biochem 2: ethanol metabolism
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
ethanol is small and readily soluble in both
water and lipids
ethanol is absorbed in ____ via ____
digestive tract by passive diffusion
Approximately _____ of ingested ethanol is metabolized by the liver
90%
the remainder is metabolized by cells of
GI tract or breast tissue, or excreted
ethanol can have adverse effects on
GI tract
ethanol decreases intestinal absorption of ____ and ____
intestinal absorption of AA and some vitamins
heavy consumption of alcohol may result in damage to _______, resulting in _____, _____ and/or increased ____ to toxins.
mucosal cells, resulting in erosion, bleeding, and/or increased permeability to toxins.
primary nutritional deficiencies w/ alc consumption - ethanol contains _____ of empty calories. alcohol can often consume _______.
ethanol contains 4.5-7kcal/g of empty calories. alc can often consume nutrient deficient diets, as most of their calories are from alc
secondary nutritional deficiencies with alc consumption
ethanol impairs absorption and/processing of
essential AA and FA
vitamin B1, B2, B6, C, folic acid, vitamin A (retinoic acid)
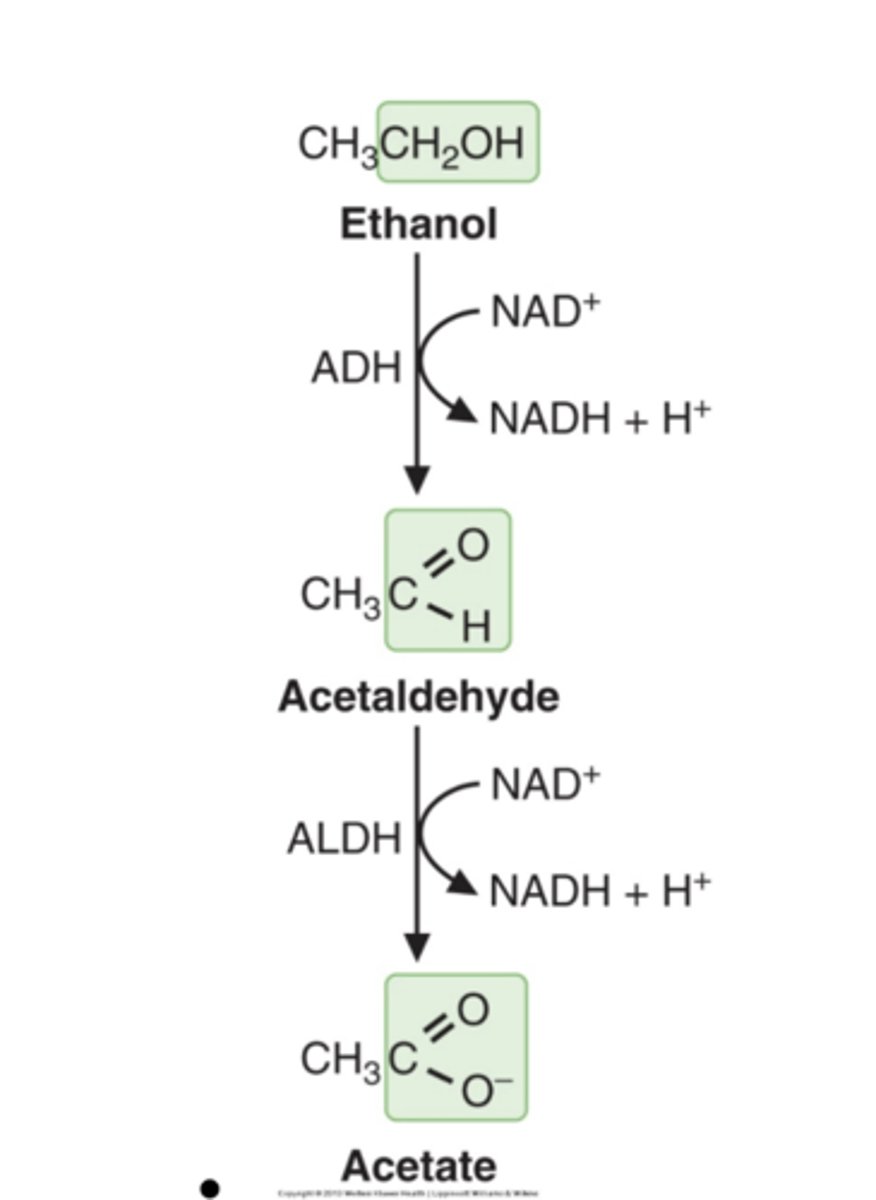
Ethanol is converted to _____ and then ______. ____ is converted to _____ and used as fuel for ______ and ______
acetaldehyde, and then acetate. Acetate is converted to acetyl CoA and used as a fuel for skeletal and heart muscle.
