Phase 1 of Glycolysis
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
what is the goal of glycolysis
use 6 carbon compounds to produce 3 carbon intermediates for production of energy in form of ATP
1st law of thermodynamics
matter can be neither created nor destroyed
where is the energy in the carbon-carbon bonds of glucose transferred
to ADP to form ATP
what is glucose broken down into in glycolysis
pyruvate
how many carbons are in pyruvate
3
how many reactions occur to produce pyruvate from glucose
10
how many ATP are used in glycolysis
2
how many ATP are gained in glycolysis
4
what is the net gain of ATP in glycolysis
2 ATP
what is the fate of pyruvate under aerobic conditions
citric acid cycle breaks down pyruvate into CO3 and H2O, reduces NAD+ and FAD to NADH and FADH2
what is the fate of pyruvate under anaerobic conditions
fermentation and anaerobic glycolysis
fermentation of pyruvate
loss of CO2 and reduction to ethanol
anaerobic glycolysis of pyruvate
reduction of pyruvate to lactate
where does fermentation and anaerobic glycolysis occur in the body
muscle cells
who was the inventor of pasteurization and determined that glucose supplied more energy in presence of O2
Louis Pasteur (1822-1895)
who was the german biochemist that determined the intermediates of glycolysis
meyerhof (1884-1951)
who was the german biochemist that worked out precise steps involved in the breakdown of glucose
embden (1874-1933)
phase 1 of glycolysis
Energy is used to make adjustments so that the six-carbon sugar molecule can be split evenly into two three-carbon pyruvate molecules
what is formed following the first "priming reaction" of phosphorylating glucose
fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
what happens to the fructose 1,6-bisphosphate following the second priming reaction
splits into 2 molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
