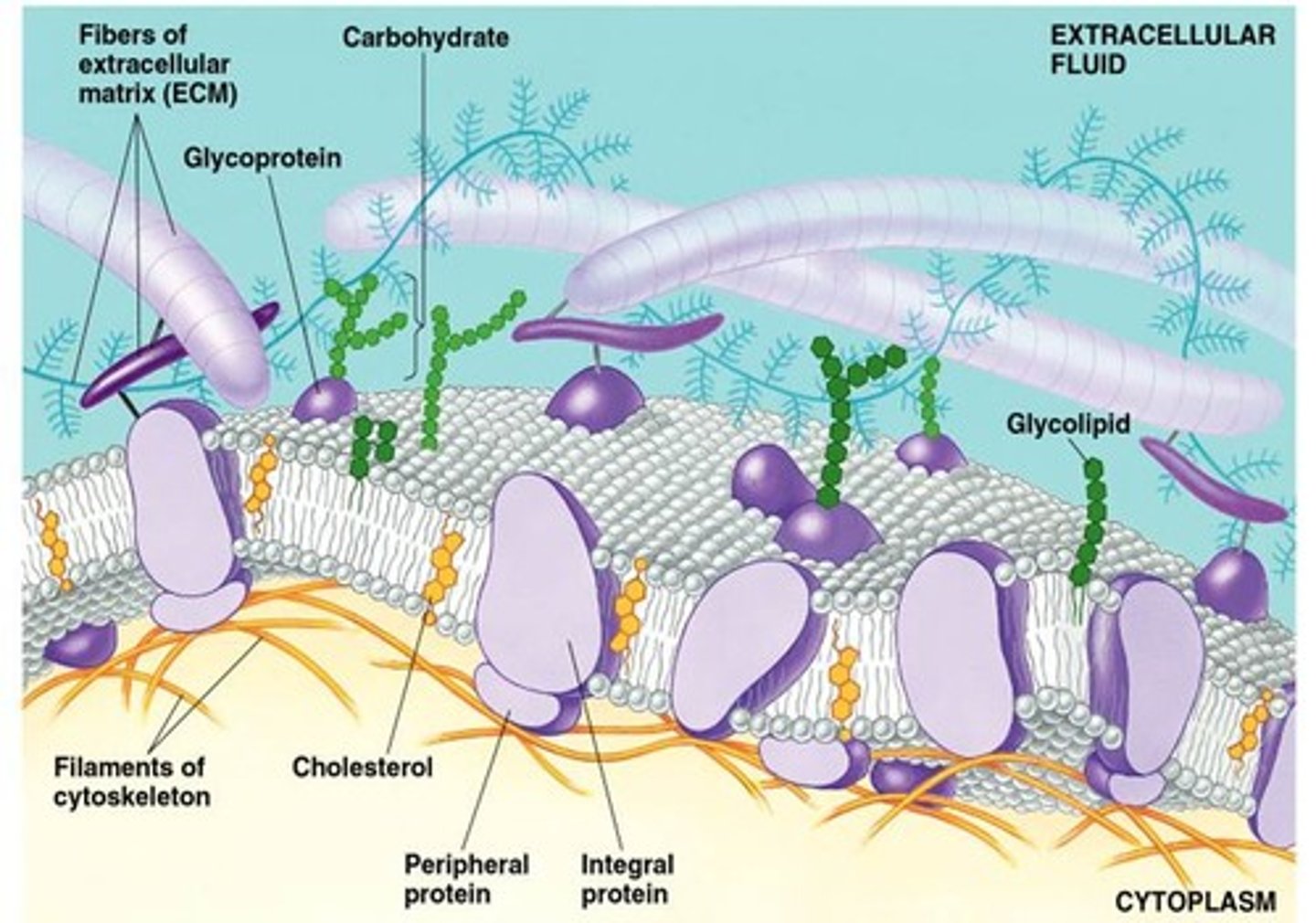
peripheral proteins
bound to the surface of the membrane
membrane protein functions
Transport proteins, cell surface receptors, identity markers, enzymes, anchoring sites, cell-adhesion proteins
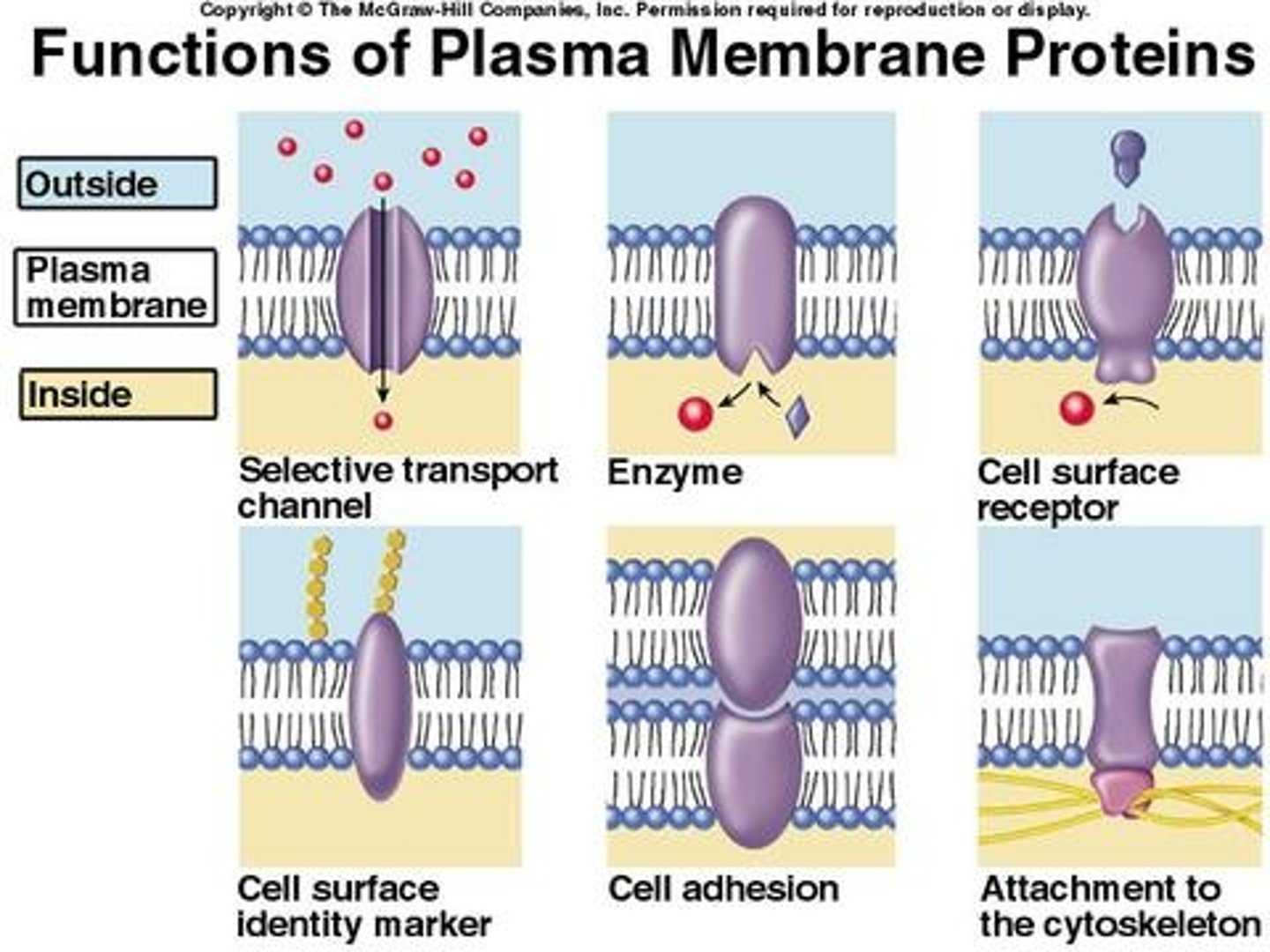
Types of transport proteins