Unpleasant effects of ethanol consumption (flushing, nausea, etc.) are due to
acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde is highly reactive; it generates ____ and binds to _____. toxicity contributes to development of ______ and _____ in the liver
ROS and binds to proteins. Toxicity contributes to development of inflammation and steatosis in the liver.
acetaldehyde is converted to ____ by _____
acetate by acetaladehyde dehydrogenase
Two enzyme systems are responsible for converting ethanol to acetaldehyde:
alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH)
microsomal ethanol oxidizing systems
major route of ethanol metabolism in the liver is via
alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH)
ADH exists as a family of isozymes with varying ______. generally, the Km values are _______
kinetic parameters for ethanol. Generally, the Km values are quite low.
ALDH exists as a ______ with a very high affinity to ______, and a cytosolic isozyme with a much lower ________
exists as a mitochondrial isozyme with a very high affinity for acetaldehyde and a cytosolic isozyme with a much lower affinity for acetaldehyde
polymorphisms in ADH and ALDH greatly affect the rate of
ethanol metabolism and/or accumulation of acetaldehyde in individuals
ethanol --> acetate
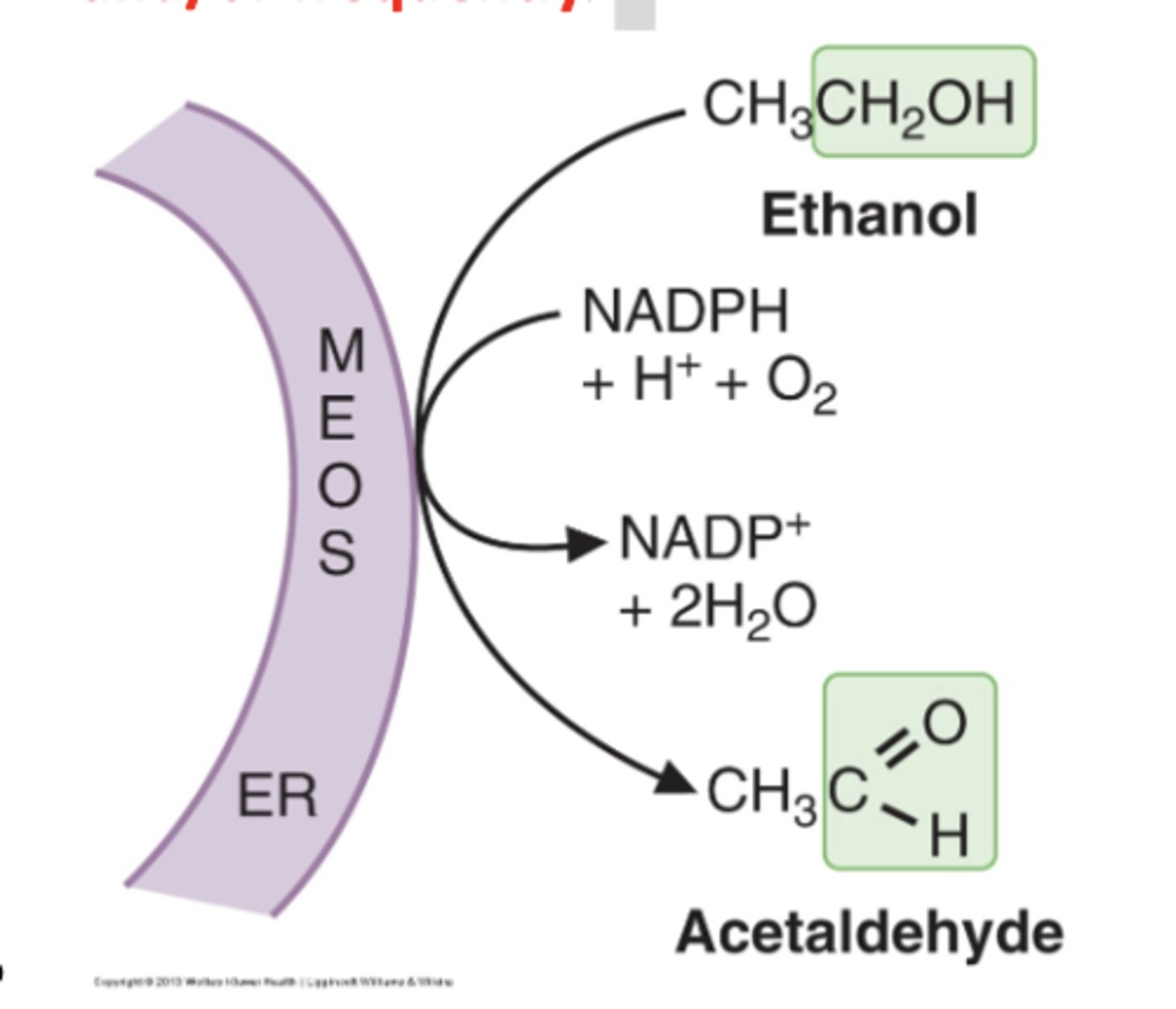
Ethanol is also oxidized to acetaldehyde by MEOS, which involves ______, primarily _____, in the ________
cytochrome P450 enzymes (primarily CYP2E1) in the hepatic endoplasmic reticulum
______ is the primary P450 in the MEOS, which is composed of additional P450s as well as corresponding cytochrome P450 reductases
CYP2E1
The Km for the MEOS system toward EtOH is
higher than that of ADH.
