DNA/Genetics
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Who discovered the nucleotides?
Hershey and Chase
Who discovered the way DNA looks?
Watson and Crick
Name the nucleotides for DNA and then RNA
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine
For RNA, replace Thymine with Uracil
What is the purpose of DNA?
Provides genetic code for a trait
What is semiconservative replication?
In semiconservative replication, the original two strands of the double helix serve as templates for new strands of DNA. When replication is complete, two double-stranded DNA molecules will be present. Each will consist of one original template strand and one newly synthesized strand that is complementary to the template.
What are the enzymes that help semi conservative replication?
DNA Helicase, DNA Primase, DNA Polymerase, and DNA Ligase
What is DNA Helicase?
"Unzips" the DNA
--Breaks the hydrogen bonds between the nucleotides
What is DNA Primase
"Highlighter"
--Highlights an area of where the new half should be built on
What is DNA Polymerase?
--"Builder"
--an enzyme that joins individual nucleotides to produce a new strand of DNA
--builds in a 5' to 3' direction ALWAYS
--proofreads
What is DNA Ligase
"The glue"
--Fills gaps left in the lagging strand
--Fills with OKAZAKI fragments
What is the leading strand?
The strand where replication moves towards the replication (follows helicase)
What is the lagging strand?
The strand where DNA replication moves away from the replication (away from helicase)
what is topoisomerase?
Keeps the DNA from winding together too much
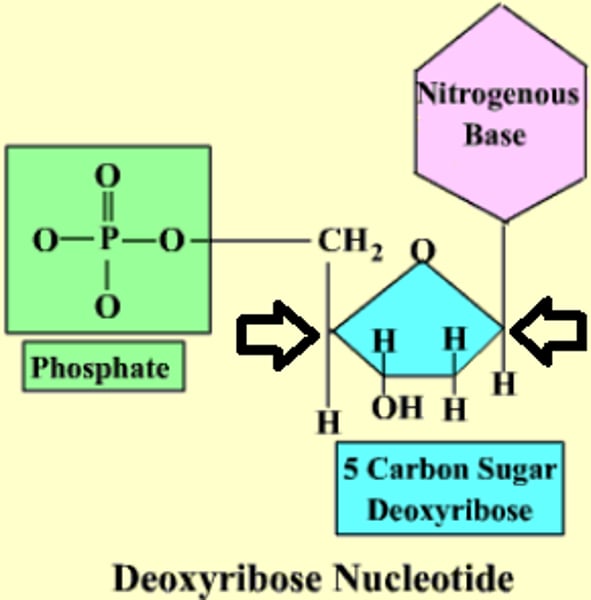
What does 5' and 3' mean?
5' is the end of DNA with a phosphate, and 3' is the end with a deoxyribose sugar
What is DNA transcription?
process of writing a copy of a DNA template into mRNA
What is RNA Polymerase?
an enzyme that binds to DNA during transcription and separates or unwinds the DNA strands.
What are the sub-steps to DNA trancription
Initiation, Elongation, and termination
What is Initiation?
RNA polymerase binds to promoter
What is a promoter?
binding site for RNA polymerase
What is elongation?
Codes along the new strand
What is termination?
Signals that the build is done and mRNA is made which goes to the Ribosome and its made into a protien
What is translation?
The transition of DNA from a nucleus to mRNA and going to the ribosome
What is tRNA?
brings an amino acid from the cytoplasm
What is a codon?
a sequence of three nucleotides that together form a unit of genetic code in a DNA or RNA molecule.