phase 2 of glycolysis
conversion of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to pyruvate and coupled formation of 4 ATP
sugars/carbohydrates/saccharides
simple organic compounds that are aldehydes or ketones with many hydroxyl groups added
what range of carbons exist in sugars
3-7
sugars contain different configural substituents which are referred to as what?
optical isomers or stereoisomers
which stereoisomer is used in glycolysis
D-carbohydrates
how to determine D and L isomers for sugars with more than 3 carbons
the position of the OH on the highest carbon number chiral carbon defines D or L
what is numbering of carbons based on
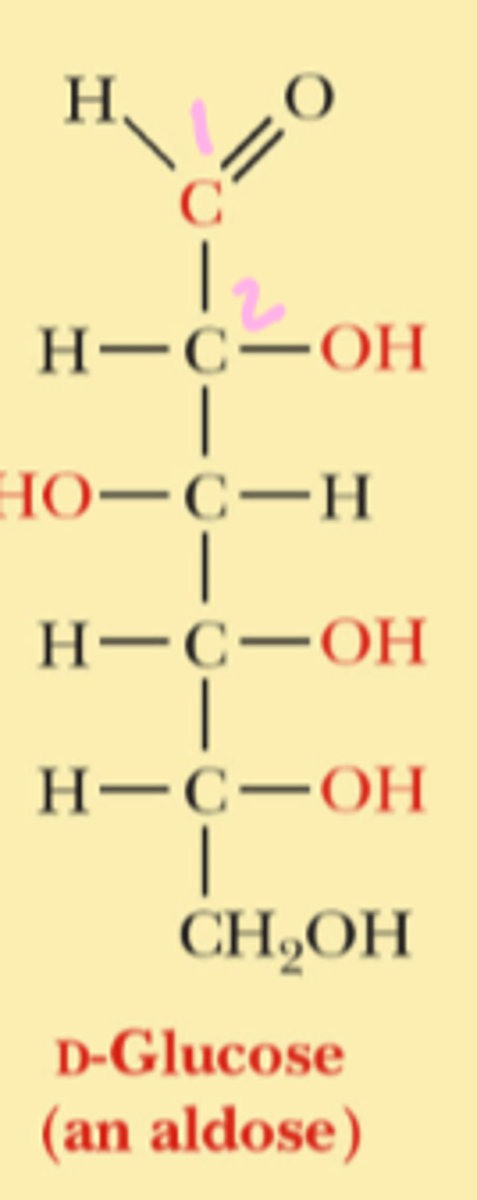
aldehyde sugars
which carbon is carbon #1 in aldehyde sugars
the most oxidized carbon
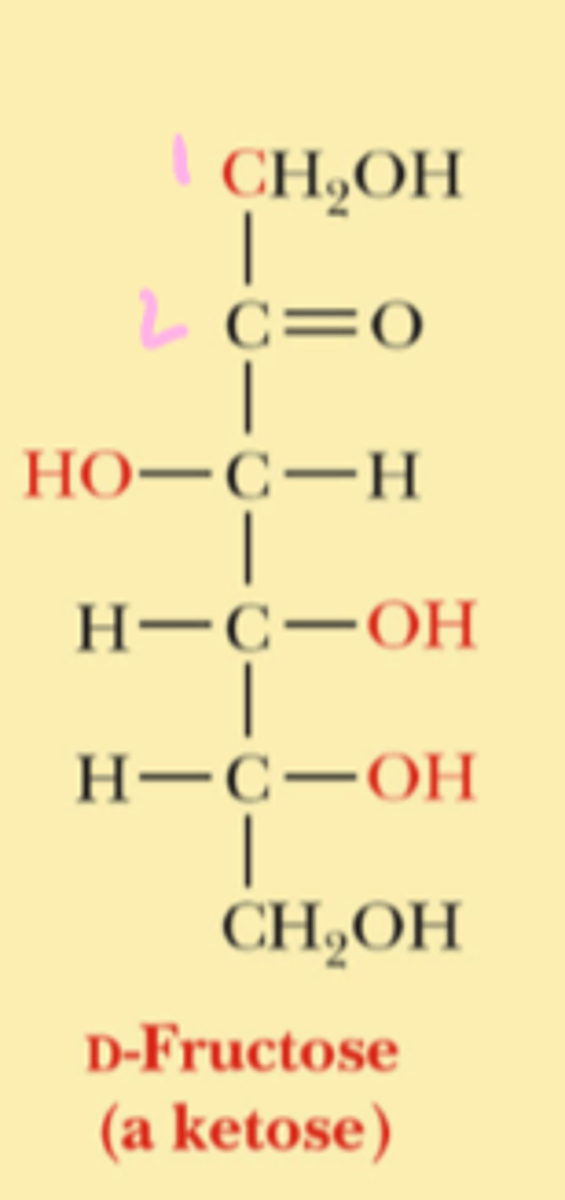
which carbon is oxidized in ketone sugars
carbon #2
which sugars normally exist as cyclic structures