channel, pump, and carrier protein
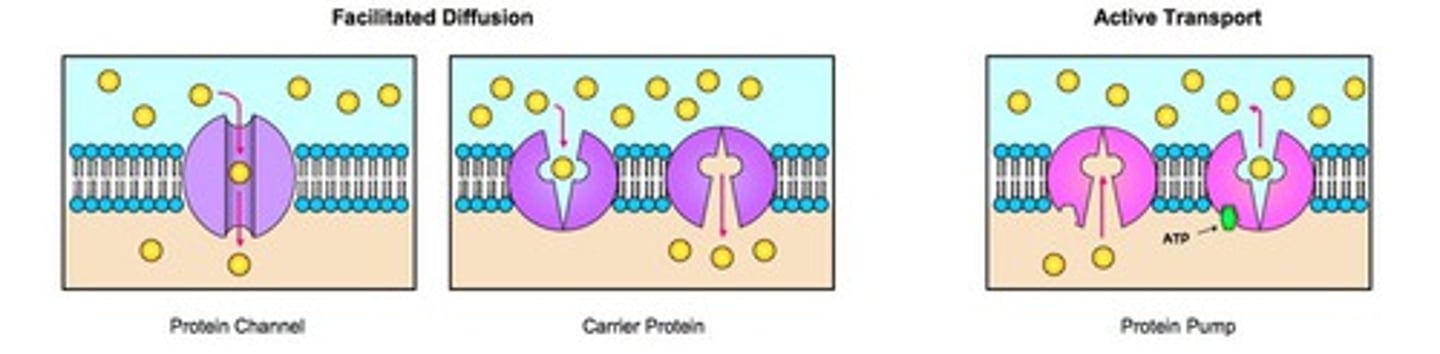
passive transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell (moving down the concentration gradient)
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference (moving against the concentration gradient) (also uses carrier proteins and solute pumps)