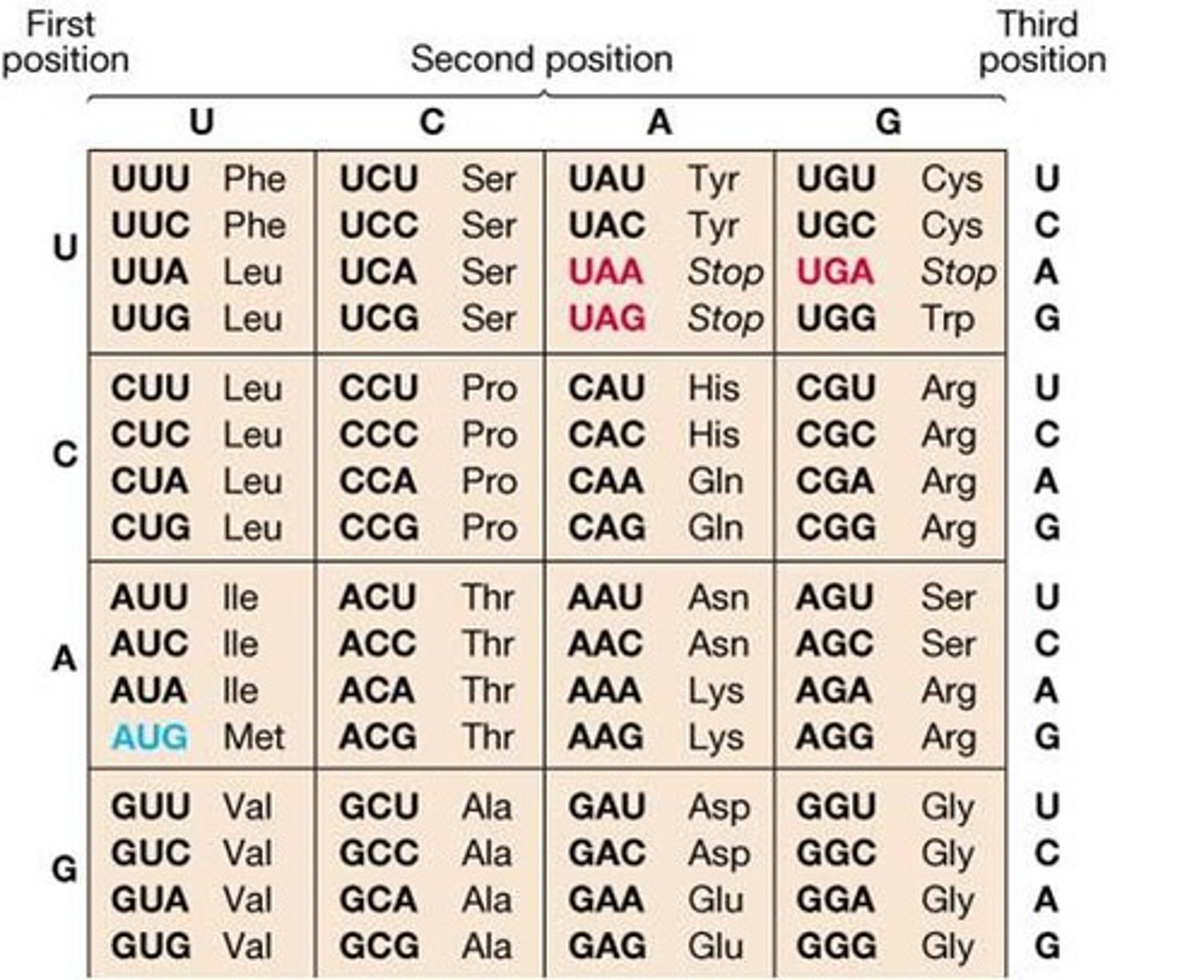
What is a Codon Chart?
A chart of codon sequences that tells you what amino acid a codon sequence on the mRNA codes for.
What are mutations in DNA
Change in DNA sequence
- have diff consequences relating to the phenotype of the animal
What are the types of mutations
deletion, insertion, substitution, chromosomal mutations, and non disjunction
What is the substitution mutation
Replacement of a single nucleotide by another nucleotide
What is the insertation mutation?
a frameshift mutation, moves all nucleotides from the right of the new nucleotide
What is the deletion mutation?
frameshift mutation, one nucleotide is taken away from a gene or DNA sequence
what is Chromosomal mutations
changes in the chromosomes where parts of the chromosomes are broken and lost during mitosis
what is non disjuction?
When an egg or sperm cell has to many or to less amounts of chromosomes
What is gene expression?
the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins
What is a operon?
a group of genes that operate together
What is a lac operon?
--A collection of genes that are important in coding for enzymes that metabolize lactose.
--If code is being used than it created a enzyme, if not than it doesn't create an enzyme
--if lactose is not present, it doesnt create an enzyme
--saves energy if no enzyme is made
What is eukaryotic regulation?
Exons and Introns
what is an exon?
An expressed sequence of DNA; codes for a protein
what is an intron
non-coding region of DNA, helps prevent mistakes