5 or 6 carbon sugars
what do the free electrons on OH of carbon 5 bond with
carbon 1, which forms a cyclic structure
pyran
six membered ring with 5 carbosn and 1 oxygen
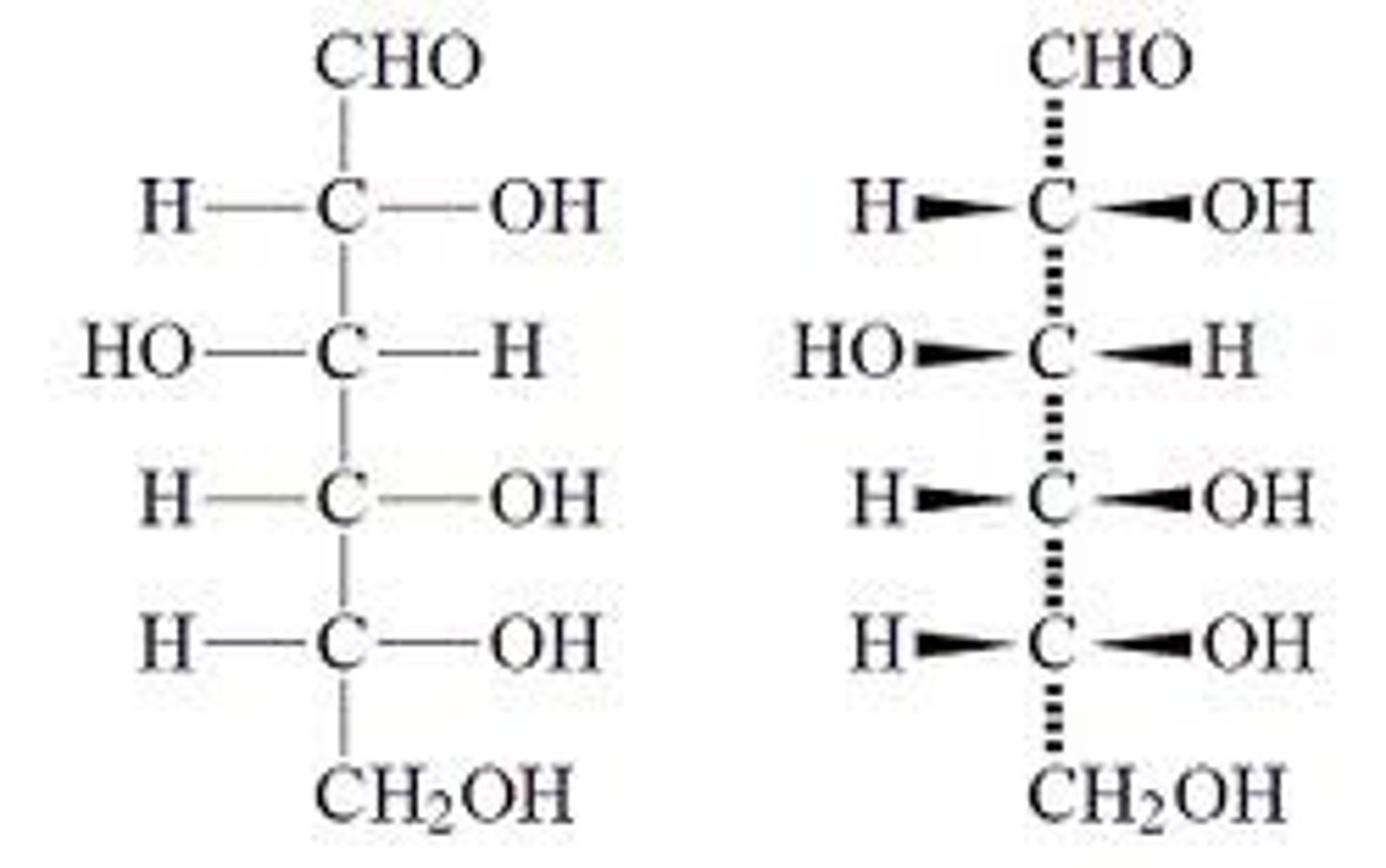
fischer projection
2D representation of the stereochemisty of 3D molecule
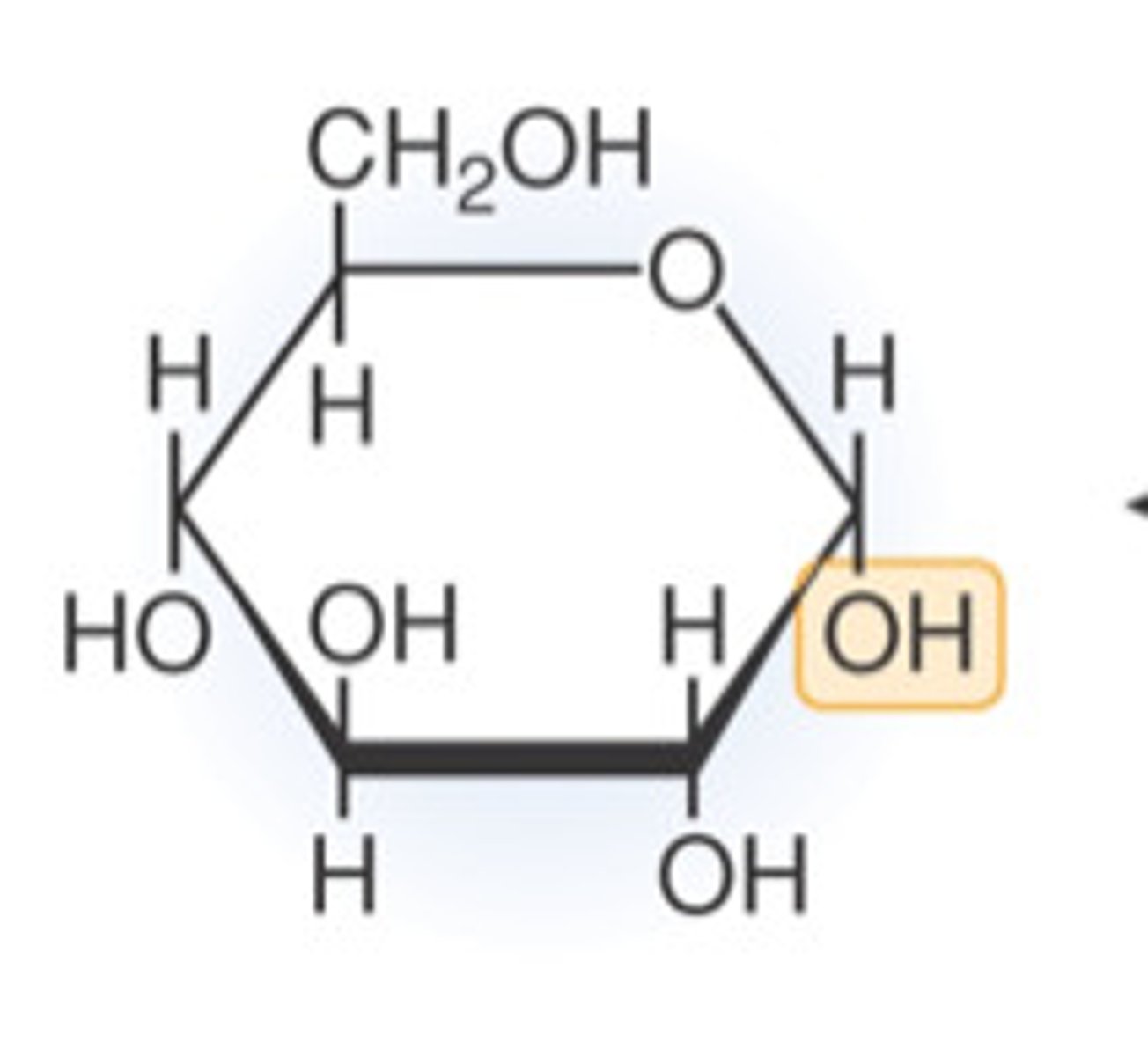
haworth projection
a perspective representation of the cyclic forms of sugars
what does step 1 of phase 1 of glycolysis produce
glucose-6-phosphate
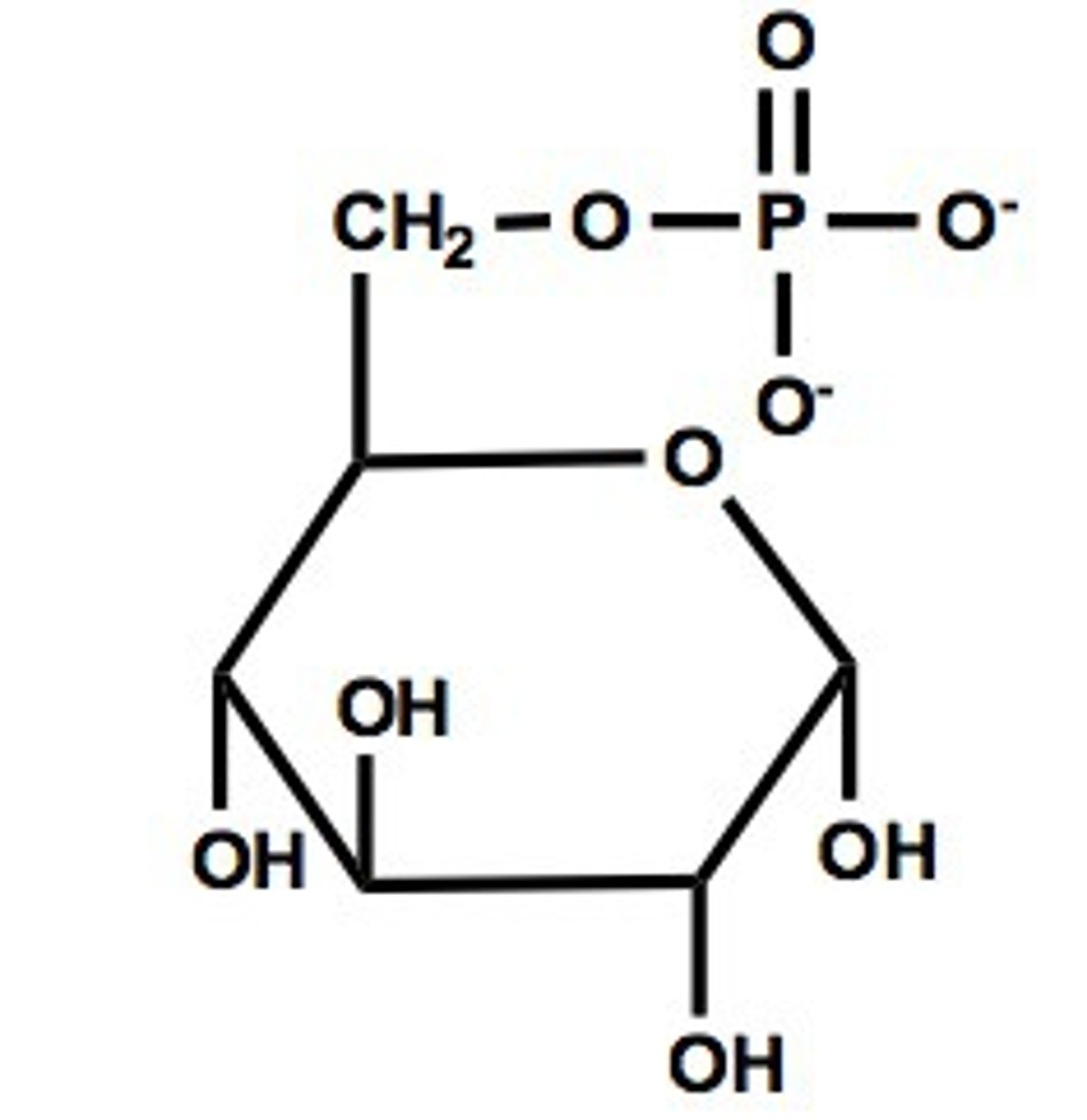
which enzyme carries out the phosphorylation of glucose to G6P (step 1, phase 1)
hexokinase
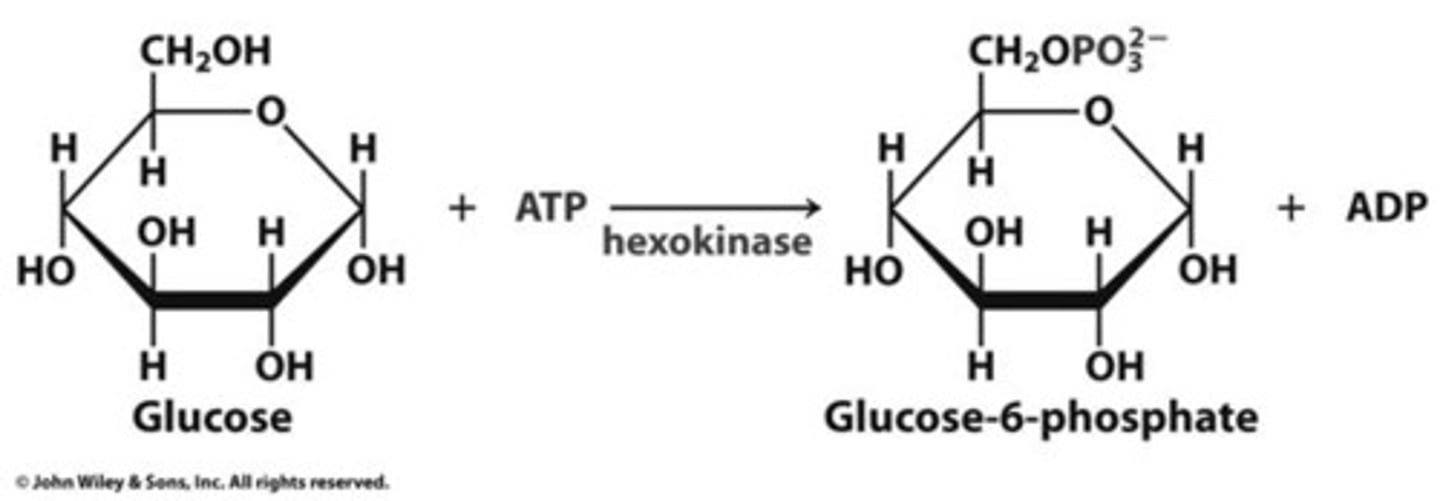
Besides hexokinase, what 2 things are required for the phosphorylation of glucose to G6P to occur
ATP and Mg2+
why is ATP required for the first step of phase 1 of glycolysis
phosphorylation of glucose without ATP is thermodynamically unfavorable (deltaG= 3.3 kcal/mole)