Furthermore, CYP2E1 expression is induced
by EtOH.
Therefore, the MEOS system plays important roles when
a person drinks heavily and/or frequently.
MEOS
alcohol induced liver disease begins with either _____ or _____. either is ____, but may progress to ______ and eventually _______
steatosis (fatty liver) or alcohol induced hepatitis (inflammation) reversible but may progress to hepatic fibrosis and eventually cirrhosis
90% of men who drink more than ______ and women who drink more than _____ will develop fatty liver
60g/d
40g/d
hepatitis, fibrosis, or cirrhosis will develop in
40% of those who have alcoholic fatty liver
stages of liver disease
fatty liver - deposits of fat cause liver enlargement
liver fibrosis - scar tissue forms
cirrhosis - growth of connective tissue destroys liver cells
ADH and ALDH consume _____ and produce ______
NAD+ and produce NADH during ethanol metabolism.
The resulting high NADH/NAD+ alters
hepatic metabolism of other fuels.
consequences of high hepatic NADH/NAD+
1. Beta oxidation of fatty acids is inhibited
2. TCA cycle is inhibited
3. Lactate cannot be converted to pyruvate in the liver
1. beta oxidation of fatty acids is inhibited - fatty acids will accumulate in the _____ and re-esterify to _____. some remain trapped in liver, resulting in _____ and others are incorporated into VLDL, contributing to ______
Fatty acids accumulate in the liver, and are re-esterified to TAG. Some remain trapped in the liver, resulting in steatosis, and others are incorporated into VLDL, contributing to hyperlipidemia.
2. TCA cycle is inhibited: _____ accumulates in hepatocytes and is converted to _____. because extra-hepatic tissues are using acetate for fuel, they will not use the _____, and ____ may result.
Acetyl-CoA accumulates in hepatocytes and is converted to ketone bodies. Because extrahepatic tissues are using acetate for fuel, they will not use the ketones, and ketoacidosis may result (Alcoholic ketoacidosis)
3. Lactate cannot be converted to pyruvate in the liver - The lactate dehydrogenase reaction
will not favor pyruvate formation in the liver.
Furthermore, gluconeogenesis from glycerol and oxaloacetate
is also inhibited.
This results in _________. Lactic acidosis can result in _______ as the kidney’s capacity to eliminate uric acid is impaired.
lactic acidosis and hypoglycemia; lactic acidosis can result in hyperuricemia
Acetaldehyde is highly reactive; it generates
ROS and binds to proteins.
acetaldehyde toxicity contributes to development of
inflammation and steatosis in the liver.
Decreased serum protein synthesis →
Edema, Ascites, & Poor blood clotting
Impaired amino acid uptake →
Elevated serum amino acids, esp. In catabolic state
Decreased urea cycle function →
Hyperammonia, Encephalopathy
Inefficient bilirubin glucuronidation→
Jaundice
Hepatocyte injury/death, resulting in release of enzymes to serum →
Elevated serum AST, ALT, and Alkaline phosphatase.
ingested alcohol is completely metabolized within
8-12 hours, but physical effects can last longer
physical effects of hangover
dehydration
hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis
GI irritation
acetaldehyde
EtOH is an
diuretic
GI irritation with alcohol -
increased gastric acid
gastritis
acetalaldehyde is a
potent vasodilator
causes headache, trembling, ill feeling
potent vasodilator -
causes flushing seen in some individuals after EtOH consumption
the amount of volatile substances, such as ______ and ______ in alcoholic beverages correlates to ______
methanol and fusel oils, severity of hangover