what is the free energy of phosphorylation of glucose without ATP
3.3 kcal/mole
what is the free energy of phosphorylation of glucose when couped with ATP
-4.0 kcal/mole
kinase
enzyme that transfers a phosphate from ATP to substrate
what happens to hexokinase when glucose binds
conformational change
what happens to glucose when it binds to hexokinase
becomes completely surrounded by enzyme and inaccessible to solute
what kind of enzyme-substrate interaction is hexokinase binding to glucose
induced-fit
what happens in step 2 of phase 1 of glycolysis
G6P is isomerized to fructose-6-phosphate (F6P)
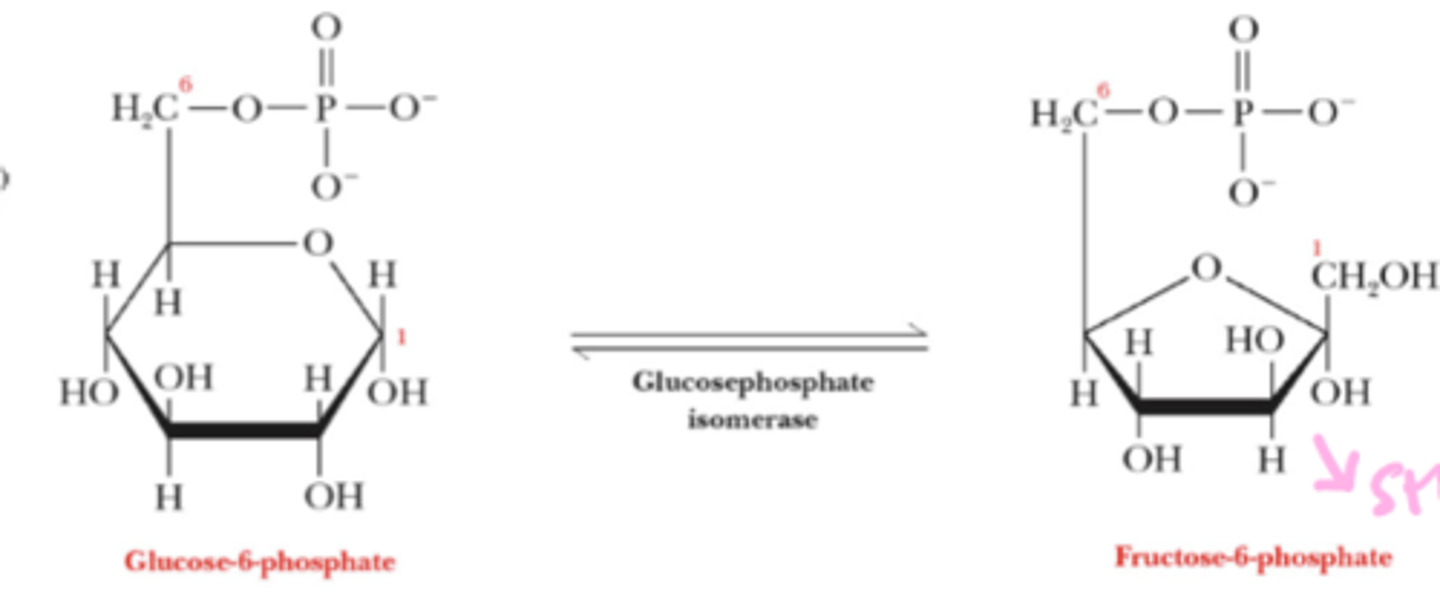
what happens to the structure following the isomerization of G6P to F6P
change from 6 membered ring to 5 membered ring
which enzyme carries out the isomerization of G6P to F6P (step 2, phase 1)
glucosephosphate isomerase
t/f: there is no net oxidation or reduction in the second step of phase 1 of glycolysis
true
1 multiple choice option
what happens in step 3 of phase 1 of glycolysis
F6P is phosphorylated to give fructose-1,6-biphosphate
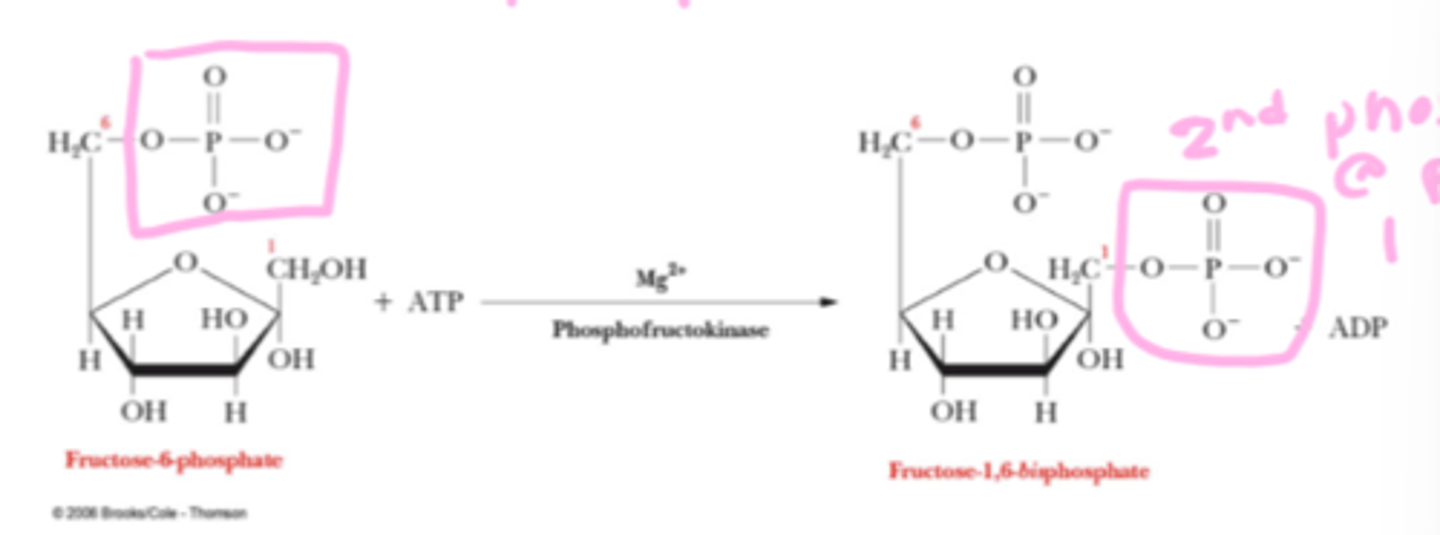
which enzyme carries out the phosphorylation of F6P to fructose-1,6-biphosphate (step 3, phase 1)
phosphofructokinase (PFK)
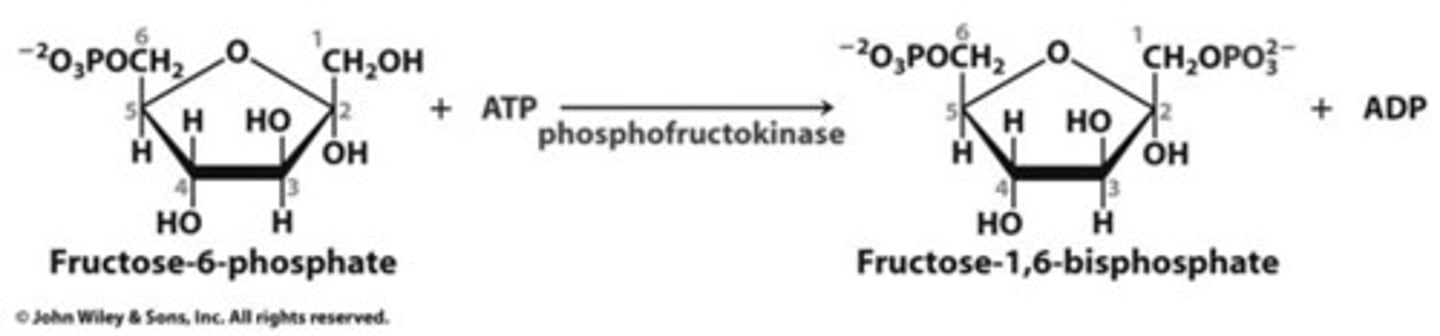
besides PFK, what else is required in step 3 of phase 1 of glycolysis (phosphorylation of F6P to fructose-1,6-biphosphate)
ATP and Mg2+
what is the free energy of phosphorylation of F6P without ATP
deltaG > 0 (thermodynamically unfavorable)
what is the free energy of phosphorylation of F6P when coupled with ATP
detaG = -3.4 kcal/mole
what happens to G6P and F6P following step 3
can be utilized by other pathways or react with phosphofructokinase (PFK)
3 multiple choice options
t/f: G6P and F6P do not have to proceed through glycolysis
true
1 multiple choice option
what happens once PFK produces fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
it is committed to glycolysis
t/f: production of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate from G6P and F6P is reversible
false
1 multiple choice option
what kind of enzyme is PFK
regulatory
what serves as an allosteric regulator of PFK
ATP
3 multiple choice options
what induces PFK enzyme activity
low [ATP]
what happens to PFK activity at high [ATP]
activity is suppressed
why is PFK activity suppressed in the presence of high cellular [ATP]
no need for ATP production since it is present in high levels
what happens at high cellular [ATP]
PFK inactivation, glycolysis shuts down
why is PFK enzyme activity induced at low cellular [ATP]
requirement for ATP
what happens at low cellular [ATP]
PFK activated, glycolysis starts up
what happens in step 4 of phase 1 of glycolysis
fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is split into two 3-carbon molecules
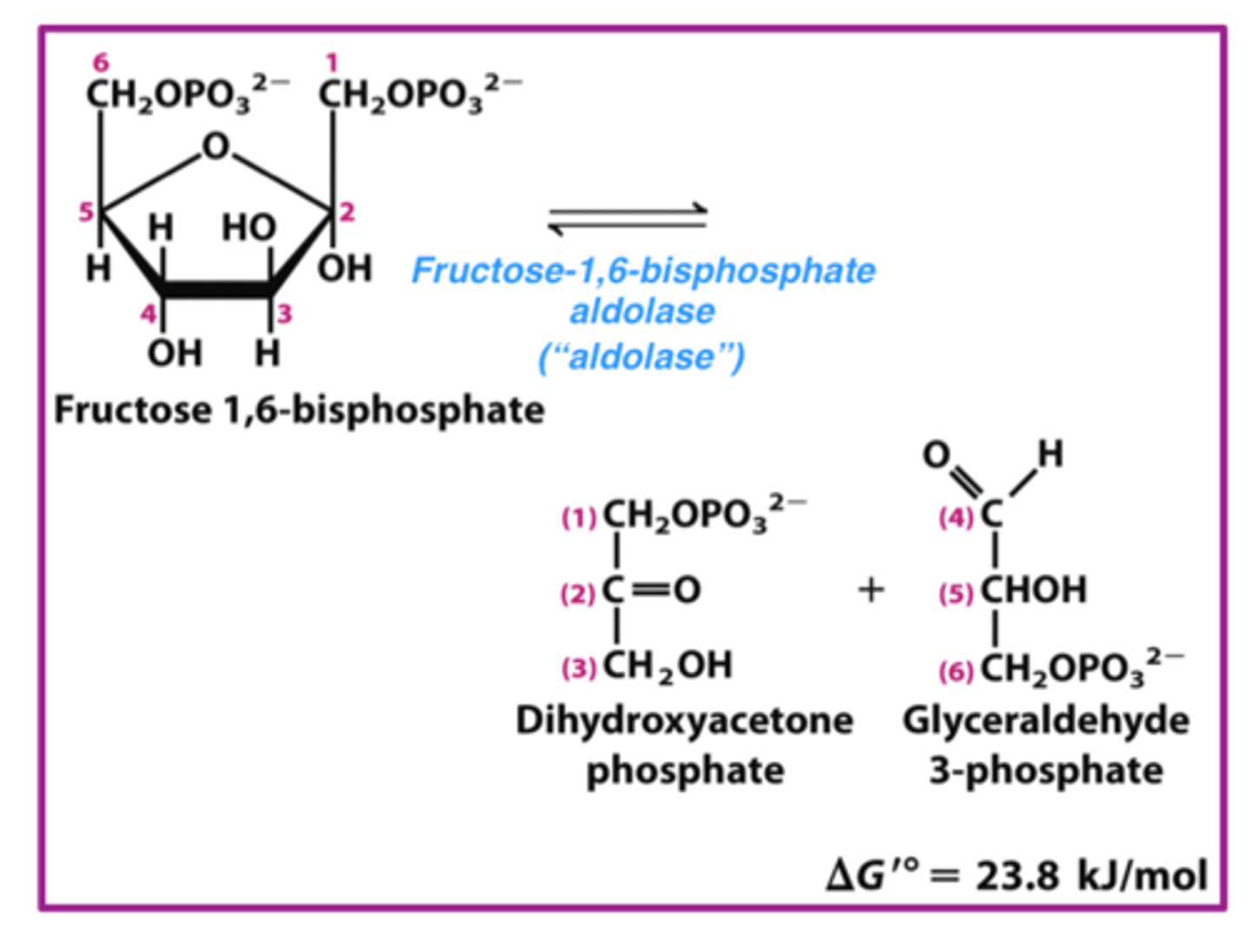
what 2 molecules is fructose-1,6-bisphosphate split into during step 4 of phase 1 of glycolysis
dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GA3P)
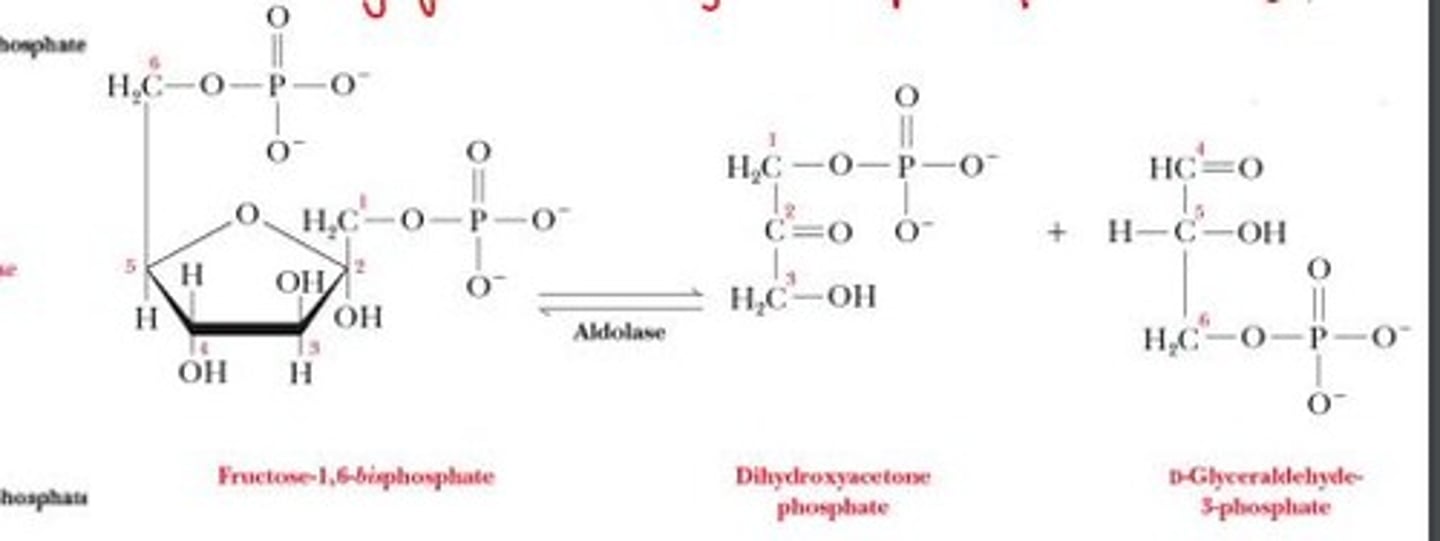
which enzyme carries out the reaction that splits fructose-1,6-bisphosphate into DHAP and GA3P
aldolase
what happens to the intermmediates once they are split into the two 3-carbon molecules (DHAP and GA3P)
they are no longer cyclic
what form are DHAP and GA3P
linear
1 multiple choice option
what happens in step 5 of phase 1 of glycolysis
DHAP is converted to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GA3P)
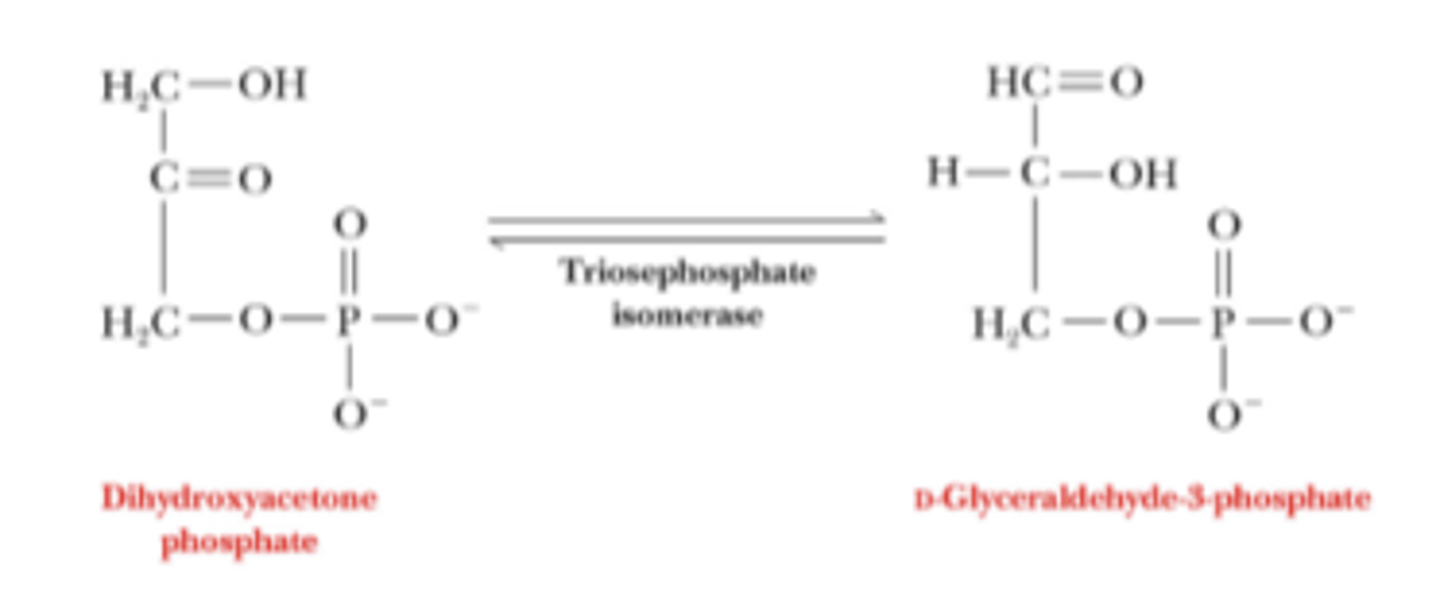
which enzyme carries out the conversion of DHAP to GA3P
triosephosphate isomerase
what is the end result of phase 1 of glycolysis
6 carbon glucose converted to two 3-carbon GA3P (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate)